Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis Symptoms: In the realm of tick-borne diseases, Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis stand as significant concerns to public health, affecting an increasing number of individuals annually.
These conditions, caused by bacteria transmitted through tick bites, present with a variety of symptoms that can lead to severe health complications if not promptly diagnosed and treated.
This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms, causes, and essential insights regarding Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, aiming to empower readers with vital knowledge to combat these illnesses.
Understanding Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are two tick-borne diseases that, while distinct, share some common traits, including their bacterial origins, transmission methods, geographic distribution, and seasonality. Understanding these diseases is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment.
The Bacteria Responsible for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Ehrlichiosis is caused by bacteria from the Ehrlichia genus, with Ehrlichia chaffeensis being the most common species affecting humans, leading to Human Monocytic Ehrlichiosis (HME). Anaplasmosis, on the other hand, is caused by Anaplasma phagocytophilum, resulting in Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis (HGA). Both bacteria are obligate intracellular pathogens, which means they can only survive and multiply within the host cells, specifically white blood cells, affecting the immune system significantly.
Geographic Distribution and Seasonality
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis have distinct geographic distributions that are closely linked to the habitats of their vector ticks. In the United States, Ehrlichiosis is predominantly found in the southeastern and south-central regions, correlating with the distribution of the lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum). Anaplasmosis is more commonly reported in the northeastern and upper midwestern states, areas that are known habitats of the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis).
These diseases also exhibit a clear seasonality, with the highest incidence occurring during the warmer months, typically from late spring through early fall. This pattern is not coincidental but rather aligns with the life cycle and feeding patterns of ticks, which are most active and likely to come into contact with humans during these periods.
Transmission to Humans
Humans contract Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis through the bite of an infected tick. It’s important to note that the tick must be attached and actively feeding for several hours before the bacteria can be transmitted. This aspect underscores the importance of preventive measures, such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and performing thorough tick checks after spending time in areas where ticks are prevalent.
Ticks pick up the bacteria by feeding on infected hosts, such as rodents or deer, which serve as reservoirs for Ehrlichia and Anaplasma. The cycle continues as these ticks then feed on humans or other mammals, transmitting the bacteria and causing disease.
However, understanding the bacteria responsible for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, their geographic distribution and seasonality, and how they are transmitted to humans is essential for awareness and prevention of these potentially serious tick-borne diseases. Awareness and prevention are key to mitigating the risk of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, emphasizing the importance of protective measures against ticks in endemic areas.
Symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Recognizing the symptoms early can lead to prompt treatment, preventing complications. This guide outlines the symptoms common to both diseases, symptoms specific to each condition, their complications, and when it’s crucial to seek medical attention.
Early Signs and Symptoms Common to Both Diseases
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis often present with similar early symptoms, making initial identification challenging without specific diagnostic tests. These symptoms typically appear within 1-2 weeks following a tick bite and include:
- Fever and chills: A sudden high fever is common.
- Headache: Severe headaches are often reported.
- Muscle aches: Generalized muscle pain can be debilitating.
- Fatigue: A profound tiredness not relieved by rest.
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea: Gastrointestinal symptoms may occur.
- Joint pains: Some individuals experience joint discomfort.
- Rash (less common in Anaplasmosis): While not always present, some individuals, especially children, may develop a rash.
Symptoms Specific to Ehrlichiosis
While many symptoms overlap with Anaplasmosis, Ehrlichiosis can also present with:
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating: Neurological symptoms are more characteristic of Ehrlichiosis.
- Eye pain or redness: Some individuals may experience ocular symptoms.
Symptoms Specific to Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis symptoms that are less common in Ehrlichiosis include:
- Abdominal pain: Some patients report pain in the abdomen.
- Lack of appetite: A decrease in hunger can be more pronounced.
Complications and Severe Manifestations
If left untreated, both diseases can lead to severe health issues, including:
- Respiratory distress: Difficulty breathing may necessitate hospitalization.
- Organ failure: The liver, kidneys, and lungs can be affected.
- Hemorrhagic complications: Severe bleeding disorders can develop.
- Neurological complications: Meningitis or encephalitis may occur, leading to long-term damage.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience the above symptoms, especially if you have a recent history of a tick bite or have spent time in areas known for ticks. Early treatment with antibiotics is effective, reducing the risk of complications.
