Ear Infection Treatment: Middle ear infections, medically termed as Otitis Media, are a common condition that can affect individuals of all ages, but they are particularly prevalent among children.
This condition can cause a significant amount of discomfort and, if not properly treated, may lead to more severe health issues.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for middle ear infections is crucial for prompt recovery and minimizing the risk of complications.
Understanding Ear Infections
Ear infections are a common health issue that affect people of all ages, though they are particularly prevalent among children. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and being aware of the impact on different age groups can help in managing this condition more effectively.
Common Causes of Ear Infections
Ear infections usually occur when a virus or bacteria get trapped in the middle ear, the area right behind the eardrum. The most common causes include:
- Cold, flu, or respiratory infections: These can lead to congestion and swelling of the nasal passages, throat, and eustachian tubes.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and blockage of the tubes.
- Sinus infections: Infections in the sinus can also affect the ear.
- Smoking: Exposure to tobacco smoke or other pollutants can increase the risk of ear infections.
- Poor hygiene: Not cleaning the ears properly can lead to infections.
Understanding these causes can help in taking preventative measures to reduce the risk of ear infections.
Symptoms of Middle Ear Infections
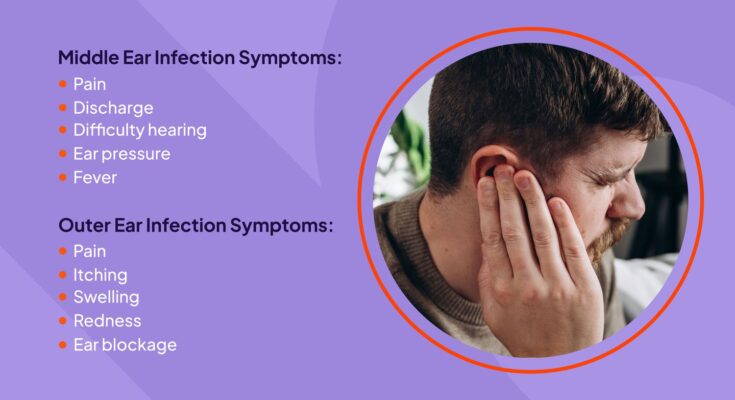
Middle ear infections, also known as otitis media, can manifest through a variety of symptoms, which may vary between children and adults. Common symptoms include:
- Ear pain: This is often more severe when lying down as pressure builds up in the middle ear.
- Difficulty hearing: Fluid build-up can muffle sounds.
- Fever: Especially in children, a fever might accompany an ear infection.
- Fluid drainage from the ear: This might indicate a ruptured eardrum.
- Irritability and sleep disturbance: Particularly in children, these symptoms are common due to discomfort.
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment.
Impact on Different Age Groups (Children vs. Adults)
Children: Children are more prone to ear infections due to the size and shape of their eustachian tubes, which are shorter and more horizontal, making it easier for fluids to get trapped in the middle ear. Ear infections can be particularly troublesome for children, leading to pain, fever, and even temporary hearing loss, which can affect speech development and academic performance.
Adults: While less common, adults can still suffer from ear infections. In adults, the condition can lead to severe ear pain, hearing difficulties, and a general sense of unwellness. Adults with recurrent ear infections should seek medical advice as it could be a sign of an underlying health issue.
However, ear infections, while common, can have a significant impact on the quality of life for individuals of all ages. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and being aware of the age-related impacts, individuals can seek timely treatment and implement preventative measures to reduce the occurrence of this uncomfortable condition.
Diagnosing Ear Infections
This article will guide you through the symptoms that indicate it’s time to see a doctor, what to expect during your visit, and the diagnostic tests commonly used to confirm an ear infection.
When to See a Doctor: Recognizing Symptoms
It’s important to be aware of the symptoms of ear infections so you can seek timely medical assistance. Common signs include:
- Ear Pain: This is often the most noticeable symptom, which may worsen when lying down.
- Trouble Hearing: Fluid buildup can make it hard to hear clearly.
- Fluid Drainage: Unusual fluid draining from the ear indicates an infection.
- Fever: A high temperature may accompany an ear infection.
- Irritability: Especially in children, increased fussiness can be a sign.
- Difficulty Sleeping: Pain and discomfort can make it hard to sleep.
If you or your child experiences these symptoms, it’s advisable to consult a doctor to prevent complications and obtain relief.
