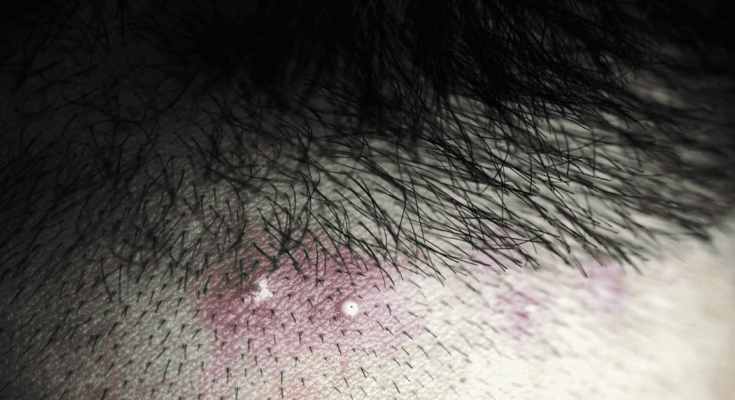
Folliculitis Symptoms: Folliculitis, a common skin condition, affects individuals globally, presenting as inflamed hair follicles.
This article explores the symptoms, causes, and comprehensive insights into managing and preventing folliculitis, aiming to be an authoritative resource for those seeking to understand this condition better.
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide, irrespective of age, gender, or ethnicity. This article aims to shed light on what folliculitis is, its various types, and the demographics most commonly affected by this condition. With an emphasis on clarity and accessibility, our goal is to provide valuable information for those looking to understand more about their skin’s health.
What is Folliculitis?
Folliculitis is an inflammation of the hair follicles, the small cavities surrounding the roots of hair. Essentially, it’s the result of a bacterial or fungal infection, though it can also arise from other causes such as irritation from shaving or the blockage of follicles. Individuals with folliculitis often notice red, swollen bumps around hair follicles, sometimes with a white, pus-filled tip. These bumps can appear anywhere on the skin that has hair, including the scalp, face, arms, legs, and groin area. Beyond the physical symptoms, folliculitis can cause discomfort, itching, and when severe, pain.
This condition impacts the skin’s appearance and can lead to self-consciousness or emotional distress for some. However, it’s typically more of a nuisance than a severe health issue, with many cases resolving on their own or with basic care. Nonetheless, understanding its types and triggers is crucial for effective management and prevention.
Types of Folliculitis
Folliculitis comes in several forms, each with its own characteristics and causes. The two main categories are superficial and deep folliculitis, depending on how much of the follicle is inflamed.
- Superficial Folliculitis: This type affects the upper part of the hair follicle and includes conditions such as bacterial folliculitis, pityrosporum folliculitis, and razor bumps. It’s generally less severe and clears up more quickly.
- Deep Folliculitis: Affecting the entire follicle, this type can lead to more serious infections. Examples include sycosis barbae, deep fungal folliculitis, and gram-negative folliculitis. Deep folliculitis tends to be more persistent and may require medical treatment.
Prevalence and Demographics
Folliculitis does not discriminate. It can affect anyone, although certain types may be more prevalent in specific demographics due to lifestyle, genetic factors, or health conditions. For instance, bacterial folliculitis is common among individuals who frequently use hot tubs (leading to the so-called “hot tub folliculitis”), while razor bumps are more prevalent among people with curly hair who shave. Moreover, those with compromised immune systems, such as patients undergoing chemotherapy or with diabetes, may be at a higher risk for developing the condition.
However, folliculitis is a widespread skin condition that, while generally not serious, can be an uncomfortable and bothersome issue for many. Understanding its types and the demographics most affected is the first step towards effective prevention and treatment. If you suspect you have folliculitis, consulting a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan is always the best course of action.
Symptoms of Folliculitis
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and management. This article explores the common symptoms associated with folliculitis, its appearance on different body parts, and highlights less common symptoms indicating a more severe form of the condition.
Common Symptoms of Folliculitis
Folliculitis typically presents with certain signs that are easy to spot. The most common symptoms include:
- Red, Swollen Bumps: These bumps may resemble acne and are often filled with pus. They are a direct result of the inflamed hair follicles.
- Itching and Soreness: The affected area may feel itchy and sore, causing discomfort.
- Tender, Painful Skin: The skin around the folliculitis may become tender and painful to touch.
- Rash: A rash may develop in the area of the inflamed follicles, further indicating skin irritation.
These symptoms can appear anywhere hair grows on the body, including the scalp, face, arms, legs, buttocks, and pubic area.
