Esophageal Varices Treatment: Esophageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus, often linked with serious conditions such as liver disease. These varices pose a significant risk because they can rupture and lead to life-threatening bleeding.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of esophageal varices is crucial for those at risk and healthcare professionals.
What are Esophageal Varices?
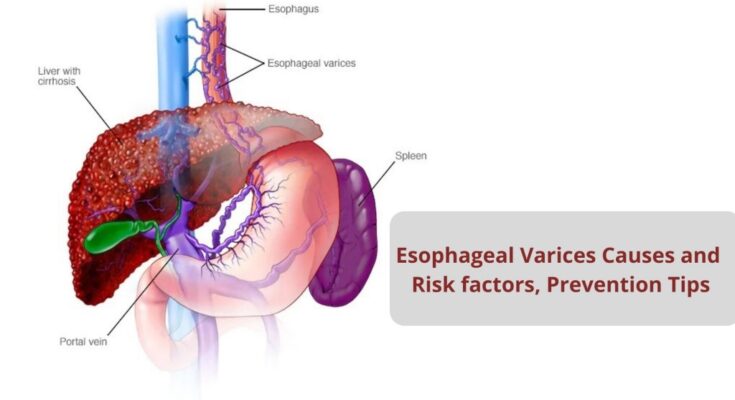
Esophageal varices are enlarged veins that occur in the esophagus, the tube connecting the throat to the stomach. These swollen veins are fragile and prone to bleeding, which can lead to a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. They are primarily associated with advanced liver disease and are a significant complication of cirrhosis (scarring of the liver). Understanding esophageal varices is crucial for those at risk, as early detection and management can help prevent life-threatening bleeding.
Causes and Risk Factors
The primary cause of esophageal varices is increased pressure in the portal vein system, known as portal hypertension. This condition is often a consequence of liver cirrhosis, where normal liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, hindering the liver’s ability to function and regulate blood flow. Several factors contribute to the development of esophageal varices, including:
- Liver Diseases: Chronic conditions like hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and alcohol-related liver disease can lead to cirrhosis and esophageal varices.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Clots in the portal vein or its branches can increase portal vein pressure and contribute to varices.
- Genetic Conditions: Rarely, inherited conditions that affect the liver and blood vessels can lead to esophageal varices.
Risk factors that exacerbate the likelihood of developing esophageal varices include severe liver disease, a history of liver or abdominal swelling, and previous episodes of variceal bleeding. Individuals with these conditions are at a heightened risk and require regular monitoring.
How They Relate to Liver Disease
Esophageal varices are closely related to liver disease, particularly cirrhosis, which is the most common cause. The relationship is primarily due to the role of the liver in managing blood flow from the intestines and spleen through the portal vein. When cirrhosis occurs, the scar tissue obstructs this flow, leading to increased pressure (portal hypertension), which, in turn, forces blood into smaller, less resistant vessels like those in the esophagus. Over time, these vessels can swell, forming varices.
The progression of liver disease and the development of esophageal varices are interconnected, highlighting the importance of liver health management. Preventing liver disease or managing it effectively in its early stages can significantly reduce the risk of complications such as esophageal varices. For those with liver disease, regular screenings for varices are recommended, as early detection and treatment can prevent bleeding, one of the most serious complications of esophageal varices.
However, esophageal varices are a severe complication often associated with advanced liver disease, particularly cirrhosis. Their development is primarily due to increased pressure in the portal vein, a condition known as portal hypertension. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and their relation to liver disease is vital for effective prevention and management strategies, underscoring the importance of liver health and regular medical monitoring for those at risk.
Signs and Symptoms of Esophageal Varices
Recognizing the signs and symptoms early can be crucial for managing this condition effectively. Here’s what you need to know.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
Esophageal varices often don’t present noticeable symptoms until they bleed. However, there are certain signs you might observe if bleeding occurs:
- Vomiting Blood: This can appear as bright red blood or dark, coffee-ground-like vomitus.
- Black, Tarry Stools: Known medically as melena, this indicates digested blood in the stools.
