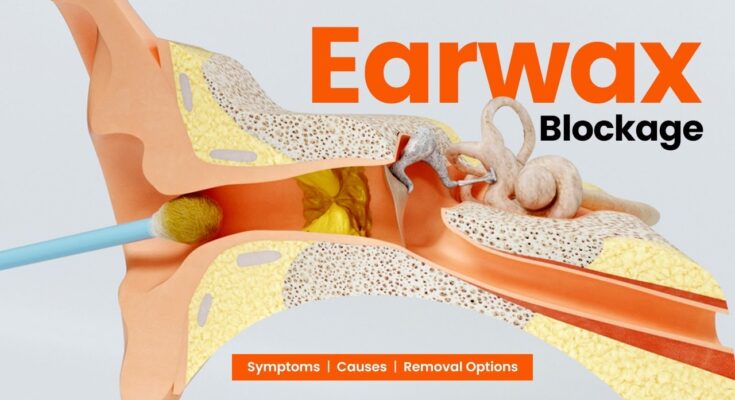
Earwax Blockage Treatment: Earwax, scientifically known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal that has protective, lubricating, and antibacterial properties.
Although it’s a helpful component in the ear’s defense system, excessive earwax can lead to blockage, discomfort, and even hearing loss.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of earwax blockage is crucial for maintaining ear health and preventing complications.
Understanding Earwax Blockage
Earwax blockage is a common condition that occurs when earwax (cerumen) accumulates in the ear canal and creates a blockage. Earwax is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal that helps protect the ears from dust, dirt, bacteria, and other microorganisms. While it usually exits the ear naturally, various factors can lead to its buildup and blockage, affecting hearing and causing discomfort. In this section, we’ll explore the common causes of earwax buildup and blockage, as well as the symptoms and signs to watch out for.
Common Causes of Earwax Buildup and Blockage
Earwax buildup and blockage can occur for several reasons, including:
- Narrow or hairy ear canals: Some people have naturally narrow or hairy ear canals, making it difficult for earwax to exit the ear naturally.
- Frequent use of earphones or hearing aids: These devices can push earwax deeper into the ear canal.
- Excessive earwax production: Some individuals produce more earwax than others, which can lead to blockages.
- Aging: The consistency of earwax changes as people age, becoming harder and more likely to block the ear canal.
- Use of cotton swabs or other objects in the ear: Inserting cotton swabs, fingers, or other objects into the ear can push earwax deeper into the canal.
Symptoms and Signs of Earwax Blockage
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of earwax blockage is crucial for timely intervention. Some of the common symptoms include:
- Hearing loss: One of the first signs of earwax blockage is a decrease in hearing sensitivity.
- Earache: The buildup of earwax can cause discomfort or pain in the affected ear.
- Tinnitus: Some people may experience ringing or buzzing in the ear, known as tinnitus.
- Itchiness: The ear canal may become itchy due to the accumulation of earwax.
- Fullness or pressure: A sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear can indicate a blockage.
- Cough: In rare cases, a blockage can stimulate a nerve in the ear, leading to a cough.
However, understanding the causes and symptoms of earwax blockage is essential for maintaining ear health. If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, rather than trying to remove the earwax yourself. Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure your ears remain healthy.
Diagnosis of Earwax Blockage
Experiencing symptoms such as a feeling of fullness in the ear, decreased hearing, or earache? It could be an earwax blockage, a common issue that affects many. Understanding when to seek medical help and how healthcare professionals diagnose this condition can guide you towards the right treatment. This article provides insights into the diagnosis of earwax blockage, emphasizing the importance of a professional evaluation while also highlighting situations where self-diagnosis might be appropriate.
When to Seek Medical Help for Earwax Blockage
It’s crucial to know when to consult a healthcare provider for earwax blockage. If you’re experiencing symptoms like hearing loss, ear discomfort, dizziness, or even a ringing sensation in your ears (tinnitus), it’s time to seek professional advice. Additionally, if you’ve attempted to clear the wax at home without success, or if you suspect the blockage might be causing an infection (evidenced by pain, discharge, or fever), professional medical evaluation becomes imperative.
