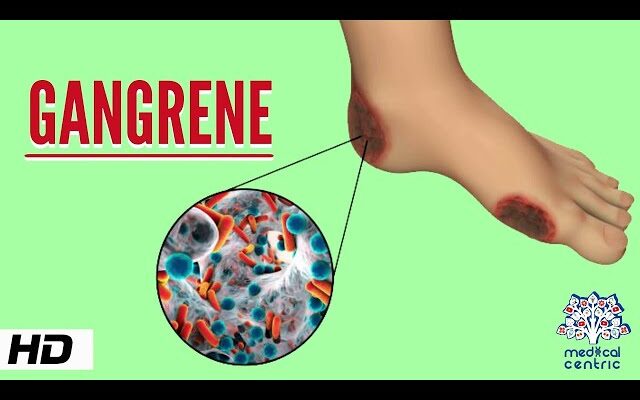
Gangrene Symptoms: Gangrene is a serious medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood flow or a serious bacterial infection.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of gangrene is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of gangrene, their specific symptoms, and the underlying causes.
Understanding Gangrene
Gangrene is a serious medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue due to either a lack of blood supply or a severe bacterial infection. Understanding how gangrene occurs and recognizing its types are crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Explanation of How Gangrene Occurs
Gangrene typically develops when the blood flow to a certain area of your body is interrupted or significantly reduced. This disruption deprives the tissue of oxygen and nutrients, causing the cells to die. The most common causes of reduced blood flow include:
- Injuries: Physical trauma such as accidents, burns, or severe bruises can damage blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow.
- Infections: Bacterial infections can produce toxins that block blood vessels.
- Chronic health conditions: Conditions like diabetes and arteriosclerosis can lead to narrowed or blocked arteries.
In some cases, gangrene can also result from bacterial infections that occur directly within body tissues. These infections release toxins that not only inhibit blood flow but also directly kill the tissue.
Types of Gangrene
Understanding the types of gangrene is essential for recognizing its symptoms and seeking timely medical intervention. The main types of gangrene include:
- Dry Gangrene: This type is commonly associated with diabetes and autoimmune diseases. It typically affects the extremities like fingers and toes and progresses slowly. The affected tissue becomes dry, shriveled, and dark (black) in color.
- Wet Gangrene: Often caused by a bacterial infection in an area with poor blood flow, wet gangrene progresses much faster than dry gangrene. It usually occurs after a severe burn or frostbite. The affected area may swell, produce a foul odor, and develop blisters filled with fluid.
- Gas Gangrene: This type is caused by a specific bacterium that produces gas within the tissue. It is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and a crackling sensation under the skin due to gas production.
- Internal Gangrene: It affects internal organs, usually resulting from a blocked blood vessel. This type is less visible than the others but can be extremely dangerous, often affecting the intestines, gallbladder, or appendix.
If you suspect gangrene, seek immediate medical attention to prevent the spread of the infection and potentially save affected limbs and tissues.
Certainly! Here’s a SEO and readability-friendly section on the causes of gangrene:
Causes of Gangrene
Gangrene, a serious medical condition characterized by the death of body tissue, arises from various causes and risk factors. Understanding these can help in prevention and early treatment.
Common Causes Leading to Gangrene
The primary cause of gangrene is a significant reduction in blood supply to the affected tissues. This reduction can stem from several conditions:
- Infections: Bacterial infections can cause gangrene by invading and killing tissue. Gas gangrene, for example, is caused by a specific type of bacteria that produces gas within tissue.
- Vascular diseases: Conditions that affect blood vessels, such as atherosclerosis and peripheral arterial disease, can lead to decreased blood flow, significantly raising the risk of gangrene.
- Injuries: Severe injuries that damage blood vessels, including burns, frostbite, and traumatic injuries, can impede blood flow to certain areas, leading to tissue death.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels associated with diabetes can damage blood vessels, reducing circulation and increasing the risk of infections and ulcers that may progress to gangrene.
Factors That Increase the Risk of Gangrene
Several factors can heighten the likelihood of developing gangrene. These risk factors include:
- Diabetes: Poor blood sugar control can cause damage to blood vessels, making it one of the top risk factors for gangrene.
- Smoking: Smoking tobacco can constrict and damage blood vessels, impairing circulation.
- Immobility: Prolonged immobility, due to any reason, can lead to poor blood circulation, especially in the extremities, increasing the risk of gangrene.
- Severe injuries and infections: Conditions that severely damage the skin and tissues, like burns or severe wounds, can increase the susceptibility to infections that may lead to gangrene.
- Age: Older adults often have reduced blood circulation, making them more susceptible to gangrene.
However, early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes for those at risk. Always consult with healthcare professionals if you notice signs of potential gangrene, such as persistent pain, skin discoloration, or unexplained sores that fail to heal.
Diagnosing Gangrene
Identifying gangrene accurately is crucial for timely and effective treatment. The diagnostic process typically begins with a physical examination and incorporates a variety of tests to confirm the presence and extent of the condition.
Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing gangrene is a thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional. During the exam, the doctor will look for signs of dead or dying tissue. These signs may include a change in skin color to shades of green, black, blue, or red, a noticeable loss of sensation in the affected area, and a foul smell if the tissue is decaying.
Imaging Tests
To get a detailed view of the affected areas, doctors often utilize imaging tests. These tests help determine how far the gangrene has spread and assess the condition of the internal tissues and structures. Common imaging tests include:
- X-rays: Useful for viewing gas formation in gangrene cases involving muscle tissue.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Offers a detailed image of soft tissues, helping to identify the type and extent of gangrene.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Provides a comprehensive view that helps distinguish between different types of gangrene and assesses the involvement of internal organs.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests play a key role in confirming the diagnosis of gangrene. These tests include:
- Blood Tests: These can detect infection and other complications associated with gangrene. Elevated white blood cell count is a common finding, indicating an immune response to infection.
- Fluid/Tissue Culture: Testing a sample of fluid or tissue from the affected area can identify the type of bacteria or other pathogens causing the infection. This helps in tailoring the most effective treatment.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis is essential in managing gangrene effectively to prevent the spread of infection and severe health complications. By combining physical assessments with sophisticated imaging and laboratory tests, healthcare providers can develop a targeted treatment plan to address this serious condition.
Treatment Options for Gangrene
Gangrene, a serious condition resulting from the loss of blood supply to tissues, causing them to die, requires prompt and effective treatment. Understanding the available treatment options can help individuals seek timely medical attention and improve outcomes.
Medical Treatments
Medical treatment for gangrene focuses on stopping the spread of infection, preserving healthy tissue, and managing pain. The treatment plan often depends on the type of gangrene and the overall health of the individual. Here are the primary medical treatments:
- Antibiotics: These are critical in fighting infection, especially if gangrene is caused by an infection. Antibiotics are usually administered intravenously to ensure they work rapidly and effectively.
- Surgery: Surgical intervention might be necessary to remove the dead tissue and prevent the spread of the infection. In severe cases, this might involve amputation of the affected limb to save the patient’s life.
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): This treatment involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized room or chamber. HBOT helps increase the amount of oxygen in the blood, which can aid the healing process of affected tissues and prevent further decay.
- Vascular Surgery: For cases where gangrene is caused by poor blood circulation, vascular surgery is employed to restore blood flow to the affected areas.
- Pain Management: Effective pain management strategies are essential, as gangrene can be extremely painful. Medications and other therapies are used to manage pain associated with the condition.
Advances in Treatment
Research and development in medical science have led to significant advances in the treatment of gangrene, enhancing the ability to save more lives and improve recovery rates. Key advancements include:
- Regenerative Medicine: Emerging techniques, such as tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, offer new hope. These methods involve the regeneration of tissues and may eventually reduce the need for amputations.
- Improved Antibiotic Therapies: The development of more effective antibiotic treatments combats resistant strains of bacteria that can cause gangrene.
- Enhanced Surgical Techniques: Minimally invasive surgical techniques have improved the outcomes for patients, reducing recovery times and improving the effectiveness of dead tissue removal.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques: These techniques allow for earlier diagnosis and more precise treatment planning, which is crucial in preventing the progression of gangrene.
- Genetic Research: Ongoing genetic research is exploring the reasons why some individuals may be more susceptible to gangrene. This could lead to preventative strategies or tailored treatments based on genetic profiles.
However, understanding these treatment options and advancements is crucial for anyone dealing with or at risk of gangrene. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital to effectively manage the condition and improve the quality of life.
Prevention and Management of Gangrene
Below, we explore key preventive measures, lifestyle changes, and early intervention strategies that can help reduce the risk of developing gangrene.
Preventive Measures
- Maintain Proper Hygiene: Regularly cleaning and drying your feet and any wounds helps prevent infections that could lead to gangrene. Use mild soap and lukewarm water, and ensure all minor cuts and abrasions are cleaned immediately.
- Control Underlying Conditions: Managing conditions like diabetes, atherosclerosis, and peripheral artery disease is crucial. Follow your healthcare provider’s advice regarding medication, diet, and exercise to maintain blood flow and prevent tissue death.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking impairs circulation and reduces the amount of oxygen that reaches your tissues. Quitting smoking can significantly lower your risk of developing gangrene.
- Inspect Your Feet Daily: Especially important for diabetics, regular checks for injuries or infections can prevent complications. Look for signs of injury, infection, or changes in skin color and seek immediate medical advice if needed.
- Dress Appropriately for the Cold: Frostbite can lead to gangrene. Wear suitable protective clothing in cold weather to keep your extremities warm.
Lifestyle Changes
- Adopt a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain healthy blood vessels and improve circulation.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity increases blood flow and helps maintain healthy blood pressure levels, both of which are essential for preventing gangrene. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week.
- Monitor and Manage Blood Sugar Levels: For those with diabetes, regular monitoring and control of blood sugar levels are imperative to prevent diabetic complications including gangrene.
