Familial Mediterranean Fever Treatment: Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a hereditary inflammatory disorder that primarily affects populations of Mediterranean origin, including but not limited to, Sephardic Jews, Armenians, Arabs, and Turks.
This condition is characterized by recurrent episodes of fever and serositis, leading to pain in the abdomen, chest, joints, and muscles.
Given the recurrent nature of the symptoms and the potential for serious complications, such as amyloidosis, accurate diagnosis and effective treatment are paramount.
Understanding Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects thousands worldwide. Primarily impacting individuals of Mediterranean descent, including those from Middle Eastern, North African, and Armenian backgrounds, FMF is a genetic disorder that can cause severe symptoms and significantly impact the quality of life. This article aims to shed light on the symptoms and triggers of FMF episodes, explore the genetic factors behind the condition, and highlight the populations most affected.
Symptoms and Triggers of FMF Episodes
FMF is characterized by recurrent episodes of fever and inflammation, with symptoms that can vary significantly in intensity and duration. Common symptoms include:
- Fever: Sudden spikes in temperature are a hallmark of FMF episodes, often accompanied by other symptoms.
- Abdominal pain: Many individuals experience severe abdominal discomfort, often mistaken for appendicitis.
- Chest pain: Inflammation can spread to the chest area, leading to pain that mimics heart or lung conditions.
- Joint pain: Swollen, painful joints, particularly in the legs, are common during FMF flare-ups.
- Rashes: Some individuals develop erysipelas-like skin rashes, mainly on the legs.
Triggers for FMF episodes can vary, with some individuals experiencing spontaneous flare-ups. However, common triggers include stress, menstrual cycles, physical exertion, and infections. Understanding and managing these triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of FMF episodes.
Genetic Factors and Populations Most Affected
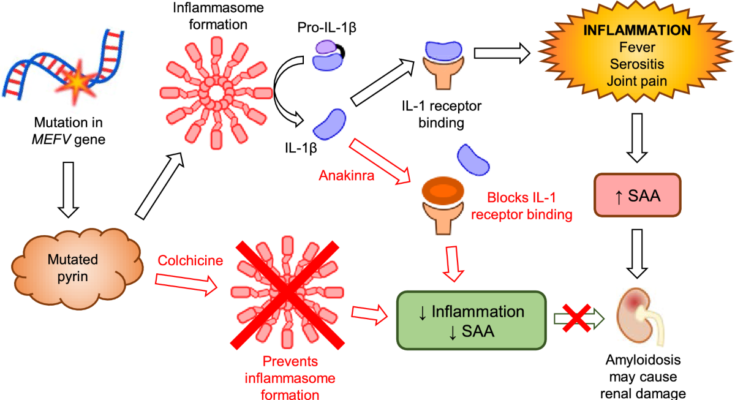
FMF is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene, which plays a crucial role in the body’s inflammatory response. The condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, meaning an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) to develop the disease. However, some individuals with only one copy of the mutation may experience milder symptoms or asymptomatic cases, indicating a complex relationship between the gene and the disease’s expression.
The populations most affected by FMF are those with genetic ties to the Mediterranean region. These include:
- Turkish: The highest prevalence of FMF is found among people of Turkish descent.
- Armenian: Individuals of Armenian heritage have a significantly high rate of FMF.
- Arab: Arab populations, particularly those from the Middle East, are also commonly affected.
- Jewish: Both Sephardic (originating from Spain and Portugal) and Ashkenazi (from Eastern Europe) Jewish populations have higher incidences of FMF.
Despite its concentration in these populations, FMF can affect individuals of any ethnic background. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing symptoms and preventing complications, such as amyloidosis, which can lead to kidney failure.
However, understanding Familial Mediterranean Fever is vital for those affected and their families. Awareness of the symptoms, triggers, and the genetic basis of FMF can lead to better disease management, improved quality of life, and more effective community support for those impacted.
Diagnosis of Familial Mediterranean Fever
Diagnosing Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) poses unique challenges, primarily due to its rare nature and symptoms that overlap with various other conditions. Understanding these challenges, the role of genetic testing, and additional diagnostic criteria is essential for patients and healthcare professionals navigating the path to an accurate FMF diagnosis.