How Healthcare Professionals Diagnose Earwax Blockage
Diagnosing earwax blockage involves a few key steps undertaken by healthcare professionals:
- Physical Examination: Initially, a healthcare provider will review your symptoms and medical history. This initial conversation helps to rule out other conditions that might mimic the symptoms of earwax blockage.
- Use of Otoscope for a Closer Look Inside the Ear: The cornerstone of diagnosing earwax blockage is the use of an otoscope. This tool allows doctors to visually inspect the ear canal and eardrum, identifying the presence and extent of earwax accumulation. An otoscope exam is painless and quick, providing immediate insights into the health of your ear canal.
The Role of Self-Diagnosis and When It’s Appropriate
While professional diagnosis is always recommended, there are instances where self-diagnosis might be appropriate. If you’re familiar with the sensation of earwax blockage and are experiencing mild symptoms, over-the-counter remedies might provide relief. However, this approach should be undertaken with caution. Incorrect self-treatment can lead to further complications, including injury to the ear canal or eardrum.
It’s important to avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, as this can push the wax deeper and cause more significant blockages. If symptoms persist despite self-care measures, or if you experience severe pain, hearing loss, or discharge, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional.
Recognizing when to seek medical help and understanding how healthcare professionals diagnose this issue can ensure that you receive appropriate care. While there’s a place for cautious self-diagnosis, professional evaluation is paramount for ensuring your ear health is properly managed.
Treatment Options for Earwax Blockage
There are several effective treatment options available, ranging from simple home remedies to professional medical interventions. This article will explore the various treatments for earwax blockage, helping you understand which option might be best for your situation.
Home Remedies and Their Effectiveness
- Over-the-Counter Ear Drops: Pharmacy shelves are stocked with ear drops specifically designed to soften earwax. These drops often contain hydrogen peroxide, saline, or mineral oils, which can help in loosening and breaking down the earwax, making it easier to remove.
- Warm Water Irrigation: Gently flushing the ear with warm water using a syringe (available in earwax removal kits) can also be effective. This method can help to soften and wash away the earwax. However, it’s important to be cautious and use a low-pressure stream to avoid damaging the ear.
- Olive or Almond Oil: A few drops of olive or almond oil in the ear before bedtime for a few days can soften the wax. This method is gentle and can be effective for mild blockages.
While home remedies can be effective for minor blockages, they are not suitable for everyone. If you have a perforated eardrum or an ear infection, these methods could be harmful. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider if you’re unsure about your condition.
Professional Treatments
When home remedies are not sufficient, or if the blockage is severe, professional medical treatment may be necessary. Here are the most common professional treatments for earwax blockage:
- Microsuction: This is a safe and quick procedure where a healthcare professional uses a microscope to get a clear view of the ear canal and a small suction device to remove the earwax. This method is generally considered to be comfortable and effective.
- Ear Irrigation by a Professional: Similar to home irrigation but performed by a healthcare provider, this method uses specialized equipment to gently flush out the earwax. It’s safer than doing it at home, as the professional can control the pressure and temperature of the water more accurately.
- Manual Removal: Sometimes, a healthcare provider may use specialized tools like a cerumen spoon or forceps to manually remove the blockage. This method is often used if the wax is too hard, too impacted, or if the ear canal is narrow.
Professional treatments are typically quick, and most people can return to their normal activities immediately after the procedure. It’s important to seek professional advice before attempting to remove earwax on your own, especially if you have underlying conditions or are experiencing significant symptoms like pain, discharge, or hearing loss.
However, while earwax is a natural and necessary part of ear health, blockages can cause discomfort and hearing issues. Fortunately, there are several effective treatments available, from simple home remedies to professional medical interventions. If you’re dealing with earwax blockage, consider the options listed above and consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for your specific needs. Prioritizing ear health and seeking appropriate treatment when necessary can help maintain your hearing clarity and overall ear well-being.
Preventing Earwax Blockage
Fortunately, there are proactive measures you can take to prevent earwax blockage while maintaining healthy ear hygiene.
