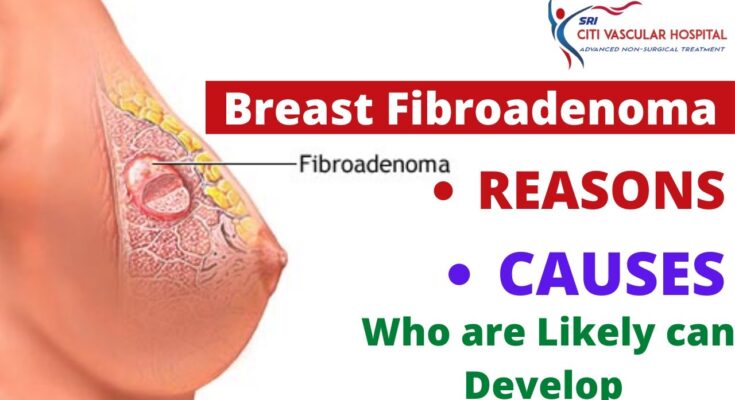
Fibroadenoma Symptoms: Fibroadenoma is a term that frequently appears in conversations about breast health, yet its specifics often remain shrouded in medical jargon.
This benign breast tumor, most common in young women, has distinct characteristics, symptoms, and causes that are vital for everyone to understand.
What is Fibroadenoma?
Fibroadenoma is a non-cancerous (benign) breast tumor that is most commonly found in young women. It’s characterized by rubbery or smooth lumps that can easily move under the skin when touched. These tumors are composed of both glandular breast tissue and stromal (connective) tissue. Fibroadenomas vary in size, and while some remain small, others can grow or even shrink over time. They are usually painless, which often leads them to be discovered incidentally during a breast exam or imaging tests.
The exact cause of fibroadenoma is not fully understood, but its development is thought to be related to reproductive hormones. They are most often diagnosed in women between the ages of 15 and 35, highlighting a possible link to periods of higher hormone levels.
Statistics on Prevalence Among Different Age Groups
Fibroadenomas are among the most common benign breast tumors in young women. They are most frequently diagnosed in women aged 15 to 35, but they can occur at any age. The prevalence of fibroadenomas decreases with age, particularly after menopause, due to changes in hormone levels.
- Young Women (15-35 years): This age group has the highest incidence of fibroadenomas. It’s estimated that at least 10% of women in this age bracket will develop a fibroadenoma at some point.
- Middle-aged Women (35-50 years): While less common, middle-aged women can still develop fibroadenomas, especially those who are undergoing hormone therapy or who have a prolonged menstrual history.
- Postmenopausal Women (50+ years): The occurrence of new fibroadenomas in postmenopausal women is rare, largely because the body produces fewer reproductive hormones, which are believed to stimulate the growth of these tumors.
Regular breast exams and awareness of changes within the breast are essential for early detection and management of any potential breast lumps, including fibroadenomas. Despite their benign nature, any new or changing lumps should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out other conditions.
Symptoms of Fibroadenoma
Recognizing the symptoms associated with fibroadenoma is crucial for early identification and management. This article provides a comprehensive overview of fibroadenoma symptoms, their characteristics, and how they differ from symptoms of other breast conditions.
Common Symptoms of Fibroadenoma
The hallmark symptom of fibroadenoma is the presence of a breast lump. However, understanding the specific characteristics of this lump and other related symptoms is essential. Here are the most common signs of fibroadenoma:
- Breast Lump: The most noticeable symptom is a smooth, firm breast lump that moves easily under the skin when touched. These lumps are usually painless.
- Shape and Size: The lumps are typically round or oval-shaped, with a well-defined border. They can vary in size, often between 1 and 5 cm in diameter.
- Consistency: Fibroadenomas feel rubbery to the touch and are usually firm yet not hard.
- Growth: They can grow in size, especially during pregnancy or hormone therapy, due to increased estrogen levels.
How to Identify Fibroadenoma Symptoms
Identifying fibroadenoma involves paying close attention to the characteristics of the breast lump. Here are some tips for identifying fibroadenoma symptoms:
- Self-Examination: Regular breast self-exams can help you become familiar with your breasts’ texture, making it easier to notice any changes or new lumps.
- Medical Examination: If you discover a lump, a healthcare provider can perform clinical breast exams and may recommend imaging tests like a mammogram or ultrasound for further evaluation.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis by analyzing a small tissue sample from the lump.
