Cushing Syndrome Treatment: Cushing Syndrome is a condition characterized by the body’s exposure to high levels of the hormone cortisol for an extended period.
Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a vital role in various bodily functions, including regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation, and controlling the sleep cycle.
However, excessive levels of cortisol can lead to a range of health issues, making early diagnosis and effective treatment of Cushing Syndrome crucial.
Understanding Cushing Syndrome
Cushing Syndrome is a condition characterized by the body’s exposure to high levels of the hormone cortisol for a prolonged period. Cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone,” plays a vital role in managing blood sugar levels, regulating metabolism, reducing inflammation, and assisting with memory formulation. However, when too much cortisol circulates in the body, it can lead to a host of health issues, including Cushing Syndrome. This condition can stem from various causes, affect multiple demographics, and present distinct symptoms that necessitate careful management and treatment.
Causes of Cushing Syndrome
The primary causes of Cushing Syndrome can be grouped into exogenous and endogenous factors. Exogenous causes are external factors, primarily the prolonged use of corticosteroid medications used to treat conditions like asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, and lupus. These medications can elevate cortisol levels, mimicking the effects of elevated cortisol produced by the body.
Endogenous causes originate from within the body and include conditions that lead to an overproduction of cortisol by the adrenal glands. These can be due to:
- Pituitary adenomas: benign tumors in the pituitary gland producing excessive amounts of ACTH, leading to increased cortisol production.
- Adrenal tumors: benign or malignant tumors directly on the adrenal glands that produce extra cortisol.
- Ectopic ACTH syndrome: non-pituitary tumors elsewhere in the body that secrete ACTH, stimulating the adrenal glands to produce more cortisol.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Cushing Syndrome is considered a rare condition, affecting about 10 to 15 people per million each year. It is more commonly diagnosed in adults between the ages of 20 and 50 years and is found to be more prevalent in females than males, with a ratio of approximately 3:1.
The demographics affected by Cushing Syndrome can vary based on the underlying cause. For example, endogenous causes such as pituitary adenomas (Cushing’s disease) are more common among young to middle-aged adults, while ectopic ACTH syndrome may be associated with older adults who have tumors in organs such as the lungs.
Understanding the causes and statistics of Cushing Syndrome is crucial for early detection and effective treatment. It highlights the importance of recognizing symptoms early and consulting healthcare professionals for diagnosis and management strategies tailored to each individual’s condition.
However, Cushing Syndrome is a complex condition with various causes and a specific demographic profile. Awareness and education about the syndrome are key to managing its effects and improving outcomes for those affected.
Signs and Symptoms of Cushing Syndrome
Understanding the signs and symptoms of this condition is crucial for early detection and management. This guide provides a detailed list of common symptoms, explores how these symptoms can impact daily life, and advises when to seek medical advice.
Detailed List of Common Symptoms
The symptoms of Cushing Syndrome can vary widely among individuals, but some are more common than others. Here are the most frequently observed signs:
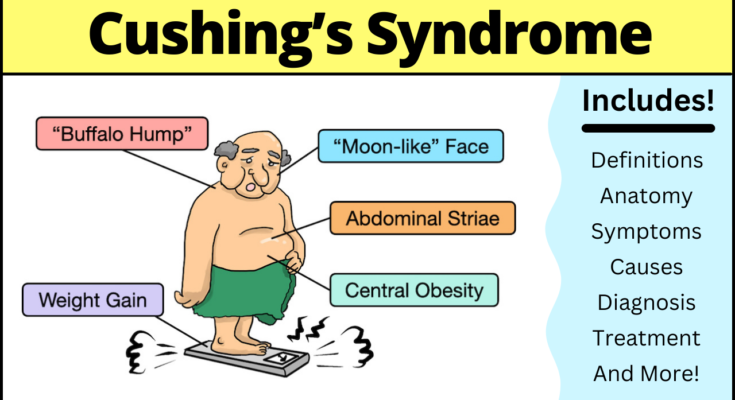
- Weight Gain: Particularly around the midsection and upper back, despite not changing eating habits significantly.
- Round, Red Face: Often described as a “moon face”.
- Skin Changes: Including thinning, bruising easily, and the development of purple or pink stretch marks on the abdomen, thighs, buttocks, arms, and breasts.
- Muscle Weakness: Leading to difficulty in standing up from a sitting position or climbing stairs.
- High Blood Pressure: Which can contribute to cardiovascular health issues.
- Mood Swings: Patients may experience significant emotional changes, including depression or anxiety.
- Increased Thirst and Urination: As the body’s balance of fluids and salts is affected.
