Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment: Ectopic pregnancy, a critical condition where the embryo implants outside the uterine cavity, poses significant health risks if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
With advancements in medical science, the awareness and management of ectopic pregnancies have improved, yet the condition remains a leading cause of morbidity in early pregnancy.
Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy is a medical condition that occurs when a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus, most commonly in a fallopian tube. Understanding the statistics, causes, and risk factors associated with ectopic pregnancy can help in early diagnosis and management.
Statistics on the Prevalence of Ectopic Pregnancies
Ectopic pregnancies represent a significant concern in reproductive health, affecting approximately 1% to 2% of all pregnancies. The incidence of ectopic pregnancies has seen variations over the years, influenced by several factors including advances in diagnostic techniques and changes in risk factors among the population. Despite medical advancements, ectopic pregnancies remain a leading cause of maternal mortality in the first trimester, underscoring the importance of awareness and early detection.
Causes and Risk Factors for Ectopic Pregnancy
Understanding the causes and identifying risk factors is crucial for the prevention and early detection of ectopic pregnancies. While the exact cause of ectopic pregnancy is not always clear, several factors may increase the risk:
- Previous Ectopic Pregnancy: Women who have experienced an ectopic pregnancy in the past are at a higher risk of having another.
- Inflammatory Diseases: Conditions like pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs), can damage and scar the fallopian tubes.
- Surgical History: Previous surgery in the pelvic area or on the fallopian tubes can lead to scarring.
- Fertility Treatments: Women undergoing fertility treatments, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), may have a higher likelihood of ectopic pregnancy.
- Contraceptive Choices: Though rare, ectopic pregnancy can occur with the use of intrauterine devices (IUDs) or after a tubal ligation, a procedure intended to prevent pregnancy.
- Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of ectopic pregnancy, with the risk rising with the number of cigarettes smoked per day.
- Age: Women over the age of 35 have a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy compared to younger women.
Ectopic pregnancy poses significant health risks and requires prompt medical attention. Recognizing the signs and understanding the risk factors can lead to earlier diagnosis and treatment, potentially saving lives. Women experiencing any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, such as sharp abdominal pain, spotting, or dizziness, should seek medical care immediately.
Fostering awareness and education on ectopic pregnancy, its causes, and risk factors is vital for the well-being of women worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in managing this complex condition, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers.
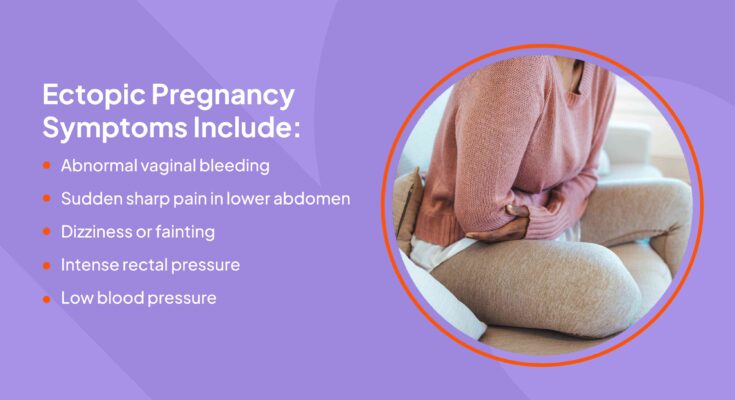
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy: What to Look Out For
Recognizing the early signs and symptoms is crucial for the health and safety of those affected. Here’s a comprehensive look at what to watch out for and when it’s essential to seek medical attention.
Early Signs and Symptoms to Watch Out For
Ectopic pregnancy symptoms can be subtle at first but become more pronounced as the condition progresses. Early detection is key, so pay close attention to the following signs:
- Abdominal or pelvic pain: Initially, this pain may be mild and can be mistaken for normal pregnancy discomfort. However, it often becomes sharp and stabbing, especially on one side.
- Vaginal bleeding: Light to heavy bleeding, different from a normal period, can occur. This bleeding may accompany the pain or happen independently.
- Shoulder pain: An unusual symptom resulting from blood leaking into the abdomen and irritating the diaphragm. This pain is felt in the shoulder tip and is a sign to seek immediate medical care.
- Dizziness or fainting: Loss of blood or rupture of the fallopian tube can lead to dizziness, fainting, or even shock, indicating a medical emergency.
- Gastrointestinal symptoms: Nausea or vomiting, often mistaken for normal pregnancy symptoms, can also signify an ectopic pregnancy.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned, especially if you know you are pregnant or think you might be, seek medical attention promptly. Ectopic pregnancies cannot continue as normal pregnancies and require immediate care to prevent severe complications.
Here are specific situations when it’s crucial to contact a healthcare provider:
- Persistent, severe abdominal or pelvic pain, especially if it is one-sided.
