Gilbert Syndrome Treatment: Gilbert Syndrome is an often misunderstood and underdiagnosed condition, characterized by a mild, chronic elevation of bilirubin in the blood.
Despite being benign and usually asymptomatic, understanding and managing this syndrome is crucial for those affected.
This article explores the diagnosis, management, and treatment of Gilbert Syndrome, providing comprehensive insights to support health and well-being.
What is Gilbert Syndrome?
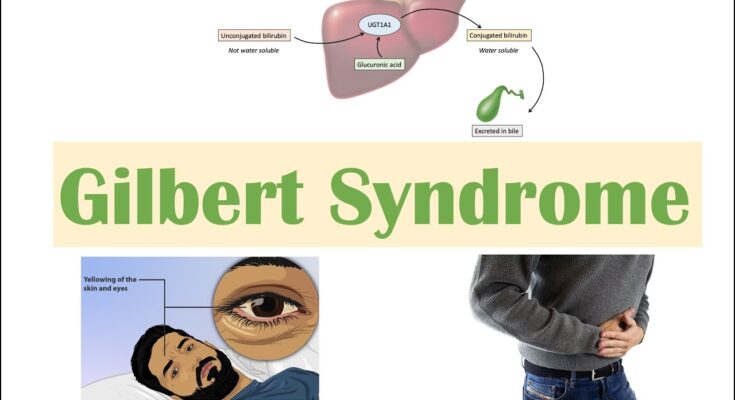
Gilbert Syndrome (GS) is a common, mild liver disorder characterized by periodic increases in bilirubin levels in the bloodstream. This condition is typically harmless and often goes undiagnosed because it usually doesn’t cause severe symptoms or require treatment. GS is inherited and affects the body’s ability to process bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the normal breakdown of red blood cells.
Characteristics of Gilbert Syndrome
Individuals with Gilbert Syndrome may experience mild jaundice, where the skin and whites of the eyes turn slightly yellowish. This is usually the only symptom and is often triggered by stress, fasting, illness, or strenuous exercise. The condition does not lead to serious health problems and typically does not shorten life expectancy. People with GS usually lead normal lives without the need for treatment.
Epidemiology: Prevalence and Demographics
Gilbert Syndrome is quite common, affecting approximately 3-12% of the population globally. It is more frequently diagnosed in men than in women. The prevalence can vary significantly between different ethnic and racial groups. For instance, GS is particularly prevalent in Caucasians and less common in Asians.
Genetic Factors Contributing to Gilbert Syndrome
The genetic basis of Gilbert Syndrome is primarily linked to a mutation in the UGT1A1 gene. This gene produces an enzyme that helps break down bilirubin. The most common mutation involves a specific promoter region of the gene known as the TATA box. Individuals with GS typically have a variant called UGT1A1*28, which leads to reduced activity of the enzyme, resulting in the buildup of bilirubin in the blood. This genetic trait is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning a person must inherit one copy of the mutated gene from each parent to be affected.
By understanding these aspects of Gilbert Syndrome, individuals can better recognize the condition and seek appropriate medical advice, although intervention is rarely needed. Awareness and education about the syndrome can help reduce unnecessary anxiety over the mild symptoms it presents.
Signs and Symptoms of Gilbert Syndrome
It is important to recognize the common symptoms of Gilbert Syndrome, understand how these symptoms can be confused with other medical conditions, and comprehend their impact on daily life and well-being.
Common Symptoms Associated with Gilbert Syndrome
Although many individuals with Gilbert Syndrome may remain asymptomatic, some common signs can appear, particularly during periods of exertion, stress, fasting, or illness. These symptoms include:
- Jaundice: A slight yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes is the most noticeable sign of GS. This occurs due to the buildup of bilirubin.
- Fatigue: Individuals with GS often report feeling unusually tired, even with adequate rest.
- Abdominal pain: Mild to moderate abdominal discomfort can occur, typically on the right side where the liver is located.
- Nausea: This can accompany abdominal pain and is often triggered by long periods without eating.
These symptoms are generally mild and transient, but they are significant enough to affect an individual’s quality of life.