- Light-headedness or Fainting: Caused by the sudden loss of blood.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired can be a symptom of chronic blood loss and anemia.
- Paleness: An indication of anemia, a common consequence of significant blood loss.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Immediate medical attention is essential if you experience any of the above symptoms, especially if you have a history of liver disease. Esophageal varices are a medical emergency when bleeding occurs. Even in the absence of symptoms, individuals diagnosed with liver cirrhosis or other conditions that increase the risk of esophageal varices should undergo regular screenings. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and significantly improve outcomes.
However, while esophageal varices might not always show symptoms until a serious complication arises, being aware of the signs and understanding when to seek medical advice can be life-saving. Regular check-ups and monitoring are key for those at risk, ensuring prompt treatment and management of this condition.
Diagnosing Esophageal Varices: A Comprehensive Guide
Esophageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus, often linked with serious conditions like liver disease. Detecting them early is crucial for managing potential complications. This guide offers a thorough overview of diagnosing esophageal varices, focusing on initial assessments, key diagnostic procedures, and understanding your diagnosis.
Initial Assessment and Physical Examination
The diagnostic journey for esophageal varices starts with an initial assessment and a comprehensive physical examination. Healthcare professionals look for signs that hint at chronic liver disease or portal hypertension, conditions often associated with varices. Symptoms like jaundice, easy bruising, and swelling in the abdomen or legs can be red flags. A detailed medical history is taken to understand risk factors, including alcohol consumption and family history of liver diseases.
Key Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Endoscopy
The cornerstone of diagnosing esophageal varices is an endoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube equipped with a camera down the throat to visually inspect the esophagus, stomach, and the start of the small intestine. It’s not only diagnostic but also helps in assessing the risk of bleeding, a serious complication of varices. The size of the varices and the presence of red signs on the varices are key predictors of bleeding risk assessed during an endoscopy.
Imaging Tests
In addition to endoscopy, imaging tests like ultrasounds and CT scans play a critical role in the diagnosis and management of esophageal varices.
- Ultrasound: Often, a Doppler ultrasound is the first imaging test used. It evaluates blood flow in the portal vein and can suggest increased pressure or obstructions, indirectly indicating the presence of varices.
- CT Scans: CT scans provide detailed images of the liver and surrounding structures, helping to identify the cause of portal hypertension and the extent of liver damage. These scans can also show the size and location of varices.
Understanding Your Diagnosis
After the diagnostic procedures, understanding your diagnosis is crucial. If varices are found, your healthcare provider will discuss the risk of bleeding and potential treatment options. The size of the varices and their location play a significant role in determining the best course of action. Treatments may include medications to reduce the risk of bleeding, endoscopic therapies to treat varices directly, and sometimes, procedures to decrease portal hypertension.
However, diagnosing esophageal varices involves a combination of clinical evaluation, endoscopy, and imaging tests. Understanding your diagnosis and the implications for your health is essential for effective management and prevention of complications. Regular follow-ups and adherence to treatment plans are key to living well with this condition.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Varices
Esophageal varices are enlarged veins in the esophagus that can bleed if they rupture. The primary goal of treatment for esophageal varices is to prevent bleeding, manage symptoms, and address the underlying cause of the condition, often liver disease. A variety of treatment options are available, ranging from non-surgical methods and lifestyle adjustments to surgical interventions. Here’s an overview of the various treatment strategies for managing esophageal varices.
Goal of Treatment
The overarching objective in treating esophageal varices is to prevent the onset of bleeding, which can be life-threatening. For those who have already experienced bleeding, the aim shifts to stopping the bleed and preventing rebleeding. Furthermore, addressing the root causes, such as liver cirrhosis, forms a critical part of the treatment approach to mitigate further health complications.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Medications
Medications, particularly Beta-blockers such as propranolol and nadolol, play a crucial role in reducing the risk of bleeding from esophageal varices. These medications work by decreasing blood pressure within the veins, thus reducing the likelihood of varices rupturing.
Endoscopic Therapies
Endoscopic therapies are minimally invasive procedures that are effective in both preventing and managing acute bleeding episodes:
- Band Ligation: This procedure involves placing a rubber band around the base of the varices to cut off blood flow, causing them to shrink and reducing the risk of bleeding.
