Endometriosis Treatment: Endometriosis is a complex gynecological condition that affects millions of women worldwide.
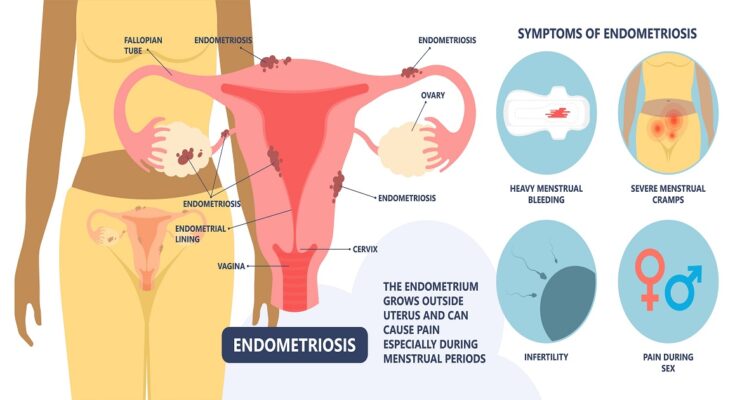
It occurs when tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus, called the endometrium, grows outside the uterus, leading to pain, infertility, and a myriad of other symptoms.
This article delves into the diagnosis and treatment options for endometriosis, aiming to provide comprehensive insights for those seeking relief and understanding.
Understanding Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a chronic condition that affects millions of women worldwide, characterized by the growth of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterus, leading to a range of symptoms that can significantly impact the quality of life. This condition often involves the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the tissue lining the pelvis, but in rare cases, it may spread beyond the pelvic region.
Common Symptoms and Their Impact on Quality of Life
The symptoms of endometriosis can vary greatly from one individual to another, but some common ones include:
- Pelvic Pain: The most notable symptom, which is often associated with menstrual periods. While many experience cramping during their menstrual cycle, those with endometriosis typically describe menstrual pain that’s far worse than usual. This pain can also increase over time.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Heavy periods (menorrhagia) or bleeding between periods (menometrorrhagia).
- Pain During Intercourse: Pain during or after sex is common among those with endometriosis, affecting relationships and emotional well-being.
- Pain with Bowel Movements or Urination: Usually observed during menstrual periods.
- Infertility: Often, endometriosis is first diagnosed in those seeking treatment for infertility, highlighting its impact on reproductive health.
The impact on quality of life can be profound, affecting physical health, emotional well-being, relationships, and even the ability to work or perform daily activities. Chronic pain can lead to fatigue, depression, and anxiety, further diminishing life quality.
Statistics on Prevalence and Diagnosis Rates
Endometriosis is more common than many might think, affecting an estimated 1 in 10 women during their reproductive years (approximately 176 million women worldwide). Despite its prevalence, the condition often goes undiagnosed due to the normalization of menstrual pain and the variability of symptoms.
- Diagnosis Delays: It is estimated that there can be a delay of 7 to 10 years between the onset of symptoms and an accurate diagnosis. This delay is attributed to the non-specific nature of symptoms, normalization of menstrual pain, and lack of awareness among both patients and healthcare professionals.
- Age Factor: While endometriosis can affect any menstruating woman, it is most commonly diagnosed in those in their 30s and 40s.
- Infertility Association: Among women facing infertility issues, about 30% to 40% have endometriosis, indicating a significant impact on reproductive health.
The high prevalence and significant impact on quality of life underscore the importance of raising awareness, improving diagnostic processes, and advancing treatment options for those affected by endometriosis. Early diagnosis and effective management are crucial in mitigating the impact of this condition on women’s lives.
The Path to Diagnosis
Understanding the hurdles in diagnosing endometriosis, the variety of diagnostic methods available, and the crucial importance of early detection can empower women and healthcare providers to take proactive steps towards health and wellness.
