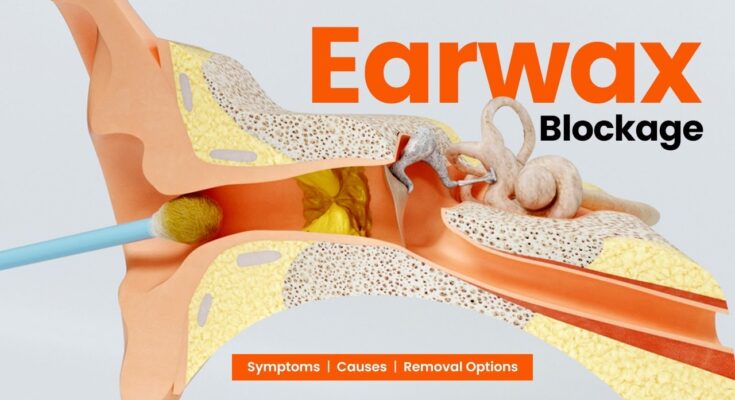
Earwax Blockage Symptoms: Earwax, medically known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal.
Its primary function is to protect the ear by trapping dirt, dust, and other particles, preventing them from reaching the delicate eardrum.
However, when earwax accumulates excessively or becomes too compacted, it can lead to a condition known as earwax blockage.
This common issue can affect individuals of all ages and backgrounds, leading to a variety of symptoms and complications if left untreated.
Understanding Earwax Blockage
Earwax, medically known as cerumen, plays a crucial role in maintaining the health of our ears. It serves as a natural barrier, protecting the ear canal from dust, debris, bacteria, and other foreign particles, thus preventing infections and aiding in keeping the ear clean. However, when the accumulation of earwax becomes excessive, it can lead to a condition known as earwax blockage. This condition can significantly differ from the normal accumulation of earwax, impacting one’s hearing and overall ear health.
How Earwax Blockage Differs from Normal Earwax Accumulation
Normal earwax accumulation is a healthy and natural process where the ear produces cerumen to protect and clean itself. Typically, old earwax moves from the ear canal to the ear opening, dries up, and falls out, often without notice. This cycle ensures that the ear canal remains protected without affecting hearing.
In contrast, earwax blockage occurs when earwax accumulates to the point where it can no longer exit the ear naturally. This excessive buildup can harden, making it difficult to wash away naturally. Several factors can contribute to this condition, including narrow or hairy ear canals, frequent use of earplugs or hearing aids, and the aging process, which can change the texture of earwax. Earwax blockage is characterized by symptoms such as a feeling of fullness in the ear, discomfort, tinnitus, hearing loss, itching, odor, and discharge.
The Role of Earwax in the Ear’s Health
Despite its unappealing reputation, earwax is beneficial to ear health. It has lubricating properties, preventing the ear canal from becoming too dry or itchy. Additionally, earwax has antibacterial and antifungal properties, helping to reduce the risk of infections within the ear canal. It acts as a protective layer, trapping dust and small particles that could potentially harm the delicate structures deeper within the ear.
However, understanding the difference between normal earwax accumulation and earwax blockage, as well as the importance of earwax, is crucial for maintaining ear health. While earwax plays a protective and cleaning role, excessive buildup leading to blockage requires attention. It is important to avoid self-cleaning practices that can push earwax deeper into the canal, such as using cotton swabs. If symptoms of earwax blockage occur, seeking professional medical advice is recommended to safely and effectively address the issue.
Symptoms of Earwax Blockage
When earwax accumulates or becomes hard, it can lead to a blockage, affecting hearing and causing discomfort. Recognizing the symptoms of earwax blockage is crucial for effective management and prevention of potential complications.
Common Symptoms Associated with Earwax Blockage
The symptoms of earwax blockage can vary from person to person, but some common indicators include:
- Hearing loss: This is often gradual and may affect one or both ears.
- Earache or a feeling of fullness in the ear: A sense of pressure inside the ear often accompanies a blockage.
- Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or other noises in the ear that are not from an external source.
- Itchiness: The ear canal can become itchy due to the buildup of wax.
- Dizziness: In some cases, a severe blockage can affect your balance.
- Ear discharge: An unusual discharge from the ear may indicate that the blockage has led to an infection.
Distinguishing Between Earwax Blockage Symptoms and Other Ear-Related Issues
While the symptoms listed above are commonly associated with earwax blockage, it’s important to note that they can also indicate other ear-related health issues, such as infections, eardrum perforation, or Meniere’s disease. Here are a few tips to help distinguish earwax blockage from other conditions:
- Symptom onset: Earwax blockage symptoms tend to develop gradually, while symptoms of an ear infection or other acute conditions may appear suddenly.