Challenges in Diagnosing FMF
Familial Mediterranean Fever, a hereditary inflammatory disorder, often presents with symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, chest pain, and arthritis, which are common to many other diseases. This symptom overlap can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis, impacting patient care and management. FMF predominantly affects people of Mediterranean descent, including those of Sephardic Jewish, Arabic, Turkish, and Armenian heritage, adding a demographic complexity to its diagnosis. Another challenge is the episodic nature of FMF flare-ups; symptoms can be intense but fleeting, further complicating the diagnostic process.
Role of Genetic Testing in FMF Diagnosis
Genetic testing plays a pivotal role in diagnosing Familial Mediterranean Fever. FMF is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene, which can be identified through genetic tests. This testing is crucial for confirming the diagnosis in symptomatic individuals and can be particularly helpful in atypical cases or when the clinical diagnosis is uncertain. However, it’s important to note that not all individuals with FMF have identifiable mutations in the MEFV gene, and some carriers of these mutations may never develop symptoms. Consequently, genetic testing should be considered as part of a comprehensive diagnostic approach, rather than the sole criterion.
Other Diagnostic Criteria and Tests
Beyond genetic testing, the diagnosis of FMF involves a combination of clinical evaluation and additional tests to rule out other conditions and confirm FMF. These include:
- Clinical Criteria: A set of criteria focusing on symptom patterns, including the frequency of fever episodes, presence of serositis (inflammation of membranes lining the chest or abdomen), and response to colchicine treatment, helps in diagnosing FMF.
- Blood Tests: Elevated levels of certain markers in the blood, such as white blood cells, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP), during episodes, indicate inflammation and support an FMF diagnosis.
- Colchicine Response Test: Colchicine is effective in treating and preventing FMF flares. A positive response to colchicine, while not exclusively diagnostic of FMF, can support the diagnosis in the context of clinical symptoms and genetic testing results.
- Imaging Tests: While not specific for FMF, imaging tests like ultrasound and CT scans can help identify complications or rule out other conditions.
However, this comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective management of FMF, ultimately improving patient outcomes. As research progresses, the diagnostic process for FMF will continue to evolve, offering hope for more straightforward and accessible diagnostic criteria in the future.
Treatment Options for Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
The management of FMF focuses on preventing these attacks and reducing their intensity when they occur. Here, we explore the current treatment strategies for FMF, emphasizing the importance of medication management, lifestyle and dietary adjustments, and the necessity of personalized treatment plans.
Medication Management
One of the cornerstones of managing Familial Mediterranean Fever is medication. The following medications are commonly used in the treatment of FMF:
- Colchicine: This is the primary treatment for FMF. Colchicine reduces inflammation and helps prevent attacks of fever and pain. It’s also effective in reducing the risk of amyloidosis, a serious complication of FMF that can lead to kidney failure.
- Biologic Therapies: For patients who cannot tolerate colchicine or for whom colchicine is not effective, biologic therapies targeting specific inflammatory pathways can be an option. These include drugs like canakinumab and rilonacept.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be used to relieve pain and inflammation during acute attacks.
Lifestyle and Dietary Adjustments
While medication plays a critical role in managing FMF, lifestyle and dietary adjustments can also help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Patients are advised to:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent dehydration, especially during fever episodes.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular, moderate exercise can help reduce the frequency of FMF attacks and improve overall wellbeing.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which might trigger FMF attacks.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
The management of Familial Mediterranean Fever varies significantly from one individual to another. Factors such as the frequency and severity of attacks, the presence of complications like amyloidosis, and the patient’s overall health and lifestyle influence the choice of treatment. Therefore, it’s crucial to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
A personalized treatment plan for FMF may include a combination of medications, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring for potential complications. Collaboration between the patient and a multidisciplinary healthcare team, including rheumatologists, genetic counselors, and dietitians, is essential to ensure the best possible outcomes.
By addressing FMF from multiple angles, patients can achieve better control over their symptoms and enjoy a higher quality of life. It’s essential for individuals with FMF to work closely with their healthcare providers to find the most effective treatment strategy for their specific situation.
Advances in Familial Mediterranean Fever Treatment: Unlocking New Horizons
Recent research findings and emerging treatments offer a beacon of hope, signaling a shift towards more effective and targeted approaches. This article delves into these groundbreaking advances, underscoring the potential of gene therapy and personalized medicine in revolutionizing FMF treatment.
