Fibromuscular Dysplasia Symptoms: Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a vascular condition that can have significant impacts on the quality of life for those affected.
It is characterized by the development of abnormal cell growth within the walls of medium and large arteries, leading to a range of complications.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the symptoms, causes, and other relevant aspects of FMD, equipping readers with the knowledge they need to identify and understand this condition.
Understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia
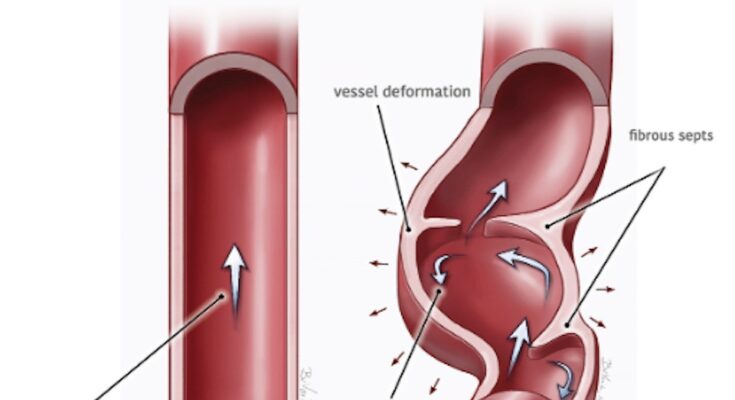
Fibromuscular Dysplasia, often abbreviated as FMD, is a rare vascular disorder that causes abnormal cell development in the walls of one or more of your arteries. This abnormal growth can lead to a variety of complications, including arterial stenosis (narrowing of the arteries), aneurysms (bulging of the arteries), or arterial dissections (tears in the artery walls). The condition is more common in certain arteries, including those that supply blood to the kidneys and brain, but it can affect any arterial bed in the body.
Prevalence and Demographics
Fibromuscular Dysplasia is considered a rare condition, though its exact prevalence is difficult to ascertain due to underdiagnosis and the often asymptomatic nature of the disease. Studies suggest FMD is more prevalent in women than in men, with the majority of diagnosed cases occurring in women in their mid-40s to 50s. However, the condition can affect individuals of all ages, including children. The demographics of FMD patients highlight a significant gender disparity, pointing towards potential genetic or hormonal factors that may influence the development and progression of the disease.
However, understanding Fibromuscular Dysplasia is crucial for early detection and management, as timely intervention can mitigate the risk of serious complications. Awareness and education about FMD are key to improving outcomes for those affected by this rare vascular disorder.
Symptoms of Fibromuscular Dysplasia
The symptoms of FMD can be subtle or non-existent in the early stages, making early diagnosis challenging. However, understanding the symptoms can lead to timely and effective management of the condition.
How Fibromuscular Dysplasia Symptoms Vary by Affected Artery
The manifestations of FMD vary significantly depending on which arteries are affected. Since FMD can involve any artery, the symptoms can range widely, from nonspecific complaints to severe, life-threatening complications.
Common Symptoms Associated with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
- Headaches and Dizziness: These are frequent complaints in individuals with FMD, particularly when the carotid arteries are involved.
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Often resulting from the narrowing of the renal arteries, which can affect kidney function and hormone levels that control blood pressure.
- Tinnitus (Ringing in the Ears): Particularly when FMD affects the carotid arteries near the ears.
- Neck Pain: This can occur when the carotid or vertebral arteries are involved.
- Reduced Kidney Function: Resulting from impaired blood flow to the kidneys due to renal artery stenosis.
Specific Symptoms Related to Artery Location
- Renal Artery Involvement: Can lead to high blood pressure and impaired kidney function, which might result in fatigue, confusion, and swelling in the hands and feet.
- Carotid Artery Involvement: May cause headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, a whooshing sound in the ears, and in severe cases, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or strokes.
- Extremity Artery Involvement: Results in pain, cramps, or fatigue in the limbs during exercise, cold limbs, or, in severe cases, limb loss due to lack of blood flow.
Identifying Fibromuscular Dysplasia Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of FMD can be challenging due to their commonality with other conditions. However, a combination of symptoms such as unexplained high blood pressure, especially in young individuals, headaches, neck pain, or pulsatile tinnitus, should prompt an evaluation for FMD.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It’s crucial to seek medical advice if you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, particularly if they are persistent or if you have a family history of FMD or sudden, unexplained strokes or high blood pressure at a young age. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent complications and improve the quality of life for those with FMD.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fibromyalgia Dysplasia
Understanding its causes and risk factors is essential for early diagnosis and management. This guide provides an overview of the current understanding of what causes FMD and the factors that may increase your risk of developing it.