- Fatigue: A pervasive sense of tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Irregular Periods for Women: Or the development of masculine features, such as facial hair.
- Decreased Libido and Erectile Dysfunction: In men, which can affect relationships and self-esteem.
How These Symptoms Impact Daily Life
The symptoms of Cushing Syndrome can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Weight gain and the appearance of stretch marks can lead to body image issues and social withdrawal. Muscle weakness and fatigue can make routine tasks challenging, affecting both personal and professional life. Emotional changes can strain relationships and make coping with stress more difficult. High blood pressure and increased susceptibility to infections can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you or someone you know is experiencing a combination of the symptoms listed above, it is essential to seek medical advice. This is particularly important if the symptoms are persistent, worsening, or impacting daily life. Early diagnosis and treatment of Cushing Syndrome can prevent the progression of symptoms and reduce the risk of complications. Healthcare providers can perform tests to diagnose the condition and recommend a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs.
However, recognizing the signs and symptoms of Cushing Syndrome is the first step toward managing this condition. By understanding how these symptoms can affect daily life, individuals can seek timely medical advice and receive the appropriate care to improve their health and well-being.
Diagnosis of Cushing Syndrome
Diagnosing this syndrome requires a detailed and systematic approach. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike. This article aims to elucidate the steps involved in diagnosing Cushing Syndrome, emphasizing the importance of initial assessments, specific diagnostic tests, and the pivotal role of endocrinologists.
Initial Assessments and Medical History Review
The journey to diagnosing Cushing Syndrome begins with a thorough initial assessment and review of the patient’s medical history. Healthcare providers start by gathering comprehensive information about the patient’s symptoms, lifestyle, and any prior health conditions. Symptoms such as rapid weight gain, particularly around the midsection and upper back, skin changes like bruising and purple stretch marks, and high blood pressure are red flags that may suggest Cushing Syndrome.
A detailed medical history review helps to identify potential causes of these symptoms, including the use of corticosteroid medications, which can mimic the effects of elevated cortisol levels. This initial screening is crucial for ruling out other conditions and determining the need for more specific diagnostic tests.
Specific Diagnostic Tests
Following the initial assessment, a series of specific diagnostic tests are employed to confirm the presence of Cushing Syndrome and identify its cause. These tests measure cortisol levels in the blood, urine, and saliva, providing comprehensive data on the body’s cortisol production:
- Blood Tests: Measure cortisol levels at different times of the day to detect abnormal fluctuations.
- Urine Tests: A 24-hour urinary free cortisol test measures the amount of cortisol excreted in the urine over a full day, offering insight into the body’s cortisol production.
- Saliva Tests: Assess cortisol levels late at night, when they’re typically lower, to detect elevated nighttime levels indicative of Cushing Syndrome.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans of the adrenal and pituitary glands can identify tumors or abnormalities causing excessive cortisol production.
These tests are critical for not only confirming the diagnosis of Cushing Syndrome but also for pinpointing the underlying cause, which is essential for effective treatment planning.
The Role of Endocrinologists in Diagnosing Cushing Syndrome
Endocrinologists play a central role in diagnosing Cushing Syndrome. Specialists in hormone-related diseases, they possess the expertise required to interpret diagnostic test results accurately and develop a comprehensive treatment strategy. Their deep understanding of the endocrine system enables them to distinguish Cushing Syndrome from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Upon confirming the diagnosis, endocrinologists work closely with patients to manage the condition, whether through medication, surgery, or other treatments. Their goal is to normalize cortisol levels, thereby alleviating symptoms and preventing complications.
Treatment Options for Cushing Syndrome
The management of this syndrome is critical to mitigate its symptoms and potential complications. Here, we explore the various treatment options, emphasizing the importance of tailoring these interventions to individual patient needs.
Surgical Treatments and Their Applicability
Surgical intervention is often considered the primary treatment for Cushing Syndrome, especially when a specific tumor causing excess cortisol production can be identified. The type of surgery depends on the tumor’s location:
- Pituitary Tumors: The most common cause of Cushing Syndrome is a tumor in the pituitary gland (Cushing’s disease). Transsphenoidal surgery, where the tumor is removed through the nose and sphenoid sinus, is the preferred method. This approach boasts a high success rate in patients with pituitary adenomas.
- Adrenal Tumors: When the syndrome results from tumors in the adrenal glands, surgical removal of the affected gland(s) is often necessary. This procedure, known as adrenalectomy, can significantly improve symptoms and hormone levels.
- Ectopic ACTH Syndrome: For those with tumors outside the pituitary or adrenal glands that produce ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), locating and removing these tumors can be challenging but is crucial for treatment.