How Symptoms May Be Mistaken for Other Conditions
The symptoms of Gilbert Syndrome are non-specific and can easily be mistaken for signs of other health issues, which can lead to misdiagnosis or unnecessary worry. For instance:
- Jaundice is often associated with more severe liver conditions such as hepatitis or bile duct obstruction.
- Fatigue could be misinterpreted as a sign of chronic fatigue syndrome, anemia, or even depression.
- Abdominal pain and nausea are common symptoms for a vast array of gastrointestinal issues, including gallstones and gastroenteritis.
Due to these ambiguities, it is crucial for healthcare providers to consider a thorough medical history and possibly conduct diagnostic tests to confirm GS.
Impact of GS on Daily Life and Well-Being
While Gilbert Syndrome is generally considered benign, the fluctuations in symptoms can interfere with daily activities and overall well-being. The unpredictability of symptoms like jaundice and fatigue may affect self-esteem and social interactions, as individuals might feel self-conscious about their appearance or unable to participate in social or professional engagements fully.
Moreover, the need to manage potential triggers—such as avoiding fasting and ensuring not to skip meals—can require lifestyle adjustments that may be cumbersome or restrictive.
However, although Gilbert Syndrome is typically mild and does not lead to serious liver damage, the symptoms can impact day-to-day life and mental health. Awareness and proper management can greatly improve the quality of life for those affected by this syndrome.
Diagnosing Gilbert Syndrome
Proper diagnosis of GS is crucial, yet often challenging due to its benign and often symptomless nature. Understanding the diagnostic criteria, the role of genetic testing, and the common challenges can help in accurately identifying and managing this condition.
Diagnostic Criteria and Medical Tests for Gilbert Syndrome
The diagnosis of Gilbert Syndrome primarily revolves around observing bilirubin levels and ruling out other potential causes of jaundice. The key diagnostic criteria include:
- Elevated Bilirubin Levels: Typically, individuals with GS have mildly elevated bilirubin levels, usually less than 3 mg/dL, without any evidence of liver damage or red blood cell destruction.
- Normal Liver Function Tests: Other liver function tests should be normal, confirming that the elevated bilirubin is not due to liver disease.
- Absence of Symptoms: Most individuals do not exhibit symptoms other than jaundice, particularly during fasting, stress, or illness.
Medical tests used to diagnose Gilbert Syndrome include:
- Blood Tests: Comprehensive blood tests measure bilirubin levels and assess liver function.
- Fasting Test: A fasting test may be conducted to observe the increase in bilirubin levels after fasting, which is a characteristic response in GS.
- Phenobarbital Challenge: This test involves administering phenobarbital, which can lower bilirubin levels in individuals with GS, helping to confirm the diagnosis.
Role of Genetic Testing in Confirming Gilbert Syndrome
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in confirming the diagnosis of Gilbert Syndrome. The disorder is caused by a mutation in the UGT1A1 gene, specifically the promoter region of this gene. Testing for this genetic mutation can definitively confirm the diagnosis:
- UGT1A1 Gene Test: A simple genetic test to identify the UGT1A1*28 allele, which is commonly found in GS patients.
- Precision and Confirmation: While the presence of elevated bilirubin levels suggests GS, genetic testing confirms the diagnosis, particularly in ambiguous cases.
Common Challenges and Misconceptions in Diagnosing Gilbert Syndrome
Diagnosing GS can be fraught with challenges and misconceptions, such as:
- Misdiagnosis: Due to its benign nature and minimal symptoms, GS is often overlooked or mistaken for more serious liver conditions.
- Misunderstanding of Symptoms: The intermittent jaundice characteristic of GS can lead to unnecessary anxiety and invasive testing.
- Genetic Testing Accessibility: While genetic testing is definitive, it might not be readily available or considered necessary in all clinical settings.
By addressing these challenges and educating both medical professionals and patients about the nuances of Gilbert Syndrome, more accurate and timely diagnoses can be achieved. This approach ensures that individuals with GS receive appropriate advice and management, avoiding unnecessary treatments and concerns.
