Functional Dyspepsia Treatment: Functional Dyspepsia (FD) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects approximately 10-30% of the population globally.
It is characterized by chronic or recurrent pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen. Despite its prevalence, FD often remains underdiagnosed due to its nonspecific symptoms and similarities to other digestive diseases.
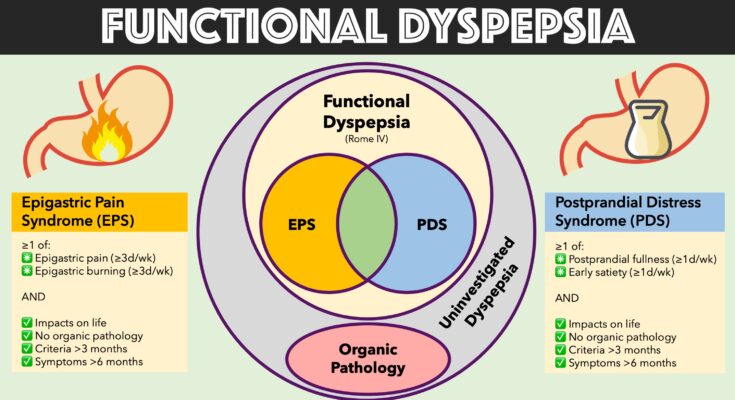
Understanding Functional Dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia is a common gastrointestinal condition that affects the upper digestive tract. Often confused with other digestive issues, functional dyspepsia is characterized by chronic discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen without a clear medical cause. Understanding this condition can help in distinguishing it from other gastrointestinal disorders and managing its symptoms effectively.
Common Symptoms Associated with Functional Dyspepsia
The symptoms of functional dyspepsia can vary widely from person to person but typically include:
- Persistent or recurring pain in the upper abdomen
- A feeling of uncomfortable fullness after a meal
- Early satiety (feeling full after eating only a small amount of food)
- Bloating in the upper abdomen
- Nausea
These symptoms often result in a significant impact on the patient’s quality of life and may vary in intensity over time.
Differences Between Functional Dyspepsia and Other Gastrointestinal Disorders
Functional dyspepsia differs from other gastrointestinal disorders in several key ways:
- Absence of Organic Cause: Unlike disorders like ulcers or GERD, functional dyspepsia does not show any organic cause upon medical imaging or endoscopy.
- Symptom Pattern: Symptoms such as pain and bloating are predominantly located in the upper abdomen, distinguishing it from conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), which usually affects the lower abdomen.
- Treatment Response: Treatments for functional dyspepsia often focus on symptom management rather than treating an underlying cause, which is more common in conditions such as ulcers, where specific medication can target the cause directly.
However, understanding these distinctions is crucial for effective management and treatment of functional dyspepsia, ensuring that patients receive appropriate care tailored to their specific symptoms rather than a one-size-fits-all approach often used for other gastrointestinal disorders.
Causes and Risk Factors of Functional Dyspepsia
Understanding the causes and risk factors of functional dyspepsia is essential for both prevention and treatment. This common digestive disorder, characterized by chronic or recurrent pain and discomfort in the upper abdomen, affects many individuals worldwide. Here, we explore the potential causes, identify key risk factors, and discuss the influence of lifestyle and dietary habits.
Potential Causes of Functional Dyspepsia
The exact causes of functional dyspepsia remain unclear, but several theories highlight its multifactorial nature:
- Gut-Brain Axis Disruption: Communication issues between the digestive tract and the brain can lead to symptoms of dyspepsia.
- Gastric Motility Disorders: Abnormalities in the way the stomach contracts and empties can cause discomfort and bloating.
- Hypersensitivity: Some people may have an increased sensitivity to stomach acid or stretching of the stomach after eating, which contributes to the symptoms.
Research is ongoing to further understand the pathophysiology behind functional dyspepsia and its origins.
Risk Factors That May Increase Susceptibility
Certain factors can increase an individual’s likelihood of developing functional dyspepsia, including:
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of digestive disorders might raise the risk.
- Medication Use: Frequent use of certain medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can irritate the stomach lining.
- Infections: Past or current infections, particularly with bacteria like Helicobacter pylori, are linked to many gastrointestinal symptoms, including dyspepsia.
