Diarrhea Treatment: Diarrhea, characterized by the frequent passage of loose, watery stools, is a common condition affecting people of all ages. It can lead to dehydration and, in severe cases, may be life-threatening.
Understanding the underlying causes, effective diagnosis methods, and comprehensive treatment options is essential for managing this condition and preventing complications.
Understanding Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common condition that affects people of all ages, characterized by frequent, loose, or watery stools. It is often a symptom of an infection in the digestive system, which can be caused by a variety of factors including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Understanding the symptoms and common causes of diarrhea is crucial for effective management and treatment. This guide provides an overview of what you need to know about diarrhea, including its symptoms and common causes, to help you better understand this condition.
Symptoms of Diarrhea
The primary symptom of diarrhea is the frequent passage of loose, watery stools. However, other symptoms can accompany this condition, indicating its severity and potential causes. These symptoms include:
- Abdominal Pain or Cramping: Many individuals experience discomfort or pain in the abdomen, which can range from mild to severe.
- Bloating: A feeling of fullness or swelling in the abdomen is common.
- Urgency: A sudden, urgent need to use the bathroom.
- Nausea and Vomiting: In some cases, diarrhea is accompanied by nausea or vomiting.
- Fever: A high temperature may indicate an infection.
- Blood or Mucus in Stool: This can be a sign of a more serious condition and should prompt immediate medical attention.
It’s important to note that while diarrhea is often mild and short-lived, lasting a few days, persistent or severe diarrhea that lasts for more than a couple of days requires medical evaluation to prevent dehydration and other complications.
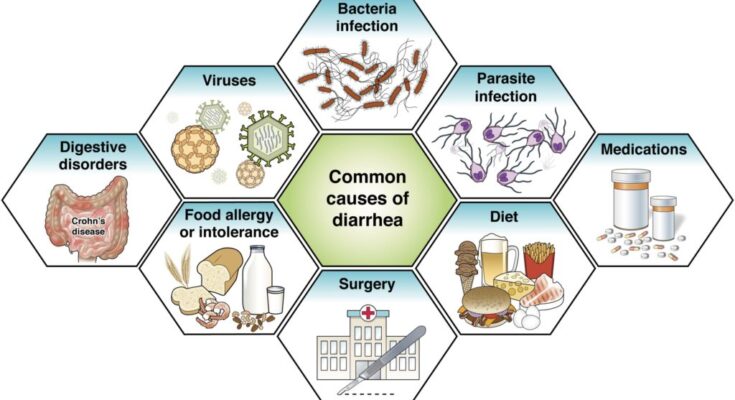
Common Causes of Diarrhea
Diarrhea can result from a variety of causes, with infections being among the most common. Here are some of the frequent culprits:
- Infections: Bacterial, viral, and parasitic infections are leading causes of diarrhea. Contaminated food or water is a common source of these infections.
- Medications: Certain medications, including antibiotics, can upset the balance of bacteria in your gut, leading to diarrhea.
- Digestive Disorders: Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, and ulcerative colitis can cause chronic diarrhea.
- Food Intolerances: Difficulty digesting certain types of food, such as lactose intolerance, can result in diarrhea after eating those foods.
- Artificial Sweeteners: Sorbitol and mannitol, found in chewing gum and diet foods, can cause diarrhea in some people.
If you experience persistent or severe diarrhea, it is important to seek medical attention to identify the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment. Staying hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet can also help manage symptoms and promote recovery.
Diagnosing Diarrhea
Diagnosing diarrhea is crucial for effective treatment and management. If you’re experiencing symptoms of diarrhea, understanding when to seek medical advice and the diagnostic processes involved can help in addressing the condition promptly and effectively.
When to See a Doctor
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional if diarrhea persists for more than a few days, if it’s accompanied by symptoms such as severe pain, dehydration, fever, or if you notice blood in the stool. These could be signs of a more serious condition that requires immediate attention.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The diagnostic process usually begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Your doctor will ask about the duration and frequency of your symptoms, your dietary habits, any recent travel, medications, and if you’ve been in contact with others who are ill. This information helps to identify potential causes and guide further testing.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests are essential in diagnosing the cause of diarrhea. These tests can include:
- Stool Tests: To check for the presence of bacteria, parasites, or viruses that can cause diarrhea. Sometimes, it’s also used to test for substances that might indicate a digestive disorder.
- Blood Tests: These can identify signs of infection, inflammation, or anemia. Blood tests can also reveal electrolyte imbalances and dehydration resulting from diarrhea.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans are sometimes necessary to visualize the digestive tract. These tests can help in identifying inflammation, blockages, or other abnormalities that might be causing diarrhea.