- Seek immediate medical care if you experience severe symptoms such as difficulty breathing, confusion, severe headaches, or uncontrolled vomiting.
- Inform your healthcare provider about potential tick exposure, as this information is crucial for a timely and accurate diagnosis.
By understanding the symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, you can take prompt action to seek treatment, potentially preventing severe complications. Always take preventive measures against tick bites when spending time outdoors, especially in wooded or grassy areas known to harbor ticks.
Causes and Risk Factors of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with these diseases is crucial for prevention and early treatment. This article delves into the role of ticks in transmitting the bacteria, identifies the specific ticks involved, outlines activities and locations that increase risk, and discusses factors contributing to severe disease outcomes.
The Role of Ticks in Transmitting the Bacteria
Ticks act as vectors for the bacteria that cause ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. These tiny creatures feed on the blood of mammals, birds, and sometimes reptiles and amphibians. When an infected tick attaches to a human for a blood meal, it can transmit the bacteria into the bloodstream, initiating infection.
Specific Ticks Involved in the Spread
The lone star tick (Amblyomma americanum) is primarily responsible for transmitting Ehrlichia chaffeensis and Ehrlichia ewingii, the bacteria that cause ehrlichiosis in the United States. Meanwhile, anaplasmosis is mainly spread by the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis) in the northeastern and upper midwestern U.S., and the western black-legged tick (Ixodes pacificus) along the Pacific coast. These ticks are also known vectors for other tick-borne diseases, highlighting the importance of tick prevention measures.
Activities and Locations That Increase Risk
Engaging in outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, hunting, and gardening in areas where these ticks are prevalent elevates the risk of exposure to ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. These activities increase the likelihood of coming into contact with infected ticks, especially in wooded, bushy, or grassy areas. The risk is higher during the warmer months when ticks are most active.
Factors That Contribute to Severe Disease Outcomes
Several factors can contribute to the severity of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis, including:
- Delay in Diagnosis and Treatment: Early recognition and treatment are crucial. A delay can lead to more severe symptoms and complications.
- Immune System Status: Individuals with weakened immune systems, whether due to certain medical conditions or medications, are at higher risk for severe disease.
- Age: Older adults may experience more severe complications from these diseases.
- Co-infections: Being infected with another tick-borne disease simultaneously can exacerbate symptoms and complicate treatment.
Preventative measures, such as using insect repellents, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular tick checks after spending time outdoors in tick-infested areas, can significantly reduce the risk of infection. If you suspect you’ve been bitten by a tick and develop flu-like symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly for assessment and potential treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are tick-borne diseases that, while potentially serious, can be effectively managed with early detection and treatment. Understanding the diagnostic tests, the importance of early detection, treatment options, and how to manage symptoms at home is crucial for those at risk.
Diagnostic Tests for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
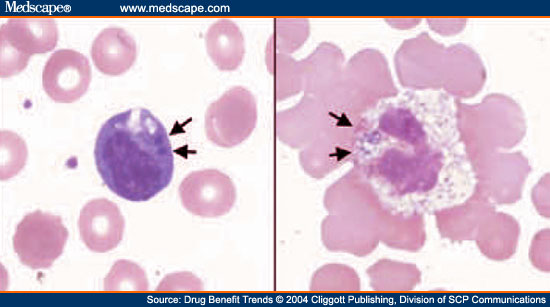
Diagnosing ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis involves a combination of clinical evaluation and specific laboratory tests. Initially, healthcare providers may rely on blood tests to look for signs of infection, such as changes in white blood cell count, platelets, and liver enzymes. The definitive diagnosis usually requires more specialized tests, including:
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) tests: These tests detect the DNA of the bacteria causing ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis directly from the blood samples.
- Serology tests: These tests look for antibodies against the bacteria in the blood, indicating a current or past infection.
- Complete blood count (CBC): This test can identify low platelet count, anemia, or low white blood cell count, which are common in these infections.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis is essential for several reasons. These diseases can progress rapidly, leading to severe symptoms and complications if left untreated. Early detection allows for the prompt initiation of treatment, significantly improving the prognosis. Symptoms to watch for include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. If you have been bitten by a tick or spent time in tick-infested areas and experience these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Treatment Options and the Role of Antibiotics
The primary treatment for both ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis is antibiotics, with doxycycline being the first choice for adults and children of all ages. Treatment usually lasts for 10-14 days, depending on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s response to therapy. Early and appropriate antibiotic treatment is typically effective, leading to a full recovery.
