Esthesioneuroblastoma Treatment: Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as olfactory neuroblastoma, is a rare form of cancer originating in the upper nasal cavity.
This malignancy affects the olfactory neuroepithelium, the area responsible for our sense of smell. Given its rarity, diagnosis and treatment require a high degree of specialization and expertise.
Understanding Esthesioneuroblastoma
Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as olfactory neuroblastoma, is a rare type of cancer that originates in the olfactory epithelium, the tissue in the upper part of the nasal cavity responsible for our sense of smell. Given its rarity and unique location, understanding its epidemiology, causes, risk factors, and the signs and symptoms to watch for is crucial for early detection and treatment. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Esthesioneuroblastoma to enhance awareness and understanding of this rare condition.
Epidemiology: Incidence and Prevalence Rates
Esthesioneuroblastoma is an exceedingly rare cancer, contributing to a very small fraction of all head and neck cancers. The exact incidence rate of Esthesioneuroblastoma is hard to pinpoint due to its rarity, but it is estimated to account for only 3% of all tumors originating from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. It can occur at any age but shows a slight predilection for individuals in their 50s and 60s. Interestingly, there’s also a smaller peak in incidence among adolescents and young adults. The prevalence of Esthesioneuroblastoma is difficult to determine, again due to its rarity and the limited number of large-scale epidemiological studies on the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of Esthesioneuroblastoma are not well understood, and as of now, no definitive risk factors have been identified. Like many cancers, it’s believed to arise from mutations in the DNA of cells, in this case, the olfactory epithelium, but what triggers these mutations remains a subject of research. There have been no established links to environmental factors, lifestyle choices, or genetic predisposition, making it difficult to pinpoint specific risk factors or preventive measures.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of Esthesioneuroblastoma can be subtle at first and often mimic those of more common nasal and sinus conditions, which can lead to delays in diagnosis. Key signs and symptoms to be aware of include:
- Persistent nasal congestion or obstruction that doesn’t improve with treatment and may be worse on one side.
- Nosebleeds, which may become frequent and difficult to manage.
- A decreased sense of smell or anosmia, which might not be noticeable until it becomes significant.
- Swelling or a lump on the face, roof of the mouth, or inside the nose.
- Changes in vision, such as double vision or decreased eyesight, if the tumor grows large enough to affect the orbital structures.
- Headaches or pain in the face or teeth that do not respond to standard treatment.
- A watery discharge from the nose.
Early detection and treatment of Esthesioneuroblastoma are vital for improving outcomes. If you or someone you know exhibits one or more of these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time, consulting a healthcare provider for further evaluation and testing is crucial.
Given its complexity and the importance of early detection, staying informed about Esthesioneuroblastoma, its potential signs, and symptoms, as well as understanding its epidemiology, can significantly impact outcomes. Awareness and education are key components in the fight against this rare cancer.
Diagnosis of Esthesioneuroblastoma
Early diagnosis is pivotal for effective treatment and improved outcomes. This comprehensive guide delves into the diagnostic process, emphasizing the roles of various imaging studies, the critical nature of biopsy and histopathological examination, and the significance of accurate staging in understanding the disease’s extent.
Initial Evaluation and Clinical Suspicion
The diagnosis journey begins with a thorough initial evaluation and clinical suspicion. Patients may present with symptoms such as nasal obstruction, epistaxis (nosebleeds), and anosmia (loss of smell), which necessitate further investigation. Healthcare providers assess these symptoms in conjunction with a detailed medical history and physical examination to determine the need for specialized diagnostic tests.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies play a crucial role in diagnosing esthesioneuroblastoma, offering a detailed view of the tumor’s location, size, and potential spread to adjacent structures or distant sites.
- CT Scan: A computed tomography (CT) scan provides precise images of the nasal cavity, sinuses, and surrounding bone structures, helping in identifying abnormal growths.