The Forefront of Research and Innovative Treatments
The landscape of FMF treatment is witnessing remarkable transformations, thanks to relentless research and innovation. Traditionally managed with anti-inflammatory drugs and Colchicine, to prevent attacks and complications, the focus is now shifting towards more nuanced and sophisticated treatments. Recent studies have highlighted the efficacy of biologic medications, such as interleukin inhibitors, in controlling symptoms in patients who are either intolerant or resistant to conventional therapies. These biologics target specific pathways involved in the inflammatory process, offering a more focused approach to managing FMF symptoms.
Gene Therapy: A Path to Precision Medicine
At the heart of the latest advancements is gene therapy, a revolutionary approach that offers the promise of not just treating but potentially curing FMF. Gene therapy involves correcting or replacing the defective gene responsible for the disease, directly addressing the root cause of FMF. This method stands out because it could lead to long-lasting relief or even a permanent cure, moving beyond merely managing symptoms. Although still in the experimental phase, the prospects of gene therapy paint an optimistic future, heralding a new era in FMF treatment where the condition could be eradicated at its genetic source.
Personalized Medicine: Tailoring Treatment to the Individual
Personalized medicine represents another frontier in the fight against FMF, propelled by advances in genetic testing and bioinformatics. This approach tailors treatment plans to the individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors, ensuring that therapies are as effective and side-effect-free as possible. For FMF patients, this could mean a future where treatments are fine-tuned to their specific genetic mutations, offering more effective management of the disease. Personalized medicine’s emphasis on the individual promises to minimize trial and error in finding the right treatment, optimizing patient outcomes.
The journey towards better treatment for Familial Mediterranean Fever is on a promising path, marked by innovative research and the advent of cutting-edge technologies like gene therapy and personalized medicine. These advancements not only offer hope for more effective management of FMF but also pave the way for potentially curing this challenging genetic disorder. As we look forward to the future, it’s clear that the landscape of FMF treatment is evolving rapidly, moving towards more personalized and precise interventions that promise to transform the lives of those affected by this condition.
Living with Familial Mediterranean Fever
With appropriate management strategies, regular monitoring, and effective coping mechanisms, individuals living with FMF can lead fulfilling lives. This article explores essential approaches to long-term care, the importance of healthcare consultations, and strategies to mitigate the impact on quality of life.
Management Strategies for Long-Term Care
Living with FMF requires a proactive approach to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Here are key strategies for long-term care:
- Adherence to Medication: Colchicine is the cornerstone of FMF treatment, effective in reducing the frequency and severity of flare-ups and preventing complications like amyloidosis. Adhering to prescribed medication regimens is crucial.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Healthy lifestyle choices, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and sufficient rest, can help manage symptoms and enhance overall well-being.
- Genetic Counseling: For individuals and families affected by FMF, genetic counseling offers valuable insights into the disorder, its inheritance patterns, and implications for family planning.
The Importance of Regular Monitoring and Healthcare Consultations
Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are vital for individuals with FMF for several reasons:
- Monitoring Disease Progression: Routine assessments can help track the effectiveness of treatment plans and make necessary adjustments.
- Early Detection of Complications: Regular check-ups enable the early detection of complications such as amyloidosis, which can be critical in preventing severe outcomes.
- Personalized Care: Ongoing communication with healthcare professionals allows for personalized care, addressing individual needs and concerns.
Impact on Quality of Life and Coping Mechanisms
FMF can pose challenges to an individual’s quality of life, affecting physical health, emotional well-being, and social interactions. Recognizing and addressing these impacts is essential:
- Emotional and Psychological Support: Access to mental health services, support groups, and counseling can provide emotional relief and practical advice for dealing with FMF.
- Education and Awareness: Educating oneself about FMF, its symptoms, treatment options, and triggers can empower individuals to take control of their health.
- Building a Support Network: Connecting with others living with FMF, whether through online forums or local support groups, can offer a sense of community and mutual support.
Embracing a comprehensive approach to care, seeking support, and maintaining open communication with healthcare providers are key to navigating the complexities of FMF and improving quality of life.
FAQs on Familial Mediterranean Fever
What is Familial Mediterranean Fever?