Specialized Tests for Chronic Diarrhea
For chronic diarrhea, which persists for several weeks, additional specialized tests might be required. These can include endoscopic procedures like colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy, where a camera is used to view the inside of the colon to detect inflammation, disease, or cancer.
By being informed about when to see a doctor and the types of tests that may be involved, you can better navigate the healthcare system and contribute to the management of your condition. Prioritizing your health by recognizing the signs and symptoms that warrant medical attention is the first step towards recovery and maintaining your well-being.
General Diarrhea Treatment Strategies
When dealing with diarrhea, implementing effective treatment strategies is crucial for quick recovery and maintaining overall health. Here’s a breakdown of general treatment approaches that are both SEO and readability friendly:
Hydration and Electrolyte Replacement
A top priority is to stay hydrated. Diarrhea can lead to a significant loss of fluids and electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium. Replenishing your body’s water and electrolyte levels is essential. Drinking plenty of fluids like water, clear broths, or oral rehydration solutions can help maintain hydration. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, as they can further dehydrate you.
Dietary Modifications
Modifying your diet temporarily can also alleviate symptoms. The BRAT diet, which stands for bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast, is often recommended for its blandness and ease on the digestive system. These foods are low in fiber and can help solidify stool. Incorporating other easily digestible foods like boiled potatoes, crackers, and cooked carrots can also be beneficial.
Foods to Eat and Avoid During a Diarrhea Episode
While some foods can help manage diarrhea, others may exacerbate the condition. It’s advisable to avoid dairy products, fatty foods, and spicy dishes, as they can irritate the digestive system. Also, steer clear of high-fiber foods like whole grains, nuts, and seeds until symptoms improve.
Over-the-Counter Medications
There are several over-the-counter medications that can help manage diarrhea. Anti-diarrheal medications like loperamide (Imodium) and bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-Bismol) can reduce the frequency of loose stools. However, they should be used with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional, especially in children.
Probiotics
Introducing probiotics into your diet can help restore the natural balance of gut bacteria, which can be disrupted during a bout of diarrhea. Probiotics are available in supplement form or in fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut. They have been shown to reduce the duration and intensity of diarrhea episodes.
Implementing these strategies can significantly aid in managing diarrhea and speeding up recovery. However, if symptoms persist or worsen, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Treating the Underlying Causes of Diarrhea
When it comes to treating diarrhea, addressing the underlying causes is paramount for effective relief and recovery. Let’s delve into the various treatments tailored to specific causes:
Antibiotics for Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections are a common cause of diarrhea, and antibiotics can be a powerful weapon in your healthcare arsenal. If a bacterial pathogen is identified as the culprit behind your symptoms, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help eradicate the infection. It’s crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the infection is fully treated and to avoid the development of antibiotic resistance.
Treatment for Parasites
Parasites, such as Giardia or Cryptosporidium, can also lead to diarrhea. These require targeted treatments that may differ from those used for bacterial infections. Antiparasitic medications are specifically designed to combat these unwelcome invaders, helping to alleviate symptoms and restore your health.
Adjusting Medications Causing Diarrhea
Sometimes, the medications you’re taking for other health issues can cause diarrhea as a side effect. If this is the case, it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider. They may adjust your dosage or switch you to an alternative medication that doesn’t upset your digestive system. However, you should never make changes to your medication regimen without professional guidance.
Managing Food Intolerances and Allergies
Food intolerances and allergies are also common culprits behind diarrhea. Lactose intolerance, gluten sensitivity, and other dietary triggers can lead to gastrointestinal distress. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is key to managing symptoms. Working with a dietitian or a healthcare provider can help you pinpoint specific food sensitivities and develop a diet plan that keeps your digestive system on track.
By tackling the root cause of diarrhea, whether it’s an infection, medication side effect, or dietary issue, you can find relief and prevent future occurrences. Remember, a tailored approach to treatment, based on the specific cause, is the most effective way to deal with diarrhea and ensure your digestive health.
Advanced Treatment Options for Chronic Diarrhea
There are now more advanced treatment options available that go beyond over-the-counter medications. These options are tailored to address the underlying causes of chronic diarrhea and provide relief to sufferers. It’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition. Here’s a closer look at some of the advanced treatment options:
Prescription Medications for Specific Conditions
Certain conditions such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) can be the culprits behind chronic diarrhea. For IBD, which includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, prescription medications can help reduce inflammation that contributes to diarrhea. This may include anti-inflammatory drugs, immune system suppressors, antibiotics, or a combination of these.
