Factor V Leiden Symptoms: Factor V Leiden is a genetic disorder that is often discussed but not always fully understood. It’s a mutation of one of the clotting factors in the blood called factor V.
This mutation can increase an individual’s risk of developing abnormal blood clots, which can lead to serious health problems.
Our aim is to provide a detailed, comprehensive guide to the symptoms and causes of Factor V Leiden, equipping you with the knowledge to manage or recognize this condition effectively.
Understanding Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden is a genetic mutation that significantly influences blood clotting, a critical process in the body’s response to bleeding. This condition represents one of the most common hereditary blood clotting disorders, shedding light on the intricate balance between coagulation and its management. In this section, we delve into the essence of Factor V Leiden, elucidating its impact on blood clotting, the genetic foundations underpinning it, and its prevalence and demographic considerations, aiming for clarity and accessibility to our readers.
How Factor V Leiden Affects Blood Clotting
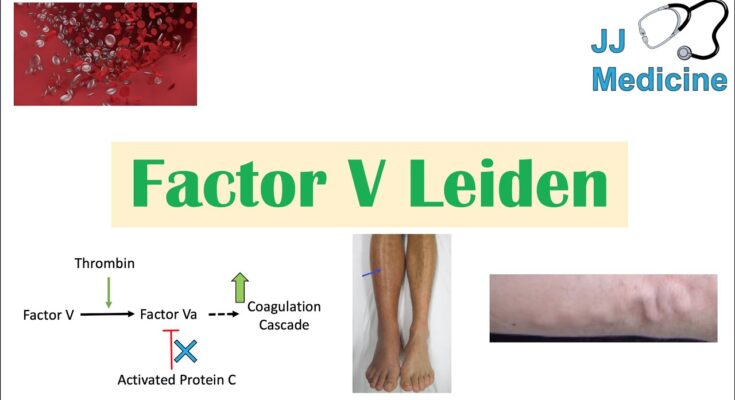
Blood clotting is an essential biological mechanism designed to prevent excessive bleeding when vessels are injured. However, in individuals with Factor V Leiden, this process is disrupted due to a specific mutation in the Factor V gene. This mutation leads to the production of a variant of the Factor V protein that is less susceptible to being deactivated by natural anticoagulants in the body. As a result, the clotting process is amplified, increasing the risk of developing abnormal and potentially harmful blood clots in veins, a condition known as venous thromboembolism (VTE).
The Genetic Basis of Factor V Leiden
The Factor V Leiden mutation is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, meaning a single copy of the altered gene can increase an individual’s risk of developing blood clots. The mutation involves a single nucleotide substitution (G1691A) in the Factor V gene, which alters the protein’s structure. This genetic change hampers the normal inactivation of the Factor V protein, tipping the balance toward clot formation. Understanding this genetic basis is crucial for diagnosing and managing individuals at risk of complications associated with Factor V Leiden.
Prevalence and Demographic Considerations
Factor V Leiden is most commonly found in people of European descent, with varying prevalence rates across different populations. Approximately 5% of Caucasians in the United States carry one copy of the Factor V Leiden mutation, making it a significant concern in these communities. The prevalence is significantly lower in people of African, Asian, and Native American ancestry. Knowledge of these demographic considerations is vital for healthcare providers to target screening efforts and provide informed care to those at higher risk.
However, Factor V Leiden is a genetic disorder that poses a significant impact on the body’s blood clotting mechanism, increasing the risk of thrombosis. Its genetic underpinnings provide a pathway for understanding and managing the condition, with prevalence and demographic factors playing crucial roles in its occurrence. Recognizing the importance of Factor V Leiden in the context of blood clotting disorders is essential for both healthcare professionals and individuals alike, promoting a proactive approach to health and wellbeing.
Understanding the Symptoms of Factor V Leiden
Recognizing the symptoms associated with Factor V Leiden is crucial for early detection and management. Here, we delve into the common symptoms, emphasize the importance of early recognition, and guide you on when to seek medical advice.
Common Symptoms Associated with Factor V Leiden
The tricky aspect of Factor V Leiden is that many individuals may not exhibit any symptoms until a clotting event occurs. However, there are specific signs you should be aware of, including:
- Swelling and Pain in One Limb: Often a sign of deep vein thrombosis, this symptom involves swelling, pain, or a warm sensation in one limb, usually the leg.
- Red or Discolored Skin: The affected area may appear red or have a noticeable color change.
- Unexplained Shortness of Breath: If a clot moves to your lungs (pulmonary embolism), it can cause sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or a cough that may produce bloody sputum.
- **Extended periods of immobility, such as long flights or bed rest, can increase the risk of symptoms manifesting due to clot formation.