Managing Symptoms at Home and When to Follow Up with Healthcare Providers
While recovering from ehrlichiosis or anaplasmosis, several strategies can help manage symptoms at home:
- Rest: Prioritize rest to help your body fight the infection.
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids to stay hydrated, especially if you have fever or sweats.
- Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers: Medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help reduce fever and alleviate pain.
It’s important to follow up with your healthcare provider if:
- Your symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment.
- You experience new symptoms.
- You have concerns about your recovery process.
However, early detection and treatment of ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis are key to preventing complications and ensuring a quick recovery. Awareness of the diagnostic tests, the critical role of antibiotics, and how to manage symptoms at home will empower individuals to take charge of their health and seek timely medical care when necessary.
Prevention and Control of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
Preventing these diseases focuses on avoiding tick bites, controlling tick populations in residential areas, and safely removing ticks as soon as they are found. Below, we outline effective strategies and measures for prevention and control.
Strategies to Avoid Tick Bites
- Use Insect Repellent: Apply EPA-registered insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or IR3535 to exposed skin and clothing. Follow the product’s instructions for safe and effective use.
- Dress Appropriately: When in tick-infested areas, wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and hats. Tuck your shirt into your pants and your pants into your socks to minimize skin exposure.
- Stay on Trails: Avoid walking through dense vegetation and leaf litter where ticks are more prevalent. Stick to the center of trails when hiking in wooded or grassy areas.
- Treat Clothing and Gear: Use products containing 0.5% permethrin to treat clothing, boots, camping gear, and even tents. It remains protective through several washings.
Tick Control Measures in Residential Areas
- Maintain Your Yard: Keep your lawn mowed and bushes trimmed. Remove leaf litter, tall grasses, and brush around your home and at the edges of the yard.
- Use Tick-Repellent Landscaping: Consider landscaping with plants that are not attractive to deer and other rodents that carry ticks. Create a barrier of wood chips or gravel between your lawn and wooded areas to restrict tick migration into recreational areas.
- Apply Tick Pesticides: If tick presence is high, consider applying pesticides in your yard. It’s essential to follow label instructions and, if necessary, hire a professional to apply the treatments safely and effectively.
- Encourage Natural Predators: Birds and certain insects can reduce tick populations. Install bird feeders and houses to attract tick-eating birds and consider beneficial insects like nematodes for tick control.
Importance of Prompt Tick Removal and How to Do It Safely
Removing a tick as soon as you find it is crucial in preventing disease transmission. The longer a tick is attached, the higher the risk of disease. Here’s how to remove a tick safely:
- Use Fine-Tipped Tweezers: Grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible.
- Pull Upward With Steady, Even Pressure: Avoid twisting or jerking the tick, as this can cause parts of the tick to break off and remain in the skin.
- Clean the Bite Area and Your Hands Thoroughly: Use rubbing alcohol, an iodine scrub, or soap and water to clean the bite site and your hands after removal.
- Dispose of the Tick Safely: Submerse the tick in alcohol, place it in a sealed bag/container, wrap it tightly in tape, or flush it down the toilet. Do not crush it with your fingers.
- Seek Medical Attention if Necessary: If you develop a rash, fever, or other symptoms of tick-borne illnesses after a tick bite, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of contracting ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis. Awareness and proactive measures are key to prevention and control of these tick-borne diseases.
FAQs on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis
What are Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis are infectious diseases caused by different species of bacteria. Ehrlichiosis is primarily caused by the Ehrlichia chaffeensis bacterium, while Anaplasmosis is caused by the Anaplasma phagocytophilum bacterium. These bacteria are transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, particularly the lone star tick (for Ehrlichiosis) and the black-legged tick, also known as the deer tick (for Anaplasmosis).
How do humans contract Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
Humans can contract these diseases through the bite of an infected tick. The tick must be attached and feeding for several hours to transmit the bacteria. It’s important to note that these diseases cannot be transmitted from person to person.
What are the symptoms of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
The symptoms of both diseases are similar and can include fever, chills, severe headaches, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and a loss of appetite. In more severe cases, they can lead to complications such as respiratory distress, bleeding disorders, and organ failure. Symptoms usually appear within 1-2 weeks after the tick bite.
