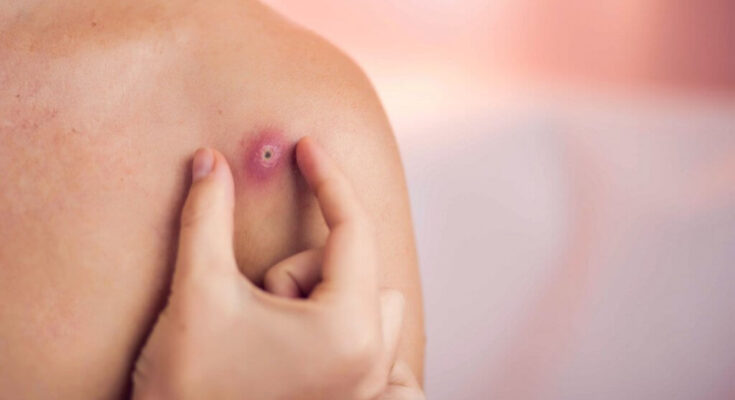
Epidermoid Cysts Treatment: Epidermoid cysts, often mistaken for sebaceous cysts, are benign growths that can appear on any part of the body.
These cysts develop under the skin as small lumps that can be moved easily. While generally not harmful, they can become a cosmetic concern or get infected, necessitating medical attention.
This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of epidermoid cysts, covering their diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Understanding Epidermoid Cysts
Epidermoid cysts, often nestled under the skin, present a common condition characterized by their distinctive features, causes, and symptoms. Understanding these cysts can help in identifying and managing them effectively. Let’s delve into the characteristics, causes, and symptoms of epidermoid cysts, ensuring clarity and accessibility for readers seeking information.
Characteristics of Epidermoid Cysts
Epidermoid cysts are benign (non-cancerous) lumps that typically develop beneath the skin. They are distinguished by their round shape and can vary in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters. The cysts contain a protein called keratin, which is a key component of skin, hair, and nails. This substance gives the cyst its white or yellow color and its often described cheesy or oily texture when expressed. A central pore may be visible on the cyst, sometimes mistaken as a blackhead.
Causes and Risk Factors for Developing Epidermoid Cysts
The formation of epidermoid cysts is usually related to the skin’s natural processes, but certain factors can increase their likelihood. These cysts can develop when hair follicles or skin pores become damaged or blocked, causing keratin to accumulate beneath the skin. Factors that might increase the risk of developing an epidermoid cyst include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of epidermoid cysts can elevate the risk.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, particularly during puberty, can trigger the formation of cysts.
- Skin trauma: Injuries or surgical wounds may lead to cyst development if the skin’s protective barrier is compromised.
- Certain skin conditions: Conditions like acne can increase the likelihood of cyst formation.
Common Locations and Symptoms of Epidermoid Cysts
Epidermoid cysts can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, back, and genitals. In most cases, these cysts are painless and grow slowly. Symptoms may not be evident unless the cyst becomes inflamed or infected, which can lead to:
- Redness and swelling: The skin around the cyst may become red and swollen if inflammation sets in.
- Pain: An infected cyst can become tender or painful to touch.
- Discharge: A ruptured cyst can release its contents, leading to possible infection and requiring medical attention.
However, epidermoid cysts are benign skin conditions with specific characteristics, causes, and symptoms. Understanding these aspects can aid in early detection and management. While they are generally not a cause for concern, any changes in size, color, or pain level should prompt a consultation with a healthcare professional to rule out infection or other underlying conditions.
Diagnosing Epidermoid Cysts
Diagnosing epidermoid cysts involves a comprehensive approach that combines clinical examination, imaging techniques, and understanding the differential diagnosis to distinguish them from other skin conditions effectively. Here’s how medical professionals approach the diagnosis:
Clinical Examination and Identification
The initial step in diagnosing an epidermoid cyst is a thorough clinical examination. These cysts are typically easy to identify due to their distinctive characteristics. They usually appear as small, round lumps under the skin, often with a central blackhead that marks the opening of the cyst. The cysts are generally slow-growing, painless, and can occur anywhere on the body, though they’re most commonly found on the face, neck, and trunk.