- Any vaginal bleeding or spotting during pregnancy should prompt a call to your doctor, even if the bleeding is not heavy.
- Signs of shock, such as dizziness, fainting, or rapid heartbeat, particularly if accompanied by bleeding or severe pain.
- Shoulder tip pain or any discomfort not typical for your body should be evaluated, especially in the context of a potential pregnancy.
Early intervention can prevent serious health issues and ensure the well-being of those experiencing an ectopic pregnancy. If you suspect you might have an ectopic pregnancy, do not wait to see if the symptoms resolve on their own. Contact your healthcare provider immediately for evaluation and treatment.
Focusing on these symptoms and knowing when to seek help can save lives. Awareness and prompt action are your best defenses against the complications of ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancy: Essential Methods and Challenges
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial to prevent severe complications, including rupture and internal bleeding. This article explores the various diagnostic methods used, the role of healthcare professionals in diagnosis, and the challenges faced during the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancies.
List of Diagnostic Methods
Several diagnostic tools and techniques are employed to detect ectopic pregnancies:
- Transvaginal Ultrasound: This is the first-line diagnostic tool for ectopic pregnancy. It involves using sound waves to create images of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It can help healthcare providers see if there’s a pregnancy outside the uterus.
- Quantitative Blood Test for hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin): Levels of hCG, a hormone produced during pregnancy, are measured through blood tests. Slow to rise, declining, or abnormally low levels of hCG can indicate an ectopic pregnancy.
- Pelvic Exam: A healthcare provider may perform a pelvic exam to locate pain, tenderness, or a mass in the area of the fallopian tubes or ovaries.
- Progesterone Blood Tests: Low levels of progesterone, another hormone critical for maintaining pregnancy, can suggest an ectopic pregnancy or a pregnancy that is likely to miscarry.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals play a critical role in diagnosing ectopic pregnancies. They are responsible for:
- Conducting thorough evaluations: This includes reviewing the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and risk factors for ectopic pregnancy.
- Interpreting diagnostic tests: Professionals must accurately interpret the results of ultrasound scans and blood tests to make a diagnosis.
- Providing guidance and support: Once diagnosed, healthcare providers must discuss treatment options with the patient, addressing any risks and answering questions to help the patient make informed decisions.
Challenges in Diagnosing Ectopic Pregnancies
Despite advancements in medical technology, diagnosing ectopic pregnancies remains challenging due to:
- Symptom overlap with other conditions: Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy, such as abdominal pain and vaginal bleeding, can mimic those of other conditions, making it difficult to diagnose without further testing.
- Varied presentations: Not all ectopic pregnancies present the same way; some may show very subtle signs or even remain asymptomatic until they become an emergency.
- Timing of diagnosis: The timing of the diagnosis is critical. Too early, and it may be difficult to differentiate from a normal early pregnancy; too late, and it may lead to complications.
However, diagnosing ectopic pregnancies involves a combination of clinical evaluation, diagnostic testing, and the expertise of healthcare professionals. Despite the challenges, early diagnosis and treatment are essential for the health and safety of the patient. Healthcare providers must use a patient-centered approach, considering the individual’s symptoms, history, and test results to accurately diagnose and manage ectopic pregnancies.
Treatment Options for Ectopic Pregnancy
Understanding the treatment options available, how doctors decide on the best course of action, and the potential risks associated with these treatments can provide crucial information for those affected. This guide aims to offer a comprehensive overview in a manner that’s accessible and informative.
Detailed Explanation of Treatment Methods
Treatment for ectopic pregnancy varies depending on the specifics of the case, including the location of the pregnancy, the patient’s symptoms, and how far along the pregnancy is. The primary methods include:
1. Medication: Methotrexate is the most common drug used to treat ectopic pregnancies. It works by stopping the growth of the embryo, allowing the body to absorb the pregnancy tissue over time. This option is usually considered when the pregnancy is detected early, and there is no rupture or significant risk of rupture.
2. Surgery: In more urgent cases, especially where there’s a risk of rupture or the pregnancy is too advanced, surgery is necessary. The two main surgical options are:
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgery where small incisions are made, and a camera is used to guide the removal of the ectopic pregnancy. This option leads to quicker recovery times and less scarring.
- Laparotomy: This is an open surgery used in more severe cases, such as when there is significant internal bleeding or the ectopic pregnancy is not accessible via laparoscopy.
Factors Influencing the Choice of Treatment
Several factors can influence the choice between medication, laparoscopy, or laparotomy, including:
- Location and size of the ectopic pregnancy: Certain locations may be more suitable for surgical intervention.
- Patient’s medical history and overall health: Pre-existing conditions can affect the suitability of methotrexate or the type of surgery.
- Levels of pregnancy-related hormones: High levels might indicate that medication alone won’t be effective.