Medications Used in the Treatment of Cushing Syndrome
In cases where surgery is not feasible or as an adjunct to surgical treatment, medications can play a pivotal role. These drugs aim to reduce cortisol production or its effects:
- Ketoconazole, Metyrapone, and Etomidate are used to inhibit cortisol synthesis.
- Mifepristone blocks the action of cortisol on its receptors.
- Pasireotide targets the pituitary adenomas to reduce ACTH production in Cushing’s disease.
These medications can have side effects and require careful monitoring by a healthcare professional.
Radiation Therapy: Purposes and Outcomes
Radiation therapy serves as an alternative or adjunct to surgery, particularly for pituitary tumors when surgery is not an option or has not been fully successful. Techniques such as stereotactic radiosurgery (e.g., Gamma Knife) deliver targeted radiation to the tumor, aiming to reduce its size and hormone secretion over time. This approach may take months or years to achieve its full effect, and ongoing monitoring of hormone levels is necessary.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Given the complexity of Cushing Syndrome and the variability in its causes and presentations, personalized treatment plans are paramount. These plans consider the patient’s specific situation, including the cause of the syndrome, the presence of other health conditions, and the patient’s overall health and preferences. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the treatment plan are crucial to manage the condition effectively and minimize side effects.
However, the treatment of Cushing Syndrome encompasses a range of options, including surgery, medication, and radiation therapy. A personalized approach, guided by a team of healthcare professionals, ensures the best possible outcomes for those affected by this condition.
Managing Cushing Syndrome
Managing Cushing Syndrome effectively requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses lifestyle modifications, psychological support, and diligent long-term health monitoring. This multifaceted strategy not only addresses the immediate symptoms but also mitigates the long-term health risks associated with the syndrome. Here’s a closer look at each aspect to help individuals navigate their journey towards better health and well-being.
Lifestyle Modifications for Symptom Management
Lifestyle changes play a pivotal role in managing the symptoms of Cushing Syndrome. These adjustments can help reduce the severity of symptoms and improve quality of life. Key strategies include:
- Balanced Diet: A nutritious diet that limits high-calorie foods can help manage weight gain and reduce the risk of developing diabetes, which are common concerns in Cushing Syndrome. Incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is advisable.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise can help combat weight gain, strengthen muscles, and improve bone density. It’s important to choose activities that are enjoyable and sustainable in the long run, taking into consideration any physical limitations.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage the stress that often exacerbates Cushing Syndrome symptoms. Finding stress-relief activities that work for you is crucial.
Psychological Support and Counseling
Cushing Syndrome can take a toll on mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and emotional distress. Seeking psychological support and counseling can be incredibly beneficial:
- Professional Counseling: A psychologist or psychiatrist can provide coping strategies to deal with the emotional and psychological challenges of the condition.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide a sense of community and mutual support. Online forums and local support groups can be valuable resources.
Long-term Health Monitoring and Follow-up Care
Ongoing health monitoring and follow-up care are essential to manage Cushing Syndrome effectively. This includes:
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Frequent visits to the healthcare provider can help monitor the condition’s progression and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
- Monitoring for Complications: Regular screening for potential complications, such as osteoporosis, hypertension, and diabetes, is critical. Early detection can lead to more effective management.
- Adjusting Treatment Plans: Treatment plans may need to be adjusted over time based on how the condition evolves and responds to current therapies.
However, managing Cushing Syndrome is a dynamic process that requires a holistic approach. By integrating lifestyle modifications, psychological support, and vigilant long-term health monitoring, individuals can effectively manage their symptoms and improve their overall quality of life. Remember, each person’s journey is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. Collaborating closely with healthcare professionals to tailor the management plan to individual needs is key to navigating Cushing Syndrome successfully.
Recent Advances in Cushing Syndrome Treatment
This article delves into the latest research findings, emerging treatments, and the promising future of Cushing Syndrome management, offering hope to those affected by this challenging endocrine disorder.
Summary of the Latest Research Findings
Recent studies have focused on improving diagnostic methods and treatment options for Cushing Syndrome. Innovative diagnostic tools have been developed, enabling earlier and more accurate detection of the condition. These advancements are crucial, as early diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes. In terms of treatment, research has highlighted the effectiveness of new medication options that offer better control over cortisol levels with fewer side effects. Additionally, advancements in surgical techniques have led to more successful outcomes for patients requiring tumor removal.
Emerging Treatments and Therapeutic Approaches
The landscape of Cushing Syndrome treatment is evolving, with several promising therapies on the horizon. Among these, targeted therapies aimed at the molecular drivers of the condition are showing great potential. These treatments focus on inhibiting the production of cortisol or blocking its effects on the body, offering a more precise approach than traditional methods.