During the examination, healthcare providers will assess the cyst’s size, location, and any signs of infection or inflammation. A detailed patient history will also be taken to understand any potential genetic predispositions, as epidermoid cysts can sometimes be hereditary.
The Role of Imaging in Diagnosing Epidermoid Cysts
Imaging techniques play a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of an epidermoid cyst and ruling out other conditions. The most commonly used imaging methods include:
- Ultrasound: This non-invasive technique can help differentiate epidermoid cysts from other types of cysts or masses by providing detailed images of the cyst’s structure.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): MRI is particularly useful in assessing the extent of larger cysts or those situated in locations difficult to examine through physical assessment alone. It offers high-resolution images, showing the cyst’s relation to surrounding tissues and structures.
These imaging modalities provide valuable information about the cyst’s content, size, and precise location, assisting in planning any necessary treatment.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Epidermoid Cysts from Other Skin Conditions
Distinguishing epidermoid cysts from other skin conditions is a critical aspect of the diagnosis process. Several other skin lesions may resemble epidermoid cysts, including:
- Lipomas: Soft, movable lumps under the skin, composed of fat cells.
- Sebaceous cysts: Often confused with epidermoid cysts, these are filled with sebum and originate from sebaceous glands.
- Dermoid cysts: Congenital cysts that can contain a variety of tissues, including hair and skin glands.
- Pilar cysts: Smooth cysts attached to hair follicles, mostly found on the scalp.
A correct diagnosis is essential for determining the appropriate treatment plan. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to rule out malignancy, especially if the cyst changes in size or appearance.
However, diagnosing epidermoid cysts is a multi-step process that involves a detailed clinical examination, the use of imaging techniques for confirmation, and a differential diagnosis to distinguish them from similar skin conditions. Understanding these steps is crucial for healthcare professionals to ensure accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Epidermoid Cysts Treatment Options
Epidermoid cysts, often found lurking beneath the skin, can appear anywhere on the body, though they’re most commonly spotted on the face, neck, and trunk. These cysts, filled with a protein called keratin, may not always cause discomfort, but knowing the right treatment options can lead to effective management and relief. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding how to treat epidermoid cysts, from non-surgical methods to surgical interventions and home care tips.
Overview of Treatment Options for Epidermoid Cysts
The treatment landscape for epidermoid cysts is diverse, ranging from watchful waiting for asymptomatic cysts to more aggressive surgical removal for those that become troublesome. The choice of treatment largely depends on the cyst’s size, location, and potential for causing discomfort or cosmetic concerns.
Non-Surgical Treatments: When Are They Appropriate?
Non-surgical methods are often the first line of defense, particularly for cysts that aren’t infected and don’t cause pain. These include:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic cysts may just need regular monitoring for any changes.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections can reduce inflammation in swollen cysts, making them less noticeable and painful.
- Antibiotics: Prescribed if the cyst becomes infected, though antibiotics do not remove the cyst itself.
Surgical Removal: Techniques and Procedures
When a cyst becomes bothersome, surgical removal is often recommended. The procedures vary in complexity and recovery time:
- Minimal Excision: This less invasive technique involves making a small incision to remove the cyst’s contents, minimizing scarring. It’s effective for smaller cysts.
- Conventional Wide Excision: This method involves a larger incision to completely remove the cyst and its sac, ensuring it doesn’t return. It’s more invasive with a higher risk of scarring.
- Laser Therapy: A high-intensity laser makes a small hole in the cyst, draining its contents and causing the cyst to shrink over time. This method is less invasive and has a shorter recovery period.
Home Care and Remedies: What Patients Should Know
For managing minor symptoms at home, consider the following:
- Warm Compresses: Applying warmth to the cyst can reduce swelling and promote drainage, especially if the cyst is inflamed.
- Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers: Ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate pain associated with the cyst.
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing: This can lead to infection or worsen the cyst’s condition.
It’s crucial for patients to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any treatment, to choose the most appropriate method based on their specific condition. While home remedies can provide temporary relief, professional medical advice is indispensable for effective management and removal of epidermoid cysts.