For IBS, which often involves a complex interplay of symptoms including diarrhea, treatment might focus on symptom management. Medications such as antispasmodics (to reduce cramping) and certain antidepressants (to manage pain and bowel movements) may be prescribed. Additionally, medications specifically targeting diarrhea predominant IBS (IBS-D) are also available and can significantly improve symptoms.
Surgical Interventions
In severe cases, particularly with certain types of IBD, surgical interventions may be considered. Surgery can remove damaged portions of the gastrointestinal tract, which can provide long-term relief from symptoms, including chronic diarrhea. However, surgery is typically considered only after other treatments have failed and depending on the specific condition and severity.
Nutritional Support and Dietary Counseling
Nutritional support and dietary counseling play a critical role in managing chronic diarrhea. A healthcare professional, often a dietitian, can work with patients to identify food triggers and develop a personalized eating plan. This may involve a low-FODMAP diet, which reduces certain carbohydrates that are hard to digest, or specific dietary adjustments to manage symptoms. Nutritional support can also include supplements if nutrient deficiencies are identified.
Implementing these advanced treatment options requires a thorough evaluation and diagnosis by healthcare professionals. They can provide a comprehensive approach that not only targets the symptoms but also addresses the root cause of chronic diarrhea. With the right treatment plan, individuals can see significant improvements in their symptoms and overall quality of life.
Home Remedies and Natural Treatments
When dealing with the discomfort and inconvenience of diarrhea, many people seek out home remedies and natural treatments as a first line of defense. These methods can be gentle on the body and offer relief with minimal side effects. Below are some effective strategies to manage diarrhea at home, focusing on hydration solutions, herbal teas, and the importance of rest and stress management.
Hydration Solutions and Recipes
One of the primary concerns with diarrhea is the risk of dehydration due to the loss of fluids. It’s crucial to replenish the body’s water and electrolytes. A simple yet effective hydration solution can be made at home by mixing:
- 1 liter of clean water
- 6 teaspoons of sugar
- Half a teaspoon of salt
This homemade oral rehydration solution can help maintain fluid balance without the need for over-the-counter solutions. Additionally, coconut water and herbal teas are excellent for staying hydrated, as they offer added nutrients and can be more palatable.
Herbal Teas and Supplements
Herbal teas are not only soothing but can also provide specific benefits for digestive health. Peppermint tea, for instance, is known for its antispasmodic properties, which can help relieve the cramping associated with diarrhea. Ginger tea is another excellent choice for its anti-inflammatory and anti-nausea effects. Both of these teas can be made from fresh or dried ingredients and consumed several times a day for relief.
Apart from teas, certain supplements such as probiotics can be beneficial. Probiotics help restore the natural balance of gut flora, which can be disrupted during a bout of diarrhea. They are available in various forms, including capsules, powders, and fermented foods like yogurt.
Importance of Rest and Stress Management
Rest is a critical component of the recovery process from any illness, including diarrhea. The body needs energy to heal, and rest provides this much-needed energy. Ensure you’re getting plenty of sleep and avoiding strenuous activities until symptoms improve.
Stress management is equally important, as stress can exacerbate gastrointestinal symptoms. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and gentle yoga can help manage stress levels and may aid in faster recovery.
By incorporating these home remedies and natural treatments into your care routine, you can ease the symptoms of diarrhea and support your body’s healing process. Remember, while these methods can be effective for mild cases, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider if symptoms persist or worsen.
Preventing Diarrhea
Preventing diarrhea is a multifaceted approach that encompasses good hygiene and sanitation practices, safe food handling and preparation, travel precautions, and vaccinations for certain causes of diarrhea. Implementing these strategies can significantly reduce the risk of developing diarrhea, which can be both uncomfortable and potentially dangerous, especially for vulnerable populations.
Hygiene and Sanitation Practices
Maintaining excellent hygiene and sanitation practices is crucial in preventing diarrhea. This includes regular handwashing with soap and water, especially before eating or preparing food and after using the bathroom. Ensuring that drinking water is safe, either by using water filters or by boiling water, is also essential in areas where water safety is a concern. Proper sewage disposal and avoiding open defecation are critical components of community sanitation efforts that can dramatically reduce the spread of diarrheal diseases.
Safe Food Handling and Preparation
Foodborne pathogens are a common cause of diarrhea. To prevent foodborne illnesses, it’s important to practice safe food handling and preparation methods. This includes thoroughly washing fruits and vegetables, cooking meat to the appropriate temperature, and avoiding cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods. Refrigerating perishable items promptly and being cautious about consuming street food or raw foods in areas with high incidences of diarrhea can also help prevent illness.