Appearance of Folliculitis on Various Body Parts
The manifestation of folliculitis can vary depending on the part of the body affected:
- Scalp: Appears as small, itchy bumps that can be sore to the touch. May lead to hair loss if left untreated.
- Face and Beard Area: Especially common in men, it can cause red, bumpy lesions that are often mistaken for acne.
- Arms and Legs: Presents as red, pimple-like bumps that can be itchy or painful.
- Buttocks and Thighs: Might manifest as large, red, inflamed spots that are tender and might be filled with pus.
Understanding where folliculitis occurs can help in identifying and treating it more effectively.
Less Common Symptoms Indicating a Severe Form
While folliculitis is generally a mild condition, certain symptoms might indicate a more severe form or complications, including:
- Fever: A high temperature can suggest an infection that has spread beyond the skin.
- Recurring or Spreading Infections: If folliculitis frequently returns or spreads to larger areas, it may signal a more severe or chronic condition.
- Boils or Carbuncles: The development of larger, painful lumps or clusters of lumps filled with pus.
- Extreme Pain: Excessive pain that does not improve with basic care may require medical attention.
If you experience any of these less common symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical advice. A healthcare provider can offer a proper diagnosis and recommend an effective treatment plan tailored to your condition’s severity.
Causes of Folliculitis
Understanding the primary causes and contributing factors is crucial for prevention and management. In this article, we delve into the root causes of folliculitis, highlighting how lifestyle and environmental factors play a pivotal role in its development.
Primary Causes of Folliculitis
Folliculitis can stem from a variety of sources, ranging from bacterial infections to physical irritation. The most common culprit is the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus, which invades hair follicles and causes infection. However, folliculitis can also be caused by fungi, viruses, and even an overgrowth of yeast on the skin.
Physical irritation from shaving or tight clothing can also trigger folliculitis. When hair follicles are damaged by friction or shaving, it creates an entry point for pathogens, leading to inflammation. Additionally, blockages of the hair follicles from sweat, oils, or makeup can exacerbate the condition, providing a breeding ground for bacteria.
Lifestyle and Environmental Contributors
Lifestyle and environmental factors significantly influence the development of folliculitis. Here are specific conditions and behaviors that increase the risk:
- Excessive Sweating: Hot and humid environments can lead to excessive sweating, increasing the likelihood of folliculitis, as moisture can trap bacteria against the skin.
- Improper Hygiene: Not showering after excessive sweating or using communal hot tubs without proper chlorination can expose the skin to bacteria that cause folliculitis.
- Friction from Clothing: Tight clothing, especially during physical activity, can irritate hair follicles. Fabrics that don’t breathe well exacerbate this issue by trapping sweat and bacteria.
- Chemical Irritations: Certain skin products, including oils and lotions, can clog pores and lead to folliculitis. It’s important to use non-comedogenic products that won’t block hair follicles.
- Shaving and Hair Removal: Improper shaving techniques, using dull razors, or frequent waxing can damage hair follicles, making them more susceptible to infection.
Preventive Measures
Understanding the causes of folliculitis is the first step in prevention. Maintaining good hygiene, wearing loose-fitting clothes, and adopting proper shaving techniques can significantly reduce the risk. If you’re prone to folliculitis, consider lifestyle adjustments and consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
In conclusion, folliculitis is influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including bacterial infections, physical irritation, lifestyle, and environmental conditions. By addressing these root causes, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing and managing this common skin condition.
Diagnosis and When to See a Doctor for Folliculitis
Knowing how folliculitis is diagnosed and understanding when it’s time to see a doctor can be crucial in managing the condition effectively and preventing complications.
The Diagnosis Process of Folliculitis
The diagnosis of folliculitis typically begins with a physical examination. A healthcare provider will examine the affected skin to identify the signs of folliculitis, such as red bumps, pus-filled lesions, and irritated skin. They will consider your medical history, including any recent exposure to hot tubs, shaving practices, or use of new skin products, which could contribute to the condition.
In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to identify the cause of folliculitis and rule out other conditions. These tests can include:
- Culture Test: A sample from the affected area may be taken to identify the bacteria, fungus, or virus causing the infection.
- Skin Biopsy: In rare instances, a small piece of skin may be removed and examined under a microscope. This is especially helpful if the condition doesn’t respond to initial treatments.
Understanding the cause of folliculitis is crucial for effective treatment. For instance, bacterial folliculitis requires antibiotics, whereas fungal folliculitis would need antifungal medications.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While mild cases of folliculitis often resolve on their own with good hygiene and over-the-counter treatments, there are certain situations where medical advice is essential:
- Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If your symptoms do not improve with home care within a week, or if they worsen, seek medical attention. This could indicate a more severe infection or an incorrect initial diagnosis.