Tips for Preventing Earwax Blockage
- Follow Proper Ear Cleaning Practices: Instead of using cotton swabs or other objects that can push earwax deeper into the ear canal, consider wiping the outer ear with a damp cloth. This method helps to clean your ears effectively without risking earwax impaction.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration can help maintain the consistency of earwax, preventing it from becoming too hard and causing blockage.
- Use Over-the-Counter Drops: Earwax removal drops are available at pharmacies. These drops can soften the wax, making it easier to exit the ear naturally. However, use them sparingly as per the instructions on the label or a healthcare provider’s advice.
- Avoid Ear Candles: Ear candling, a practice that involves inserting a lit, hollow, wax-covered candle into the ear, is not recommended. It’s proven to be ineffective and potentially dangerous.
- Limit the Use of Earplugs and Headphones: Frequent use of earplugs and in-ear headphones can push wax deeper into the ear canal. Try to limit their use and keep them clean to prevent earwax buildup.
- Consider Your Ear Health in Your Routine: Incorporate ear care into your daily or weekly health routine, but remember, less is often more. Ears are self-cleaning organs, and excessive cleaning can do more harm than good.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider for Earwax Removal
It’s essential to recognize when professional help is needed for earwax removal. You should consult a healthcare provider in the following situations:
- Experiencing Symptoms of Earwax Blockage: If you’re experiencing symptoms such as ear pain, a feeling of fullness in the ear, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), itching, discharge, odor, or hearing loss, it may indicate a blockage.
- Home Removal Methods Fail: If at-home earwax removal methods do not alleviate the blockage or symptoms persist, it’s time to seek medical advice.
- History of Ear Problems: Individuals with a history of ear problems, surgeries, or ear drum perforation should consult a healthcare provider before attempting any home removal methods.
- Signs of Infection: If you suspect an infection, characterized by severe pain, fever, or continued discharge, seek professional medical attention promptly.
A healthcare provider can safely remove earwax through irrigation, suction, or with specialized tools, ensuring your ears remain healthy and your hearing unimpaired. Remember, preventing earwax blockage starts with understanding proper ear care and recognizing when to seek professional help.
Complications of Untreated Earwax Blockage
Untreated earwax blockage, also known as cerumen impaction, can lead to a range of complications that affect hearing, comfort, and overall ear health. Understanding these potential issues emphasizes the importance of managing earwax buildup effectively.
Hearing Loss
One of the most immediate and noticeable complications of untreated earwax blockage is a reduction in hearing ability. Earwax can accumulate to the point where it obstructs the ear canal, preventing sound waves from reaching the eardrum effectively. This form of conductive hearing loss can significantly impact daily life, making it difficult to understand conversations, enjoy music, and stay alert to sounds in the environment.
Ear Infections
The accumulation of earwax can create an environment conducive to bacterial and fungal growth, leading to external ear infections, known as otitis externa. Symptoms may include pain, itching, discharge, and a feeling of fullness in the ear. If left untreated, these infections can become chronic and lead to more serious complications.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, or the perception of ringing or noise in the ears, can be exacerbated by earwax blockage. While tinnitus has various causes, the pressure from accumulated earwax can irritate the ear canal and eardrum, leading to an increase in the intensity or onset of tinnitus symptoms.
Perforated Eardrum
Attempting to remove earwax without professional help can lead to accidents, such as perforating the eardrum with cotton swabs or other objects. A perforated eardrum not only causes pain and potential hearing loss but also increases the risk of infections reaching the middle ear.
Impacted Earwax
Over time, untreated earwax can become hard and compacted, making it difficult to remove and causing significant discomfort. This can lead to a condition known as impacted earwax, requiring medical intervention to safely remove the blockage and alleviate symptoms.
Preventing Complications
To prevent these complications, it’s advisable to seek professional medical advice if you suspect an earwax blockage. Healthcare providers can safely remove earwax using techniques that minimize the risk of infection, injury, and other complications. Regular check-ups and practicing safe ear cleaning methods can also help maintain ear health and prevent earwax from building up to problematic levels.
