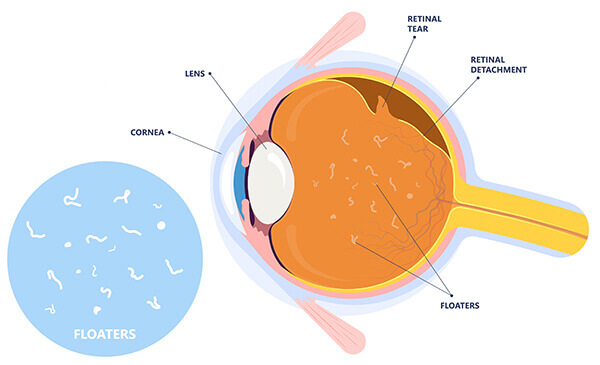
Eye Floaters Symptoms: Eye floaters are tiny spots, specks, lines, or shapes that drift through your field of vision. While they may seem to be in front of your eye, they are actually floating inside it.
Small shadows cast on your retina by these floating particles cause the floaters you see. Typically benign, eye floaters are a common visual phenomenon, especially as people age.
However, understanding their symptoms and causes is essential for recognizing when they may indicate a more serious underlying condition.
Symptoms of Eye Floaters
It’s essential to understand that while eye floaters can be a common occurrence, particularly as you age, they can also signal underlying eye conditions. Let’s delve into the symptoms and indications for when you should seek medical attention.
Understanding the Symptoms
Eye floaters are characterized by several distinct symptoms:
- Spots or Strings: These can be small and dark, shaped like dots, circles, lines, or even cobwebs, that appear in your vision.
- Moving Shapes: Floaters tend to move as your eyes move. They drift away when you try to look at them directly and can dart back quickly when you shift your gaze.
- More Noticeable Against Bright Backgrounds: Floaters are more visible when looking at a uniform, bright background like the sky, a blank wall, or a lit computer screen.
It’s important to note that occasional floaters are typical and usually not a cause for concern. They often result from the natural aging process, where the vitreous (a gel-like substance inside your eye) starts to liquefy and separate, causing these shadowy figures to appear in your vision.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While floaters are often harmless, certain situations warrant immediate medical evaluation:
- Sudden Increase in Floaters: A dramatic surge in the number of floaters could indicate a vitreous or retinal detachment, conditions that require prompt treatment to prevent lasting damage.
- Flashes of Light: Seeing sudden flashes of light in the same eye as the floaters could suggest the vitreous pulling away from the retina or a retina beginning to tear.
- Loss of Peripheral Vision: If you notice a shadow or curtain falling across any part of your vision, this could signal a retinal detachment, a severe and sight-threatening condition.
However, while eye floaters can often be a benign aspect of aging, any sudden changes in their appearance, especially when accompanied by flashes of light or vision loss, should prompt an immediate visit to an eye care professional. Monitoring your eye health and staying informed about symptoms like these are crucial steps in maintaining good visual health.
Common Causes of Eye Floaters
Certain conditions can cause or exacerbate the presence of eye floaters. Here’s a closer look at the most common causes.
Aging and Its Impact on the Eye’s Vitreous Humor
As we age, the vitreous humor, a gel-like substance filling the middle of the eye, begins to liquefy and shrink. This process can cause microscopic fibers within the vitreous to clump together, casting shadows on the retina that we perceive as floaters. This is a natural part of aging and is the most common cause of eye floaters.
Inflammation in the Back of the Eye
Inflammation in the layers of the uvea in the back of the eye, known as posterior uveitis, can lead to the release of inflammatory debris into the vitreous. This debris can appear as floaters. Uveitis can be triggered by infection, inflammatory diseases, or other causes.
Bleeding in the Eye
Bleeding within the eye, often due to conditions like diabetic retinopathy, trauma, or blocked blood vessels, can lead to the appearance of eye floaters. The blood cells can cast shadows on the retina, similar to how the clumps within the vitreous humor do.
Torn Retina
A retinal tear is a serious condition that can produce floaters. When the vitreous humor shrinks, it can pull on the retina with enough force to tear it. Once the retina is torn, fluid can seep behind it and lift it off the back of the eye, leading to a detachment. This is often marked by a sudden increase in the number of floaters, possibly accompanied by flashes of light.
