Cryoglobulinemia Symptoms: Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood, known as cryoglobulins, which precipitate or clump together at low temperatures.
This unique condition can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, affecting various organs and systems within the body.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of cryoglobulinemia is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management.
What is Cryoglobulinemia?
Cryoglobulinemia is a rare condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood, known as cryoglobulins, that precipitate or clump together at low temperatures. This unique property of cryoglobulins can lead to a range of symptoms and complications, as these clumps can block blood vessels and restrict blood flow to various parts of the body. The resulting symptoms often include skin rashes, joint pain, weakness, and damage to organs such as the kidneys and liver. Understanding cryoglobulinemia is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management of the condition.
Types of Cryoglobulinemia
There are three main types of cryoglobulinemia, each defined by the kind of immunoglobulins (antibodies) making up the cryoglobulins and the underlying causes associated with them:
- Type I Cryoglobulinemia: This type is associated with monoclonal immunoglobulins, usually linked to hematological conditions like multiple myeloma or lymphoproliferative disorders. It is the least common but can be the most severe in terms of organ involvement.
- Type II Cryoglobulinemia: Also known as mixed cryoglobulinemia, this type involves both monoclonal and polyclonal immunoglobulins. It is often associated with chronic infections, such as hepatitis C.
- Type III Cryoglobulinemia: Involves polyclonal immunoglobulins and is frequently linked to autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammatory conditions. This type is often triggered by infections, autoimmune diseases, or other underlying health conditions.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Cryoglobulinemia is considered a rare disease, though its exact prevalence is challenging to determine due to the range of underlying causes and the variability of symptoms. Estimates suggest that mixed cryoglobulinemia (Type II) is the most common form, often associated with hepatitis C infections. The prevalence of cryoglobulinemia varies by region, largely influenced by the distribution of hepatitis C and other contributing diseases.
Demographically, cryoglobulinemia can affect individuals of any age, but it is more frequently diagnosed in adults between the ages of 40 and 60. There appears to be a slight female predominance in most studies. The demographics affected by cryoglobulinemia can also vary depending on the underlying cause; for example, regions with higher rates of hepatitis C infection may see higher instances of the disease.
However, cryoglobulinemia is a complex condition with varying types and symptoms, affecting a diverse population. Awareness and understanding of this rare disease are essential for timely diagnosis and treatment, improving outcomes for those affected.
Symptoms of Cryoglobulinemia
Below, we provide a detailed breakdown of the common symptoms, delve into the rare or severe symptoms, and explain how symptoms can vary between the different types of cryoglobulinemia.
Common Symptoms of Cryoglobulinemia
The symptoms of cryoglobulinemia often relate to the decreased blood flow that results from the clumping of cryoglobulins. Common symptoms include:
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon: This is characterized by a color change in your fingers and toes, usually in response to cold temperatures or stress.
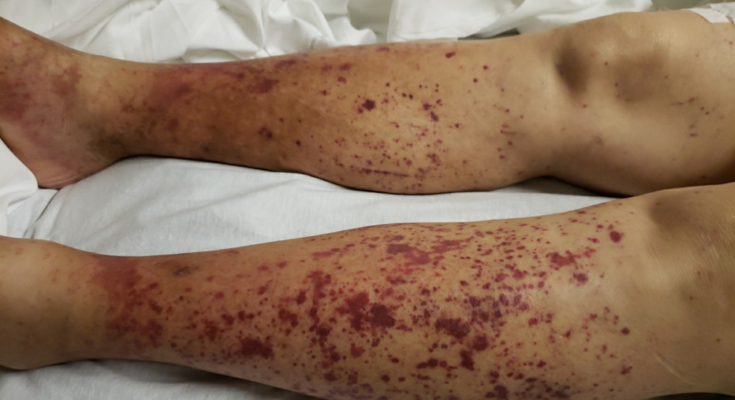
- Skin Lesions: Purpura (purple-colored spots on the skin), usually on the legs, is a typical sign.
- Weakness and Fatigue: A general feeling of tiredness and lack of energy is common among sufferers.
- Joint Pain: Arthralgia or arthritis, particularly in the small joints of the hands and feet, can occur.
- Numbness or Tingling: Peripheral neuropathy, affecting the nerves, can lead to these sensations.