Familial Mediterranean Fever is an autoinflammatory disease that causes recurrent fevers and painful inflammation of your abdomen, lungs, and joints. It is a genetic condition most common among people of Mediterranean ancestry.
What causes FMF?
FMF is caused by mutations in the MEFV gene. This gene mutation leads to an improper regulation of the body’s inflammatory response, causing uncontrolled inflammation that results in the symptoms associated with the disease.
What are the symptoms of FMF?
The most common symptoms of FMF include recurrent fevers, abdominal pain, chest pain, joint pain, and rashes. The severity and frequency of these symptoms can vary greatly among individuals.
How is FMF diagnosed?
Diagnosis of FMF is based on a combination of clinical symptoms, family history, and genetic testing. Genetic testing can confirm the presence of mutations in the MEFV gene, which is definitive for FMF.
Can FMF be cured?
While there is no cure for FMF, it can be managed effectively with medications. The most commonly used medication is colchicine, which can reduce the frequency and severity of attacks and prevent complications.
How does FMF affect daily life?
With proper management, most individuals with FMF can lead normal, active lives. It is important for patients to adhere to their treatment plans and to be aware of what triggers their symptoms to manage the condition effectively.
Is FMF contagious?
No, FMF is not contagious. It is a genetic disorder, which means it is inherited from parents and not caused by an infection or spread through contact.
Can FMF lead to other health problems?
If left untreated, FMF can lead to complications such as amyloidosis, which is a buildup of protein in organs that can lead to kidney failure and other serious health issues. However, with appropriate treatment, the risk of complications is significantly reduced.
Can diet and lifestyle changes help manage FMF?
While medications are the cornerstone of FMF management, some people find that certain lifestyle changes can help manage their symptoms. These might include a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding triggers known to provoke flare-ups. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before making any significant changes.
Conclusion
In closing, the recognition, diagnosis, and effective treatment of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) hold paramount importance in the realm of rare genetic disorders. This condition, characterized by recurrent fevers and painful inflammation, can severely impact the quality of life for those affected. A timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial, as it opens the door to targeted treatments that can significantly mitigate symptoms and prevent long-term complications, such as amyloidosis.
The journey of understanding and managing FMF is ongoing. Research continues to play a critical role in uncovering the complexities of this condition, leading to the development of more effective treatment options and management strategies. It’s through these scientific endeavors that we can look forward to advancements in genetic testing, personalized medicine, and ultimately, a cure for FMF.
Beyond the scientific community, the support for patients and their families is equally important. Living with a chronic condition like FMF can be challenging, but with the right support networks and resources, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Patient advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and online communities offer invaluable support, education, and the opportunity to connect with others facing similar challenges.
As we move forward, let us remain committed to the cause of advancing research and providing comprehensive support to those affected by Familial Mediterranean Fever. Together, we can make a significant impact on the lives of individuals with FMF, empowering them to navigate their condition with confidence and hope for the future. The path to a deeper understanding and better management of FMF is a collaborative effort, requiring the dedication of researchers, clinicians, patients, and their families. Let’s continue to support each other in this journey, fostering an environment where discoveries are made, lives are improved, and hope is renewed.
References:
In the pursuit of offering our readers comprehensive and reliable information on the treatment of Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF), we have compiled a list of authoritative resources. These references have been selected for their credibility and depth of research on FMF, its symptoms, treatment options, and ongoing management strategies. We encourage our readers to explore these links for a deeper understanding and validation of the treatments discussed.
- Mayo Clinic: Renowned for its patient-centered approach, the Mayo Clinic offers an accessible overview of Familial Mediterranean Fever, emphasizing symptoms, causes, and comprehensive treatment options. This source is ideal for patients and their families seeking clear and concise information. Explore Familial Mediterranean Fever at Mayo Clinic
- PubMed Central (PMC): For those interested in the latest research articles and clinical studies on FMF, PubMed Central provides open access to a wealth of scientific literature. It is a key resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, and academically inclined patients. Search for FMF Studies on PubMed Central
By consulting these references, readers can gain a thorough understanding of Familial Mediterranean Fever, including the latest treatment strategies and research findings. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or a healthcare professional, these resources offer valuable insights into managing and treating FMF.