Other Eye Conditions and Diseases
Various other eye conditions and diseases can contribute to the presence of floaters. These include but are not limited to, infections, injuries, and changes in the eye structure. Each condition can introduce materials into the vitreous that cast shadows on the retina.
If you notice a sudden increase in floaters, especially if accompanied by flashes of light or vision loss, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to addressing any potential eye health issues.
Risk Factors and Prevention of Eye Floaters
Understanding the risk factors and learning about prevention can help you maintain optimal eye health. Let’s delve into who is at higher risk for developing eye floaters and explore whether prevention is possible, along with providing an overview of eye health tips.
Who is at Higher Risk?
- Age: Individuals over the age of 50 are more likely to experience eye floaters. As the eye ages, the vitreous humor (the gel-like substance filling the eye) begins to liquefy and contract, leading to the formation of floaters.
- Nearsightedness: People with myopia (nearsightedness) are at an increased risk. High levels of nearsightedness can cause changes in the vitreous humor, making floaters more likely.
- Post-Eye Surgery: Those who have undergone cataract operations or other eye surgeries might notice an increase in floaters due to changes within the eye’s interior.
- Eye Trauma: Any injury to the eye can lead to the development of floaters by disrupting the vitreous humor.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes can affect the eyes and lead to diabetic retinopathy, a condition that increases the risk of floaters.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Eye inflammation (uveitis) can result in the release of debris into the vitreous, forming floaters.
Can Eye Floaters Be Prevented?
While it’s not always possible to prevent eye floaters, especially those caused by aging or genetics, you can take steps to reduce your risk and maintain good eye health:
- Regular Eye Examinations: Regular check-ups with an eye care professional can help detect changes in your eyes early on.
- Protect Your Eyes: Wear protective eyewear during activities that could lead to eye injuries, and always shield your eyes from harmful UV rays with sunglasses.
- Manage Health Conditions: Keeping systemic health conditions like diabetes under control can minimize eye complications.
- Healthy Lifestyle: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly antioxidants like vitamin C and E, can support eye health. Staying hydrated and avoiding smoking can also contribute to the overall well-being of your eyes.
Eye Health Tips
- Breaks During Screen Time: To reduce eye strain, follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
- Balanced Diet: Incorporate foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, zinc, and vitamins C and E to support eye health.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity improves circulation, which is beneficial for eye health.
However, while certain risk factors for eye floaters can’t be entirely controlled, adopting a proactive approach towards eye health can potentially mitigate risks and promote long-term well-being. If you’re concerned about eye floaters or other vision changes, consulting an eye care professional is always the best course of action.
Diagnosing Eye Floaters: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the diagnostic process for eye floaters can help individuals recognize the importance of timely consultation with healthcare professionals. This guide outlines the steps involved in diagnosing eye floaters and the pivotal role of eye exams in identifying conditions related to eye floaters.
The Diagnostic Process for Eye Floaters
Healthcare professionals follow a systematic approach to diagnose eye floaters, ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s eye health. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Patient History: The initial step involves gathering detailed information about the patient’s medical history, including any previous eye conditions, surgeries, or injuries. The healthcare professional will ask about the onset, duration, frequency, and characteristics of the floaters. Understanding the patient’s overall health and any medications they are taking is also crucial as some conditions and treatments can contribute to the presence of floaters.
- Visual Acuity Test: This test measures the patient’s ability to see objects at various distances clearly. It helps determine if the floaters have impacted the visual acuity.
- Dilated Eye Exam: By dilating the pupils with eye drops, the eye care professional can examine the retina and the vitreous humor—the gel-like substance inside the eye where floaters originate. This comprehensive examination is crucial for identifying not only the presence of floaters but also any underlying conditions that may be causing them.
- Tonometry: This procedure measures the pressure inside the eye, which is vital for detecting glaucoma, a condition that could potentially contribute to the formation of floaters.
- Ultrasound Imaging: In cases where the eye’s interior cannot be thoroughly observed due to eye conditions like cataracts, an ultrasound may be performed. This imaging test provides a detailed view of the eye’s interior structures, aiding in the detection of any abnormalities that could be associated with floaters.
The Role of Eye Exams in Diagnosing Conditions Related to Eye Floaters
Eye exams play a crucial role in not only diagnosing eye floaters but also identifying any related conditions. Through comprehensive eye examinations, healthcare professionals can detect early signs of eye diseases that might not yet be symptomatic. Conditions such as retinal tears, detachments, or bleeding within the eye can manifest initially as floaters. Early detection of these issues is vital for preventing potential vision loss.