- Patient preference: After discussing the risks and benefits, some patients may have a preference for one type of treatment over another.
Potential Risks and Complications of Treatments
While treatments for ectopic pregnancy are generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications involved:
- For medication: Possible side effects of methotrexate include nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. There’s also a small risk that the medication won’t end the pregnancy, necessitating surgery.
- For surgery: Risks include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs. In laparoscopy, there’s a slight chance that the surgeon may need to switch to a laparotomy during the procedure if complications arise.
Both treatment paths require careful monitoring by healthcare professionals to manage any risks or complications. Patients may also need emotional support, as ectopic pregnancies can be distressing experiences.
However, treatment for ectopic pregnancy depends on a variety of factors, including the specifics of the case and the patient’s preferences. Both medication and surgery offer effective solutions, but they come with their own sets of risks and considerations. By understanding these options and their potential implications, patients can make informed decisions about their care.
Aftercare and Recovery of Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often requires prompt medical intervention. Following treatment, which may include medication or surgery, the journey towards recovery encompasses physical healing and emotional support. Understanding what to expect during this period can help individuals navigate their path to recovery with confidence.
What to Expect After Treatment
Aftercare for an ectopic pregnancy is tailored to the individual’s needs, depending on the treatment received. For those who undergo medication treatment, monitoring hormone levels until they return to pre-pregnancy levels is standard. This process can take several weeks and requires regular blood tests. If surgery was necessary, physical recovery might involve managing pain, caring for the incision site, and gradually resuming daily activities.
It’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s advice closely during this time. This includes taking prescribed medications, attending all follow-up appointments, and watching for signs of complications, such as infection or excessive bleeding. Most individuals can return to their normal activities within a few weeks, but it’s important to allow yourself time to heal and not rush the process.
Emotional and Psychological Support
The emotional impact of an ectopic pregnancy can be profound. Feelings of grief, loss, and anxiety are common, and it’s crucial to seek support. Many find solace in counseling, support groups, or talking with friends and family. Remember, it’s okay to seek help and take time to mourn your loss. Professional mental health support can provide coping strategies and emotional healing.
Future Pregnancy Planning and Considerations
Planning for a future pregnancy after an ectopic pregnancy involves careful consideration and consultation with healthcare providers. The risk of a repeat ectopic pregnancy is higher for individuals who have experienced one before, so it’s important to discuss your risk factors and any necessary precautions with your doctor.
Most are advised to wait a few months before trying to conceive again to allow the body and mind to fully recover. During this waiting period, focus on regaining strength and emotional stability. Your healthcare provider can offer guidance on the best time to try for another pregnancy and any steps you can take to reduce your risk of another ectopic pregnancy, such as addressing underlying health issues.
However, the recovery from an ectopic pregnancy is a multifaceted process that encompasses physical healing, emotional support, and planning for the future. By understanding what to expect and accessing the resources available, individuals can navigate this challenging time with resilience and hope. Remember, it’s important to prioritize your health and well-being, seeking professional guidance and support as you move forward.
Prevention and Risk Reduction for Ectopic Pregnancy
Reducing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy, a condition where a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, is vital for the health and safety of women. While it’s not always possible to prevent an ectopic pregnancy, certain measures can help minimize the risks. Here, we offer practical tips and emphasize the importance of regular medical check-ups and early diagnosis to enhance your reproductive health.
Tips for Reducing the Risk of an Ectopic Pregnancy
- Quit Smoking: Smoking cigarettes is associated with an increased risk of ectopic pregnancies. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce this risk and improve your overall health.
- Practice Safe Sex: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), such as chlamydia and gonorrhea, can cause inflammation and scarring in the fallopian tubes, increasing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Using condoms during intercourse can help prevent these infections.
- Limit the Number of Sexual Partners: Reducing the number of sexual partners can decrease the likelihood of contracting STIs, thereby reducing the risk of an ectopic pregnancy.
- Screening and Treatment for STIs: Regular screening for sexually transmitted infections, especially if you have new or multiple sexual partners, can help detect and treat infections early, preventing complications that could lead to an ectopic pregnancy.
- Manage Existing Health Conditions: Conditions like endometriosis and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy. Managing these conditions with the help of a healthcare provider can reduce risks.
- Consider Fertility Treatment Options: If you’re considering fertility treatments, discuss the associated risks of ectopic pregnancy with your healthcare provider. Certain treatments, like in vitro fertilization (IVF), may have different risks associated with ectopic pregnancies.
The Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups and Early Diagnosis
Routine medical check-ups play a critical role in identifying risk factors and early signs of potential complications, including ectopic pregnancies. Early diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy is crucial for preventing severe complications, such as internal bleeding, and for preserving fertility. Here’s why regular visits to your healthcare provider are essential:
- Early Detection: Regular check-ups can help detect conditions that increase the risk of an ectopic pregnancy, such as PID or tubal damage, allowing for timely intervention.