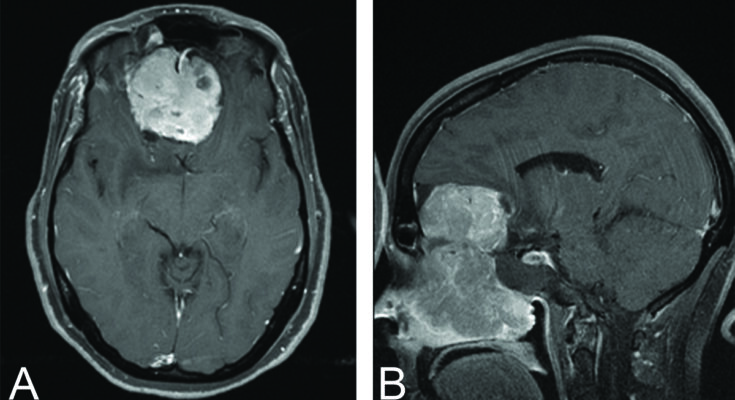
- MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is preferred for its superior contrast resolution, which is invaluable in delineating the tumor’s extent and its relationship with nearby soft tissues and the brain.
- PET Scan: A positron emission tomography (PET) scan can assess the metabolic activity of the tumor, aiding in detecting metastasis and evaluating the tumor’s response to treatment.
These imaging techniques collectively offer comprehensive insights, guiding the treatment planning by delineating the tumor’s characteristics and involvement with neighboring structures.
Biopsy and Histopathological Examination
A biopsy, the removal of a small tissue sample for microscopic examination, is imperative for confirming the diagnosis of esthesioneuroblastoma. The procedure might vary from a simple needle biopsy to more complex surgical interventions, depending on the tumor’s location and size. Histopathological examination of the biopsy specimen is crucial, as it provides definitive evidence of esthesioneuroblastoma through the identification of unique cellular features and patterns, distinguishing it from other neoplasms.
Staging: Understanding the Extent of the Disease
Staging is a systematic process to determine the extent of cancer spread, both locally and throughout the body. For esthesioneuroblastoma, the Kadish staging system is commonly used, classifying the disease into three stages based on the tumor’s location and spread:
- Stage A: The tumor is confined to the nasal cavity.
- Stage B: The tumor extends to the sinuses.
- Stage C: There is further spread beyond the nasal cavity and sinuses, potentially involving the orbit, skull base, or distant metastasis.
Accurate staging is fundamental for developing an effective treatment strategy, predicting outcomes, and facilitating comparisons across clinical studies.
However, the diagnosis of esthesioneuroblastoma involves a multi-faceted approach combining clinical evaluation, advanced imaging studies, biopsy, and careful staging. These steps are essential in confirming the diagnosis, understanding the disease’s extent, and formulating an appropriate treatment plan to enhance patient survival and quality of life.
Treatment Options for Esthesioneuroblastoma
The treatment strategy often involves a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating surgical intervention, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and emerging treatments. Understanding the available options can empower patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions tailored to individual cases.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery stands as a cornerstone in the management of esthesioneuroblastoma, aiming to remove the tumor completely while preserving critical functions. The types of surgical procedures vary based on the tumor’s size, location, and stage:
- Endoscopic Resection: A minimally invasive technique that uses an endoscope to remove the tumor through the nasal passages, reducing recovery time and complications.
- Craniofacial Resection: A more extensive surgery that may involve opening the skull to access and remove the tumor, often necessary for larger or more complex cases.
Surgery is generally considered the best option when the tumor is localized, operable, and can be safely excised without significant damage to critical structures. The potential risks and outcomes of surgical treatment hinge on the tumor’s specifics and the procedure’s complexity, with complications possibly including bleeding, infection, and impacts on olfactory and respiratory functions.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy plays a pivotal role in treating esthesioneuroblastoma, especially for tumors that are inoperable, after surgery to target residual cancer cells, or when the cancer recurs. It can be delivered through:
- External Beam Radiation: Directs high-energy beams at the tumor from outside the body, meticulously planned to minimize exposure to healthy tissues.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery: A highly precise form of radiation therapy that delivers a concentrated dose to the tumor, often used for smaller or well-defined tumors.