- Visible earwax: Sometimes, you might be able to see the earwax buildup when looking in a mirror or might feel it when lightly touching the ear canal entrance.
- No fever: Ear infections often come with a fever, but earwax blockage does not.
When to Seek Medical Advice for Earwax Blockage Symptoms
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent symptoms that do not improve with over-the-counter treatments.
- Sudden or unexplained hearing loss.
- Severe pain, fever, or discharge from the ear, as these may indicate an infection.
- If you’re prone to recurrent earwax blockages or have previously had ear surgery, regular check-ups with your doctor can help manage the condition effectively.
However, should symptoms persist or if you’re unsure about the cause of your symptoms, seeking medical advice is always the best course of action to ensure your ear health is maintained.
Causes of Earwax Blockage
This article explores the factors contributing to excessive earwax production, how lifestyle or ear cleaning practices can lead to blockage, and the impact of anatomical differences and health conditions.
Factors Contributing to Excessive Earwax Production
The body may produce more earwax due to several reasons, including genetic predisposition and environmental factors. People working in dusty or dirty environments might experience an increase in earwax production as the body attempts to protect the ears from debris. Additionally, stress and anxiety can stimulate the glands in the ear, leading to more wax buildup.
Lifestyle or Ear Cleaning Practices Leading to Blockage
Inappropriate ear cleaning practices significantly contribute to earwax blockages. The use of cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other objects to clean the ears can push wax deeper into the ear canal, causing impaction. Moreover, individuals using earplugs or hearing aids are more prone to earwax blockage as these devices can prevent earwax from naturally exiting the ear canal. Lifestyle factors, such as using earphones frequently, can also contribute to increased earwax accumulation due to the blockage of earwax expulsion pathways.
Impact of Anatomical Differences and Health Conditions
Anatomical differences in ear canal shape can naturally lead to more frequent earwax blockages. Some individuals have narrower or more curved ear canals, hindering the natural migration of earwax out of the ear. Health conditions like eczema or psoriasis can also affect the ear canal skin, leading to excessive earwax production or blockages. Additionally, older adults often experience more earwax blockages due to the wax becoming harder and more difficult to expel naturally.
However, understanding these causes is essential for taking preventive measures and seeking appropriate treatment to maintain healthy ear function. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help manage earwax buildup effectively and avoid complications associated with blockages.
Diagnosis and Detection of Earwax Blockage
Diagnosing earwax blockage is a critical step in ensuring your ear health is maintained. Healthcare professionals employ various methods and tools to accurately diagnose this condition. Understanding these processes can help individuals recognize when to seek medical attention. Additionally, being aware of the symptoms of earwax blockage can enable self-assessment and prompt consultation with a healthcare provider. This article provides insights into how healthcare professionals diagnose earwax blockage, the tools and tests used in diagnosis, and tips for recognizing symptoms of earwax blockage at home.
How Healthcare Professionals Diagnose Earwax Blockage
Healthcare professionals typically begin with a thorough medical history and physical examination. The physical exam focuses on the ear, using a tool called an otoscope. An otoscope is a device fitted with a light and magnifying lens that allows the doctor to view the ear canal and eardrum clearly. This examination helps the healthcare provider determine the presence of earwax blockage and assess its severity.
List of Tools and Tests Used in the Diagnosis of Earwax Blockage
- Otoscope: The primary tool for examining the ear canal and eardrum.
- Audiometry Tests: Used to assess hearing loss, which can be a symptom of earwax blockage.
- Tympanometry: This test evaluates the functioning of the middle ear and eardrum movement, indirectly indicating the presence of a blockage.
- Microscopy: Some specialists use binocular microscopes to get a detailed view of the ear canal and eardrum, aiding in precise diagnosis and treatment.
These tools and tests provide a comprehensive assessment of ear health and help in diagnosing earwax blockage accurately.
Self-Assessment Tips: Recognizing Symptoms of Earwax Blockage at Home
Being aware of the symptoms of earwax blockage can help individuals identify when they might need professional medical evaluation. Here are some tips for recognizing earwax blockage at home:
- Hearing Loss: Gradual decrease in hearing on one or both sides can be a sign of earwax buildup.
- Earache: Pain in the ear that persists might indicate blockage.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing noise in the ear could be caused by accumulated earwax.