- Psychological Factors: Stress, anxiety, and depression are significantly associated with the onset and exacerbation of functional dyspepsia symptoms.
Identifying these risk factors can help in managing or even preventing the disorder.
The Role of Lifestyle and Dietary Habits
Lifestyle and dietary choices play a crucial role in the management of functional dyspepsia. Consider these guidelines:
- Balanced Meals: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can prevent the stomach from becoming too full and reduce discomfort.
- Limiting Irritants: Avoiding spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol can help minimize symptoms.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can reduce stress and improve gastrointestinal health.
By modifying dietary habits and lifestyle, individuals can significantly impact their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
While the exact causes of functional dyspepsia are still being researched, understanding the risk factors and the impact of lifestyle and diet provides valuable insights into managing this disorder. Individuals experiencing persistent symptoms should consult a healthcare provider to tailor a treatment approach that considers these elements.
Diagnosing Functional Dyspepsia
Proper diagnosis is crucial for effective management. Here’s an overview of the diagnostic procedures typically used to identify this condition, highlighting the importance of medical history, physical examinations, and the need to exclude other similar gastrointestinal issues.
Common Diagnostic Procedures for Functional Dyspepsia
- Medical History and Symptoms Review: One of the first steps in diagnosing functional dyspepsia involves a detailed discussion about the patient’s medical history and symptoms. Healthcare providers will inquire about the nature, duration, and timing of abdominal pain, as well as associated symptoms such as bloating, belching, or early satiety.
- Physical Examination: During the physical exam, doctors will look for any abdominal tenderness or signs that might suggest complications or alternative diagnoses. This examination helps in assessing the general state of health and detecting any physical signs of gastrointestinal disease.
- Laboratory Tests: Basic blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests, and pancreatic enzymes, may be ordered to rule out other conditions that can mimic functional dyspepsia.
- Endoscopy: Often recommended if symptoms are severe, persistent, or if there is a need to rule out serious conditions such as peptic ulcers or gastric cancer. During an endoscopy, a flexible tube with a camera is inserted through the mouth to view the upper digestive tract.
- Breath Tests: These tests can detect infections like Helicobacter pylori, a common bacterial cause of ulcers, which can contribute to dyspeptic symptoms.
- Ultrasound: This imaging test is utilized to check for gallstones and other abnormalities in the gallbladder and surrounding organs that could cause similar symptoms.
Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
Collecting a comprehensive medical history and conducting a thorough physical examination are essential components of the diagnostic process. These initial steps can provide valuable clues that guide further testing and help distinguish functional dyspepsia from other gastrointestinal disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome or gallbladder disease.
Importance of Ruling Out Other Conditions
Functional dyspepsia shares symptoms with several other gastrointestinal disorders, including peptic ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It is crucial to rule out these conditions before a definitive diagnosis of functional dyspepsia is made. Excluding other causes ensures that the treatment plan is appropriate and targeted, thereby improving patient outcomes. Diagnostic tests such as endoscopy or ultrasound are particularly useful in identifying physical manifestations of these other conditions.
By accurately diagnosing functional dyspepsia, healthcare providers can tailor treatment strategies that effectively address the patient’s specific symptoms and improve their quality of life. This diagnostic clarity is achieved through a combination of detailed patient history, careful physical examination, and selective use of diagnostic tests.
Treatment Options for Functional Dyspepsia
Fortunately, several effective treatment strategies are available. Here, we explore the various approaches to managing functional dyspepsia, including pharmacological treatments, dietary adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and complementary therapies.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological interventions are commonly prescribed to alleviate the symptoms of functional dyspepsia. These include:
- Antacids and Acid Blockers: These medications, such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and H2-receptor antagonists, reduce stomach acid production, which can help relieve stomach pain and heartburn.
- Prokinetics: These drugs help to speed up gastric emptying and improve coordination in the digestive tract, which can reduce bloating and discomfort.
- Antidepressants: Low doses of certain antidepressants may be used to help modulate pain perception in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Antispasmodics: These medications can help to relieve stomach cramping and pain by reducing involuntary muscle spasms in the digestive tract.
It is important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate medication based on individual symptoms and health status.