The Significance of Recognizing Symptoms Early
Early detection of Factor V Leiden symptoms can significantly reduce the risk of severe complications. Clots can lead to life-threatening conditions like pulmonary embolism or stroke. Recognizing and addressing symptoms promptly can lead to early intervention, which may include medication to thin the blood and prevent clot formation, thereby safeguarding against potential health crises.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Immediate medical advice should be sought if you experience any of the following:
- Unexplained and persistent swelling, pain, or redness in any limb.
- Sudden difficulty breathing, chest pain, or coughing up blood.
- A family history of Factor V Leiden or clotting disorders, even if symptoms are not yet present.
Moreover, if you know you carry the Factor V Leiden mutation, regular check-ups and discussions with your healthcare provider can help manage your condition effectively.
However, while Factor V Leiden may not always present clear symptoms until a clot occurs, being vigilant about the signs and understanding the risks can be life-saving. Early recognition and prompt medical consultation play pivotal roles in managing this genetic condition, ensuring a proactive approach to health and wellbeing.
Causes and Risk Factors of Factor V Leiden
Understanding the causes, how it’s inherited, and the risk factors associated with this mutation can help manage and reduce the risk of complications.
The Genetic Mutation Responsible for Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden results from a specific mutation in the F5 gene. This mutation leads to a change in the Factor V protein, making it resistant to the action of activated protein C, a protein that normally helps control blood clotting. As a result, individuals with Factor V Leiden have a higher tendency to form blood clots.
How Factor V Leiden is Inherited
Factor V Leiden is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. This means that only one copy of the mutated gene, inherited from either parent, is sufficient to increase an individual’s risk of developing blood clots. If an individual inherits two copies of the mutation (one from each parent), the risk and severity of clotting problems are significantly increased.
Risk Factors for Developing Symptoms Associated with Factor V Leiden
While having the Factor V Leiden mutation increases the risk of blood clotting, not everyone with the mutation will develop symptoms. Several factors can influence the likelihood and severity of clotting issues:
- Family History of Blood Clots: A family history of blood clots, especially at a young age, can indicate a higher risk. This suggests a genetic predisposition, such as Factor V Leiden, that increases clotting risk.
- Lifestyle and Environmental Factors: Certain lifestyle choices and environmental factors can exacerbate the risk of blood clots. These include smoking, obesity, prolonged immobility (such as long flights or bed rest), and hormone therapy or birth control pills, especially in women.
- Other Health Conditions: Some health conditions can further increase the risk of blood clots in individuals with Factor V Leiden. These include cancer, pregnancy, and surgeries. Conditions that affect blood flow or the inner lining of the blood vessels (such as varicose veins) also heighten risk.
However, understanding these risk factors is crucial for managing Factor V Leiden. Individuals known to carry this mutation should consult healthcare providers to assess their risk and develop a management plan that may include lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and possibly medication to prevent clotting issues. Early detection and proactive management can significantly reduce the risk of serious complications associated with this genetic condition.
Diagnosing Factor V Leiden: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing this condition accurately is crucial for effective management and treatment. This guide outlines the importance of recognizing symptoms, the medical tests required for diagnosis, and the essential steps to understand test results, including genetic counseling.
The Role of Symptoms in Diagnosing Factor V Leiden
While Factor V Leiden itself often does not present direct symptoms, its primary concern is its potential to cause abnormal blood clotting. Symptoms that might suggest a clotting disorder include unexplained swelling or pain in the legs, sudden breathlessness, and chest pain. These symptoms warrant further investigation, especially if there’s a known family history of Factor V Leiden or clotting disorders. Recognizing these signs early can be the first step towards a timely diagnosis.
Medical Tests and Screenings for Factor V Leiden
Diagnosing Factor V Leiden involves specific medical tests aimed at identifying the genetic mutation responsible for the condition. The primary tests include:
- Blood Clotting Tests (Coagulation Tests): While these tests can’t directly diagnose Factor V Leiden, they can indicate abnormal clotting activity, suggesting the need for further genetic testing.
- Genetic Testing: This is the definitive test for diagnosing Factor V Leiden. It involves analyzing the patient’s DNA to identify the specific mutation in the Factor V gene.
It’s essential for individuals with a family history of the condition or those who have experienced unexplained clotting events to undergo these screenings.
Understanding Test Results and Genetic Counseling
Interpreting the results of Factor V Leiden testing can be complex. A positive test indicates the presence of the Factor V Leiden mutation, which may increase the risk of clotting disorders. However, the presence of the mutation does not guarantee that an individual will experience clotting issues. Conversely, a negative result significantly reduces the likelihood of Factor V Leiden but does not eliminate the risk of other clotting disorders.