- Sclerotherapy: This involves injecting a solution into the varices to cause them to harden and subsequently shrink, which helps prevent bleeding.
Surgical Treatment Options
For those who do not respond to non-surgical treatments or have significant bleeding, surgical options may be considered:
- Shunt Surgeries: The Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) procedure is one such option. It involves creating a new path for blood flow within the liver to reduce pressure in the varices and prevent bleeding.
- Liver Transplantation: In cases where liver disease is the underlying cause of esophageal varices, a liver transplant may be necessary. This option is considered when other treatments have failed and the liver is severely damaged.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical and surgical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage esophageal varices:
- Avoiding alcohol consumption to reduce further liver damage.
- Eating a healthy diet to support liver health and overall well-being.
- Managing weight to reduce the risk of complications associated with liver disease.
It’s important for individuals with esophageal varices to work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on their specific condition and overall health. Early diagnosis and intervention can significantly improve outcomes for those with this condition.
Complications of Esophageal Varices
Understanding the complications and preventive measures for esophageal varices is crucial for those at risk. Here, we delve into the risks of untreated esophageal varices and outline strategies for preventing bleeding and rupture, emphasizing both SEO and readability.
Risks of Untreated Esophageal Varices
Leaving esophageal varices untreated poses significant health risks, primarily due to the potential for bleeding. When the varices bleed, it can be life-threatening, requiring immediate medical attention. The initial bleeding episode has a high mortality rate, highlighting the importance of early detection and treatment. Other risks include:
- Severe Blood Loss: Bleeding from varices can lead to significant blood loss, causing anemia and hypovolemic shock, a condition characterized by low blood volume and inadequate blood flow to organs and tissues.
- Infection: Patients with bleeding varices are at an increased risk of developing infections, including spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, a severe infection of the abdomen.
- Ascites: This condition, involving fluid accumulation in the abdomen, can worsen due to portal hypertension associated with untreated varices.
Prevention of Bleeding and Rupture
Preventing the bleeding and rupture of esophageal varices is key to managing the condition and reducing the risk of complications. Strategies include:
- Medication: Nonselective beta-blockers, such as propranolol or nadolol, can lower the pressure in varices, reducing the risk of bleeding. These medications are often prescribed to people at risk of a first bleeding episode or after an initial bleeding event to prevent recurrence.
- Endoscopic Treatments: Endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) involves using a special band to tie off bleeding varices, while endoscopic sclerotherapy involves injecting a solution into the varices to shrink them. Both methods are effective in preventing bleeding.
- Screening and Surveillance: Regular endoscopic screenings can identify esophageal varices at an early stage, allowing for timely treatment before complications arise. This is particularly important for individuals with known risk factors, such as cirrhosis.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Reducing alcohol consumption, managing weight, and controlling liver disease progression through a healthy diet and medication adherence can also help lower the risk of variceal bleeding.
However, esophageal varices present significant health risks if left untreated, including the risk of life-threatening bleeding, infection, and worsened liver conditions. However, with proper medical intervention, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring, the complications associated with esophageal varices can be effectively managed and prevented. If you or someone you know is at risk, it’s crucial to seek medical advice and undergo regular screenings to mitigate these risks and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle.
Living with Esophageal Varices
Living with esophageal varices requires careful management and adjustments in lifestyle and diet. These dilated blood vessels, often a complication of liver disease, can pose serious health risks if not properly monitored and managed. This guide aims to provide valuable insights into how individuals with this condition can lead a healthier and more comfortable life through effective lifestyle modifications, dietary adjustments, and the importance of regular medical follow-ups.
Managing Your Condition with Lifestyle and Diet
1. Lifestyle Modifications: Leading a liver-friendly lifestyle is crucial for individuals with esophageal varices. This involves avoiding alcohol, which can further damage the liver and exacerbate the condition. Quitting smoking is also recommended, as smoking can impair liver function and increase the risk of complications. Engaging in regular, gentle exercise can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce pressure on the veins in your esophagus.