Challenges in Diagnosing Endometriosis
The road to a correct diagnosis of endometriosis is often long and winding, marked by several significant challenges:
- Symptom Overlap: The symptoms of endometriosis, such as pelvic pain, heavy menstrual bleeding, and infertility, mimic those of other conditions like ovarian cysts, pelvic inflammatory disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. This similarity can lead to misdiagnosis or delays in receiving the correct diagnosis.
- Variability of Symptoms: Symptoms can vary dramatically from one individual to another, making it difficult for healthcare providers to immediately pinpoint endometriosis as the cause.
- Lack of Awareness: Despite its prevalence, there remains a gap in awareness about endometriosis among both the general public and healthcare professionals. This lack of awareness can hinder timely and accurate diagnosis.
List of Diagnostic Methods
To navigate these challenges, a variety of diagnostic methods are employed, each with its own role in uncovering this elusive condition:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough physical examination, including pelvic exams, can sometimes reveal cysts or scars indicative of endometriosis.
- Ultrasound: While not definitive for endometriosis, ultrasound can identify cysts associated with the condition, known as endometriomas.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI provides detailed images of the organs and tissues, which can help in planning surgery by showing the location and size of endometrial lesions.
- Laparoscopy: This minimally invasive surgery is the gold standard for diagnosing endometriosis. A surgeon makes small incisions in the abdomen to insert a laparoscope, allowing them to see and sometimes treat endometrial tissue directly.
The Importance of Early Detection and Diagnosis
Early detection and diagnosis of endometriosis are paramount for several reasons:
- Improving Quality of Life: Early diagnosis can lead to earlier treatment, reducing the severity of symptoms and improving the overall quality of life for those affected.
- Preventing Progression: Timely treatment can slow the progression of endometriosis, potentially averting complications such as infertility and chronic pain.
- Empowerment Through Knowledge: Understanding their condition empowers women to make informed decisions about their health and treatment options.
By overcoming the challenges of diagnosis, employing a variety of diagnostic methods, and recognizing the importance of early detection, individuals and healthcare providers can work together towards managing this complex condition and improving outcomes for those affected.
Endometriosis Treatment Options
The treatment of endometriosis focuses primarily on managing symptoms, improving fertility for those affected, and enhancing the overall well-being of the individual. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution, but a range of treatment options are available that can be tailored to fit each person’s unique situation.
Overview of Treatment Goals
The main goals of endometriosis treatment include:
- Managing Symptoms: This includes alleviating pain and reducing the severity of symptoms to improve the patient’s quality of life.
- Improving Fertility: For those looking to conceive, treatments aim to enhance fertility that might be impaired by endometriosis.
- Preventing Disease Progression: Slowing or halting the progression of the disease is a key focus to prevent further complications.
List of Endometriosis Treatment Options
There are several approaches to managing and treating endometriosis, each with its own benefits and considerations:
Medications
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen and naproxen can help manage pain. In more severe cases, prescription painkillers may be recommended.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormonal treatments can help reduce or eliminate menstruation, in turn, slowing endometrial tissue growth and reducing symptoms.
Surgical Options
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgery to remove or destroy growths and scar tissue.
- Hysterectomy: In severe cases, removing the uterus and possibly ovaries and fallopian tubes might be considered, especially for women who aren’t planning future pregnancies.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): For women facing infertility due to endometriosis, IVF offers a chance to conceive. It involves fertilizing an egg outside the body and implanting it in the uterus.
The Role of Lifestyle Changes and Alternative Therapies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and alternative therapies can play a crucial role in managing endometriosis symptoms:
- Diet and Nutrition: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation and support overall health.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce pain and improve mood and overall well-being.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress, which may exacerbate symptoms.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and chiropractic care have been explored as options to help manage pain and improve quality of life, though more research is needed to fully understand their effectiveness.
It’s important to discuss all treatment options with a healthcare provider who can help tailor a management plan based on the individual’s symptoms, treatment goals, and overall health. Living with endometriosis can be challenging, but with the right approach, symptoms can be managed, and quality of life can be improved.