However, while earwax serves an important role in protecting the ear, excessive buildup without proper management can lead to a variety of health issues. Awareness and appropriate care are key to preventing the complications associated with untreated earwax blockage, ensuring good ear health and well-being.
FAQs About Earwax Blockage Treatment
What is Earwax Blockage?
Earwax, or cerumen, is a natural substance produced by glands in the ear canal that helps protect the ear. Blockage occurs when earwax accumulates and hardens in the ear canal, potentially causing discomfort, hearing loss, or other symptoms.
How Can I Tell If I Have an Earwax Blockage?
Symptoms of earwax blockage include earache, a feeling of fullness in the affected ear, ringing in the ear (tinnitus), hearing loss, itching, odor, or discharge. If you experience these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
What Are the Treatment Options for Earwax Blockage?
Treatment typically involves safely removing the excess earwax. This can be done at home with over-the-counter ear drops designed to soften the wax or by a healthcare provider using methods such as irrigation, suction, or manual removal with special tools.
Is It Safe to Remove Earwax at Home?
While there are safe methods to remove earwax at home, such as using ear drops or warm water, you should never insert objects like cotton swabs, bobby pins, or other items into your ear canal. These can push the wax further into the ear and potentially cause injury. If you’re unsure, it’s best to seek professional help.
Can Earwax Blockage Be Prevented?
Yes, to some extent. Avoid inserting objects into your ears, as this can push wax deeper and contribute to blockages. Instead, clean the outer ear gently with a washcloth. If you’re prone to producing a lot of earwax, consider regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to manage the condition before it becomes problematic.
When Should I See a Doctor for Earwax Blockage?
You should consult a doctor if you experience symptoms of earwax blockage, especially if you have severe pain, a fever, or a noticeable hearing loss. Additionally, if at-home treatments do not alleviate the blockage, professional removal may be necessary.
Can Earwax Blockage Affect My Hearing?
Yes, earwax blockage can temporarily affect your hearing by blocking sound waves from reaching the inner ear. The degree of hearing loss can vary, but it typically improves once the blockage is removed.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage individuals experiencing symptoms of earwax blockage to seek professional advice. Healthcare providers can offer personalized diagnosis and treatment, ensuring the health and safety of your ears. Remember, attempting to remove earwax with improper tools or techniques can lead to further complications. Trusting a professional with the care of your ears not only ensures the effective treatment of current issues but also prevents potential problems in the future.
Taking care of your ears is a critical component of your overall health. By staying informed about the signs of earwax blockage and the importance of professional treatment, you can maintain your hearing health and avoid unnecessary complications. Don’t let earwax issues go untreated; seek the advice of a healthcare provider to ensure your ears remain healthy and fully functional.
References
References are crucial for validating the information provided and for offering readers avenues for further exploration on the topic of Earwax Blockage Treatment Symptoms. Below, you’ll find a curated list of reputable sources that delve into various aspects of this condition, from identification and understanding of symptoms to the range of treatment options available. These links serve as a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to deepen their knowledge or seeking solutions to earwax blockage issues.
- Mayo Clinic – Earwax Blockage: Explore an in-depth overview of symptoms, causes, and treatments for earwax blockage. This resource is an excellent starting point for understanding the condition and its impact on health. Visit Mayo Clinic
- WebMD – Understanding Earwax Blockage: WebMD offers insights into the prevention, symptoms, and treatment options for earwax blockage, providing a comprehensive look at how to manage this condition effectively. Explore WebMD
- Healthline – How to Safely Remove Earwax at Home: Healthline provides practical advice and steps for safely removing earwax at home, alongside when to seek professional help. This guide is particularly useful for those looking for home-based solutions. Read on Healthline
- American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery: Get professional insights into the best practices for earwax removal and the treatment of blockages from a leading authority in the field. This resource is invaluable for understanding the medical perspective. Learn More Here
Ensuring the accuracy of the information you receive is crucial for effective treatment and management of earwax blockage. The links provided above are from reputable sources known for their reliable and up-to-date health information. Whether you’re seeking to understand more about the symptoms, looking for treatment options, or interested in preventative measures, these references will guide you towards the right information.