Treatment Options for Gilbert Syndrome
Below, we explore the various treatment options, lifestyle and dietary recommendations, strategies to reduce bilirubin levels, and the importance of regular medical follow-up.
Lifestyle and Dietary Recommendations
For those diagnosed with Gilbert Syndrome, making certain lifestyle and dietary changes can be beneficial in managing symptoms:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking ample water helps to flush toxins from the body, which may aid in reducing bilirubin levels.
- Balanced Diet: Eating a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support liver health and overall well-being.
- Limit Fasting and Crash Diets: Since fasting can elevate bilirubin levels, it’s advisable to avoid skipping meals or engaging in crash diets.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol can stress the liver, so reducing or avoiding it can be beneficial for individuals with Gilbert Syndrome.
Managing Symptoms: Strategies to Reduce Bilirubin Levels
Although there is no specific treatment required for Gilbert Syndrome, certain strategies can help manage and reduce bilirubin levels:
- Moderate Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall liver function and help maintain optimal health.
- Avoiding Known Triggers: Certain conditions like dehydration, illness, or stress can trigger symptoms. Identifying and avoiding these triggers can help manage bilirubin levels.
- Medication Review: Some medications can exacerbate the symptoms of Gilbert Syndrome. It’s crucial to discuss all current medications with a healthcare provider to ensure they are safe to use.
Importance of Regular Medical Follow-Up
While Gilbert Syndrome is usually harmless, regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are essential to:
- Monitor Liver Function: Routine checks can ensure that bilirubin levels are within a safe range and the liver is functioning properly.
- Update Health Status: Regular visits allow for ongoing assessment of symptoms and overall health.
- Screen for Other Conditions: It helps in early detection and management of any other potential health issues.
However, while Gilbert Syndrome typically requires minimal medical intervention, adhering to a healthy lifestyle, managing symptoms through strategic choices, and maintaining regular medical check-ups are key to managing this condition effectively.
Advanced Treatment Strategies for Gilbert Syndrome
Gilbert syndrome is a mild liver disorder characterized by slightly elevated levels of bilirubin in the blood, typically not requiring treatment. However, certain circumstances may necessitate advanced treatment strategies. This section explores when such treatments are considered, delves into ongoing research on potential medications and therapies, and assesses the role of alternative treatments and supplements.
When and Why Advanced Treatments Might Be Considered
Advanced treatments for Gilbert syndrome are considered under specific conditions such as persistent jaundice, which can affect quality of life by causing symptoms like fatigue, abdominal pain, and skin itching. These symptoms, though typically mild, might prompt the use of more focused therapeutic strategies if they become bothersome or lead to social or psychological distress. Additionally, situations requiring the rapid reduction of bilirubin levels, such as during acute illnesses or before certain medical procedures, might also justify advanced treatment approaches.
Research on Potential Medications and Therapies
Current research into medications and therapies for Gilbert syndrome is largely exploratory, given the benign nature of the condition. Studies have investigated the use of certain drugs like phenobarbital, which can lower bilirubin levels by enhancing its processing in the liver. However, due to potential side effects, such treatment is not commonly recommended. Researchers are also looking into the genetic aspects of Gilbert syndrome to develop targeted therapies that can more effectively manage the condition with minimal side effects.
Role of Alternative Treatments and Supplements
The role of alternative treatments and dietary supplements in managing Gilbert syndrome is an area of growing interest. Some preliminary studies suggest that natural supplements like milk thistle, which promotes liver health, may be beneficial. Additionally, lifestyle adjustments, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding fasting or excessive physical stress, can help manage symptoms. However, it’s crucial for patients to consult healthcare providers before starting any new treatment or supplement to ensure it’s safe and suitable for their specific health needs.
However, while Gilbert syndrome usually does not require treatment, advanced therapeutic strategies may be considered in certain scenarios to alleviate symptoms or reduce bilirubin levels. Ongoing research and a cautious approach towards alternative treatments and supplements are advisable to ensure optimal management of the condition.
Living with Gilbert Syndrome
Here, we discuss how individuals with Gilbert Syndrome can manage their condition daily, navigate the psychological and social landscapes, and find valuable support resources.