Current Understanding of Causes
Genetic Factors: Researchers believe genetics play a significant role in the development of FMD. While no specific genes have been conclusively linked to the condition, it’s thought that certain genetic predispositions might increase susceptibility.
Hormonal Influences: Hormonal factors are also under investigation as potential contributors to FMD. The condition is more prevalent in women, suggesting that hormones like estrogen may influence its development.
Risk Factors for Developing FMD
Age and Gender Considerations: FMD most commonly affects women in their 40s and 50s, but it can occur at any age and in men, though less frequently. Understanding this demographic predisposition helps in identifying and monitoring at-risk individuals.
Family History and Genetics: Having a family member with FMD increases your risk of developing the condition. This familial pattern underscores the importance of genetics in FMD, although the exact inheritance mechanism is not yet fully understood.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: While the role of lifestyle and environmental factors in FMD is less clear than genetic and hormonal influences, maintaining a healthy lifestyle may reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. This includes managing blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight.
However, being aware of the risk factors—especially age, gender, family history, and possibly lifestyle and environmental influences—can help in early detection and management. As research continues, a clearer understanding of FMD causes and risk factors will likely emerge, improving diagnosis and treatment options.
Complications of Fibromyalgia Dysplasia (FMD)
Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD) is a vascular disease that can have serious health implications if left untreated. This condition primarily affects the arteries, leading to irregular cell growth within the arterial walls. Without timely intervention, FMD can result in a range of complications, underscoring the critical importance of early diagnosis and effective management strategies.
Potential Health Complications Due to Untreated FMD
Untreated FMD poses significant risks, as it can lead to narrowing or blockage of the arteries (stenosis), aneurysms (bulging of the arteries), and arterial dissections (tears in the artery walls). These complications can have profound effects on the body, depending on which arteries are affected. For instance:
- Renal artery stenosis can lead to hypertension (high blood pressure) and chronic kidney disease.
- Cerebrovascular involvement can increase the risk of stroke, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), and severe headaches.
- Coronary artery complications can contribute to chest pain, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and other heart-related issues.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Management
The potential severity of these complications makes early diagnosis and management of FMD crucial. Early detection allows for the implementation of treatment strategies that can significantly mitigate the risks associated with the disease. Treatment plans often include medication to manage symptoms, lifestyle modifications to improve overall vascular health, and in some cases, surgical interventions to repair or bypass the affected arteries.
Early management not only helps in controlling the symptoms and preventing complications but also improves the quality of life for individuals with FMD. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure that any changes in the condition are promptly addressed, reducing the risk of severe outcomes.
However, understanding the potential risks associated with untreated FMD highlights the importance of early diagnosis and proactive management. By taking steps to diagnose and treat FMD early, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing life-threatening complications, ensuring a healthier, more stable future.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options for Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD)
Diagnosing and treating FMD effectively is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing serious outcomes. Below, we explore the comprehensive approaches to diagnosis and treatment strategies for FMD, along with guidance for living with the condition.
Overview of Diagnostic Approaches
Early and accurate diagnosis of FMD is vital for effective management. Diagnostic approaches include:
- Physical Examination and Patient History: A thorough physical examination, complemented by a detailed patient history, is the first step in diagnosing FMD. Physicians look for physical signs of vascular abnormalities and gather information about symptoms, family history, and risk factors.
- Imaging Tests: Advanced imaging techniques play a critical role in diagnosing FMD.
- Ultrasound: Often used as a preliminary imaging test, ultrasound can detect abnormalities in blood flow that suggest FMD.
- CT Scan: A CT scan provides detailed images of the arteries, helping identify the location and severity of artery narrowing or aneurysms.
- MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers high-resolution images of blood vessels and is useful in assessing vascular damage without the need for dyes or radiation.
Treatment Strategies for Managing FMD Symptoms
The treatment for FMD focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications. Treatment strategies include:
- Medications for Hypertension and Pain: Blood pressure medications are commonly prescribed to manage hypertension, a frequent complication of FMD. Pain relievers may also be recommended to alleviate discomfort.