- Recurring Folliculitis: Frequent episodes of folliculitis may require a healthcare provider’s intervention to determine the underlying cause and prevent future outbreaks.
- Severe Symptoms: If you experience severe pain, large, swollen bumps, or signs of a spreading infection (such as fever or pus), it’s important to consult a doctor promptly. These could be signs of a more serious condition requiring specialized treatment.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, due to conditions like diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or certain medications, should seek medical advice early, as they may be more prone to complications.
If you’re unsure whether your symptoms warrant a doctor’s visit, err on the side of caution and consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention can make a significant difference in your recovery and overall skin health.
Preventing Folliculitis: Practical Hygiene and Skincare Tips
By adhering to good hygiene practices and avoiding known irritants, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing folliculitis. Here, we’ll explore practical tips for maintaining the health of your skin and minimizing exposure to risk factors.
Embrace Good Hygiene Habits
1. Regular Cleansing: Daily washing with a gentle, fragrance-free soap helps remove excess oil, sweat, and bacteria from your skin. This is particularly important after sweating heavily or engaging in activities that expose your skin to dirt and bacteria.
2. Use Moisturizers: Keeping your skin hydrated with a suitable moisturizer helps maintain its barrier function, preventing bacteria from entering hair follicles. Opt for non-comedogenic products that don’t clog pores.
3. Wear Breathable Clothing: Clothes that allow your skin to breathe, especially during exercise, can reduce sweat and oil build-up. Choose fabrics like cotton or moisture-wicking materials to keep your skin dry and cool.
Avoid Known Irritants
1. Be Mindful of Shaving: Shaving can irritate the skin and increase the risk of folliculitis. To minimize irritation, always use a sharp razor, shave in the direction of hair growth, and apply a soothing shaving cream or gel. Consider using an electric razor or clipper for less close shaves, which are gentler on the skin.
2. Limit Tight Clothing: Tight clothing and gear can irritate your skin and trap heat and moisture, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive. Whenever possible, opt for loose-fitting attire that doesn’t rub against your skin.
3. Reduce Friction: Friction from repeated actions or tight-fitting clothes can damage the skin and make it more susceptible to folliculitis. Use protective barriers like moisture-wicking fabrics during physical activities and ensure that clothing and gear fit properly.
4. Chemical Exposures: Be cautious of products that can irritate your skin. Avoid using oils that can block pores and be selective with skincare and haircare products. If you notice certain products exacerbate skin issues, discontinue their use and consult with a dermatologist for alternatives.
Recognize and Mitigate Risk Factors
Certain conditions and behaviors can increase your risk of developing folliculitis. Recognizing and mitigating these factors is key to prevention:
- Hot Tubs and Pools: Poorly maintained hot tubs and pools can harbor bacteria that cause folliculitis. Shower immediately after using communal bathing facilities and ensure that private pools and hot tubs are regularly cleaned and chlorinated.
- Pre-existing Skin Conditions: Individuals with dermatitis or other skin conditions are at a higher risk. Manage these conditions with appropriate treatments and skincare routines.
- Immune System Health: A strong immune system helps fight off infections that can lead to folliculitis. Maintain a healthy diet, get regular exercise, and ensure adequate sleep to support your immune system.
Remember, if you’re struggling with persistent skin issues, consulting a dermatologist is always the best course of action to identify and treat the underlying causes effectively.
Treatment Options for Folliculitis
It’s crucial to understand the various treatment options available to effectively manage this condition. From medical treatments to home remedies and lifestyle adjustments, there are multiple ways to alleviate the symptoms of folliculitis and promote healing.
Medical Treatments
Medical intervention often depends on the severity and type of folliculitis. Here are some commonly prescribed treatments:
- Topical Antibiotics: For mild cases, creams or ointments containing antibiotics can help kill the bacteria causing the infection.
- Oral Antibiotics: More severe or recurrent cases might require oral antibiotics to fight the infection from within.
- Antifungal Medications: If the folliculitis is caused by a fungal infection, antifungal creams or oral medications may be recommended.
- Corticosteroid Creams: These can be used to reduce inflammation and itching in the affected area.
- Laser Hair Removal: For chronic and recurrent cases, particularly those caused by ingrown hairs, laser hair removal can be an effective solution to prevent future issues.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
In addition to medical treatments, certain home remedies and lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and prevent further irritation:
- Warm Compress: Applying a warm, moist washcloth to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and encourage draining of pus from lesions.