Fertility and Endometriosis: Understanding the Impact and Exploring Treatment Options
Endometriosis is a condition that not only affects millions of women worldwide but also poses significant challenges to fertility. This chronic condition occurs when the tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus, called the endometrium, grows outside the uterus. This can lead to painful periods, chronic pelvic pain, and, importantly for many women, difficulties in conceiving. Understanding how endometriosis impacts fertility and exploring the available treatment options is essential for women who wish to conceive.
How Endometriosis Affects Fertility
Endometriosis can impact fertility in several ways. The condition can cause inflammation and scarring, which may affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the lining of the uterus, making it more difficult for sperm to reach the egg or for an embryo to implant successfully. In more severe cases, the fallopian tubes may become blocked entirely. Approximately 30% to 50% of women with endometriosis may experience difficulties in becoming pregnant, making it a significant concern for those looking to start or expand their families.
Treatment Options for Women Wishing to Conceive
Fortunately, there are several treatment options available for women with endometriosis who wish to conceive. Treatment plans should be personalized, taking into account the severity of the condition, the woman’s age, and her specific fertility goals. Here are some of the options:
- Medication and Hormone Therapy: While not directly a treatment for infertility, medication can help manage the symptoms of endometriosis and may indirectly improve fertility by reducing inflammation and pain. Hormone therapy, such as birth control pills or gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, can temporarily halt the growth of endometrial tissue, though it’s not suitable for women actively trying to conceive.
- Surgical Options: Surgery to remove endometrial growths can improve fertility by reducing inflammation and removing physical barriers to conception. Laparoscopy, a minimally invasive surgical procedure, is commonly used to remove or burn away endometriosis implants and scar tissue. Studies suggest that fertility can improve for some women following surgery.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART): For women who have difficulty conceiving naturally, assisted reproductive technologies such as In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) offer hope. IVF involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a lab, and then implanting the fertilized egg(s) into the uterus. IVF has shown success in helping women with endometriosis conceive, especially when other treatments have not been effective.
- Fertility Preservation: For women not ready to conceive but concerned about their future fertility, egg freezing (oocyte cryopreservation) can be an option to consider. This allows women to preserve their eggs at a younger age, which can then be used for ART procedures later.
With a range of treatment options available, from medication and surgery to advanced reproductive technologies, women with endometriosis have several paths to pursue their dream of parenthood. It’s crucial to consult with healthcare providers to tailor a treatment plan that suits individual needs and fertility goals. Hope and help are at hand for those affected by endometriosis, offering a route to overcome the challenges and achieve a successful pregnancy.
Living with Endometriosis: Managing Chronic Pain and Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
Living with endometriosis can be a challenging journey, marked by episodes of chronic pain and significant impacts on daily life and mental health. However, with the right strategies and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and lead fulfilling lives. This guide offers advice on managing chronic pain, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and the importance of support groups and mental health resources.
Managing Chronic Pain
Chronic pain associated with endometriosis can often be debilitating. Here are strategies to help manage this pain:
- Medication: Over-the-counter pain relievers and prescription medications can help manage endometriosis pain. Always consult with a healthcare professional to find the right medication and dosage for you.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat to the lower abdomen can help relax contracting muscles and alleviate pain. Consider using a heating pad or a warm bath as part of your pain management routine.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist specializing in pelvic pain can provide exercises and techniques to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which may help reduce pain.
- Dietary Changes: Some people find relief from endometriosis symptoms by making dietary changes, such as reducing intake of foods that promote inflammation. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may be beneficial.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate chronic pain. Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress levels.
Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle can have a significant impact on managing endometriosis symptoms. Here are key aspects to consider:
- Regular Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise can help reduce pain by improving circulation and reducing stress. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling can be particularly beneficial.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall health and possibly help manage endometriosis symptoms.
- Adequate Sleep: Quality sleep is crucial for managing pain and stress. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a relaxing bedtime routine to improve your sleep quality.
