Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Treatment: Dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs) are rare, abnormal connections between the arteries and veins in the dura mater, the tough outer membrane that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
These vascular disorders can lead to significant neurological symptoms and complications, making early diagnosis and effective treatment paramount.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of DAVFs, including their causes, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and the latest treatment options available to manage this condition.
Understanding Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Dural arteriovenous fistulas (dAVFs) are rare, abnormal connections that form between the arteries and veins within the dura mater, the tough outer layer that covers the brain and spinal cord. These unusual connections can disrupt the normal flow of blood, leading to various symptoms depending on their location and severity. Understanding dAVFs is crucial for early detection and effective management. This article delves into the causes and risk factors associated with dAVFs, as well as their prevalence and demographic trends.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of dural arteriovenous fistulas is often unclear, but they may develop as a result of several factors:
- Sinus Thrombosis: A blood clot in the brain’s venous sinuses can lead to increased pressure and eventually the formation of a dAVF.
- Head Injury: Trauma to the head can damage blood vessels and may contribute to the development of dAVFs.
- Surgery: Surgical procedures involving the brain or spinal cord might inadvertently lead to dAVFs.
- Infections: Infections that affect the brain or its surrounding structures can cause inflammation and damage to blood vessels, potentially leading to dAVFs.
- Genetic Predisposition: Although rare, some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to vascular malformations, including dAVFs.
Risk Factors
While dAVFs can occur in anyone, certain factors may increase the risk:
- Age: People over the age of 50 are more likely to develop dAVFs.
- Gender: There is a slight male predominance in the occurrence of dAVFs.
- Existing Vascular Conditions: Individuals with a history of blood vessel problems are at a higher risk.
Prevalence and Demographics
Dural arteriovenous fistulas are considered rare, with estimates suggesting they account for 10-15% of all intracranial arteriovenous malformations. The incidence rate is approximately 0.15 to 0.2 cases per 100,000 people per year. While dAVFs can occur at any age, they are most commonly diagnosed in middle-aged and elderly individuals. There is a slight male predominance, though certain types of dAVFs may be more common in women.
The demographics of dAVFs can vary based on geographic and genetic factors, but overall, they are a global concern with cases reported in diverse populations worldwide. Awareness and understanding of dAVFs among healthcare professionals and the general public are essential for timely diagnosis and treatment, which can significantly improve outcomes for affected individuals.
However, while the exact causes of dural arteriovenous fistulas remain somewhat elusive, certain conditions and risk factors are known to contribute to their development. Although rare, their impact on individuals’ health can be significant, making awareness and early detection crucial for effective management.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas (DAVF)
Recognizing the symptoms and understanding the importance of early detection are crucial for effective treatment and preventing potential complications. This section will explore the common symptoms associated with DAVF, highlight the significance of recognizing early signs, and guide you on when to seek medical advice.
Common Symptoms Associated with DAVF
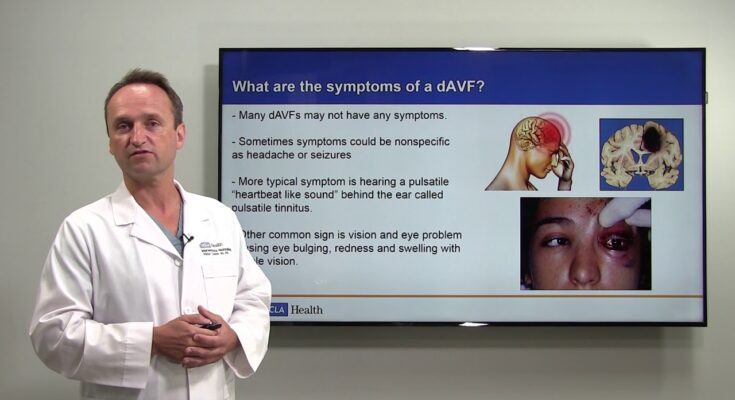
The symptoms of DAVF can vary significantly depending on the location and severity of the condition. Some individuals may experience no symptoms at all, while others may face serious neurological issues. Commonly reported symptoms include:
- Pulsatile tinnitus: A whooshing or ringing sound in one or both ears that syncs with the heartbeat.
- Headaches: Persistent or severe headaches that do not improve with typical treatment.
- Visual disturbances: Issues such as blurred vision or a decrease in visual acuity.
- Neurological deficits: Weakness, numbness, or even paralysis affecting one side of the body.
- Seizures: In severe cases, individuals may experience seizures.
Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Early detection of DAVF is vital for preventing the progression of the condition and avoiding irreversible damage. When DAVF is left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including stroke, brain damage, and even death. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms is the first step in seeking timely medical intervention, which can significantly improve the prognosis.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, particularly if they are persistent or worsening, it is crucial to seek medical advice as soon as possible. Early consultation with a healthcare professional can facilitate a prompt diagnosis through imaging tests such as MRI or angiography. Seeking medical advice early can also open up a range of treatment options that may be less invasive and more effective at an early stage of the condition.
However, understanding the common symptoms of Dural arteriovenous fistulas and the importance of early detection cannot be overstressed. Recognizing the signs and knowing when to seek medical advice are essential steps toward ensuring timely and effective treatment, ultimately enhancing the quality of life and outcomes for those affected by DAVF.
Diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
Diagnosing Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas (DAVF) is a critical step in ensuring patients receive the right treatment to manage this complex condition effectively. Understanding the diagnostic process, including the initial assessment, medical history, and the various imaging techniques used, can provide valuable insights into this condition.
Initial Assessment and Medical History
The diagnosis of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas begins with a thorough initial assessment and a detailed medical history. Healthcare professionals will first inquire about the patient’s symptoms, which may include headaches, ringing in the ears (tinnitus), and other neurological signs. Understanding the patient’s medical history, including any prior injuries, surgeries, or conditions that could contribute to the development of DAVF, is crucial. This step lays the foundation for a precise diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Imaging Techniques for Diagnosing DAVF
Advancements in imaging technology have significantly improved the diagnosis of DAVF. Below are the key imaging techniques utilized:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a non-invasive imaging method that provides detailed images of the brain and surrounding blood vessels. It’s particularly useful in diagnosing DAVF because it can detect abnormalities in blood flow and the condition of blood vessels. MRI is known for its ability to provide clear images without using ionizing radiation, making it a preferred choice for many patients and healthcare providers.
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
A CT scan is another critical imaging tool in diagnosing DAVF. It uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images of the brain, offering valuable insights into the presence of abnormal blood vessels. In some cases, a contrast dye may be injected to enhance the visibility of the blood vessels, further aiding in the diagnosis.
Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
DSA stands as the gold standard for diagnosing DAVF. This invasive procedure involves injecting a contrast dye into the bloodstream and taking X-ray images to visualize blood flow through the veins and arteries. DSA provides detailed information about the location and severity of the fistula, enabling precise diagnosis and guiding treatment planning.
Other Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
Besides the primary imaging techniques, other tests and procedures may be employed to diagnose DAVF accurately. These might include blood tests to rule out other conditions and ultrasound to assess blood flow. In some cases, additional MRI or CT angiography could be recommended to gather more information about the blood vessels’ structure and function.
By leveraging MRI, CT scans, DSA, and other diagnostic tests, healthcare providers can accurately identify DAVF and develop effective treatment strategies. Understanding these diagnostic steps is crucial for patients and families navigating the complexities of this condition, promoting informed decisions and optimized care outcomes.
Comprehensive Treatment Approaches for Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
This article explores the comprehensive treatment options available for DAVFs, ranging from medical management to emerging therapies and research in the field.
Medical Management
Medical management of DAVFs primarily focuses on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Medications may be prescribed to manage associated symptoms such as headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits. While medical management does not address the fistula directly, it plays a critical role in enhancing the patient’s quality of life and stabilizing their condition before more definitive treatments can be applied.
Minimally Invasive Treatments
Minimally invasive treatments have become a cornerstone in the management of DAVFs, offering effective outcomes with reduced risks and shorter recovery times compared to traditional surgery. These treatments include:
Embolization
Embolization is the most commonly utilized minimally invasive treatment for DAVFs. It involves the insertion of a catheter through the blood vessels to the site of the fistula, where embolic agents (materials designed to block the abnormal blood flow) are deployed. This procedure can significantly reduce the risk of bleeding and neurological damage by diverting blood flow away from the fistula. Embolization is often preferred due to its high success rate and lower risk of complications.
Surgical Options
In cases where minimally invasive treatments are not feasible or have been unsuccessful, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgery aims to disconnect the abnormal arterial-venous connections directly, restoring normal blood flow. This approach is generally reserved for more complex or aggressive DAVFs, as it involves higher risks and a longer recovery period. However, with skilled surgical teams and advanced techniques, surgical treatment can offer a definitive cure for DAVFs.
Emerging Therapies and Research in DAVF Treatment
The field of DAVF treatment is continuously evolving, with ongoing research focusing on improving existing therapies and developing new approaches. Innovations such as stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) offer non-invasive alternatives to traditional surgery and embolization, targeting the fistula with focused radiation to close off the abnormal connections. Additionally, gene therapy and regenerative medicine are emerging as potential future strategies to repair or regenerate the affected blood vessels.