Differentiating Fibroadenoma from Other Breast Conditions
Distinguishing fibroadenoma from other breast conditions, including breast cancer, is vital. Here are some differences:
- Mobility: Fibroadenoma lumps are usually mobile under the skin, unlike cancerous lumps which are often fixed in place.
- Consistency: Breast cancer lumps may feel hard and irregular, contrasting with the smooth and rubbery texture of fibroadenoma.
- Pain: While fibroadenomas are generally painless, breast cancer lumps may be accompanied by pain or discomfort, although not always.
- Skin Changes: Breast cancer may also present with skin changes, such as dimpling, puckering, or nipple discharge, which are not typical symptoms of fibroadenoma.
Regular breast self-exams and timely consultation with healthcare providers upon noticing changes can lead to early detection and effective management of fibroadenoma. Remember, while fibroadenomas are benign, any new breast changes should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other conditions.
Causes and Risk Factors of Fibroadenoma
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with fibroadenoma is crucial for early detection and management. This article delves into the primary causes, the role of hormonal influences, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices in the development of fibroadenomas.
Causes of Fibroadenoma
The exact cause of fibroadenoma remains unclear; however, it is closely linked to reproductive hormones. These tumors are most prevalent during reproductive years, indicating hormones like estrogen play a significant role in their growth.
Hormonal Influences on Fibroadenoma Development
Hormonal fluctuations significantly impact the development of fibroadenomas. They are particularly responsive to estrogen, which is why these growths often occur in young women, pregnant women, or those using hormone therapy. During pregnancy, fibroadenomas can increase in size due to heightened estrogen levels but typically shrink after menopause, reflecting the decreased influence of estrogen.
Genetic Factors
While most fibroadenomas are sporadic, there is evidence to suggest a genetic component in some cases. Individuals with a family history of breast cancer or fibroadenomas may have a higher risk of developing these tumors. Specific genetic mutations have been identified in a minority of cases, suggesting genetics can play a role in the development of fibroadenomas.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices may also influence the risk of developing fibroadenomas, though the relationship is not as clear-cut as with hormonal and genetic factors. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight might contribute to lower risk, though more research is needed in this area.
In summary, fibroadenomas are influenced by a combination of hormonal changes, genetic predispositions, and potentially lifestyle choices. Understanding these factors can help in the early detection and management of fibroadenomas, contributing to better breast health. While the exact causes are not entirely understood, being aware of the risk factors can empower women to take proactive steps towards their health.
Diagnosing Fibroadenoma
Understanding the diagnostic process for fibroadenoma is crucial for early detection and effective management of this condition. Fibroadenomas are non-cancerous breast tumors that are most common among women in their 20s and 30s, but they can occur at any age. The diagnosis involves a combination of self-examination, clinical exams, and specialized tests. Here’s a detailed look into how fibroadenomas are diagnosed:
The Role of Self-Examination and Clinical Exams in Early Detection
Self-Examination: Regular breast self-exams are a proactive way to familiarize oneself with the normal feel and appearance of their breasts. This practice makes it easier to notice any unusual changes or lumps. If a lump is found, it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s cancerous, but it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for a professional evaluation.
Clinical Breast Exam (CBE): During a CBE, a healthcare provider examines the breasts and underarm areas for any lumps or abnormalities. They may also assess the skin texture, nipple discharge, and any changes in size or shape. If any irregularities are found, further testing will be recommended.
Types of Tests Used to Diagnose Fibroadenoma
1. Mammography: Mammograms are X-ray images of the breast that can help identify abnormalities or lumps that cannot be felt during a physical exam. Fibroadenomas usually appear as well-defined, solid, round lumps on a mammogram, distinguishing them from cancerous tumors, which are often irregular in shape.
2. Ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create images of the breast tissue. It’s particularly useful in determining if a lump is solid (like a fibroadenoma) or filled with fluid (like a cyst). This distinction is vital for the diagnosis and management plan.
3. Biopsy: When the imaging tests suggest a lump could be a fibroadenoma, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small tissue sample from the lump is removed and examined under a microscope. There are various biopsy techniques, including fine-needle aspiration, core needle biopsy, and surgical biopsy.
4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): Though not commonly used for diagnosing fibroadenomas, MRI can provide detailed images of the breast and is sometimes recommended in complex cases to gather more information about the lump.
However, early detection through self-examination and regular clinical exams is paramount in managing fibroadenomas effectively. If you discover any changes or lumps in your breasts, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly to receive a proper diagnosis and peace of mind.