- Fullness in the Ear: A sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear often accompanies earwax blockage.
- Dizziness: Earwax blockage can sometimes lead to dizziness or vertigo.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Remember, while self-assessment can guide you, it should not replace professional medical evaluation and treatment.
By recognizing the symptoms of earwax blockage and understanding how healthcare professionals diagnose the condition, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining ear health. Regular check-ups and cleaning, when necessary, can prevent earwax blockage and its associated discomforts, ensuring good ear health and well-being.
Treatment Options for Earwax Blockage
There are various treatment options available, ranging from home remedies to medical treatments. In this section, we will explore these options in detail, highlighting their effectiveness, what works, what to avoid, and the latest advancements in medical treatments.
Home Remedies and Their Effectiveness
Many individuals turn to home remedies as a first step in treating earwax blockage. These remedies are often simple, cost-effective, and can be done without the need for a visit to the doctor. Some popular home remedies include:
- Olive Oil: A few drops of olive oil in the affected ear can soften the earwax, making it easier to remove. This method is safe and can be effective, but it may take several days to see results.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Using a solution of hydrogen peroxide and water can help dissolve the earwax. However, this should be done with caution, as it can cause irritation if used too frequently or in high concentrations.
- Warm Water: Gently flushing the ear with warm water using a syringe (without the needle) can help dislodge the blockage. Ensure the water is body temperature to avoid dizziness.
While these home remedies can be effective for mild cases of earwax blockage, they are not suitable for everyone. It is important to avoid inserting any objects into the ear, as this can push the wax further in or damage the ear canal.
Over-the-Counter Solutions: What Works and What to Avoid
Over-the-counter (OTC) ear drops are a widely available and convenient option for treating earwax blockage. These drops often contain substances like saline, mineral oil, glycerin, or hydrogen peroxide to soften and break up the earwax. When choosing OTC solutions, look for products specifically designed for earwax removal, and follow the instructions carefully.
It is important to avoid using OTC ear candles, as they have been proven ineffective and potentially dangerous, posing risks of burns and ear canal damage.
Medical Treatments: From Ear Irrigation to Microsuction
For persistent or severe earwax blockage, seeking medical treatment is advisable. Health professionals can offer safe and effective treatments, including:
- Ear Irrigation: This involves using a special syringe to flush out the earwax with water or a saline solution. Ear irrigation is effective but may not be suitable for individuals with ear infections, eardrum perforation, or those who have had ear surgery.
- Microsuction: This is a minimally invasive procedure where a small suction device is used to remove earwax under direct vision. Microsuction is considered safe, quick, and generally more comfortable than irrigation.
- Manual Removal: Using specialized instruments, a healthcare provider can manually remove earwax. This method is particularly useful when the wax is too hard to irrigate or when microsuction is not available.
However, while home remedies and OTC solutions can be effective for mild earwax blockage, it’s crucial to proceed with caution and avoid methods that could harm the ear. For persistent or severe cases, professional medical treatments offer safe and effective options. If you’re unsure about the best course of action, consulting with a healthcare provider is always the best approach.
Treatment Options for Earwax Blockage
There are various treatment options available, ranging from home remedies to medical treatments. In this section, we will explore these options in detail, highlighting their effectiveness, what works, what to avoid, and the latest advancements in medical treatments.
Home Remedies and Their Effectiveness
Many individuals turn to home remedies as a first step in treating earwax blockage. These remedies are often simple, cost-effective, and can be done without the need for a visit to the doctor. Some popular home remedies include:
- Olive Oil: A few drops of olive oil in the affected ear can soften the earwax, making it easier to remove. This method is safe and can be effective, but it may take several days to see results.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: Using a solution of hydrogen peroxide and water can help dissolve the earwax. However, this should be done with caution, as it can cause irritation if used too frequently or in high concentrations.
- Warm Water: Gently flushing the ear with warm water using a syringe (without the needle) can help dislodge the blockage. Ensure the water is body temperature to avoid dizziness.
While these home remedies can be effective for mild cases of earwax blockage, they are not suitable for everyone. It is important to avoid inserting any objects into the ear, as this can push the wax further in or damage the ear canal.
Over-the-Counter Solutions: What Works and What to Avoid
Over-the-counter (OTC) ear drops are a widely available and convenient option for treating earwax blockage. These drops often contain substances like saline, mineral oil, glycerin, or hydrogen peroxide to soften and break up the earwax. When choosing OTC solutions, look for products specifically designed for earwax removal, and follow the instructions carefully.