Genetic counseling plays a pivotal role following the diagnosis. It involves discussing the implications of the test results, understanding the risk of developing clotting issues, and the potential need for preventive measures. Counseling provides a crucial support system for making informed health decisions and understanding the impact on family members, considering the hereditary nature of the condition.
Diagnosing Factor V Leiden requires a combination of vigilant symptom assessment, precise medical testing, and thorough interpretation of test results, underpinned by comprehensive genetic counseling. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are paramount in managing the condition effectively and minimizing the risk of complications. Individuals with a personal or family history of blood clots are encouraged to discuss their risk factors and testing options with a healthcare provider.
Managing and Treating Factor V Leiden Symptoms
Factor V Leiden is a genetic mutation that increases the risk of developing abnormal blood clots. This condition can be managed effectively through a combination of lifestyle adjustments, medication, and long-term management strategies. By adopting a proactive approach, individuals with Factor V Leiden can lead healthy, active lives while minimizing the risk of complications.
Lifestyle Adjustments to Minimize Risk
Lifestyle changes are a foundational aspect of managing Factor V Leiden. These adjustments are aimed at reducing the risk of blood clot formation:
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity improves blood circulation and lowers the risk of clot formation. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, most days of the week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight increases the pressure on your veins, especially in your legs, which can increase the risk of clots. Work towards a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is crucial. Staying hydrated helps prevent blood from thickening and reduces the risk of clotting.
- Avoid Prolonged Immobility: During long trips or periods of inactivity, take breaks to stand up, stretch, and walk around every 1-2 hours.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking affects blood clotting and circulation, increasing the risk of clots significantly. Quitting smoking is one of the best steps you can take for your overall health.
Medication Options to Prevent and Treat Blood Clots
In some cases, lifestyle adjustments may not be enough to manage the risk of clotting effectively. Medication can play a critical role:
- Anticoagulants: Often referred to as blood thinners, these medications help prevent clots from forming or existing clots from getting larger. Warfarin and direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) like rivaroxaban are commonly prescribed.
- Antiplatelet Drugs: For some individuals, antiplatelet drugs like aspirin may be recommended to prevent clot formation, especially in cases where anticoagulants are not suitable.
It’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to determine the best medication strategy for your specific situation. Regular monitoring and follow-ups are essential to ensure effectiveness and adjust treatment as needed.
Long-term Management Strategies for Individuals with Factor V Leiden
Managing Factor V Leiden is a lifelong commitment. Beyond lifestyle adjustments and medication, long-term management involves:
- Regular Health Check-ups: Regular visits to your healthcare provider for blood tests and health assessments are crucial. These check-ups help monitor your condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
- Education and Awareness: Educating yourself about the signs and symptoms of blood clots can enable early detection and treatment. Symptoms can include unexplained swelling, pain, warmth, and redness in the legs or arms.
- Family Planning: Factor V Leiden can have implications for pregnancy, increasing the risk of clotting. Women with this condition should consult healthcare providers for a tailored management plan during pregnancy and postpartum.
By staying informed, working closely with healthcare professionals, and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals with Factor V Leiden can manage their condition successfully and reduce the risk of serious complications.
Prevention Strategies for Individuals with a Family History of Factor V Leiden
Factor V Leiden is a genetic disorder that affects blood clotting. Individuals with a family history of this condition are at a heightened risk and need to adopt specific preventive measures to manage and mitigate these risks. Understanding the importance of regular check-ups, screenings, and lifestyle modifications can significantly contribute to reducing the overall risk associated with Factor V Leiden.
Importance of Regular Check-Ups and Screenings
Regular check-ups and screenings play a pivotal role in the early detection and management of Factor V Leiden. It is recommended that individuals with a family history of this condition consult with their healthcare provider to determine an appropriate screening schedule. These check-ups often include blood tests that can identify the Factor V Leiden mutation, allowing for timely interventions and personalized management plans. Early detection through routine screenings can be life-saving, providing opportunities for interventions before any serious complications, such as blood clots, arise.
Lifestyle Modifications to Reduce Overall Risk
In addition to regular medical screenings, individuals at risk can take proactive steps through lifestyle modifications to minimize their chances of developing complications associated with Factor V Leiden. These include:
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight increases the pressure on veins and can contribute to the risk of clotting. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help in maintaining a healthy weight.
- Staying Active: Regular physical activity helps keep the blood flowing smoothly and can reduce the risk of blood clots. Even simple activities like walking can have significant benefits.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking is known to affect blood clotting and vessel health. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing blood clots.