Moreover, regular eye exams allow for the monitoring of changes in the number, size, or pattern of floaters, which could indicate progression or improvement of an underlying condition. By assessing the eye’s health over time, eye care professionals can provide tailored advice and treatment options to manage or mitigate the impact of eye floaters and related conditions on the patient’s quality of life.
However, while eye floaters are often benign, a thorough diagnostic process is essential for ruling out more serious conditions. Regular eye exams serve as a preventive measure, helping to ensure the maintenance of good eye health and the early detection of any eye-related diseases. If you experience a sudden increase in floaters, especially if accompanied by flashes of light or a loss of peripheral vision, seek immediate medical attention, as these symptoms could signify a more serious issue.
Treatment Options for Eye Floaters
This guide provides an overview of when treatment for eye floaters is necessary and the available treatment options, including observation, medication, laser therapy, and surgery, to help you navigate this condition with confidence.
When is Treatment Necessary?
Most eye floaters are benign and don’t require treatment. They’re often the result of age-related changes in the vitreous, the gel-like substance that fills the inside of your eyes. However, treatment may become necessary if:
- The floaters are dense enough to impair vision.
- They are accompanied by flashes of light, signaling potential retina issues.
- They appear suddenly or increase rapidly in number, indicating a possible retinal detachment or other serious conditions.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek immediate medical attention. An eye care professional can assess your situation and determine if treatment is needed to prevent more serious eye problems.
List of Available Treatment Options
Observation
In many cases, simply monitoring the floaters is the best course of action. Over time, you may not notice them as much, as your brain adapts to their presence. Regular eye exams will ensure they aren’t a sign of underlying issues.
Medication
Currently, there are no medications specifically approved to treat eye floaters. However, if an underlying condition causes the floaters, treating that condition can alleviate the symptoms. Always consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Laser Therapy
Laser vitreolysis is a non-invasive procedure where lasers are used to break up floaters into smaller, less noticeable fragments. This option may be suitable for certain types of floaters and is performed by an ophthalmologist. While effective for some, it’s not universally recommended due to potential risks and varying success rates.
Surgery
In severe cases where floaters significantly impair vision, a vitrectomy may be performed. This surgical procedure removes the vitreous gel, along with the floaters, from the eye. The vitreous is then replaced with a saline solution. While effective, surgery carries risks such as retinal detachment and cataracts, and is typically considered only as a last resort.
However, understanding when treatment is necessary and the options available can empower you to make informed decisions about your eye health. Always consult with an eye care professional to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Living with Eye Floaters: Managing Symptoms and Adapting to Daily Life
Eye floaters, those tiny shadows or shapes that drift across your vision, can range from being slightly annoying to significantly impacting your daily activities. Although they’re usually harmless and often part of the natural aging process, knowing how to manage their presence can greatly improve your quality of life. In this guide, we’ll explore effective tips for dealing with eye floaters and provide advice on when it’s essential to consult with an eye care professional.
Tips for Managing Symptoms
1. Adjust Lighting Conditions: Sometimes, the visibility of eye floaters can depend on the lighting environment you’re in. Bright, harsh lights can make floaters more noticeable. Try adjusting the lighting in your workspace or home to softer, more diffused lighting. This can help reduce the prominence of floaters in your vision.
2. Take Breaks During Screen Time: Extended periods of focusing on screens can not only strain your eyes but can also make floaters more apparent. Ensure to take regular breaks using the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds. This helps minimize eye strain and may reduce the noticeability of floaters.
3. Practice Eye Exercises: Some eye exercises can help manage the symptoms of eye floaters. Focusing on different distances and practicing eye movements can sometimes help in making floaters less bothersome. However, it’s essential to approach these exercises with caution and consult with an eye care professional for personalized advice.
4. Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration is vital for maintaining overall eye health. Sometimes, dehydration can exacerbate the visibility of eye floaters. Make sure you’re drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
5. Utilize Sunglasses: Bright outdoor light can make floaters more noticeable. Wearing sunglasses with UV protection can not only protect your eyes from harmful rays but also reduce the intensity of light entering your eyes, making floaters less visible.