What to Expect During a Doctor’s Visit
During your appointment, the doctor will:
- Review Symptoms and Medical History: Be prepared to discuss the symptoms and their duration, as well as any history of ear infections.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will use an instrument called an otoscope to look at the outer ear and eardrum for signs of infection.
- Assessment of Hearing: A basic test may be conducted to check if hearing is affected.
This evaluation helps the doctor determine the presence of an ear infection and its severity.
Diagnostic Tests for Ear Infections
Several diagnostic tools can be used to assess ear infections more thoroughly:
- Otoscopy: The primary method where an otoscope is used to view the eardrum and ear canal.
- Tympanometry: A test that uses air pressure to check the mobility of the eardrum, indicating fluid behind it.
- Acoustic Reflectometry: Measures how sound reflected from the eardrum can indicate fluid buildup.
- Tympanocentesis: Rarely used, this involves piercing the eardrum to drain fluid for testing, mainly if there are recurring infections or treatment failure.
However, understanding these steps and diagnostic options can demystify the process of diagnosing ear infections, making it less daunting for patients seeking medical care. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing complications and ensuring a speedy recovery.
Treatment Options for Ear Infections
Understanding the range of treatment options available is crucial for managing symptoms and promoting healing. This article explores the various treatments for ear infections, emphasizing goals, home remedies, medications, and alternative treatments.
Overview of Treatment Goals for Ear Infections
The primary goals in treating ear infections include relieving pain, eliminating the infection, preventing complications, and reducing the risk of recurrence. Treatment strategies are often determined by the type of ear infection, its severity, and the patient’s age and health condition.
Home Remedies and Pain Management Techniques
Home remedies play a vital role in alleviating the discomfort caused by ear infections. Pain management techniques such as applying warm compresses to the affected ear can provide immediate relief. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, are effective for reducing fever and easing pain. However, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before administering any medication, especially to children.
Medications for Ear Infections
Antibiotics: Not all ear infections require antibiotics. They are typically prescribed for bacterial infections, especially in cases involving young children or infections that don’t improve on their own. Antibiotics can be administered orally or as ear drops, depending on the infection type and patient age.
Ear Drops: Ear drops may contain antibiotics to fight infection, steroids to reduce inflammation, or analgesics for pain relief. They are particularly useful in treating outer ear infections (otitis externa). Always follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on the correct usage of ear drops.
The Role of Warm Compresses and Pain Relievers
Warm compresses applied to the outer ear can help reduce pain and discomfort associated with ear infections. Non-prescription pain relievers, when used as directed, can significantly alleviate symptoms, allowing individuals to rest and recover more comfortably.
Alternative Treatments and Their Effectiveness
Some individuals explore alternative treatments, such as herbal remedies, chiropractic adjustments, and homeopathy, for ear infections. While these may offer relief to some, it’s essential to approach alternative treatments with caution and consult a healthcare provider before trying them. The effectiveness of alternative treatments can vary, and they should not replace conventional medical care, especially in severe cases.
While home remedies and over-the-counter medications can provide significant relief, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan, especially if symptoms persist or worsen. By understanding the various treatment options and their proper application, individuals can effectively manage ear infections and achieve a quicker recovery.
Complications and Risks of Untreated Ear Infections
Below, we detail the potential complications of untreated middle ear infections and discuss why timely treatment is crucial to prevent these adverse outcomes.
Potential Complications of Untreated Middle Ear Infections
- Hearing Loss: Persistent or severe infections can damage the structures of the middle ear, leading to temporary or permanent hearing impairment. This is particularly concerning in children, for whom hearing is essential for language development and learning.
- Spread of Infection: Without treatment, the infection can spread to nearby tissues, including the inner ear, brain, or mastoid bone (located just behind the ear). This can lead to more severe conditions such as mastoiditis, meningitis, or a brain abscess, all of which are medical emergencies.
- Tympanic Membrane Perforation: Repeated infections or a long-standing infection can cause the eardrum to rupture. While the eardrum often heals itself, severe or recurrent perforations may require surgical repair to prevent hearing loss and reduce the risk of further infections.
- Cholesteatoma Formation: This is a more rare but serious complication where a skin cyst grows in the middle ear as a result of chronic infection. It can erode the bones of the middle ear, leading to hearing loss and potentially affecting the facial nerve.