Potential Complications and Management of Epidermoid Cysts
Understanding these potential issues and knowing when to seek medical attention are key steps in maintaining skin health and preventing further problems.
Recognizing and Managing Potential Complications
Complications from epidermoid cysts may include infection, rupture, and sometimes, the formation of a painful abscess. An infected cyst is characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and may exude a thick, yellow, foul-smelling material. It’s essential to monitor these cysts for any changes in size, color, or pain level, which could indicate an underlying issue.
If a cyst becomes inflamed or infected, medical treatment is necessary. Management may involve antibiotics to tackle infection or a minor surgical procedure to drain the cyst. In some cases, complete removal of the cyst is recommended to prevent recurrence and ensure it doesn’t evolve into a more serious condition.
When to Seek Medical Attention for an Infected Cyst
It’s crucial to seek professional medical advice if you notice signs of infection or significant changes in an epidermoid cyst. This includes:
- Increased redness or swelling around the cyst
- Warmth over the cyst, suggesting infection
- Pus or discharge, indicating a rupture
- Fever or other systemic symptoms, which could suggest a spreading infection
A healthcare provider can accurately diagnose the condition and recommend the appropriate treatment, including whether drainage or removal is necessary.
Preventing Recurrence After Treatment
After receiving treatment for an epidermoid cyst, particularly if it has been removed, following your healthcare provider’s post-treatment instructions is essential for healing and preventing recurrence. Keeping the area clean, avoiding unnecessary irritation, and monitoring for signs of new growths can help maintain skin health.
In some cases, your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes or skin care routines that can reduce the likelihood of developing new cysts. It’s also important to attend follow-up appointments to ensure the area is healing correctly and to address any concerns promptly.
Recognizing the signs of potential problems, seeking timely medical intervention, and taking steps to prevent recurrence can help manage these skin growths effectively. Always consult a healthcare professional if you’re concerned about a cyst or its treatment. Keeping an open line of communication with your doctor and following their advice can ensure the best outcomes for your skin health.
Living with Epidermoid Cysts
Epidermoid cysts, benign lumps beneath the skin, often elicit a mix of curiosity and concern among those diagnosed with them. While they are typically harmless, understanding how to manage their symptoms, mitigate their impact on quality of life, and learn from others’ experiences can empower individuals to live comfortably with this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies to Manage Symptoms
1. Gentle Skincare: Maintaining a gentle skincare routine can prevent irritation around the cyst. Opt for mild, non-comedogenic products that don’t block pores.
2. Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the cyst can reduce swelling and promote healing, especially if the cyst becomes inflamed or bothersome.
3. Avoid Picking or Squeezing: Though tempting, manipulating the cyst can lead to infections or scarring. It’s best to leave it untouched or seek professional medical advice for removal options.
4. Dress Comfortably: Wear loose-fitting clothes to avoid friction that might irritate the cyst. Soft, breathable fabrics are ideal.
Impact on Quality of Life and How to Mitigate Negative Effects
The presence of an epidermoid cyst, especially if visible or in a sensitive area, can affect an individual’s self-esteem and comfort. Here are ways to lessen their impact:
1. Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding that these cysts are benign and common can alleviate personal and societal concerns.
2. Professional Consultation: Regular check-ups with a dermatologist can reassure you about the cyst’s benign nature and provide professional advice on management or removal.
3. Mental Health Support: If your cyst significantly impacts your mental health, consider counseling or support groups to share your feelings and experiences with others who understand.
Patient Testimonials and Experiences
Hearing from those who’ve navigated life with epidermoid cysts can provide comfort and practical advice:
- John’s Journey: “After my diagnosis, I focused on maintaining a healthy lifestyle and keeping my skin clean. It made all the difference in managing my cyst without surgery.”
- Maria’s Story: “I used to be self-conscious about my cyst. Talking to others who had gone through the same experience helped me embrace it as a part of me.”
- Alex’s Advice: “Warm compresses were a game-changer for reducing discomfort. Also, finding a dermatologist I trusted was key.”
However, while epidermoid cysts can pose challenges, adopting effective management strategies, understanding their impact, and connecting with others can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, you’re not alone, and many resources and communities are available to support you on your journey.