The benefits of radiation therapy include its ability to target and destroy cancer cells while sparing surrounding healthy tissue. However, potential side effects like skin irritation, fatigue, and changes in taste or smell may occur, varying in intensity based on the treatment’s duration and dose.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy may be indicated in various scenarios for esthesioneuroblastoma treatment, such as to shrink tumors before surgery, treat metastases, or as part of a palliative care regimen. Common chemotherapeutic agents and regimens include platinum-based drugs and combination therapies, tailored to the patient’s overall health and cancer specifics.
While chemotherapy can effectively target cancer cells, it also carries the potential for side effects, including nausea, hair loss, and increased susceptibility to infections. The expected outcomes and the severity of side effects largely depend on the type and duration of the chemotherapy regimen.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
The landscape of esthesioneuroblastoma treatment continues to evolve, with new and experimental modalities offering hope for more effective and less toxic options:
- Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genes, proteins, or the tumor’s environment that contributes to cancer growth and survival, aiming for precision in treatment with fewer side effects.
- Immunotherapy: Employs the body’s immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells, a promising approach currently under investigation in clinical trials.
Clinical trials are crucial for advancing our understanding and treatment of esthesioneuroblastoma, potentially unveiling novel therapies that could improve outcomes and quality of life for patients.
However, the treatment of esthesioneuroblastoma requires a tailored, multidisciplinary approach. By combining established methods with emerging therapies, there’s hope for more effective treatments with fewer side effects, paving the way for better patient outcomes in this rare and challenging cancer.
Multidisciplinary Approach to Treatment: Navigating Esthesioneuroblastoma with a Team
When it comes to treating complex conditions like esthesioneuroblastoma, a rare cancer that originates in the nasal cavity, a multidisciplinary approach isn’t just beneficial—it’s essential. This strategy emphasizes the importance of a cohesive team, consisting of various specialists, working in tandem to provide the most comprehensive and effective care for patients. Let’s delve into why this team approach is crucial and the roles different specialists play in managing esthesioneuroblastoma.
The Significance of a Team Approach
A multidisciplinary team approach ensures that patient care is holistic, covering all bases from diagnosis to post-treatment recovery. This collaboration between specialists from different fields brings diverse perspectives and expertise to the table, leading to more accurate diagnoses, tailored treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. In the realm of esthesioneuroblastoma, where treatment can be particularly complex due to the tumor’s location and potential impact on critical functions, such as smell and sight, the synergy of a multidisciplinary team is invaluable.
Roles of Different Specialists
- Oncologists: These cancer specialists lead the charge in designing and overseeing the treatment plan. Medical oncologists focus on chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and other drug-based treatments, while radiation oncologists specialize in the use of radiation therapy to target cancer cells.
- Surgeons: Given the tumor’s location, ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) surgeons, or otolaryngologists, often play a key role. They are skilled in performing surgery in sensitive areas, striving to remove the tumor while preserving as much function as possible. Neurosurgeons may also be involved if the cancer affects or is close to the brain.
- Radiologists: These specialists are crucial for accurately diagnosing esthesioneuroblastoma and monitoring its response to treatment. Through advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, radiologists can pinpoint the tumor’s size, location, and impact on surrounding structures.
- Pathologists: By examining tissue samples under a microscope, pathologists determine the specific type and grade of cancer, which is vital for guiding treatment decisions.
- Rehabilitation Specialists: Given the potential impact on functions like breathing, speaking, and swallowing, rehabilitation specialists, including speech therapists and physiotherapists, are key to a patient’s recovery and quality of life post-treatment.
- Palliative Care Specialists: They provide support for managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for patients undergoing treatment.
By bringing together the expertise of oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, and other specialists, this approach ensures that patients receive the most comprehensive and customized care possible. It highlights the importance of a team in tackling the complexities of cancer treatment, ensuring that every aspect of the patient’s journey is addressed.