- Speech and Developmental Delays in Children: Since hearing is crucial for speech development and learning, untreated ear infections can lead to delays in speech, social, and cognitive development in children.
The Importance of Timely Treatment to Prevent Complications
Seeking prompt medical attention for ear infections is vital. Early treatment not only alleviates pain and discomfort but also significantly reduces the risk of the complications listed above. Treatment options may include pain management, antibiotics, and in some cases, surgical interventions to drain fluid and alleviate pressure in the middle ear.
It’s particularly important for parents and caregivers to monitor children for signs of ear infections, such as ear pain, difficulty hearing, or fluid draining from the ear. Given the potential for serious complications and the risk of developmental delays, consulting a healthcare provider at the first sign of an ear infection in a child is imperative.
However, while ear infections may seem like minor health issues, untreated infections can lead to severe complications and long-term health problems. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent these risks, safeguard hearing, and ensure overall well-being. Whether you’re an adult experiencing symptoms of an ear infection or caring for a child who may be affected, seeking medical advice promptly is the best course of action.
Prevention Tips for Ear Infections
Ear infections can be uncomfortable and, at times, lead to more serious health issues. Fortunately, there are effective ways to reduce your risk. By understanding and implementing preventive measures, the role of vaccines, and making certain lifestyle and environmental adjustments, you can significantly lower your chances of developing an ear infection.
Preventive Measures to Reduce the Risk of Ear Infections
Prevention is key when it comes to ear infections. Here are some practical steps you can take:
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regular hand washing can prevent the spread of germs that might lead to ear infections.
- Avoid Smoke Exposure: Smoke can irritate the Eustachian tubes, increasing the risk of ear infections. Keep your environment smoke-free.
- Manage Allergies: Proper management of allergies can reduce nasal congestion, thereby decreasing the risk of ear infections.
- Breastfeeding: If possible, breastfeeding for at least six months can provide antibodies that help protect against ear infections in infants.
The Role of Vaccines in Preventing Ear Infections
Vaccines play a crucial role in preventing ear infections. They help protect against certain bacteria and viruses that can cause ear infections:
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: Protects against pneumococcus, a common cause of ear infections.
- Flu Vaccine: Reduces the risk of influenza, which can lead to secondary ear infections.
- Haemophilus Influenzae Type b (Hib) Vaccine: Prevents Hib disease, which can lead to ear infections.
Ensuring that you and your child are up to date with vaccinations can significantly reduce the risk of ear infections.
Lifestyle and Environmental Adjustments to Lower Infection Rates
Making certain changes in your daily life and environment can also help prevent ear infections:
- Avoid Cold and Flu: Minimize exposure to those who are sick to prevent illnesses that can lead to ear infections.
- Use Earplugs in Polluted or Dusty Environments: This can help prevent irritants from entering the ear canal.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet and Exercise Routine: A healthy immune system can fight off infections more effectively.
- Proper Ear Care: Avoid inserting objects into the ear canal, which can damage the skin and lead to infections.
By integrating these preventive measures, vaccines, and lifestyle and environmental adjustments into your routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of ear infections. Staying informed and proactive about your health is the best strategy to keep ear infections at bay.
When to Seek Professional Help for an Ear Infection
Identifying the right time to seek help can prevent complications and ensure a swift recovery. Here’s what you need to know about recognizing the signs of worsening ear infections, the importance of follow-up appointments, and when to consider consulting an Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) specialist.
Signs That Your Ear Infection Is Getting Worse
Ear infections typically present symptoms like earache, a sense of fullness, hearing loss, and sometimes, fever. However, certain signs indicate that the infection is worsening, necessitating immediate medical attention:
- Persistent or Increasing Pain: If ear pain persists beyond a couple of days or intensifies, it’s a clear signal that the infection may be getting worse.
- Discharge from the Ear: Any discharge, especially if it’s pus-like or bloody, points to a possible complication of the ear infection.
- High Fever: A fever higher than 101°F (38°C) accompanying an ear infection suggests your body is fighting a more serious infection.
- Hearing Loss: If you notice a significant reduction in hearing capability, the infection might be affecting the middle ear, where it can cause more damage.
- Dizziness or Balance Issues: These symptoms can indicate that the infection has spread to the inner ear.