When to Follow Up with an Eye Care Professional
While eye floaters are typically benign, there are certain situations where they could indicate more serious eye conditions. It’s crucial to consult an eye care professional if you experience:
- A sudden increase in the number of floaters.
- Flashes of light in the same eye as the floaters.
- A shadow or curtain that affects any part of your vision.
- Any sudden changes in your vision.
These symptoms could be signs of retinal detachment or other severe eye conditions that require immediate attention. Regular eye exams are also essential for monitoring the health of your eyes and ensuring that any changes in your vision are addressed promptly.
Living with eye floaters can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can manage their symptoms and reduce their impact on your daily life. Remember, maintaining regular communication with your eye care professional is key to safeguarding your vision and overall eye health.
FAQ Section: Eye Floaters – Symptoms and Causes
What Are Eye Floaters?
Eye floaters are small, dark shapes that float in your vision. They can appear as spots, threads, or fragments of cobwebs, which move as your eyes move and seem to dart away when you try to look at them directly. Although eye floaters can be annoying, they usually don’t interfere with your sight.
What Causes Eye Floaters?
Most commonly, eye floaters are caused by age-related changes that occur as the jelly-like substance (vitreous) inside your eyes becomes more liquid. Tiny fibers within the vitreous tend to clump and can cast tiny shadows on your retina, which are seen as floaters. Other causes include inflammation in the back of the eye, bleeding in the eye, or a torn retina. Eye surgeries and eye medications can also cause eye floaters.
Are Eye Floaters a Sign of a Serious Condition?
In many cases, eye floaters are not a cause for concern and are simply a nuisance. However, if you experience a sudden increase in floaters, especially if they are accompanied by flashes of light or a loss of peripheral vision, it could indicate a more serious condition like a retinal detachment, which requires immediate medical attention.
Can Eye Floaters Be Prevented?
Preventing eye floaters is not always possible, especially since they are often a natural part of the aging process. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and regular eye check-ups can help detect and manage conditions that might lead to floaters, such as controlling high blood pressure or diabetes.
Will Eye Floaters Go Away on Their Own?
Eye floaters can sometimes improve over time and become less bothersome. Your brain may also adapt to them, making them less noticeable. However, in some cases, they may not disappear entirely.
When Should I See a Doctor?
You should schedule an eye examination if you’re concerned about eye floaters or if the floaters:
- Suddenly increase in number.
- Are accompanied by flashes of light.
- Appear alongside a loss of peripheral vision.
These symptoms could indicate a serious condition requiring prompt treatment.
By understanding the common symptoms and causes of eye floaters, individuals can better assess when to seek medical advice and how to manage this condition effectively. Regular eye examinations are key to ensuring that any changes in eye health are monitored and addressed promptly.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the symptoms and causes of eye floaters is essential for maintaining optimal eye health. Eye floaters can manifest as small, shadowy shapes that appear to drift through your field of vision. They are often harmless but can sometimes signal underlying health issues that require immediate attention. The causes range from natural aging of the eye to more serious conditions such as retinal detachment or eye injuries.
Recognizing when your symptoms might be out of the ordinary is crucial. Common indicators include a sudden increase in the number of floaters, the appearance of flashes of light, or any changes in your field of vision. These symptoms should not be ignored, as they could be signs of more severe eye conditions.
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing these symptoms to seek professional medical advice. An eye care specialist can provide a comprehensive examination, diagnose the underlying cause of eye floaters, and recommend the appropriate treatment plan. Early detection and intervention can prevent potential complications and preserve your vision.
Taking proactive steps towards understanding and addressing the symptoms of eye floaters not only ensures the health of your eyes but also contributes to your overall well-being. Remember, your eyes are a window to the world; keeping them healthy is paramount.
References
For those looking to deepen their understanding of eye floaters and their symptoms, the following resources offer comprehensive insights backed by medical expertise:
- Mayo Clinic – An extensive overview of eye floaters, including causes, symptoms, and when to seek medical advice. Access the guide here: Eye Floaters: Symptoms & Causes.
- National Health Service (UK) – Offers guidance on symptoms, causes, and when to seek medical help for eye floaters. Read their advice here: Eye Floaters, Flashes, and Spots.
These resources are selected for their reliability and the quality of information they provide. They can serve as a starting point for anyone seeking to understand eye floaters better or experiencing symptoms and wondering about the next steps.