How are Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, symptom assessment, and laboratory tests. Blood tests can detect antibodies against the bacteria or the DNA of the bacteria itself, confirming the presence of the infection.
What treatments are available for Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis?
The primary treatment for both Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis is antibiotics, with doxycycline being the most effective option for individuals of all ages. Early treatment is crucial to prevent severe complications. It’s important to start treatment as soon as a diagnosis is suspected, even before laboratory test results are available.
Can Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis be prevented?
Yes, the best way to prevent these diseases is by avoiding tick bites. This can be achieved by using insect repellents, wearing long sleeves and pants when in wooded or grassy areas, and performing thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors. Reducing tick habitats in your surroundings can also decrease the risk of tick-borne diseases.
Are Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis common?
The prevalence of these diseases can vary significantly by geographic location and season. They are more common in areas where the carrier ticks are prevalent, especially during the warmer months when ticks are most active. Public health agencies monitor and report cases, so staying informed about local tick activity can help assess risk.
Conclusion:
In wrapping up our discussion on Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, two tick-borne diseases that pose significant health risks, it’s crucial to revisit the importance of recognizing their symptoms and understanding their causes. Early identification of signs such as fever, muscle aches, and fatigue can make a substantial difference in the treatment outcome. Understanding that these diseases stem from the bite of infected ticks emphasizes the need for preventive measures.
The significance of prevention cannot be overstated. Engaging in preventive practices such as using insect repellent, wearing protective clothing, and performing regular tick checks after spending time outdoors can greatly reduce the risk of infection. Furthermore, early treatment is paramount. If caught early, Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis can typically be treated effectively with antibiotics, highlighting the importance of consulting a healthcare provider promptly if symptoms arise after a tick bite.
We encourage our readers not only to take this information to heart but also to share it with friends and family. Spreading awareness about the symptoms, causes, and preventive measures of these diseases can play a vital role in reducing their impact. Staying informed and vigilant is our best defense against the health threats posed by ticks. Together, through awareness and proactive measures, we can protect ourselves and our loved ones from the risks of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis.
Let’s make a collective effort to share this knowledge and remain informed. By doing so, we contribute to a healthier, safer environment for all. Remember, your awareness and actions can save lives. Stay informed, stay safe.
References
For those interested in delving deeper into the symptoms, treatments, and scientific understanding of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis, the following sources provide reputable and comprehensive information. These resources are valuable for both medical professionals seeking detailed insight and individuals looking for reliable information on these tick-borne diseases.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Ehrlichiosis Overview:
The CDC’s dedicated page on Ehrlichiosis offers an in-depth look at the disease, including symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention tips. It’s a crucial resource for understanding how Ehrlichiosis affects humans and the steps you can take to protect yourself.
Visit the CDC’s Ehrlichiosis page - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Anaplasmosis Overview:
Similarly, the CDC provides comprehensive information on Anaplasmosis. This resource includes detailed descriptions of symptoms, diagnostic criteria, treatment options, and preventative measures, making it an essential tool for anyone looking to learn more about Anaplasmosis.
Visit the CDC’s Anaplasmosis page - Mayo Clinic – Ehrlichiosis:
The Mayo Clinic offers a patient-friendly overview of Ehrlichiosis, covering symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment options. This article is particularly useful for individuals seeking a straightforward explanation of the disease and its impact on human health.
Read more at the Mayo Clinic - American Lyme Disease Foundation – Anaplasmosis Information:
The American Lyme Disease Foundation provides a detailed account of Anaplasmosis, emphasizing its transmission, symptoms, and prevention. This resource is invaluable for those looking to understand the connection between tick-borne diseases and how they can be managed.
Explore Anaplasmosis information - Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Guidelines:
For a more clinical perspective, the IDSA’s guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis offer an authoritative resource. These guidelines are intended for healthcare professionals and provide evidence-based recommendations for managing these diseases.
Access the IDSA Guidelines
These references are chosen for their authority, accuracy, and accessibility, making them ideal starting points for anyone looking to learn more about Ehrlichiosis and Anaplasmosis. Whether you are a medical professional, a patient, or simply someone interested in tick-borne diseases, these resources can provide you with a solid foundation of knowledge.