The Importance of Follow-Up Appointments
Follow-up appointments play a crucial role in ensuring the ear infection is completely resolved and to prevent any potential complications. These appointments allow your healthcare provider to:
- Monitor the progress of your treatment.
- Ensure the infection has fully cleared.
- Address any lingering symptoms or side effects.
- Make adjustments to treatment if necessary.
Neglecting follow-up care can lead to the recurrence of infection or chronic ear conditions that are harder to treat.
When to Consider Seeing a Specialist (ENT)
In some cases, your primary care doctor may recommend consulting an ENT specialist. Consider seeing an ENT if:
- Recurrent Infections: If you’re experiencing frequent ear infections, an ENT can help determine the underlying cause and offer more specialized treatments.
- Chronic Ear Infections: Chronic infections or fluid in the ear that doesn’t clear up with standard treatment may require the expertise of an ENT.
- Complications: Symptoms like persistent hearing loss, dizziness, or facial weakness might indicate complications that require specialized care.
- Surgical Evaluation: Some conditions, such as persistent effusion (fluid), may benefit from surgical intervention, such as the insertion of ear tubes, which an ENT can perform.
Recognizing when to seek professional help and following through with recommended care, including specialist consultations when necessary, are key to managing ear infections effectively. By staying vigilant for signs of complications and adhering to follow-up care, you can ensure the best possible outcome for your ear health.
Future Directions in Ear Infection Treatment
With advancements in medical research and technology, the future of ear infection treatment is evolving, promising more effective and efficient approaches to managing this condition. This section explores the emerging treatments and research in managing ear infections, alongside the potential for new vaccines or preventive measures.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Medical researchers are tirelessly working towards innovative solutions to treat ear infections more effectively. One of the most promising areas of research includes the development of novel antibiotics that are more targeted and have fewer side effects. These new formulations aim to combat the bacteria causing ear infections more efficiently, reducing the treatment duration and minimizing the risk of antibiotic resistance.
Another exciting development is the use of biofilms to treat chronic ear infections. Biofilms, which are thin, slimy layers of bacteria, have been challenging to treat with traditional antibiotics. However, researchers are now finding ways to disrupt these biofilms, making the bacteria more vulnerable to treatment. This approach could revolutionize the treatment of chronic ear infections, offering hope to those who suffer from recurrent episodes.
Furthermore, advancements in gene therapy and immunotherapy are being explored as potential treatments for ear infections. By targeting the underlying causes of inflammation and infection at the molecular level, these therapies could offer more personalized and long-lasting solutions to ear infections.
The Potential for New Vaccines or Preventive Measures
Vaccination has been one of the most successful public health initiatives, and there is potential for new vaccines to prevent ear infections. Scientists are currently investigating vaccines that target the specific bacteria and viruses responsible for ear infections. By enhancing the body’s immune response to these pathogens, these vaccines could significantly reduce the incidence of ear infections, especially in children who are most at risk.
Additionally, preventive measures are being refined to reduce the risk of ear infections. Public health campaigns focusing on hygiene practices, such as proper handwashing and avoiding smoke exposure, are crucial. Moreover, advancements in diagnostic tools can lead to earlier detection and treatment, preventing the progression of the infection and reducing the need for antibiotics.
The future of ear infection treatment is bright, with numerous promising research avenues and potential treatments on the horizon. From advanced antibiotics and biofilm-disrupting technologies to groundbreaking vaccines and preventive measures, the goal is to reduce the prevalence and impact of ear infections significantly. As these emerging treatments and preventive strategies develop, there is hope for more effective, efficient, and personalized approaches to managing ear infections, ultimately improving the quality of life for millions affected by this condition.
FAQ Section: Understanding Ear Infections and Treatments
What causes ear infections?
Ear infections are usually caused by bacteria or viruses. These infections often occur when the Eustachian tubes, which run from each ear to the back of the throat, become swollen or blocked. This can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, creating an environment ripe for infection. Common factors that contribute to ear infections include colds, allergies, sinus infections, smoking, and changes in air pressure.
How can I tell if I or my child has an ear infection?
Symptoms of ear infections can vary between individuals but typically include ear pain, difficulty hearing, fluid draining from the ear, fever, and in children, increased irritability. In infants, signs such as tugging at the ear, excessive crying, and trouble sleeping can also indicate an ear infection.