Advancements in imaging technologies and diagnostic tools also play a crucial role in the treatment of DAVFs, enabling more precise localization and characterization of the fistulas. This not only improves the efficacy of treatments but also reduces the risk of complications by allowing for more targeted interventions.
Recovery and Management Post-Treatment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas
After receiving treatment for dural arteriovenous fistulas (DAVFs), understanding the journey towards recovery, effective management strategies, and preventive measures for recurrence is paramount. This guide provides insights into expected outcomes, rehabilitation, follow-up care, and tips for maintaining long-term health and preventing recurrence.
Expected Outcomes After Treatment
The treatment of DAVFs, whether through surgery, embolization, or radiotherapy, aims to eliminate the abnormal connections between arteries and veins, restoring normal blood flow. Patients can expect significant improvements in symptoms and a reduction in the risk of complications such as bleeding or stroke. However, the success rate and recovery process may vary depending on the location of the fistula, the treatment method, and the patient’s overall health. Most individuals experience a gradual alleviation of symptoms, with full recovery times ranging from a few weeks to several months.
Rehabilitation and Follow-up Care
Rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process, especially for patients who have experienced neurological symptoms or complications. A tailored rehabilitation program may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, aiming to improve mobility, strength, and cognitive functions.
Follow-up care is equally important to monitor the patient’s progress, manage any lingering symptoms, and detect potential complications early. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider, typically involving imaging tests such as MRI or angiography, help ensure the DAVF has been successfully treated and remains closed.
Managing Long-term Health and Preventing Recurrence
Long-term health management post-DAVF treatment involves adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying vigilant for new or returning symptoms, and adhering to a personalized care plan. Patients are advised to maintain a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, manage stress, and avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle modifications can contribute to overall vascular health and reduce the risk of other vascular conditions.
While recurrence of DAVFs is relatively rare, being informed about the signs and symptoms of a possible recurrence is crucial. Early detection and treatment are key to preventing complications. Patients should promptly report any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare provider.
By understanding the expected outcomes, participating actively in rehabilitation, adhering to follow-up care, and taking steps to maintain long-term health and prevent recurrence, patients can achieve the best possible recovery and quality of life post-treatment.
FAQs about Dural Arteriovenous Fistulas Treatment
What is a Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (DAVF)?
A Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (DAVF) is an abnormal connection between the arteries and veins in the dura mater, the tough outer membrane covering the brain and spinal cord. This condition can lead to significant blood flow issues, potentially causing a range of neurological symptoms and complications.
How is DAVF treated?
Treatment for DAVF often involves procedures aimed at closing off the abnormal connection between the arteries and veins. The most common treatment options include endovascular embolization, where materials are used to block the abnormal blood vessels, and surgical removal of the fistula. The choice of treatment depends on the fistula’s size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Is DAVF treatment safe?
While all medical procedures carry some risk, treatments for DAVF are generally considered safe and are performed by specialized interventional neuroradiologists or neurosurgeons. The risks associated with DAVF treatment are typically much lower than the risks of leaving the condition untreated, which can include stroke, brain hemorrhage, and other serious complications.
What can I expect after DAVF treatment?
Recovery after DAVF treatment varies depending on the specific procedure performed and the individual’s health condition. Many patients can expect a hospital stay of a few days following the procedure, with follow-up appointments to monitor healing and progress. Some may experience immediate relief of symptoms, while for others, it may take time for symptoms to improve.
Are there any side effects of DAVF treatment?
As with any medical procedure, there can be side effects associated with DAVF treatment. These may include discomfort at the site of the procedure, temporary neurological symptoms, or, in rare cases, more serious complications. Your healthcare team will discuss potential side effects with you in detail before the procedure.
How successful is DAVF treatment?
Success rates for DAVF treatment are generally high, with many patients experiencing significant improvement or complete resolution of their symptoms. The success of treatment depends on various factors, including the fistula’s location and complexity. Your medical team will provide you with more detailed information based on your specific situation.
Can DAVF recur after treatment?
Although relatively uncommon, it is possible for DAVF to recur after treatment. Regular follow-up with your healthcare provider is important to monitor for any signs of recurrence and to ensure the continued health of your brain and blood vessels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding dural arteriovenous fistulas, their diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for both healthcare professionals and patients.
Proactive healthcare, combined with patient awareness, can significantly contribute to the effective management of dAVFs, leading to improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Emphasizing these key points not only enhances the visibility of vital information but also underscores the importance of informed and engaged patient care in the context of dAVFs.