It is important to avoid using OTC ear candles, as they have been proven ineffective and potentially dangerous, posing risks of burns and ear canal damage.
Medical Treatments: From Ear Irrigation to Microsuction
For persistent or severe earwax blockage, seeking medical treatment is advisable. Health professionals can offer safe and effective treatments, including:
- Ear Irrigation: This involves using a special syringe to flush out the earwax with water or a saline solution. Ear irrigation is effective but may not be suitable for individuals with ear infections, eardrum perforation, or those who have had ear surgery.
- Microsuction: This is a minimally invasive procedure where a small suction device is used to remove earwax under direct vision. Microsuction is considered safe, quick, and generally more comfortable than irrigation.
- Manual Removal: Using specialized instruments, a healthcare provider can manually remove earwax. This method is particularly useful when the wax is too hard to irrigate or when microsuction is not available.
However, while home remedies and OTC solutions can be effective for mild earwax blockage, it’s crucial to proceed with caution and avoid methods that could harm the ear. For persistent or severe cases, professional medical treatments offer safe and effective options. If you’re unsure about the best course of action, consulting with a healthcare provider is always the best approach.
When to See a Doctor for Earwax Blockage
Earwax, a natural secretion designed to protect the ear, can sometimes accumulate excessively, leading to blockage. While earwax blockage is common and often manageable at home, certain signs necessitate professional medical attention. Understanding when to seek help is crucial for preventing complications such as hearing loss, infection, or eardrum damage.
Identifying Signs That Require Professional Medical Attention
It’s important to be aware of symptoms that indicate your earwax blockage may need a doctor’s care. Consider seeing a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent Hearing Loss: A slight decrease in hearing is common with earwax buildup, but if you notice a significant or prolonged loss of hearing, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Ear Pain or Discomfort: While some discomfort might occur with earwax buildup, intense or persistent pain is not normal and should be evaluated.
- Dizziness or Vertigo: Feeling unsteady or dizzy can indicate that the blockage is affecting your inner ear, which requires medical attention.
- Ringing in the Ears (Tinnitus): Persistent buzzing or ringing sounds may be related to blockage or other ear issues.
- Foul-smelling Discharge: Any discharge from the ear, especially if it smells bad, could indicate an infection.
- Fever or Persistent Cough: Sometimes, earwax blockage can lead to secondary symptoms such as fever or a cough, signaling a more serious condition.
What to Expect During a Doctor’s Visit for Earwax Blockage
A visit to the doctor for earwax blockage is typically straightforward and painless. Here’s what you can expect:
- Medical History and Symptoms Review: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any home treatments you’ve tried.
- Ear Examination: Using a tool called an otoscope, the doctor will carefully examine your ears for blockage, infection, or other issues.
- Earwax Removal: If necessary, the doctor may remove the earwax using methods such as irrigation, suction, or with a small instrument.
- Follow-Up Recommendations: You’ll receive advice on preventing future blockages and possibly a follow-up appointment to ensure the issue is resolved.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider About Earwax Blockage Symptoms
Being proactive during your visit can help you understand and manage your condition better. Consider asking your healthcare provider the following questions:
- What is the best method to remove earwax at home, and what should I avoid?
- How often should I have my ears checked for earwax buildup?
- Are there any signs of complications I should watch for after removal?
- Could my earwax blockage be a sign of an underlying health issue?
- Are there any preventive measures I can take to avoid future blockages?
By recognizing when to seek medical attention for earwax blockage and knowing what to expect during a doctor’s visit, you can ensure your ears remain healthy and functional. Asking informed questions during your visit can further enhance your understanding and ability to manage earwax-related issues.
FAQs on Earwax Blockage
1. What is earwax blockage?
Earwax blockage occurs when earwax (cerumen) accumulates in the ear canal to an extent where it can cause symptoms or block the passage of sound. It is a common condition that can affect people of all ages.
2. What causes earwax to build up?
Several factors can contribute to earwax build-up, including the natural shape of your ear canal, excessive hair, narrow ear canals, aging, and the frequent use of earplugs or hearing aids. Some individuals naturally produce more earwax than others.
3. What are the symptoms of earwax blockage?
Symptoms of earwax blockage include earache, a feeling of fullness in the affected ear, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), hearing loss, itching, dizziness, and ear infection. If you experience any of these symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
4. How can I safely remove earwax at home?
For safe at-home removal, you can try over-the-counter drops designed to soften earwax. Alternatively, a few drops of baby oil, mineral oil, glycerin, or hydrogen peroxide can also help soften the wax. Avoid using cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other objects to remove earwax, as these can push the wax further into the ear canal or damage the ear.