Daily Management Strategies for Individuals with GS
For most individuals with Gilbert Syndrome, daily management focuses on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and monitoring symptoms. Here are practical strategies that can help:
- Dietary Adjustments: Although no specific diet is required, eating balanced meals can help manage potential symptoms. Avoid fasting or skipping meals, as this can trigger bilirubin levels to rise.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain liver health and flush toxins from the body.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health and help maintain normal liver function.
- Monitor Symptoms: Keeping a diary of any symptoms and the circumstances in which they occur can be useful. This information can help healthcare providers make informed decisions about your care.
Psychological and Social Aspects of Living with a Chronic Condition
Living with a chronic condition like Gilbert Syndrome can affect more than just physical health—it can also impact mental health and social interactions. Individuals might experience:
- Stress or Anxiety: Concerns about symptoms or the unpredictability of the condition can lead to stress or anxiety.
- Social Challenges: Misunderstandings about the non-contagious and benign nature of GS might lead to unnecessary social stigma or isolation.
Coping strategies include:
- Education: Learning as much as possible about GS can alleviate fears and empower individuals.
- Communication: Discussing your condition with friends, family, and colleagues can help them understand your situation and reduce misconceptions.
Support Resources: Support Groups, Online Forums, and Healthcare Guidance
Finding support is crucial in managing any chronic condition, including Gilbert Syndrome. Support can come from various sources:
- Support Groups: Many communities offer local or online support groups for those with liver disorders, including GS. These groups provide a platform to share experiences and coping strategies.
- Online Forums: Websites like Reddit and HealthUnlocked offer forums where individuals with GS can connect and exchange information.
- Healthcare Providers: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are essential. They can offer guidance, monitor liver health, and address any concerns.
However, while Gilbert Syndrome may require minimal medical management, the importance of supportive resources, effective communication, and healthy lifestyle choices cannot be overstressed. By adopting comprehensive management strategies and leveraging available support resources, individuals with GS can lead full and healthy lives.
Recent Advances in Gilbert Syndrome Research
Gilbert Syndrome (GS) is a common but often misunderstood genetic liver disorder characterized by intermittent jaundice caused by elevated bilirubin levels. Despite its benign nature, ongoing research is crucial for improving diagnosis, management, and treatment. This article explores the latest advances in GS research, highlighting key developments in genetics and the future prospects for managing the condition.
Overview of the Latest Research Findings Related to GS
Recent studies have provided new insights into the genetic basis and clinical implications of Gilbert Syndrome. Research has identified specific mutations in the UGT1A1 gene that significantly impact bilirubin metabolism. This discovery has led to better screening methods that can diagnose GS more accurately and differentiate it from more severe liver disorders. Furthermore, studies have suggested that individuals with GS might have a reduced risk of developing certain cardiovascular diseases due to the antioxidant properties of bilirubin. These findings not only refine our understanding of GS but also suggest potential protective factors associated with the condition.
Developments in Genetic Research and Its Implications for Treatment
The advancements in genetic research have been pivotal in shaping the approach to GS treatment. With the identification of the UGT1A1 gene mutation as a key factor in GS, targeted genetic testing has become a fundamental tool in diagnosing the syndrome. This genetic perspective allows for a more personalized approach to managing the condition. For instance, understanding an individual’s specific genetic mutation helps predict the severity of the syndrome and guides lifestyle and dietary recommendations to manage bilirubin levels effectively.
Future Prospects in the Treatment and Management of GS
Looking ahead, the future of GS treatment appears promising with several potential advancements on the horizon. Researchers are exploring the role of pharmacogenomics in treating GS, where medications can be tailored to the genetic profile of an individual to optimize the management of bilirubin levels. Moreover, ongoing clinical trials are investigating new drugs that could potentially enhance the activity of the UGT1A1 enzyme, thus reducing bilirubin levels more effectively. Lifestyle interventions, such as diet modifications and stress management, continue to be studied for their therapeutic benefits in reducing symptoms associated with GS.
