Genital Warts Symptoms: Genital warts represent one of the most common types of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) globally. Caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), these growths are both a medical and cosmetic concern, affecting millions each year.
This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms and causes of genital warts, aiming to empower readers with knowledge and preventative strategies.
Understanding Genital Warts
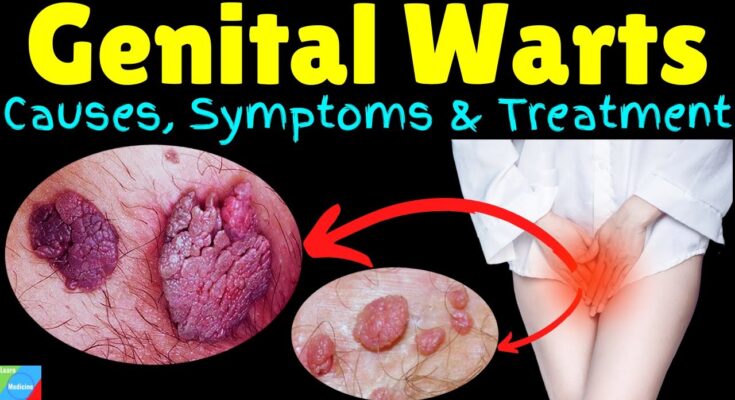
Genital warts are small, raised skin lesions that can appear on the genital area. They are caused by certain strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and are recognized as one of the most common sexually transmitted infections (STIs). These warts can vary greatly in size and appearance and may be smooth or rough. Despite their unsettling appearance, genital warts are typically benign, meaning they are not cancerous.
Genital warts are a direct result of an HPV infection. HPV is a widespread virus with several strains, some of which are linked to different health issues, including cancers. However, the specific strains that cause genital warts do not generally lead to cancer. Transmission of HPV can occur through direct skin-to-skin contact, typically during vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the virus.
It’s crucial to understand that while HPV infections are incredibly common, not everyone with HPV will develop genital warts. Some individuals may carry the virus and transmit it to others without ever showing symptoms themselves. This makes understanding and preventing HPV transmission important for sexual health.
Symptoms of Genital Warts
Some people might exhibit noticeable symptoms, while others may not have any visible signs at all. Understanding the various manifestations of this condition is crucial for early detection and treatment.
Visual Symptoms of Genital Warts
For those who develop physical signs, the symptoms of genital warts include:
- Clusters of Warts: They may appear as small bumps, might be raised or flat, and can sometimes form a cluster that resembles a cauliflower.
- Location-Specific Growth: Warts can occur on the vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, scrotum, groin, or thigh.
- Color Variation: While generally flesh-colored, they can also be white, pink, or gray.
- Discomfort or Itching: Affected areas may feel itchy or may occasionally bleed, especially if irritated by friction or contact.
Asymptomatic Cases
Many individuals with genital warts do not show any visible symptoms. Asymptomatic carriers can still transmit the virus to sexual partners, which makes regular screenings important for sexually active individuals, particularly since HPV can also be linked to certain types of cancer.
Quick Guide to Symptoms of Genital Warts
For quick reference, here is an infographic-style bullet point summary of the key symptoms:
- Appearance: Small, flesh-colored or gray bumps; may resemble a cauliflower in clusters.
- Location: Can appear on genital areas, including vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, scrotum, and also around the groin or thighs.
- Sensation: Itching or discomfort in the affected area; possible bleeding with irritation.
- Asymptomatic: No visible warts or symptoms, but still capable of transmitting HPV.
Being aware of these symptoms can help in recognizing the need for a medical consultation. Regular check-ups and open communication with partners about sexual health are essential steps in managing and preventing the spread of genital warts.
Causes and Risk Factors of Genital Warts
Understanding the transmission and risk factors associated with genital warts can help in prevention and management.
Transmission of Genital Warts
The most common mode of transmission for genital warts is through sexual contact. This includes vaginal, anal, and oral sex. HPV can spread even when an infected person shows no signs or symptoms. Because the virus resides on the genital skin, it can easily be transferred through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activities.
Risk Factors for Genital Warts
Several factors can increase the risk of developing genital warts:
- Unprotected Sex: Not using condoms or other barrier methods significantly increases the risk of acquiring HPV and, consequently, genital warts.