Are there different types of ear infections?
Yes, the three main types of ear infections are acute otitis media (AOM), otitis media with effusion (OME), and chronic otitis media with effusion (COME). AOM involves parts of the middle ear becoming infected and swollen, often accompanied by fluid behind the eardrum. OME occurs when fluid remains in the middle ear but without bacterial or viral infection symptoms. COME refers to fluid persistently returning to the middle ear, leading to possible hearing issues.
What treatment options are available for ear infections?
Treatment depends on the type and severity of the ear infection. Pain management, including over-the-counter pain relievers and warm compresses, can be helpful. For bacterial infections, antibiotics may be prescribed. It’s crucial to follow the healthcare provider’s instructions on medication use. In cases of frequent infections or persistent fluid, surgical options like ear tubes may be recommended.
Can ear infections be prevented?
While not all ear infections are preventable, certain steps can reduce the risk. These include practicing good hygiene, avoiding smoke exposure, breastfeeding infants when possible, and ensuring vaccinations are up-to-date. Keeping children away from known allergens and managing allergies can also help prevent ear infections.
When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
Consult a healthcare provider if you or your child experiences symptoms of an ear infection, especially if symptoms are severe, persist for more than a day, or are accompanied by a high fever. For infants under 6 months, seek medical advice at the first sign of infection.
Can ear infections lead to complications?
Although rare, untreated ear infections can lead to more serious complications such as hearing loss, speech or developmental delays in children, mastoiditis (a bone infection behind the ear), and meningitis. Prompt treatment reduces the risk of complications.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our discussion on the significance of accurately diagnosing and treating ear infections, it’s crucial to underscore the importance of this health issue. Ear infections, if left unchecked, can lead to more severe complications, including hearing loss, delayed speech development in children, and even the spread of infection to other parts of the body. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking appropriate treatment is not just advisable; it’s imperative for overall health and well-being.
Preventive measures play a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of ear infections. Simple steps such as practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, and keeping up with vaccinations can significantly reduce the incidence of these infections. Moreover, during flu and cold seasons, taking extra precautions to stay healthy can also help prevent the onset of ear infections.
However, prevention is just one part of the equation. Knowing when to seek professional advice is equally important. If you or your child experience symptoms of an ear infection, such as ear pain, difficulty hearing, or fluid drainage from the ear, consulting a healthcare professional promptly is critical. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the infection from worsening and safeguard against potential complications.
In summary, the effective diagnosis and treatment of ear infections are paramount to maintaining good auditory health and preventing further health issues. By taking preventive measures and seeking professional advice when necessary, individuals can protect themselves and their loved ones from the discomfort and risks associated with ear infections. Let’s prioritize our ear health today for a healthier, happier tomorrow.
References
When it comes to managing ear infections, having access to reliable and authoritative sources can significantly enhance your understanding and ability to effectively respond to this common health issue. Below, we provide a list of reputable references that offer in-depth insights into ear infection treatments. These resources are valuable for anyone looking to validate the information provided and expand their knowledge on the subject.
References on Ear Infection Treatment
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – The CDC website offers comprehensive guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of ear infections. It’s a credible source for public health information backed by extensive research.
Visit CDC Ear Infection Information - Mayo Clinic – Known for its patient-centered approach to care, the Mayo Clinic provides detailed articles on the symptoms, causes, and treatment options for ear infections, including both medical and home remedies.
Explore Mayo Clinic Ear Infection Resources - American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) – The AAP offers guidelines and articles on ear infections tailored to children, who are most often affected by this condition. Their resources are invaluable for parents and caregivers.
Read AAP Guidelines on Ear Infections - WebMD – As a trusted source for medical information, WebMD provides easy-to-understand content on ear infections, covering symptoms, causes, risk factors, and treatment methods, including when to see a doctor.
Check Out WebMD for Ear Infection Insights - Healthline – Healthline offers evidence-based information on health and wellness, including detailed guides on ear infection symptoms, treatments, and prevention strategies, all reviewed by medical experts.
Learn More at Healthline
These resources are designed to be user-friendly, catering to both medical professionals and the general public. They offer insights into the latest treatment methodologies, diagnostic tools, and preventative measures for ear infections. By consulting these sources, readers can ensure they are receiving accurate and current information, empowering them to make informed decisions about their health or the health of their loved ones.