- Avoiding Trigger Foods: Some individuals may find that certain foods exacerbate their symptoms. Common triggers include caffeine, alcohol, and high-fat foods.
The Importance of Support Groups and Mental Health Resources
Living with a chronic condition like endometriosis can take a toll on mental health. Support groups and mental health resources play a critical role in managing this aspect of the condition:
- Support Groups: Joining an endometriosis support group can provide a sense of community and understanding. Sharing experiences and tips with others who are facing similar challenges can be incredibly comforting and informative.
- Professional Help: Seeking the assistance of a mental health professional can be beneficial in managing the emotional and psychological impacts of living with endometriosis. Therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can be particularly effective in dealing with chronic pain.
- Online Resources: Numerous online platforms offer resources, information, and communities for individuals with endometriosis. These can be valuable sources of support and information.
Managing endometriosis is a multifaceted challenge that encompasses physical, emotional, and mental health aspects. By adopting comprehensive management strategies, seeking the support of healthcare professionals and support groups, and prioritizing mental health, individuals with endometriosis can lead healthier and more comfortable lives. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and there are resources and communities ready to support you every step of the way.
Recent Advances in Endometriosis Treatment
Recent advances in treatment and research findings are paving the way for innovative approaches to manage this often debilitating condition. This article delves into the latest research findings and emerging treatments for endometriosis, as well as the promising future of personalized medicine in its management.
Innovative Research Findings
Recent studies have shed light on the genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying endometriosis, offering new insights into its pathogenesis. Advances in genomic and transcriptomic analyses have identified specific genetic variants and molecular pathways that contribute to the development and progression of endometriosis. These discoveries are crucial, as they open the door to targeted therapies that can address the root causes of the disease rather than just alleviating symptoms.
Furthermore, research into the immune system’s role in endometriosis has highlighted the potential for immunotherapy in treatment. Studies suggest that the condition may involve auto-immune components, with the body’s immune response playing a significant role in the inflammation and pain associated with endometriosis. This has led to the exploration of drugs that can modulate the immune system’s response as potential treatments.
Emerging Treatments
One of the most exciting developments in endometriosis treatment is the emergence of non-hormonal therapies. While hormonal treatments have been a mainstay for managing endometriosis, they are not suitable for all patients and can have significant side effects. New non-hormonal drugs are being developed that target specific molecular pathways involved in endometriosis, offering hope for more effective and personalized treatment options.
Additionally, advances in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery, have improved the management of endometriosis. These surgical advances not only reduce recovery time and complications but also improve the precision in removing endometriotic lesions, leading to better outcomes for patients.
The Future of Personalized Medicine
The future of endometriosis treatment lies in personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and the specific characteristics of their disease. The integration of genomics and data analytics into clinical practice will enable healthcare providers to predict which treatments will be most effective for each patient, reducing the trial-and-error approach currently common in endometriosis treatment.
Furthermore, the development of biomarkers for endometriosis will facilitate early detection and monitoring of the disease, allowing for timely and targeted interventions. Personalized medicine will also focus on comprehensive care, incorporating pain management, fertility preservation, and psychological support tailored to each patient’s needs.
However, recent advances in the understanding and treatment of endometriosis are promising. With the ongoing research into the genetic and molecular bases of the disease and the development of new treatment options, there is hope for more effective and personalized approaches to managing endometriosis. The future of endometriosis care is bright, with personalized medicine leading the way towards more targeted, effective, and compassionate care for those affected by this challenging condition.
FAQs on Endometriosis Treatment
What is endometriosis?
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus, known as the endometrium, grows outside the uterus. This can cause pain, irregular bleeding, and sometimes fertility issues. It’s a chronic condition that affects millions of women worldwide.
How is endometriosis diagnosed?
Endometriosis is primarily diagnosed through a combination of pelvic exams, ultrasound imaging, and sometimes laparoscopy—a surgical procedure that allows a doctor to view the inside of the pelvic cavity directly. Medical history and symptom tracking are also key components in diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for endometriosis?