Early Intervention Strategies
- Seek Immediate Medical Attention for Signs of Infection: Early signs of infection, such as increased redness, pain, swelling, or pus, should prompt an immediate visit to your healthcare provider. Early detection and treatment of infections can prevent the progression to gangrene.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider, especially if you have underlying conditions that increase your risk, can help catch potential issues early before they lead to serious complications.
- Educate Yourself and Others: Being informed about the risks and symptoms of gangrene can lead to quicker decisions about seeking medical care. Education about the condition can also help you understand and adhere to preventive measures more strictly.
By adopting these preventive measures, making informed lifestyle changes, and applying early intervention strategies, you can significantly reduce the risk of developing gangrene. Early and proactive management is key to preventing the severe consequences of this condition.
FAQs on Gangrene Symptoms
1. What is gangrene and what causes it?
Gangrene is a serious condition where a loss of blood supply causes body tissue to die. It can affect any part of the body but commonly impacts the extremities like fingers, toes, and limbs. Gangrene usually results from an infection or injury that interrupts blood flow. Factors like diabetes, atherosclerosis, and smoking can increase the risk.
2. What are the common symptoms of gangrene?
The symptoms of gangrene vary depending on the type but typically include:
- Sudden, severe pain followed by a feeling of numbness
- Discoloration of the affected area, turning it greenish-black, blue, or red
- Foul-smelling discharge if the area becomes infected
- Swelling and the feeling of cold in the affected area
3. Are there different types of gangrene? If so, what are they?
Yes, there are different types of gangrene, each with distinct characteristics:
- Dry gangrene is characterized by dry and shriveled skin that changes color to dark brown or black. It’s often associated with diabetes.
- Wet gangrene develops rapidly due to infection in an injury or surgical wound where the blood supply is blocked.
- Gas gangrene is caused by a bacterial infection that produces gas within tissue and is a deadly form of gangrene requiring immediate treatment.
4. How can you tell if you might have gangrene?
Early detection is crucial. Watch for unexplained pain and numbness, persistent sores or infections, and noticeable color changes in your extremities. These symptoms, especially if accompanied by a foul odor or discharge, should prompt immediate medical attention.
5. Is gangrene treatable?
Yes, gangrene is treatable, especially if caught early. Treatment typically involves removing the dead tissue, treating any infection, and restoring blood flow to the affected area. In severe cases, amputation of the affected limb may be necessary to prevent the spread of the infection.
6. How can gangrene be prevented?
Preventing gangrene involves managing underlying conditions such as diabetes, improving blood flow, and taking care of your limbs. Avoid smoking, monitor your feet and hands regularly for wounds or infections, and seek prompt medical treatment for any injuries.
7. When should you see a doctor for gangrene symptoms?
You should see a doctor if you notice any signs of infection, persistent sores, sudden severe pain, or changes in skin color. Early medical intervention can significantly improve the prognosis for gangrene.
Conclusion
Recognizing the symptoms of gangrene is crucial for prompt treatment and prevention of severe complications. This condition, characterized by the death of body tissue due to a lack of blood flow or a serious bacterial infection, can lead to dire health consequences if not addressed swiftly. Key symptoms include sudden pain, skin discoloration, swelling, and the emission of a foul odor from the affected area. Early detection can significantly increase the effectiveness of treatment options and can potentially save limbs and lives.
Individuals who are at higher risk, including those with diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, or a compromised immune system, should be particularly vigilant about monitoring their health for signs of gangrene. It is imperative for at-risk individuals to maintain regular consultations with healthcare professionals. These regular check-ups can lead to early diagnosis and treatment, which are vital for preventing the progression of gangrene.
Seeking timely medical advice not only helps in managing the symptoms effectively but also in adopting lifestyle and health management strategies that can prevent the condition from developing. Remember, your health is invaluable; do not hesitate to reach out to your medical provider if you suspect any symptoms of gangrene. Early intervention is your best defense against this serious condition.
References
For a deeper understanding and verification of the information presented regarding the symptoms of gangrene, consider exploring the following reputable sources. These references offer detailed insights and expanded knowledge, which can enhance your comprehension of gangrene symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures.
- Mayo Clinic – The Mayo Clinic provides a comprehensive overview of gangrene, including its symptoms, causes, and treatments. The site is well-known for its reliable and up-to-date medical content. Read more about Gangrene Symptoms at Mayo Clinic.
- MedlinePlus – A service of the U.S. National Library of Medicine, MedlinePlus offers accessible, peer-reviewed information on gangrene that can be useful for both patients and healthcare professionals. Visit MedlinePlus for more on Gangrene.
- WebMD – WebMD is another trusted source for medical information online. Their entry on gangrene provides a detailed look at the condition’s signs, possible complications, and different forms. Learn more about Gangrene on WebMD.
- Healthline – Known for its clear, authoritative health advice, Healthline discusses the identification and management of gangrene, along with personal health tips to prevent the disease. Explore Gangrene Information on Healthline.
These sources are esteemed in the medical community and provide valuable, scientifically-backed information that can help readers understand the complexities of gangrene and its implications on health.