Treatment Options for Fibroadenoma
Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for making informed decisions about your health. Recent advances have expanded these options, especially in the realm of non-invasive treatments, making the management of fibroadenomas less daunting than ever before.
List of Treatment Options
- Observation and Monitoring: Often, the first approach recommended is a “watchful waiting” strategy. Fibroadenomas may not require immediate treatment if they are small, symptomless, and don’t change over time. Regular check-ups and ultrasounds are used to monitor the fibroadenoma for any changes.
- Surgical Removal: In cases where the fibroadenoma is large, growing, or causing discomfort, surgical removal might be recommended. The most common procedure is a lumpectomy, which involves removing the tumor while preserving as much surrounding breast tissue as possible.
- Cryoablation: This is a minimally invasive procedure that uses extreme cold to destroy the fibroadenoma. A thin probe is inserted into the tumor, and liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and kill the abnormal cells. This option is typically considered for tumors less than 2 cm in diameter.
- Laser Ablation: Another minimally invasive technique, laser ablation uses focused laser energy to heat and destroy the fibroadenoma tissue. This method is gaining popularity due to its precision and the minimal scarring it leaves.
Advances in Non-Invasive Treatment Methods
The field of fibroadenoma treatment has seen significant advancements in non-invasive methods, aimed at reducing the physical and emotional impact of treatment. These cutting-edge options include:
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU): A truly non-invasive treatment that uses ultrasound waves to heat and destroy the tumor tissue without any incisions. HIFU is performed under MRI guidance, allowing for precise targeting of the fibroadenoma while sparing the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA uses radio waves to heat and destroy the fibroadenoma. While minimally invasive, it requires only a small incision for the needle electrode. This technique is particularly effective for fibroadenomas that are difficult to reach surgically.
These non-invasive and minimally invasive treatments offer several benefits over traditional surgery, including reduced recovery times, minimal scarring, and lower risks of complications. They represent a significant step forward in the treatment of fibroadenomas, providing women with effective options that minimize the impact on their bodies and their lives.
When considering treatment for fibroadenoma, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional who can provide guidance based on the specific characteristics of the tumor and your overall health. Advances in treatment technology mean that more options are available than ever before, empowering you to make the choice that’s right for you.
The landscape of fibroadenoma treatment is evolving rapidly, offering hope and new possibilities for those affected by this condition. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the future of fibroadenoma management looks promising, aiming for even more effective and less invasive treatment options.
Managing Symptoms of Fibroadenoma
Managing symptoms of fibroadenoma involves a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle adjustments and understanding when it’s time to seek medical advice. This guide aims to provide you with actionable insights and tips for effectively managing fibroadenoma symptoms, enhancing your quality of life and ensuring your health remains a top priority.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies for Fibroadenoma
Dietary Modifications: Incorporating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can have a positive impact on your overall health and may aid in managing fibroadenoma symptoms. Foods high in antioxidants may help reduce inflammation, potentially influencing the condition’s progression.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain a healthy weight, reduce stress, and improve your overall well-being. Moderate exercises such as walking, swimming, or yoga are recommended to support health without putting excessive strain on the body.
Stress Reduction Techniques: Chronic stress can have a variety of negative effects on the body, including potential impacts on fibroadenoma symptoms. Practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can be beneficial in managing stress levels.
Avoiding Caffeine and Alcohol: Some individuals may find that reducing intake of caffeine and alcohol can help alleviate symptoms. While evidence is anecdotal, limiting these substances is generally good for health and worth trying to see if symptoms improve.
When to See a Doctor
Understanding when to consult a healthcare professional is crucial in managing fibroadenoma effectively. Here are key indicators that it’s time to see a doctor:
Changes in Size or Shape: If you notice any changes in the size, shape, or feel of the fibroadenoma or if new lumps appear, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation. These changes can sometimes indicate complications or the development of additional conditions.
Persistent Pain or Discomfort: While fibroadenomas are usually painless, any persistent pain or discomfort warrants a visit to the doctor. It’s important to rule out other causes and to discuss pain management strategies.
Signs of Infection: Redness, warmth, swelling, or pus around the area of the fibroadenoma can be signs of an infection. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Concerns About Cancer: Although fibroadenomas are typically benign, it’s understandable to have concerns about cancer. If you have a family history of breast cancer or personal concerns, discussing them with a doctor can provide reassurance and necessary screening.
Prioritizing your health by maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and monitoring your symptoms can make a significant difference in your well-being. Remember, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and to ensure timely intervention for any concerns.
FAQs about Fibroadenoma Symptoms
What is a Fibroadenoma?