- Multiple Sexual Partners: The likelihood of contracting genital warts increases with the number of sexual partners a person has.
- Weakened Immune Systems: Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether from immune-suppressing drugs or conditions like HIV/AIDS, are more susceptible to HPV infections.
Prevention: The Role of HPV Vaccines
One of the most effective preventive measures against genital warts is vaccination against HPV. Vaccines like Gardasil 9 are designed to protect against the most common HPV types associated with genital warts and cervical cancer. Immunization is recommended for preteens (both boys and girls) aged 11 to 12 years, but it can be administered as early as age 9 and through age 26 for those who have not been previously vaccinated. Vaccination before the onset of sexual activity is ideal for maximum effectiveness.
However, while genital warts are a common and often distressing condition, understanding their causes, modes of transmission, and risk factors can lead to effective prevention strategies, including the use of HPV vaccines. Engaging in protected sex, limiting the number of sexual partners, and receiving the HPV vaccine are practical steps individuals can take to protect themselves against genital warts.
Diagnosing Genital Warts
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prevention of potential complications. Here’s how healthcare providers typically diagnose genital warts and the importance of regular screenings.
Role of Visual Examination
The primary method for diagnosing genital warts involves a visual examination by a healthcare provider. During the examination, doctors look for characteristic lesions that appear as small bumps or groups of bumps in the genital area. These can vary in size and may be raised or flat, single or multiple. A visual exam not only helps in identifying visible warts but also assesses their extent and any possible impacts on physical health.
Additional Diagnostic Tests
While a visual exam is often sufficient to diagnose genital warts, additional tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis or plan treatment. These tests include:
- HPV Tests: This test involves sampling cells from the genital area to detect high-risk types of HPV that are more likely to lead to cervical cancer, though it’s less commonly used specifically for diagnosing visible genital warts.
- Biopsy: In uncertain cases or when the warts have an unusual appearance, a biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a small piece of tissue from the wart for microscopic examination.
Importance of Regular Screenings
For sexually active individuals, regular screenings are vital. These screenings help in early detection and treatment of genital warts and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Regular health checks can also provide education on preventive measures, further reducing the risk of acquiring or spreading HPV and other STIs.
By prioritizing regular visits to a healthcare provider, individuals can maintain their sexual health and prevent the spread of infections. Always consult a healthcare professional if you notice any unusual symptoms or changes in your genital area.
Treatment Options for Genital Warts
Genital warts, caused by certain types of the human papillomavirus (HPV), can be distressing, but various treatment options are available. Addressing genital warts effectively involves a combination of medical interventions, possible surgical procedures, and supportive home care.
Available Treatments (Medical and Surgical)
1. Topical Medications: These include prescription creams and solutions such as imiquimod (boosts the immune system), podofilox (destroys wart tissue), and trichloroacetic acid (burns off warts chemically).
2. Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the warts with liquid nitrogen, a common and effective method for removing warts.
3. Surgical Options:
- Electrocautery: Burning off the warts with electrical current.
- Laser Treatment: Using a laser to destroy wart tissue, suitable for extensive or tough-to-treat warts.
- Excision: Cutting out the warts, often used for smaller or less tricky areas.
4. Injection Therapy: Interferon injections are sometimes used for severe wart cases, although this is less common due to potential side effects and high cost.
Home Care and Over-the-Counter Options
While prescription treatments are generally necessary, some supportive measures can be taken at home:
- Over-the-Counter Solutions: Salicylic acid treatments, similar to those used for common warts, can help reduce genital warts. These should be used cautiously and only according to a healthcare provider’s instructions due to the sensitive area involved.
- Aloe Vera: Known for its soothing properties, applying aloe vera gel can help ease irritation.
- Warm Baths: Soaking in a warm bath can alleviate discomfort and keep the area clean, which is crucial for healing.
Importance of Consulting with a Healthcare Provider
It is vital to consult with a healthcare provider when treating genital warts. Self-treatment can lead to complications, incorrect use of medications, and ineffective treatment. A healthcare provider can diagnose the condition correctly, recommend the most appropriate treatment options, and monitor progress. Additionally, since HPV is a sexually transmitted infection (STI), professional guidance on prevention and management is crucial for affected individuals and their partners.