Coping with Esthesioneuroblastoma: A Comprehensive Guide
Psychological Impact of Diagnosis and Treatment
The diagnosis of esthesioneuroblastoma, a rare cancer affecting the nasal cavity, can be overwhelming for patients and their loved ones. The journey from diagnosis through treatment involves not just physical challenges but significant emotional and psychological hurdles as well. Understanding and acknowledging the emotions that come with this diagnosis is crucial. Patients may experience a wide range of feelings, including shock, fear, anger, and disbelief. As treatment progresses, these emotions can evolve, leading to anxiety, depression, or even a sense of isolation.
It’s essential for patients and their caregivers to recognize that these feelings are normal and valid. Seeking professional psychological support can be incredibly beneficial. Mental health professionals specializing in oncology can offer coping strategies tailored to the unique challenges of cancer treatment. Furthermore, participating in support groups where individuals can share their experiences and feelings with others facing similar challenges can provide a sense of community and understanding.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients and Families
Navigating the complexities of esthesioneuroblastoma treatment requires a robust support system. This support can come from various sources, including healthcare teams, family members, friends, and cancer support organizations. Establishing a strong communication line with medical professionals can help demystify the treatment process and make it more manageable.
For families and patients, leveraging resources like counseling services, financial aid programs, and educational materials from cancer support organizations can be incredibly helpful. These resources can provide not only practical assistance but also emotional support. Organizations such as the American Cancer Society offer comprehensive guides on coping with cancer, support group information, and even lodging during treatment for patients traveling far from home.
Rehabilitation and Follow-up Care
The road to recovery from esthesioneuroblastoma can be long and requires a dedicated approach to rehabilitation and follow-up care. Post-treatment care is focused on managing side effects, monitoring for recurrence, and addressing any long-term impacts of the disease or its treatment. Rehabilitation services, such as physical therapy, speech therapy, and nutritional counseling, can play a significant role in improving quality of life and aiding recovery.
Regular follow-up visits with the oncology team are critical to ensure that any signs of recurrence are detected early. These visits are also an opportunity to address ongoing physical or emotional challenges. Patients should feel empowered to discuss any concerns or symptoms they experience and inquire about resources for continued support.
From dealing with the initial diagnosis to navigating treatment and entering into recovery, patients and their families should prioritize seeking out support and resources tailored to their needs. By embracing a holistic approach to care, individuals facing esthesioneuroblastoma can find strength and resilience on their journey toward healing.
FAQs on Esthesioneuroblastoma and Its Treatment
What is Esthesioneuroblastoma?
Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as olfactory neuroblastoma, is a rare cancer that originates in the upper part of the nasal cavity. This area is closely associated with the sense of smell, hence the name. Esthesioneuroblastoma can affect individuals of any age but is most commonly diagnosed in adults.
What are the Symptoms of Esthesioneuroblastoma?
The symptoms of esthesioneuroblastoma can vary but often include a blocked nose, nosebleeds, and a decreased sense of smell. As the tumor grows, it may cause more severe symptoms, such as swelling of the face or eyes, difficulty with vision, and pain in the face or teeth.
How is Esthesioneuroblastoma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, imaging tests (such as MRI or CT scans), and a biopsy of the tumor. The biopsy is crucial for confirming the diagnosis and determining the specific characteristics of the cancer.
What are the Treatment Options for Esthesioneuroblastoma?
Treatment options for esthesioneuroblastoma depend on the stage and location of the tumor but may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Surgery aims to remove as much of the tumor as possible, while radiation and chemotherapy may be used to target any remaining cancer cells.
Is Surgery Always Necessary for Esthesioneuroblastoma?
While surgery is a common treatment for esthesioneuroblastoma, it may not be necessary for every patient. The decision depends on the tumor’s size, location, and whether it has spread to other parts of the body. Your healthcare team will recommend the best treatment plan based on your specific situation.
Can Esthesioneuroblastoma Recur After Treatment?