FAQs about Epidermoid Cysts and Their Treatment
What is an epidermoid cyst?
An epidermoid cyst is a non-cancerous lump beneath the skin, which often appears on the face, neck, or trunk. These cysts develop when skin cells, instead of shedding normally, move deeper into your skin and multiply. The interior of these cysts is filled with a soft, whitish substance made up of dead skin cells and keratin.
Are epidermoid cysts dangerous?
Typically, epidermoid cysts are not dangerous and are considered benign. However, if they become infected, they can become red, swollen, and painful. Rarely, skin cancers can masquerade as epidermoid cysts, so it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis if you notice changes in the cyst’s appearance or if it becomes painful.
Can epidermoid cysts go away on their own?
In some cases, epidermoid cysts may resolve on their own without treatment. The body can reabsorb the contents of the cyst over time. However, cysts often remain stable or could grow larger. It’s important to monitor the cyst for any changes and consult with a healthcare professional for advice.
How are epidermoid cysts treated?
The treatment for epidermoid cysts often involves surgical removal, especially if the cyst is causing discomfort, is infected, or the patient desires removal for cosmetic reasons. The procedure is typically done under local anesthesia and involves making a small incision to remove the cyst. In some cases, if the cyst is infected, the doctor may first treat the infection before recommending removal.
Is it safe to pop an epidermoid cyst at home?
It is not recommended to try and pop or squeeze an epidermoid cyst at home. This can lead to infection, scarring, and potentially spread the cystic material, making the cyst more likely to recur. Professional medical treatment is the safest and most effective way to manage these cysts.
Will removing an epidermoid cyst leave a scar?
Any surgical procedure carries the risk of scarring, and the removal of an epidermoid cyst is no exception. However, healthcare professionals are skilled in minimizing scar appearance, often making them less noticeable. Discussing concerns about scarring with your doctor before the procedure can help set realistic expectations.
Can epidermoid cysts recur after removal?
There is a chance that an epidermoid cyst can recur, especially if the cyst wall is not completely removed during the initial surgery. Recurrence is less likely when the procedure is performed by an experienced healthcare provider who ensures the entire cyst and its lining are removed.
Conclusion
In summary, the significance of early diagnosis and the right approach to treating Epidermoid Cysts cannot be overstated. These common skin occurrences, though generally not harmful, can lead to discomfort and potential complications if left unchecked. Recognizing the signs early and seeking professional medical advice ensures that treatment is both effective and timely, reducing the risk of any adverse outcomes.
We strongly encourage everyone to pay close attention to their skin health. If you notice any unusual lumps, bumps, or changes in your skin, it’s imperative to consult with a healthcare professional. Personalized medical advice is crucial because it takes into account your unique health history and circumstances, leading to a treatment plan that is tailored specifically for you.
Remember, your health should always be a priority. Taking the initiative to consult with medical professionals about any concerns is a step in the right direction. Early intervention not only aids in the effective management of conditions like Epidermoid Cysts but also contributes to overall health and well-being.
Let this article serve as a reminder of the power of informed action and the importance of professional medical advice. Take care of your skin, listen to your body, and never hesitate to seek out the guidance of healthcare experts. Your health is worth it.
References
For those seeking further information or validation of the treatments discussed for epidermoid cysts, the following reputable sources offer comprehensive insights and detailed guidance. These references provide valuable knowledge for both medical professionals and individuals looking to understand more about the diagnosis, treatment options, and management of epidermoid cysts.
- Mayo Clinic – An extensive resource that covers a wide range of health topics, including epidermoid cysts. Their article on cysts provides detailed information on symptoms, causes, risk factors, complications, and treatment options. Visit Mayo Clinic on Epidermoid Cysts.
- National Health Service (NHS) UK – The NHS provides a patient-focused overview of epidermoid cysts, including advice on self-care and professional treatments. It’s an excellent resource for understanding the UK’s approach to managing this condition. NHS UK Insights on Epidermoid Cysts.
By consulting these sources, readers can gain a well-rounded understanding of epidermoid cysts, from symptoms and causes to the latest treatment methods. This information can empower individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health and treatment options.