- Staying Hydrated: Adequate hydration is essential for preventing blood from thickening. Aim to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Managing Other Risk Factors: It’s important to manage other conditions that can increase the risk of blood clots, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, through medication and lifestyle changes.
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor health status and adjust prevention strategies as needed. By combining regular medical screenings with lifestyle modifications, individuals at risk can lead healthier lives while managing their genetic predisposition to blood clotting disorders.
FAQs: Understanding Factor V Leiden
What is Factor V Leiden?
Factor V Leiden is a genetic mutation that can increase your risk of developing abnormal blood clots. This condition affects the clotting process, making it more likely for clots to form in veins, a condition known as venous thromboembolism.
How common is Factor V Leiden?
Factor V Leiden is the most common hereditary blood clotting disorder in the United States and affects about 5% of American Caucasians. It is less common in other ethnic groups.
What are the symptoms of Factor V Leiden?
Many people with Factor V Leiden never develop symptoms. However, those who do may experience signs of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), such as swelling, pain, and redness in the leg. If a clot travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), symptoms might include shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood.
How is Factor V Leiden diagnosed?
A blood test can determine if you have the Factor V Leiden mutation. This test is often recommended if you have a personal or family history of blood clots, especially at a young age.
Can Factor V Leiden be treated?
While there’s no cure for Factor V Leiden, treatments focus on preventing blood clots. This might include medications like anticoagulants, lifestyle changes, or both, depending on your risk factors and health history.
Should I get tested for Factor V Leiden?
Testing is recommended if you have a family history of the condition or unexplained blood clots. Discuss with your healthcare provider to determine if testing is appropriate for you.
Can Factor V Leiden affect pregnancy?
Yes, women with Factor V Leiden have an increased risk of developing blood clots during pregnancy or after childbirth. It’s important to manage this risk with your healthcare provider if you’re pregnant or planning to become pregnant.
How can I reduce my risk of blood clots if I have Factor V Leiden?
Staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, not smoking, and managing other health conditions can help reduce your risk. Your doctor may also recommend medication or other preventive measures.
Is Factor V Leiden inheritable?
Yes, Factor V Leiden is passed down through families. If one parent has the mutation, there’s a 50% chance of passing it to children. If both parents have the mutation, the risk to children is even higher.
Can lifestyle changes help manage Factor V Leiden?
Absolutely. Lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding smoking can significantly reduce the risk of developing blood clots.
Conclusion:
In summarizing the critical aspects of Factor V Leiden, it is paramount to reiterate the significance of recognizing its symptoms and understanding the underlying causes. This genetic condition, which influences blood clotting, poses a silent threat that can escalate into severe health complications if left unchecked. Awareness and early detection are key in managing the risks associated with Factor V Leiden effectively.
For individuals who find themselves at a higher risk—whether due to family history, personal health history, or other contributing factors—it is imperative to seek medical testing and advice. Modern advancements in medical testing provide a straightforward pathway to identifying the presence of Factor V Leiden, thereby empowering individuals with the knowledge needed to take proactive steps in their healthcare journey.
Encouragement is extended to all who may be at risk to pursue testing and consult with healthcare professionals. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of your genetic makeup and its implications on your health can pave the way for tailored preventive measures, lifestyle adjustments, and, if necessary, medical interventions that can significantly enhance quality of life and prevent potential complications.
In closing, the journey towards understanding and managing Factor V Leiden begins with awareness and action. By recognizing the symptoms, understanding the causes, and seeking professional guidance, at-risk individuals can navigate their health landscape with confidence and reassurance. Let this knowledge serve as a catalyst for positive health decisions, fostering a future where the impacts of Factor V Leiden are effectively mitigated through informed awareness and proactive healthcare strategies.
References
For comprehensive insights and further validation of the information presented on Factor V Leiden symptoms, consider exploring the following reputable sources:
- Mayo Clinic provides an extensive overview of Factor V Leiden, detailing symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Their resource is invaluable for individuals seeking to understand the medical nuances of this condition. Visit Mayo Clinic’s Factor V Leiden page for more information.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) offers a deep dive into the genetic aspects and health implications of Factor V Leiden. It’s a go-to source for understanding the condition’s impact on public health. Access their insights at CDC’s Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK sheds light on the practical aspects of living with Factor V Leiden, including symptom management and lifestyle adjustments. Their guidance is especially useful for patients and caregivers. Learn more on NHS’s Factor V Leiden overview.
These sources have been carefully selected for their credibility and depth of information on Factor V Leiden and its symptoms. They provide a solid foundation for readers seeking to validate the content provided and expand their understanding of this genetic condition.