- Monitoring Health After an Ectopic Pregnancy: If you’ve had an ectopic pregnancy in the past, your healthcare provider can monitor your health more closely in subsequent pregnancies to ensure early detection and management of any complications.
- Guidance and Support: Healthcare providers can offer personalized advice on reducing your risk factors and support you through decisions related to pregnancy and fertility treatments.
However, early diagnosis through routine healthcare visits can mitigate complications, ensuring a safer pregnancy journey. Embrace these preventive measures and consultations with your healthcare provider as essential steps towards safeguarding your reproductive health.
FAQs About Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment
What is ectopic pregnancy treatment?
Ectopic pregnancy treatment involves medical or surgical interventions to remove the ectopic tissue and ensure the health and safety of the individual. Treatment options include medication like methotrexate, which stops the growth of the pregnancy, or surgery, typically through laparoscopy, to remove the ectopic pregnancy.
How is an ectopic pregnancy diagnosed?
Ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed through a combination of physical exams, ultrasounds, and blood tests that measure levels of the hormone hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin). These tests help locate the pregnancy and assess its development.
Can I get pregnant again after an ectopic pregnancy?
Yes, many individuals successfully conceive after an ectopic pregnancy. However, having an ectopic pregnancy does increase the risk of having another. It’s important to consult with healthcare providers for personalized advice and monitoring in future pregnancies.
What are the signs of an ectopic pregnancy?
Signs of an ectopic pregnancy can include light vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, dizziness, and shoulder pain. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if you know you’re pregnant, seek medical attention immediately.
Is ectopic pregnancy treatment urgent?
Yes, ectopic pregnancy treatment is considered urgent to prevent complications, such as rupture, which can be life-threatening. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage the condition more effectively.
Can ectopic pregnancy be prevented?
Currently, there’s no guaranteed way to prevent an ectopic pregnancy. However, reducing risk factors, such as smoking, and treating conditions that may contribute to ectopic pregnancies, like pelvic inflammatory disease, can lower your risk.
What is the recovery time after ectopic pregnancy treatment?
Recovery time varies depending on the type of treatment received. After methotrexate, it might take a few weeks for hCG levels to return to normal, with close monitoring by healthcare providers. Surgical recovery typically involves a few days of rest and limited activity, with full recovery taking a few weeks.
Will I need to stay in the hospital after treatment?
Hospital stay depends on the type of treatment. Methotrexate often doesn’t require a hospital stay, but surgery may involve a short hospitalization to ensure your well-being post-operation.
Conclusion:
Awareness of the symptoms and risks associated with ectopic pregnancy is crucial for early detection and treatment. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and, in severe cases, fainting or shock. Understanding these signs and seeking prompt medical care can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of complications.
We encourage all readers to stay informed about the signs and risks of ectopic pregnancy. It’s essential to consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and to receive timely, appropriate care. Your health professional can offer the most accurate diagnosis and treatment options suited to your specific situation. Remember, early intervention is key in managing ectopic pregnancy, underscoring the importance of awareness and proactive healthcare engagement.
References:
For those seeking further reading and validation of the information provided on Ectopic Pregnancy Treatment, the following sources are recommended. These reputable sources offer in-depth insights and valuable information for anyone looking to understand more about the diagnosis, treatment options, and care required for ectopic pregnancies.
- Mayo Clinic – Ectopic Pregnancy Overview and Treatments: The Mayo Clinic offers a comprehensive overview of ectopic pregnancies, including symptoms, causes, risk factors, and various treatment options available. This resource is valuable for individuals looking for trusted medical information. Read more at Mayo Clinic.
- American Pregnancy Association – Ectopic Pregnancy: The American Pregnancy Association provides detailed information on ectopic pregnancy, including early signs, diagnosis, and treatment. It’s an excellent resource for expectant mothers and families. Explore American Pregnancy Association.
- WebMD – Understanding Ectopic Pregnancy: WebMD offers insights into the understanding of ectopic pregnancies, focusing on the identification, medical procedures, and post-treatment care. This source is known for its accessibility and straightforward explanations suitable for a wide audience. Visit WebMD.
- The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust – Living with Ectopic Pregnancy: For those looking for support and information from a community perspective, The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust provides resources, personal stories, and guidance on living with and recovering from an ectopic pregnancy. Learn more at The Ectopic Pregnancy Trust.
- Healthline – Ectopic Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes, Risks, and Treatment: Healthline offers a well-structured guide on ectopic pregnancies, detailing symptoms, potential causes, risk factors, and treatment methods. It’s an excellent starting point for individuals seeking clear and concise information. Discover more on Healthline.
These sources have been carefully selected for their reliability, depth of information, and accessibility to ensure that readers have access to the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding ectopic pregnancy treatment.