By exploring both medical and supportive home care treatments, individuals dealing with genital warts can manage their symptoms effectively under professional guidance, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Preventing Genital Warts
Preventing genital warts involves a combination of vaccination, safe sexual practices, and open communication with sexual partners. Here’s how you can protect yourself and others from this infection:
Vaccination
The most effective way to prevent genital warts is to get vaccinated against HPV. The HPV vaccine is safe and highly effective in preventing the types of HPV that cause most genital warts and cervical cancers. It is recommended for preteens (ages 11 to 12) but can be given as early as age 9 and up to age 45 in some cases. Getting vaccinated before becoming sexually active is ideal, but older individuals can still benefit from the vaccine.
Safe Sexual Practices
Using condoms and dental dams every time you engage in sexual activity can significantly reduce the risk of transmitting HPV and other STIs. While they do not provide 100% protection against HPV, they can help lower the overall risk of transmission. It’s also wise to limit the number of sexual partners and avoid sexual contact with anyone who has visible signs of genital warts.
Regular Health Screenings
Regular screenings and check-ups can help detect early signs of HPV infection and other STIs before they lead to more serious conditions. Women are advised to have regular Pap tests, which can detect precancerous and cancerous cells caused by HPV. Both men and women should consider regular HPV screenings if recommended by their healthcare provider.
Importance of Communication
Open communication with your sexual partners about STIs is crucial. Discussing your sexual health, STI testing, and HPV vaccination status with potential partners is important for mutual protection. Honesty about one’s health status and sexual history can reduce the risk of STI transmission and help maintain overall sexual health integrity.
By taking these preventative measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing genital warts and other complications associated with HPV. Education and awareness about HPV and genital warts are also key in reducing the stigma associated with this and other STIs.
FAQs About Genital Warts Symptoms and Causes
What are the common symptoms of genital warts?
Genital warts typically appear as small, flesh-colored or gray swellings in your genital area. They can be raised or flat, single or multiple, small or large, and sometimes they form clusters resembling a cauliflower. While some individuals may experience itching, discomfort, or pain in the affected area, others might not notice any symptoms at all.
What causes genital warts?
Genital warts are caused by certain strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV). They are commonly transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and occasionally oral sex. Not everyone who has HPV develops genital warts, but the virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted even when warts are not visible.
Can genital warts be cured?
While there is no cure for the virus itself, treatments are available for the symptoms. Genital warts can be treated through medications that are applied directly to the area or through surgical procedures to remove the warts. However, even after treatment, the virus can remain in the body, and warts may recur.
Are genital warts a serious health risk?
In most cases, genital warts themselves do not pose a serious health risk and are considered more of an aesthetic or discomfort issue. However, certain types of HPV associated with genital warts can lead to more serious conditions, such as cervical cancer in women, which underscores the importance of regular medical check-ups and screenings.
How can I prevent genital warts?
The most effective way to prevent genital warts is to get vaccinated against HPV. Vaccines can protect against the strains most likely to cause genital warts and cervical cancer. Additionally, using condoms during sexual activity can reduce the risk of contracting HPV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs), though they do not provide complete protection against viruses spread through skin-to-skin contact.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of genital warts is crucial for effective management and treatment. By being informed about the common signs, such as small bumps in the genital area, and potential causes, including the human papillomavirus (HPV), individuals can take proactive steps towards their health.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing symptoms or concerned about genital warts to seek professional medical advice. Consulting a healthcare provider ensures a correct diagnosis and the most appropriate treatment options. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and help prevent transmission to others.
Take control of your health by staying informed and consulting professionals when concerns arise. Your well-being is worth the effort.
References
For further reading on the symptoms of genital warts and for additional verification of the information discussed, consider exploring the following reputable sources:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC offers comprehensive guides and up-to-date research on genital warts, including symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies. Access their resources at CDC Genital Warts Information.
- World Health Organization (WHO) – The WHO provides detailed reports and global statistics on the prevalence of genital warts and other HPV-related conditions. Learn more through their portal at WHO Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
- Mayo Clinic – For a detailed overview of symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and treatment methods for genital warts, visit the Mayo Clinic’s page at Mayo Clinic Genital Warts.
- National Health Service (NHS) – The NHS website contains patient-friendly information and guidance on numerous health conditions, including genital warts. They provide a comprehensive section at NHS Choices – Genital Warts.
These resources are excellent starting points for anyone seeking more in-depth knowledge about genital warts, their symptoms, and available treatments.