5. When should I see a doctor for earwax removal?
You should consult a doctor if you experience symptoms of earwax blockage, especially if you have diabetes, a compromised immune system, a history of ear surgery, or if you are unable to remove the wax at home. A healthcare provider can safely remove the earwax using irrigation, suction, or specialized tools.
6. Can earwax blockage be prevented?
Preventing earwax blockage involves avoiding the insertion of objects into the ear canal, including cotton swabs, which can push wax deeper into the ear. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help monitor earwax build-up, especially if you’re prone to blockages.
7. Is it necessary to remove earwax?
Earwax serves as a natural defense mechanism for the ear, trapping dirt and slowing the growth of bacteria. In most cases, the ear cleans itself, and manual removal of earwax is not necessary unless it causes symptoms or blockage.
8. Can earwax blockage affect my hearing?
Yes, significant build-up of earwax can block the ear canal and temporarily reduce hearing in the affected ear. Hearing usually returns to normal once the blockage is removed.
9. Are there any complications associated with earwax blockage?
If left untreated, earwax blockage can lead to ear discomfort, infection, and temporary hearing loss. However, with proper management and care, these complications are easily preventable.
10. How often should I clean my ears?
Ear cleaning practices vary among individuals. It’s important to understand that the ears usually clean themselves. If you’re prone to earwax build-up, a healthcare provider can recommend a safe cleaning routine specific to your needs.
Conclusion:
In wrapping up our discussion on earwax blockage, it’s essential to revisit the pivotal insights shared about the symptoms and causes of this common yet often overlooked condition. Earwax blockage can lead to a range of symptoms, including hearing loss, earache, a feeling of fullness in the ear, tinnitus, itching, and even infections. These manifestations arise from various causes, including the natural accumulation of earwax, the use of earplugs or hearing aids, and the habit of inserting objects into the ears, which can push wax deeper into the ear canal.
The significance of maintaining ear health cannot be overstated. Our ears are intricate systems that not only allow us to hear but also play a crucial role in balance and spatial orientation. Therefore, taking preventive measures to avoid blockages, such as avoiding inserting objects into the ears and seeking regular medical check-ups, can go a long way in preserving ear function and overall well-being.
For individuals experiencing persistent or severe symptoms associated with earwax blockage, it’s imperative to seek professional medical advice. While home remedies can offer relief in minor cases, a healthcare provider can offer safe and effective treatments, such as ear irrigation or microsuction, to remove the blockage without risking damage to the ear canal or eardrum.
In conclusion, being informed about the symptoms and causes of earwax blockage, understanding the importance of ear health, and taking proactive steps towards seeking medical advice when needed, are key to preventing complications and ensuring the longevity of your hearing and ear health. Remember, your ears are vital, and taking care of them is a sound investment in your overall quality of life.
References
For those seeking more in-depth information on the symptoms of earwax blockage and seeking reputable sources for validation, the following resources provide valuable insights and detailed explanations. Each link offers a comprehensive overview of the condition, its symptoms, and potential treatments, guiding readers through the nuances of earwax blockage with scientific accuracy and clarity. These resources ensure that readers have access to reliable information, enhancing their understanding and ability to address earwax blockage effectively.
- Mayo Clinic – Earwax Blockage: The Mayo Clinic offers an extensive article on earwax blockage, covering symptoms, causes, and treatment options. This trusted medical resource provides a thorough overview, backed by the expertise of medical professionals. Read more at Mayo Clinic.
- WebMD – Understanding Earwax Blockage: WebMD’s section on earwax blockage provides insights into the condition, including how it occurs, common symptoms, and various treatment methodologies. Known for its accessible health-related content, WebMD is a go-to source for health information. Explore further on WebMD.
- Healthline – Earwax Blockage: Healthline offers a detailed article on earwax blockage, focusing on symptoms, home remedies, and when to see a doctor. The article is designed for readability and is backed by medical review to ensure accuracy. Discover more at Healthline.
- American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery: This professional organization provides a resource on earwax and its management, including prevention of blockage. It’s an excellent source for those looking for information grounded in the expertise of ENT specialists. Learn more from AAO-HNS.
These resources have been selected for their credibility, depth of information, and ease of understanding, making them ideal references for anyone looking to learn more about earwax blockage and its implications on health. Whether you are experiencing symptoms of earwax blockage or simply wish to educate yourself about the condition, these links provide valuable insights from reputable medical sources.