Travel Precautions
Travelers are often at risk for traveler’s diarrhea due to exposure to unfamiliar pathogens. To reduce this risk, travelers should practice caution by consuming only bottled or purified water, avoiding ice in drinks, eating foods that are cooked and served hot, and avoiding raw fruits and vegetables unless they can peel them themselves. Researching the destination’s sanitation practices and food safety standards before traveling can also prepare travelers to take necessary precautions.
Vaccinations
For certain causes of diarrhea, such as rotavirus and cholera, vaccinations are available and can provide effective protection. These vaccines are particularly important for children, travelers to areas with high rates of these diseases, and individuals with weakened immune systems. Consulting with a healthcare provider about necessary vaccinations before international travel or in response to local outbreaks can significantly reduce the risk of contracting these diseases.
Implementing these strategies can greatly reduce the incidence of diarrhea and its associated risks. By focusing on prevention through hygiene, safe food practices, travel precautions, and vaccinations, individuals and communities can protect themselves and contribute to overall public health.
FAQs about Diarrhea Treatment
What is the best initial treatment for diarrhea?
The first line of treatment for diarrhea is often hydration. Diarrhea can cause a loss of fluids and electrolytes, so it’s important to drink plenty of water, broth, or oral rehydration solutions. These solutions can help replace lost fluids and minerals to prevent dehydration. Avoid caffeine and alcohol as they can worsen dehydration.
Can I eat normally if I have diarrhea?
When you have diarrhea, it’s advisable to follow a bland diet initially. Foods such as bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (often referred to as the BRAT diet) can help make your stools firmer and are easy on your digestive system. Gradually reintroduce other foods back into your diet once your symptoms improve. Avoid dairy products, fatty foods, and foods high in fiber until you’re feeling better, as they can aggravate your symptoms.
Are over-the-counter medications safe for treating diarrhea?
Yes, over-the-counter (OTC) medications like loperamide (Imodium) can help reduce the frequency of diarrhea. However, they should be used with caution and not for prolonged periods unless advised by a healthcare professional. It’s also important to note that these medications are not suitable for everyone, including children under a certain age and people with specific health conditions. Always read the label and, if in doubt, consult a healthcare provider.
When should I see a doctor for diarrhea?
Seek medical advice if your diarrhea is severe, persists for more than two days without improvement, or is accompanied by symptoms such as high fever, blood in the stool, severe abdominal pain, or signs of dehydration (e.g., dizziness, dry mouth, very dark urine). These could be signs of a more serious condition that requires medical attention.
Can probiotics help with diarrhea?
Probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria found in certain yogurts and supplements, can help restore the natural balance of your gut flora and may help shorten the duration of diarrhea, especially if it’s caused by antibiotic use or a viral infection. While the evidence is promising, it’s a good idea to discuss probiotic use with a healthcare provider, particularly for children or individuals with underlying health conditions.
Is diarrhea contagious?
Diarrhea itself is not contagious, but it can be caused by infections that are contagious, such as those caused by viruses (e.g., norovirus), bacteria (e.g., salmonella, E. coli), or parasites. Good hygiene practices, including thorough handwashing with soap and water, can help prevent the spread of these infections.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our discussion on the significance of accurately diagnosing and treating diarrhea, it’s crucial to remember that this common condition not only affects millions worldwide but can also lead to severe dehydration and other health complications if not managed properly. The cornerstone of managing diarrhea effectively lies in understanding its underlying causes, which can range from infections and dietary issues to more serious chronic diseases.
We cannot stress enough the importance of seeking professional medical advice for diarrhea that is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other worrying symptoms such as high fever, blood in the stool, or signs of dehydration. Early and accurate diagnosis can pave the way for effective treatment, ensuring a quicker recovery and preventing complications.
Remember, while mild cases of diarrhea can often be managed at home with adequate hydration and diet adjustments, it’s essential to listen to your body. If you experience symptoms that are out of the ordinary or diarrhea that doesn’t improve within a few days, consulting a healthcare provider is the best course of action. They can offer tailored advice, conduct necessary tests, and prescribe treatment that’s appropriate for your specific situation.
Taking proactive steps towards understanding and managing diarrhea not only helps in alleviating the immediate discomfort but also plays a vital role in safeguarding your overall health and well-being. So, don’t hesitate to reach out for medical advice when needed. Your health is worth it.