However, the field of Gilbert Syndrome research is evolving rapidly, with genetic insights opening new avenues for more effective diagnosis and management. As understanding deepens and treatment approaches become more refined, individuals with GS can look forward to more targeted and effective solutions for managing their condition.
FAQs about Gilbert Syndrome Treatment
1. What is the treatment for Gilbert Syndrome?
Gilbert Syndrome is a mild liver disorder that typically does not require specific treatment. The liver enzyme abnormality found in this condition is benign and usually does not lead to serious health issues. Most individuals with Gilbert Syndrome do not experience any symptoms and hence, no treatment is necessary.
2. Are there any lifestyle changes recommended for managing Gilbert Syndrome?
While there is no treatment needed for Gilbert Syndrome, making certain lifestyle changes can help manage any mild symptoms that might occur, such as fatigue or jaundice during periods of illness. These changes include staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, avoiding fasting or skipping meals, and minimizing stress. It’s also advisable to avoid known liver toxins, such as excessive alcohol and certain medications that can stress liver function.
3. Do I need to take medication for Gilbert Syndrome?
No, Gilbert Syndrome generally does not require medication. Since this condition is primarily characterized by occasional increases in bilirubin levels, medications are not necessary. If you are concerned about symptoms or management of this condition, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
4. When should I see a doctor for Gilbert Syndrome?
You should consult your healthcare provider if you experience symptoms like severe jaundice, unexplained abdominal pain, or significant changes in your health status. While these are not commonly associated with Gilbert Syndrome, they may warrant a medical evaluation to rule out other conditions.
5. Can Gilbert Syndrome lead to more serious liver problems?
Gilbert Syndrome is generally considered a benign and lifelong condition that does not lead to liver damage or serious complications. However, because it involves liver enzyme processes, it’s important to maintain regular health check-ups to monitor your overall liver health.
Conclusion
In summary, the treatment of Gilbert Syndrome primarily focuses on managing symptoms and ensuring a high quality of life, as the condition itself is typically benign and does not require direct medical treatment. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding fasting, and reducing stress, are often recommended to minimize the appearance of symptoms like jaundice.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for Gilbert Syndrome. It not only prevents unnecessary treatments but also helps in distinguishing it from more severe liver disorders. An appropriate diagnosis relies on a combination of blood tests, family history, and the exclusion of other illnesses.
The management of Gilbert Syndrome is relatively straightforward and non-invasive. Education about the condition and regular health monitoring are key components. Patients should be informed about potential triggers that could exacerbate symptoms and the generally benign nature of the syndrome.
Understanding Gilbert Syndrome and implementing effective management strategies are essential for living comfortably with the condition. This emphasizes the importance of healthcare providers staying informed about the latest recommendations for diagnosing and managing this syndrome, ensuring that patients receive the best care possible.
References
For those seeking further information on Gilbert Syndrome and its treatment options, the following sources provide reputable and valuable insights. These links offer comprehensive details for validation of the information presented, enhancing your understanding of Gilbert Syndrome and its management.
- Mayo Clinic – A reliable resource for understanding the basics of Gilbert Syndrome, including symptoms, causes, and diagnostic approaches. Explore their detailed overview here: Gilbert Syndrome – Mayo Clinic.
- National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) – NORD provides a thorough explanation of Gilbert Syndrome, emphasizing genetic aspects and treatment options. Read more at: Gilbert Syndrome – NORD.
- Healthline – This resource offers practical advice on managing Gilbert Syndrome, including lifestyle tips and dietary recommendations. Access the guide here: Managing Gilbert Syndrome – Healthline.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in scientific research, PubMed Central features numerous studies on Gilbert Syndrome. A good starting point is the comprehensive review found here: Recent Research on Gilbert Syndrome – PubMed Central.
- Genetics Home Reference – Provided by the U.S. Library of Medicine, this source delves into the genetic background of Gilbert Syndrome, offering insights into how it affects liver function. Learn more: Genetics of Gilbert Syndrome – Genetics Home Reference.
By consulting these resources, you can gain a deeper understanding of Gilbert Syndrome and ensure the information you rely on is accurate and up-to-date.