Treatment for endometriosis can vary based on the severity of symptoms and whether you’re trying to conceive. Options include pain relief medications, hormone therapy (such as birth control pills, GnRH agonists, and progestin therapy), and surgical options like laparoscopy to remove endometrial tissue or, in severe cases, hysterectomy.
Can endometriosis be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for endometriosis, but many treatments can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The approach to treatment is often personalized, taking into account your symptoms, age, and reproductive goals.
Is surgery for endometriosis always necessary?
Surgery is not always necessary for endometriosis. For many, symptoms can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes. However, surgery might be recommended if you have severe pain that isn’t relieved with medication, if you have significant scarring or adhesions, or if you’re having difficulty getting pregnant.
How does endometriosis affect fertility?
Endometriosis can affect fertility in some women, but it’s not an absolute barrier to pregnancy. Many women with endometriosis can conceive naturally or with fertility treatments. If you’re trying to get pregnant, it’s important to talk with a fertility specialist to understand how endometriosis may affect your fertility and explore your options.
Can diet and lifestyle changes help manage endometriosis symptoms?
Yes, diet and lifestyle changes can play a role in managing endometriosis symptoms for some women. Anti-inflammatory diets, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques have been reported to help reduce symptoms. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to tailor a plan that’s right for you.
Will I need to take medication for the rest of my life?
Not necessarily. The need for medication depends on your symptoms, how they evolve over time, and your life stage, such as whether you’re trying to conceive. Some women may find their symptoms improve with age or after pregnancy, while others may need long-term management.
Conclusion:
Healthcare professionals can offer tailored treatment plans based on the severity of the condition, symptoms, and individual health goals. They can also provide support and resources for managing symptoms and navigating the emotional challenges that often accompany endometriosis.
Remember, early intervention can significantly impact the management of endometriosis. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms suggestive of endometriosis, do not hesitate to seek professional medical advice. Working closely with healthcare providers ensures the best outcomes and supports individuals in leading a healthier, more comfortable life.
In closing, while the journey to diagnose and treat endometriosis may seem daunting, it is crucial to remember that help is available. Knowledge, awareness, and professional guidance are key components in effectively managing this condition. Let us prioritize health, seek the necessary medical attention, and support one another in the journey towards wellness.
References
For those looking to dive deeper into the topic of endometriosis treatment, the following reputable sources offer a wealth of information. These resources have been selected for their credibility and comprehensive coverage of treatment options, research findings, and patient care strategies.
- Mayo Clinic – Endometriosis: The Mayo Clinic provides a detailed overview of endometriosis, including symptoms, causes, and a wide array of treatment options. Their resource is an excellent starting point for individuals seeking a foundational understanding of the condition. Read more at the Mayo Clinic.
- Endometriosis.org: As a leading global forum for endometriosis, this site offers information on the latest research, treatment options, and support resources for individuals affected by endometriosis. It’s a hub for patients, researchers, and healthcare providers alike. Explore Endometriosis.org.
- The Endometriosis Foundation of America (EndoFound): This organization focuses on increasing disease recognition, providing advocacy, facilitating expert surgical training, and funding landmark endometriosis research. Visitors to the site can find extensive materials on managing endometriosis and related patient stories. Visit EndoFound.
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG): ACOG offers a comprehensive guide on the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis. Their guidelines are particularly useful for healthcare providers but are also accessible to patients looking for evidence-based treatment information. Check out ACOG’s Resources.
- PubMed Central (PMC): For those interested in the scientific and medical study of endometriosis, PubMed Central offers access to thousands of peer-reviewed articles. It’s a valuable resource for in-depth research articles, reviews, and clinical trial findings. Search PMC for Endometriosis Studies.
By consulting these references, readers can access reliable and up-to-date information on endometriosis treatment. Whether you’re a patient seeking understanding and relief, a healthcare provider looking for the latest treatment protocols, or a researcher delving into the complexities of the disease, these resources provide a solid foundation for further exploration.