- Surgical and Non-Surgical Procedures: Depending on the severity and location of the arterial lesions, surgical intervention, such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery, may be necessary. Non-surgical treatments like angioplasty can also be effective in opening narrowed arteries and restoring blood flow.
Living with Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Living with FMD requires adopting lifestyle adjustments and self-care measures to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Lifestyle Adjustments and Self-Care Measures: Healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking, can help manage FMD symptoms. Regular monitoring and medical check-ups are essential for early detection of potential complications.
- Support Resources and Patient Communities: Support from family, friends, and patient communities can be invaluable. Online forums and local support groups offer a platform to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional support.
However, while Fibromuscular Dysplasia presents challenges, a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment, coupled with effective lifestyle and self-care strategies, can significantly improve outcomes for those living with FMD. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, staying informed about the condition, and connecting with support networks are key to managing FMD effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) About Fibromuscular Dysplasia
1. What is Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
Fibromuscular Dysplasia is a vascular disease that causes abnormal growth or development of cells in the walls of medium and large arteries in the body. This can lead to a range of complications, including narrowed arteries (stenosis), aneurysms, or tears in the artery walls (dissections).
2. What are the symptoms of Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
Symptoms can vary significantly depending on which arteries are affected. Common symptoms include high blood pressure, headaches, ringing in the ears, dizziness, neck pain, and in some cases, stroke or transient ischemic attacks (mini-strokes). Many individuals with FMD may not experience any symptoms until a complication arises.
3. How is Fibromuscular Dysplasia diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of patient history, physical examination, and imaging studies. Ultrasound, CT angiography, and magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) are among the imaging techniques used to visualize the arteries and identify signs of FMD.
4. Can Fibromuscular Dysplasia be cured?
While there is no cure for FMD, the condition can often be managed effectively with a combination of medications, lifestyle changes, and, in some cases, surgical interventions. The goal of treatment is to manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve quality of life.
5. Is Fibromuscular Dysplasia hereditary?
The exact cause of FMD is not fully understood, but it appears to be sporadic, meaning it occurs by chance. However, there are studies that suggest a possible genetic component, meaning that FMD can run in families, though this is rare.
6. Who is at risk for developing Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
FMD most commonly affects women in their mid-40s, but it can occur in anyone at any age, including children and men. The reasons for the higher prevalence in women are not well understood.
7. Where can I find support and more information about Fibromuscular Dysplasia?
Numerous organizations and support groups offer resources, support, and information for individuals affected by FMD and their families. It’s essential to consult healthcare providers for medical advice and information specific to individual cases.
Conclusion:
We cannot overstate the importance of being vigilant about the symptoms of FMD. Early detection can lead to timely intervention, reducing the risk of developing more severe complications. Whether you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that could be indicative of FMD, such as unexplained hypertension or headaches, it’s imperative to take these signs seriously.
Encouragingly, advancements in medical research and diagnostic techniques have improved the management of FMD. However, the first step towards benefiting from these advancements is consulting with healthcare providers. If you have concerns about FMD symptoms, or if something feels amiss with your health, reaching out to a medical professional is the best course of action. They can provide a thorough evaluation, accurate diagnosis, and guide you through the appropriate treatment options tailored to your situation.
Remember, your health is invaluable, and being proactive about it can make all the difference. Consult healthcare providers with any concerns about FMD symptoms, and take a step forward in safeguarding your well-being today.
References
For readers seeking further information and verification of the symptoms associated with Fibromuscular Dysplasia (FMD), the following reputable sources offer valuable insights and detailed explanations. Each link leads directly to articles, research papers, or official pages that delve into the various aspects of FMD, including symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. These resources have been carefully selected for their authority in the medical field and their commitment to providing up-to-date, accurate information.
- Mayo Clinic – Fibromuscular Dysplasia Overview: The Mayo Clinic offers a comprehensive overview of FMD, including symptoms, causes, and treatment methods. This resource is ideal for individuals seeking a thorough understanding of the condition from a trusted medical institution. Read more at the Mayo Clinic.
- PubMed Central (PMC) – Recent Advances in Fibromuscular Dysplasia: For those interested in the scientific and clinical research aspect of FMD, PubMed Central offers access to a multitude of research articles and studies. This particular paper discusses the latest advances in understanding the pathology, diagnosis, and management of FMD. Access the research on PMC.
These resources are intended to serve as a starting point for individuals seeking to understand Fibromuscular Dysplasia better. While the internet offers a vast amount of information, it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for diagnoses, personalized advice, and treatment plans.