2. Dietary Adjustments: Diet plays a pivotal role in managing esophageal varices. A low-sodium diet is often recommended to reduce the risk of fluid accumulation in the body, which can increase pressure in the veins. Including foods rich in fiber can help prevent constipation, thereby reducing the risk of bleeding. Moreover, eating small, frequent meals can help prevent excessive pressure on the varices. It’s advisable to consult with a nutritionist who can tailor a diet plan to your specific needs.
Importance of Regular Medical Follow-Up and Monitoring
Regular medical follow-ups are essential for individuals with esophageal varices. These appointments allow healthcare providers to monitor the condition of the varices and assess liver function. Endoscopic screenings are a crucial part of this monitoring process, as they can help detect changes in the size or severity of the varices, which may indicate a need for treatment adjustments.
During these visits, doctors can also evaluate the effectiveness of current management strategies and make necessary modifications. They may recommend medications to reduce the risk of bleeding from the varices or suggest interventions to decrease the pressure in the veins. In some cases, procedures like banding or sclerotherapy may be necessary to treat varices that have a high risk of bleeding.
By adopting a liver-friendly lifestyle, making informed dietary choices, and maintaining close communication with healthcare providers, individuals with esophageal varices can manage their condition effectively and minimize the risk of complications. Remember, early detection and proactive management are key to living a healthier life with esophageal varices.
Prevention and Risk Reduction of Esophageal Varices
In this comprehensive guide, we explore effective strategies to prevent the development of esophageal varices and manage the underlying liver disease.
Understand the Importance of Liver Health
The key to preventing esophageal varices lies in promoting liver health and managing any underlying liver conditions. Since esophageal varices are primarily caused by increased pressure in the portal vein (portal hypertension) as a result of liver cirrhosis or other liver diseases, maintaining liver health is paramount.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making healthy lifestyle choices is crucial in reducing the risk of developing liver disease, which in turn, helps prevent esophageal varices. Here are some practical steps:
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake is a major risk factor for liver disease. Limiting alcohol or abstaining entirely can significantly reduce the risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Obesity can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), another risk factor for esophageal varices. A balanced diet and regular exercise are key.
- Avoid Hepatotoxic Substances: Certain medications and toxins can harm the liver. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting new medications, and avoid exposure to harmful substances.
Regular Medical Monitoring and Vaccination
For individuals at risk of liver disease or those already managing a liver condition, regular medical monitoring is essential. This includes:
- Routine Liver Function Tests: These tests help track the health of your liver over time and identify any potential issues early.
- Vaccinations: Vaccines for hepatitis A and B are available and recommended for individuals at risk of these infections, as they can lead to liver disease and subsequent complications like esophageal varices.
Management of Underlying Liver Disease
Effective management of any existing liver disease is the cornerstone of preventing esophageal varices. This might include:
- Medications: To control liver disease and reduce portal hypertension.
- Endoscopic Surveillance: Regular endoscopic exams can detect early signs of esophageal varices, allowing for timely treatment.
- Surgery or Other Procedures: In severe cases, procedures like a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) may be recommended to reduce portal vein pressure and prevent variceal bleeding.
Preventing esophageal varices starts with a commitment to liver health and proactive management of liver disease. By adopting healthy lifestyle habits, undergoing regular medical monitoring, and effectively managing any existing liver conditions, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing esophageal varices. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.
Remember, early detection and intervention are key to preventing complications associated with esophageal varices and maintaining overall health and well-being.
FAQs Section: Understanding Esophageal Varices
What are Esophageal Varices?
Esophageal varices are swollen blood vessels that occur in the esophagus, the tube that connects the throat to the stomach. These varices are a result of high blood pressure in the portal vein, which supplies blood to the liver. This condition is most commonly associated with liver disease and cirrhosis.
How do I know if I have Esophageal Varices?
Symptoms of esophageal varices may not be present until they bleed. However, possible signs include vomiting blood, black or tarry stools, and in severe cases, shock due to blood loss. It’s essential to seek medical advice if you suspect you have esophageal varices or experience these symptoms.
What causes Esophageal Varices?