Dietary and Lifestyle Modifications to Manage Symptoms
Modifying your diet and lifestyle can significantly reduce the symptoms of functional dyspepsia. Consider implementing the following changes:
- Eat Smaller, More Frequent Meals: Large meals can exacerbate symptoms, so eating smaller, more frequent meals can help.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Spicy foods, caffeine, alcohol, and fatty foods are known to trigger dyspepsia symptoms in some people.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight can increase abdominal pressure and worsen symptoms.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can help manage stress levels.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
In addition to traditional medical treatments, some individuals find relief from functional dyspepsia through alternative approaches:
- Herbal Remedies: Ginger, peppermint, and chamomile have been noted for their digestive benefits. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any herbal supplement.
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest that acupuncture can help in managing the symptoms of dyspepsia by promoting relaxation and pain relief.
- Probiotics: These can help in maintaining gut health and might contribute to alleviating dyspeptic symptoms.
By exploring a combination of these treatments, individuals suffering from functional dyspepsia can often find considerable relief. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment to ensure it is safe and appropriate for your specific health needs.
Managing Functional Dyspepsia: Practical Tips
Managing this condition effectively involves a combination of diet, lifestyle adjustments, and stress management techniques. Here, we explore practical tips to help individuals cope with the symptoms of functional dyspepsia.
Daily Management Tips for Individuals with Functional Dyspepsia
The key to managing functional dyspepsia effectively lies in recognizing and adjusting daily habits that may trigger symptoms. Here are several tips that can help:
- Eat smaller, more frequent meals: Large meals can exacerbate indigestion. Try consuming smaller portions spread out over the day instead of three large meals.
- Avoid trigger foods: Common triggers include spicy foods, caffeine, chocolate, and fatty foods. Keep a food diary to identify specific triggers for you.
- Stay upright after eating: Lying down immediately after meals can worsen symptoms. Aim to stay upright for at least 30 minutes post-meal.
- Chew food thoroughly: Taking time to chew food well can aid digestion and reduce symptoms of dyspepsia.
How to Track and Modify Diet to Reduce Symptoms
Modifying your diet is crucial in managing functional dyspepsia. Here’s how you can track and adjust your eating habits:
- Keep a detailed food diary: Record everything you eat and drink, along with any symptoms you experience. This can help identify potential trigger foods to avoid.
- Increase fiber intake: While fiber is beneficial, introduce it slowly. High-fiber foods can sometimes exacerbate symptoms, so it’s important to monitor your body’s response.
- Consider potential irritants: Alcohol and acidic foods like tomatoes and citrus can trigger symptoms. Limit these in your diet and note any changes in your symptoms.
- Consult a dietitian: A professional can provide personalized dietary advice, which can be tremendously helpful in managing symptoms.
Stress Management and Its Impact on Functional Dyspepsia
Stress is a significant factor in the exacerbation of functional dyspepsia symptoms. Managing stress effectively can lead to noticeable improvements:
- Practice relaxation techniques: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help manage stress and also improve digestive function.
- Adequate sleep: Ensure you get enough restful sleep, as sleep deprivation can increase stress and worsen symptoms.
- Seek professional help: If stress is a major issue, consider talking to a mental health professional who can provide coping strategies.
By implementing these practical tips, individuals with functional dyspepsia can often manage their symptoms more effectively and improve their quality of life. Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor these suggestions to your specific needs and confirm that your symptoms are truly functional dyspepsia.
Latest Research and Developments in Functional Dyspepsia
Recent Advances in Understanding Functional Dyspepsia
Functional dyspepsia, often characterized by chronic upper abdominal discomfort and pain without an identifiable cause, has seen significant advancements in understanding through recent research. Studies have focused on the complex interactions between the brain and the digestive system, exploring how factors like stress, diet, and gut microbiota influence symptoms. Recent findings highlight the role of visceral hypersensitivity and motility disorders in functional dyspepsia, providing a clearer picture of its pathophysiology. These insights are crucial for developing more targeted and effective treatments, emphasizing a multidisciplinary approach to care.