- Proper Hygiene: Keeping the affected area clean and dry is paramount. Gently wash with a mild soap and water daily.
- Avoid Irritating Products: Stay clear of oily or greasy skincare products that can exacerbate folliculitis. Opt for non-comedogenic products instead.
- Wear Loose Clothing: Tight clothing can irritate the hair follicles. Wearing loose, breathable fabrics can help prevent friction and sweat accumulation.
- Shaving with Care: If shaving is necessary, always use a clean, sharp razor. Consider shaving in the direction of hair growth and use a shaving gel to reduce irritation.
However, if symptoms persist or worsen, consulting with a healthcare professional is advised to ensure appropriate treatment and to prevent complications. Always remember, the key to managing folliculitis effectively lies in a comprehensive approach tailored to your specific condition and needs.
FAQs on Folliculitis Symptoms
What does folliculitis look like?
Folliculitis typically appears as small, red, or pink bumps at the hair follicles. In some cases, these bumps may be filled with pus, causing them to resemble whiteheads. The surrounding skin might also appear inflamed and tender to touch. In chronic cases, folliculitis can lead to darker skin patches and scarring.
Can folliculitis cause itching?
Yes, folliculitis can be itchy and sometimes even painful, especially when the bumps are irritated by clothing or when they’re located in areas of frequent movement. It’s important not to scratch the bumps to avoid further irritation or infection.
How do I know if I have folliculitis or acne?
While folliculitis and acne may look similar, they are different conditions. Folliculitis bumps usually appear around hair follicles and might have a visible hair in the center of the bump. Acne, on the other hand, tends to occur in areas with a higher concentration of oil glands, like the face, chest, and back. Acne is also more likely to include blackheads and cysts.
Is folliculitis contagious?
Folliculitis itself is not contagious, but it can be caused by infectious agents such as bacteria, fungi, or viruses that can spread from one person to another under certain conditions. However, not all forms of folliculitis result from infectious causes.
Can shaving cause folliculitis?
Yes, shaving can cause a type of folliculitis known as “razor bumps” or pseudofolliculitis barbae. This condition occurs when hair re-enters the skin, leading to inflammation. Using a dull razor blade or shaving too closely can increase the risk of developing razor bumps.
When should I see a doctor for folliculitis?
You should consult a healthcare provider if the symptoms of folliculitis worsen, do not improve with home care, or if you experience recurrent episodes. Additionally, if the bumps spread rapidly, turn into large, red, painful boils, or if you develop a fever, these could be signs of a more serious infection requiring medical attention.
Conclusion:
If you’ve noticed signs that might suggest the presence of folliculitis, it’s essential to take these symptoms seriously. Consulting a healthcare provider is a vital step in getting an accurate diagnosis. Only through professional evaluation can the specific cause of your condition be identified, allowing for the most effective treatment plan to be developed. This could range from topical treatments to antibiotics, depending on the severity and nature of the infection.
We cannot overstate the importance of professional medical advice in these situations. Attempting to self-diagnose or treat could lead to complications or exacerbate the problem. A healthcare provider can also offer valuable advice on preventing future occurrences, from changing your shaving technique to selecting suitable fabrics that reduce skin irritation.
In embarking on a journey towards understanding and addressing folliculitis, you’re taking a significant step towards safeguarding not only your skin health but your overall confidence and quality of life. Remember, the key to managing folliculitis effectively lies in early detection, understanding its causes, and seeking professional guidance. Your skin, as your body’s largest organ, deserves the utmost care, and addressing issues like folliculitis promptly ensures that it remains healthy, resilient, and beautiful.
References
For those seeking more detailed information or looking to validate the facts presented about folliculitis symptoms, we’ve compiled a list of reputable sources. These links lead to authoritative sites where you can delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures for folliculitis. Understanding the condition thoroughly can help in managing it effectively and preventing future occurrences.
- Mayo Clinic – Folliculitis Overview: Explore a comprehensive guide on folliculitis, including symptoms, causes, and treatment options, curated by experts in dermatology at the Mayo Clinic. Read more.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Hot Tub Rash and Folliculitis: The CDC offers guidance on hot tub rash, a common type of folliculitis, including prevention tips and how to safely enjoy recreational water activities. Learn more.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK – Folliculitis: The NHS provides a UK perspective on folliculitis, offering insights into symptoms, home care advice, and when to seek medical attention. Check it out.
These resources have been carefully selected for their authority, accuracy, and the quality of information they provide on folliculitis. Whether you’re a patient, caregiver, or just someone interested in learning more about skin health, these links offer valuable insights into managing and understanding folliculitis.