Yes, esthesioneuroblastoma can recur after treatment. Regular follow-up appointments and imaging tests are essential for monitoring your condition and detecting any signs of recurrence early.
What is the Prognosis for Esthesioneuroblastoma?
The prognosis for esthesioneuroblastoma varies depending on several factors, including the stage of the cancer at diagnosis, the success of treatment, and the patient’s overall health. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
Are There Any Side Effects of Treatment?
Treatment for esthesioneuroblastoma, like all cancer treatments, can have side effects. These may include fatigue, changes in sense of smell or taste, and difficulty with breathing or swallowing. Your healthcare team will work with you to manage any side effects you experience.
Where Can I Find Support and More Information?
Finding support is crucial when dealing with a rare condition like esthesioneuroblastoma. Many hospitals and cancer centers offer support groups and counseling services. Additionally, online resources and communities can provide valuable information and connect you with others who understand what you’re going through.
Conclusion:
Support systems play a vital role in the treatment journey. Encouragement from family, friends, and support groups can provide much-needed emotional and psychological support. Additionally, patients should seek information from reliable sources to fully understand their condition and treatment options, empowering them to make informed decisions about their care.
Innovations in medical research continue to offer hope, with ongoing studies focused on improving outcomes and quality of life for esthesioneuroblastoma patients. Participation in clinical trials may also provide access to new therapies that are not yet widely available.
In summary, while esthesioneuroblastoma presents significant challenges, the evolving landscape of medical treatment and support offers hope. By actively engaging in their treatment plan, seeking out comprehensive care, and leveraging support systems, patients can navigate their journey with optimism and strength. The future holds promise for improvements in treatment and outcomes, reinforcing the importance of hope and perseverance in the face of adversity.
References
In the realm of medical information, particularly concerning treatments for specific conditions like Esthesioneuroblastoma, citing reputable sources is paramount. These references not only validate the information provided but also offer readers avenues for further reading and deeper understanding. Below, we have compiled a list of authoritative sources that shed light on various aspects of Esthesioneuroblastoma treatment. Each source has been selected for its credibility, comprehensiveness, and relevance to patients, caregivers, and medical professionals seeking current and reliable data on this topic.
- National Cancer Institute (NCI) – As a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, the NCI is a leading authority on cancer research and patient care. Their website provides detailed information on cancer types, treatments, and the latest research advancements.
Visit NCI’s Esthesioneuroblastoma Treatment Overview - Mayo Clinic – Renowned for its patient care and research, Mayo Clinic offers comprehensive guides on a wide array of medical conditions, including Esthesioneuroblastoma. Their content is regularly updated and reviewed by medical professionals, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Explore Mayo Clinic’s Approach to Esthesioneuroblastoma - PubMed Central (PMC) – An invaluable resource for accessing free, full-text articles from biomedical and life sciences journals. PMC is a service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM) and offers peer-reviewed articles that can provide in-depth scientific insights into Esthesioneuroblastoma treatment methodologies.
Search for Esthesioneuroblastoma Treatment Articles on PMC - American Cancer Society (ACS) – ACS is a nationwide, community-based voluntary health organization dedicated to eliminating cancer. Their website features a wealth of information on cancer types, including patient support resources and treatment options.
Read About Treatment Options at American Cancer Society - Cancer Research UK – As the world’s largest independent cancer research organization, Cancer Research UK offers detailed information on cancer types, research updates, and treatment options available in the UK and beyond.
Discover Cancer Research UK’s Insights on Esthesioneuroblastoma
Each of these sources provides a unique perspective and wealth of knowledge on Esthesioneuroblastoma, from diagnosis and treatment options to the latest research findings and clinical trials. Patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers can leverage this information to make informed decisions and stay abreast of advancements in the field.
By engaging with these references, readers are equipped to deepen their understanding of Esthesioneuroblastoma and explore the breadth of treatment options and research avenues. Remember, while these sources are reputable and offer high-quality information, it’s always crucial to consult with healthcare professionals for personal medical advice and treatment planning.