A fibroadenoma is a benign (non-cancerous) breast lump that often develops in young women. They are usually painless, solid, round, and move easily when touched. Fibroadenomas are among the most common benign breast lumps diagnosed in women.
How Do I Know If I Have a Fibroadenoma?
The primary symptom of a fibroadenoma is a palpable lump in the breast that feels rubbery and moves easily under the skin. These lumps are usually painless. However, the only way to confirm a diagnosis is through a medical evaluation, which may include a mammogram, ultrasound, or biopsy.
Are Fibroadenomas Painful?
In most cases, fibroadenomas are not painful. However, some individuals may experience slight tenderness or discomfort, especially in the days leading up to their menstrual period due to hormonal changes.
Can Fibroadenomas Change Size?
Yes, fibroadenomas can change in size. They might grow larger during pregnancy or hormone therapy due to increased levels of estrogen. Conversely, they can decrease in size after menopause when the level of estrogen decreases.
Should I Be Worried About Fibroadenomas?
While fibroadenomas are benign and not associated with breast cancer, any new breast lump should be evaluated by a healthcare provider. It’s essential to monitor the lump for any changes in size or feel and report these changes to your doctor.
How Are Fibroadenomas Treated?
Treatment for fibroadenomas varies depending on the size, symptoms, and the individual’s comfort. Options include monitoring the lump for any changes, surgical removal, or non-surgical removal methods like cryoablation. The choice of treatment should be made in consultation with a healthcare provider.
Can Fibroadenomas Go Away on Their Own?
Yes, in some cases, fibroadenomas can shrink or even disappear over time without treatment. This is more likely to happen after menopause.
How Can I Prevent Fibroadenomas?
Currently, there is no known way to prevent fibroadenomas. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular breast exams can help in early detection and management of any changes in your breasts.
Conclusion
Regular self-examination cannot be overstressed as a vital practice for everyone. It serves as the first line of defense in identifying unusual changes or lumps in breast tissue. While the process may seem daunting or anxiety-inducing to some, it is a crucial component of personal health maintenance. Knowing the normal feel and appearance of your breasts can make all the difference in early detection strategies.
Moreover, fostering an open and ongoing dialogue with healthcare providers is essential. Medical professionals can offer guidance, support, and clarity on the nature of fibroadenomas and the best course of action if one is discovered. They can demystify the process, provide reassurance, and, if necessary, recommend further diagnostic tests or treatments.
In conclusion, awareness and proactive health measures are key to managing fibroadenomas. Regular self-examination and seeking timely advice from healthcare providers are indispensable tools in this endeavor. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can effectively navigate their health journeys, ensuring peace of mind and well-being.
References
For those seeking to expand their understanding and validate the information provided about fibroadenoma symptoms, the following reputable sources offer comprehensive insights. These resources have been carefully selected to ensure readers have access to reliable, expert information:
- Mayo Clinic – Fibroadenoma Overview: The Mayo Clinic provides a thorough overview of fibroadenomas, including symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. This resource is valuable for individuals looking for medically reviewed information from a trusted healthcare institution. Visit Mayo Clinic’s Fibroadenoma Page.
- American Cancer Society – Understanding Fibroadenomas: The American Cancer Society offers detailed information on fibroadenomas, emphasizing their non-cancerous nature, symptoms, and how they differ from other breast lumps. It’s an essential read for anyone wanting to learn more about fibroadenomas in the context of breast health. Explore the American Cancer Society’s Fibroadenoma Resource.
- WebMD – Fibroadenoma Symptoms and Treatments: WebMD provides a comprehensive guide on fibroadenomas, focusing on symptoms, treatments, and management. This source is known for its easy-to-understand health information, making it a great starting point for readers unfamiliar with medical terminology. Check Out WebMD’s Guide on Fibroadenomas.
- Breast Cancer Now – Fibroadenoma Information: Breast Cancer Now, a UK-based charity, offers insights into fibroadenomas with a focus on how they are diagnosed and managed. Their information is tailored for those who might be experiencing symptoms and looking for guidance on the next steps. Read More at Breast Cancer Now.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK – Fibroadenoma: The NHS website provides a straightforward overview of fibroadenomas, including symptoms, how they’re found, and treatment methods. It’s a credible source for readers in the UK and beyond seeking information from a public health perspective. Visit the NHS Fibroadenoma Page.
By exploring these references, readers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of fibroadenomas, from symptoms to treatment options. These sources are invaluable for anyone looking to validate the information provided and delve deeper into the topic.