The primary cause of esophageal varices is anything that can increase pressure in the portal vein, such as liver cirrhosis, thrombosis, or hepatitis. Conditions that damage the liver and affect blood flow can lead to the development of esophageal varices.
How are Esophageal Varices diagnosed?
Doctors typically use endoscopy to diagnose esophageal varices. This involves inserting a thin tube with a camera down the throat to examine the esophagus. Other tests might include blood tests, imaging tests such as ultrasound or CT scans, and procedures to measure the pressure inside the portal vein.
What treatment options are available for Esophageal Varices?
Treatment aims to prevent bleeding in at-risk varices and to manage bleeding if it occurs. Options include medications like beta-blockers to reduce blood pressure in the veins, endoscopic treatments to band or seal the varices, and in severe cases, surgery or procedures to redirect blood flow (shunts) may be necessary.
Can lifestyle changes help with Esophageal Varices?
While lifestyle changes cannot cure esophageal varices, they can help manage underlying liver conditions and reduce the risk of varices worsening. Recommendations include abstaining from alcohol, eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing any associated conditions like hepatitis or obesity.
What are the complications associated with Esophageal Varices?
The most significant risk is bleeding, which can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. Other complications include infection, scarring of the esophagus, and, in severe cases, liver failure.
Can Esophageal Varices be prevented?
Preventing esophageal varices involves managing the conditions that contribute to their development, such as cirrhosis and high blood pressure in the liver. Regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and managing liver health can reduce the risk.
Conclusion
In wrapping up, the significance of acknowledging and managing esophageal varices cannot be overstated. These enlarged veins within the esophagus, often a consequence of serious liver conditions, pose a significant risk of bleeding—a scenario that can have dire outcomes if not addressed promptly and properly. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking immediate medical advice are critical steps towards mitigating such risks.
It is imperative for individuals diagnosed with esophageal varices to adhere strictly to their treatment plans. The advancements in medical interventions and therapies offer a beacon of hope, significantly reducing the potential complications and improving the quality of life for affected individuals. From lifestyle adjustments to medication, and in some cases, surgical options, the spectrum of available treatments is broad and tailored to meet the needs and conditions of each patient.
Moreover, the journey towards recovery and management of esophageal varices is not a solitary one. It requires a cohesive effort between patients, healthcare providers, and support systems. Encouragement to maintain follow-up appointments, adhere to prescribed treatments, and make necessary lifestyle changes is crucial. These steps not only contribute to the effective management of esophageal varices but also to the overall health and well-being of the individual.
In conclusion, recognizing the critical nature of esophageal varices and adhering to the recommended treatment protocols is paramount. It is a call to action for individuals at risk or diagnosed with this condition to seek and stick with their treatment plans. The path to managing esophageal varices effectively is through awareness, timely medical intervention, and a committed adherence to treatment. Together, these efforts pave the way for a healthier, more secure future for those affected by this condition.
References
For those interested in exploring the treatment options and more in-depth information regarding Esophageal Varices, we’ve curated a list of reputable sources. These references serve as a valuable resource for validating the information provided and expanding your understanding of this serious medical condition.
- Mayo Clinic – Esophageal Varices: Mayo Clinic offers a comprehensive overview of esophageal varices, including symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options. This resource is beneficial for patients and healthcare professionals alike seeking detailed information on the condition. Visit Mayo Clinic’s Esophageal Varices page.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK): NIDDK offers educational content on esophageal varices, covering the basics of the condition, its association with other diseases, and the available treatment options. Their materials are designed to aid in understanding the complex nature of esophageal varices. Read more at NIDDK on Esophageal Varices.
- PubMed Central (PMC): For those seeking academic and research-oriented material, PubMed Central is an invaluable repository of medical literature. It hosts numerous research articles, studies, and reviews on esophageal varices, providing insights into the latest advancements in treatment and management. Search for Esophageal Varices studies on PMC.
By consulting these references, readers can gain a comprehensive understanding of esophageal varices, from diagnosis to treatment options. These resources are pivotal for those looking to deepen their knowledge and for healthcare professionals staying abreast of the latest practices in the field.