Another area of interest is the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques. These procedures, including endoscopic surgery, provide options for patients with adrenal tumors, resulting in shorter recovery times and reduced complications. Furthermore, the exploration of gene therapy as a potential treatment avenue opens up new possibilities for addressing the root causes of Cushing Syndrome.
The Future of Cushing Syndrome Management
Looking ahead, the future of Cushing Syndrome management appears bright, with ongoing research aimed at refining and discovering new treatment modalities. Personalized medicine, which tailors treatment to the individual’s genetic makeup, is expected to play a significant role in future therapies. This approach promises to improve the efficacy of treatment plans and minimize adverse effects, offering a more patient-centered approach to care.
In addition, continuous advancements in technology and medicine are expected to further enhance diagnostic tools, making it possible to identify Cushing Syndrome at its earliest stages. Early detection, combined with innovative treatment options, will significantly improve the quality of life for those affected by this condition.
However, the recent advances in the treatment of Cushing Syndrome reflect a growing understanding of the condition and a commitment to improving patient outcomes. With emerging treatments and a focus on personalized care, the future for those managing Cushing Syndrome is looking increasingly optimistic. As research continues to evolve, it is expected that even more effective and targeted therapies will become available, marking a new era in the management of this complex condition.
FAQs About Cushing Syndrome Treatment
What is Cushing Syndrome?
Cushing Syndrome is a hormonal disorder caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol. It can result from taking glucocorticoid drugs or the body producing excess cortisol due to tumors.
How is Cushing Syndrome treated?
Treatment for Cushing Syndrome varies based on the underlying cause. Options include medication to control cortisol production, surgery to remove tumor(s), radiation therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage symptoms. A healthcare provider will recommend the best treatment plan based on individual conditions.
Can Cushing Syndrome be cured?
Yes, in many cases, Cushing Syndrome can be cured, especially when it is caused by benign tumors that can be surgically removed. However, the prognosis depends on the specific cause, the presence of any complications, and the overall health of the individual.
What are the side effects of Cushing Syndrome treatment?
Side effects depend on the treatment type. Surgical treatments can involve risks of infection, bleeding, or complications from anesthesia. Medications may cause side effects such as gastrointestinal issues, mood changes, or increased risk of infection. Your healthcare provider will discuss potential side effects and how to manage them.
How long does treatment for Cushing Syndrome take?
The duration of treatment varies. Surgery may offer a quicker resolution, but recovery times can vary. Medication and lifestyle changes may require a longer duration to see significant improvements. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers are crucial to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
Will I need to take medication for life after treatment for Cushing Syndrome?
This depends on the cause of Cushing Syndrome and the treatment approach. Some individuals may need lifelong medication to manage cortisol levels if the source of excess cortisol cannot be entirely removed or if the condition recurs.
Can lifestyle changes help with Cushing Syndrome?
While lifestyle changes alone cannot cure Cushing Syndrome, they can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Recommendations may include a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and avoiding substances that can worsen symptoms.
Is it possible for Cushing Syndrome to come back after treatment?
Yes, there is a possibility of recurrence, especially if the treatment does not completely remove or resolve the underlying cause. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are essential to detect and address any recurrence early.
Can I see a specialist for Cushing Syndrome treatment?
Absolutely. It’s often recommended to consult an endocrinologist, a specialist in hormonal disorders, for diagnosis and treatment of Cushing Syndrome. They can provide specialized care and a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
What support is available for individuals undergoing treatment for Cushing Syndrome?
Support from healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, surgeons, and mental health specialists, is crucial. Additionally, support groups and counseling services can offer emotional support and practical advice for managing the condition and its treatment.
Conclusion
The journey through understanding Cushing Syndrome underscores the critical importance of early diagnosis and the implementation of effective treatment strategies. Recognizing the signs and symptoms early on can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected, reduce the risk of complications, and potentially lead to a more favorable prognosis. It’s essential to be vigilant about the health signals our bodies send us, as this condition can often masquerade as other less serious health issues.
If you suspect that you or someone you know may be exhibiting symptoms of Cushing Syndrome, it’s imperative to seek medical advice promptly. Healthcare professionals can provide a comprehensive evaluation, confirm a diagnosis through appropriate tests, and discuss the most effective treatment options tailored to individual needs. Remember, taking action early can make a substantial difference in the outcome.
We encourage everyone to prioritize their health and to not hesitate in consulting with a medical expert if there are concerns about Cushing Syndrome or any other health anomalies. Your health is invaluable, and taking proactive steps towards managing your well-being is the best investment you can make.