Current Research on New Treatment Methods
Innovation in treatment strategies for functional dyspepsia is ongoing, with several promising directions being explored. Recent clinical trials have investigated the efficacy of new pharmacological treatments, including novel prokinetics and neuromodulators that aim to address underlying motility and sensory disturbances. Additionally, the potential of dietary interventions and probiotics in managing symptoms is being closely examined. These studies contribute to a growing body of evidence that supports a more personalized treatment approach, taking into account the unique physiological and psychological aspects of each patient.
Future Directions in the Treatment and Management of Functional Dyspepsia
Looking ahead, the future of managing functional dyspepsia lies in personalized medicine and integrated care models. Research is increasingly focusing on genetic markers and biomarkers that can predict treatment responses, thereby optimizing patient-specific therapeutic strategies. There is also a growing interest in the integration of psychological therapies with traditional medical treatments to address the multifactorial nature of the disorder. Furthermore, ongoing advancements in technology, such as digital health tools and AI-driven diagnostic systems, promise to enhance the precision and effectiveness of functional dyspepsia management.
By continuing to explore these avenues, medical professionals are poised to significantly improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from functional dyspepsia, emphasizing a more holistic and patient-centered approach to healthcare.
FAQs on Functional Dyspepsia Treatment
What is functional dyspepsia?
Functional dyspepsia, often referred to as indigestion, is a common digestive disorder. It causes discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen, usually without an identifiable medical cause. Symptoms can include bloating, nausea, belching, and a feeling of fullness.
What are the treatment options for functional dyspepsia?
Treatment for functional dyspepsia aims to alleviate symptoms. Common approaches include lifestyle modifications such as eating smaller, more frequent meals, avoiding trigger foods, and managing stress. Medications may include antacids, proton pump inhibitors, or prokinetics. In some cases, psychological therapies like cognitive behavioral therapy are recommended.
How long does it take for treatment to work?
The effectiveness of treatment can vary. Some patients might notice improvement within a few weeks, while others may require a longer period to see significant changes. It’s important to follow the treatment plan and communicate with your healthcare provider about any ongoing symptoms.
Can diet changes help manage functional dyspepsia?
Yes, dietary changes can significantly help manage symptoms. It’s advisable to avoid spicy and fatty foods, caffeine, and alcohol, which can trigger symptoms. Incorporating easily digestible foods and eating slowly can also provide relief.
Is functional dyspepsia a chronic condition?
Functional dyspepsia is often a chronic condition, but many individuals find their symptoms can be managed effectively with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are important to monitor and adapt treatment strategies as needed.
When should I see a doctor for functional dyspepsia?
You should consult a doctor if you experience persistent symptoms of dyspepsia, such as prolonged stomach pain, frequent nausea, or significant changes in appetite. Additionally, seek medical attention if new symptoms appear, or if existing ones worsen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, if you suspect that you may be experiencing symptoms of functional dyspepsia, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional. While this article provides general information, only a qualified medical practitioner can offer a proper diagnosis and recommend an effective treatment plan tailored to your specific condition.
Ignoring symptoms or delaying professional consultation can lead to unnecessary discomfort and potentially complicate your health situation. Remember, the key to managing functional dyspepsia effectively lies in understanding your condition and following professional advice.
Take the step today and schedule a visit with your doctor to discuss your symptoms and explore your treatment options. Prioritizing your health is the best investment you can make for a better quality of life.
References
For those interested in exploring more about the treatment of Functional Dyspepsia, the following references are highly recommended. These sources are reputable and provide further reading to validate the information discussed in this article. They offer a comprehensive view on the current treatments, advancements, and research in managing Functional Dyspepsia.
- Mayo Clinic – This resource offers a detailed overview of Functional Dyspepsia, including symptoms, causes, and treatments. Access their insights here.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) – The NIDDK provides in-depth information on digestive diseases including Functional Dyspepsia. They cover a range of treatment options and current research. Learn more here.
- PubMed Central – For those interested in the latest research studies and clinical trials on Functional Dyspepsia, PubMed Central is an invaluable resource. It offers access to numerous scholarly articles that can be found here.
- WebMD – WebMD provides user-friendly content that explains the symptoms, causes, and potential treatments of Functional Dyspepsia. Their resource can be viewed here.
These resources are excellent starting points for both patients and healthcare providers looking to deepen their understanding of Functional Dyspepsia and explore the range of treatment options available. They are not only informative but also up-to-date with the latest medical guidelines and research findings.