Rare or Severe Symptoms
In some cases, cryoglobulinemia can lead to more severe health issues, including:
- Kidney Damage: Glomerulonephritis, caused by the deposition of cryoglobulins in the kidneys, can lead to kidney failure if untreated.
- Skin Ulcers: Severe cases might progress from purpura to open, non-healing sores.
- Breathing Problems: Lung involvement can lead to shortness of breath or chronic cough.
- Digestive Issues: Some individuals may experience abdominal pain or blood in the stool due to vasculitis affecting the stomach and intestines.
Variations Between Types of Cryoglobulinemia
Cryoglobulinemia is categorized into three main types, each with distinct symptoms:
- Type I: This type is often associated with blood disorders like multiple myeloma. It primarily leads to symptoms related to blood circulation, such as Raynaud’s phenomenon and skin necrosis.
- Type II and III: These types are mixed cryoglobulinemias and are more commonly associated with autoimmune disorders and chronic infections like hepatitis C. They often present with more systemic symptoms, including joint pain, kidney involvement, and widespread vasculitis.
Understanding the variations between these types is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. The type of cryoglobulinemia not only influences the symptomatology but also guides the therapeutic approach.
If you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms, particularly in combination or with a known risk factor for cryoglobulinemia, seeking medical advice is essential. Early intervention can improve outcomes and quality of life for those affected by this complex condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Cryoglobulinemia
Understanding the causes and risk factors of cryoglobulinemia is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. One significant cause is immune system dysfunction, which we will explore in detail.
Immune System Dysfunction: A Primary Cause
The immune system plays a vital role in protecting the body from infections and diseases. However, when it malfunctions, it can produce antibodies that instead of fighting infections, target the body’s own tissues, leading to autoimmune diseases. Cryoglobulinemia often arises as a part of this autoimmune process. The abnormal cryoglobulins produced are essentially immune complexes that can precipitate at cold temperatures, leading to inflammation and damage to blood vessels, a condition known as vasculitis.
Types of Cryoglobulinemia Linked to Immune Dysfunction
Cryoglobulinemia is classified into three types, based on the kind of antibodies involved:
- Type I Cryoglobulinemia is typically associated with blood cancers, such as multiple myeloma or lymphoma, where a single type of antibody is produced in excess.
- Type II and Type III Cryoglobulinemia are both mixed types, involving more than one kind of antibody. These forms are often associated with autoimmune diseases like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, and chronic infections such as hepatitis C, which can trigger an abnormal immune response.
Risk Factors for Developing Cryoglobulinemia
Several factors can increase the risk of developing cryoglobulinemia, particularly relating to immune system dysfunction:
- Chronic Infections: Hepatitis C is a significant risk factor for types II and III cryoglobulinemia. Other infections, such as HIV and hepatitis B, can also contribute.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Conditions like Sjögren’s syndrome, lupus, and rheumatoid arthritis can predispose individuals to cryoglobulinemia due to their impact on the immune system.
- Blood Cancers: Lymphoma and multiple myeloma, which affect the blood’s plasma cells, can lead to type I cryoglobulinemia.
- Genetic Factors: There may be a genetic predisposition that affects the immune system, increasing the likelihood of developing cryoglobulinemia.
Recognizing the risk factors and how they contribute to the disease can help in early detection and treatment, potentially mitigating the severe complications associated with cryoglobulinemia. If you suspect you are at risk or are experiencing symptoms of cryoglobulinemia, consulting a healthcare provider for a comprehensive evaluation is crucial.
Diagnosis of Cryoglobulinemia
Recognizing and diagnosing cryoglobulinemia early is crucial for managing symptoms and preventing severe complications. This article delves into the significance of early diagnosis, the various tests and procedures used to identify cryoglobulinemia, and the challenges faced during its diagnosis.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia is paramount for several reasons. It enables healthcare providers to initiate treatment strategies promptly, potentially preventing the progression of the disease and avoiding irreversible organ damage. Early intervention can also alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and decrease the risk of complications such as kidney failure and nerve damage. Since cryoglobulinemia can be secondary to other conditions like hepatitis C, early detection can also help in managing the underlying cause, further preventing disease progression.
Tests and Procedures for Diagnosing Cryoglobulinemia
Diagnosing cryoglobulinemia involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests, which help in confirming the presence of cryoglobulins and assessing organ involvement. The following are the primary tests and procedures used:
- Blood Tests (Cryocrit): The most direct method for diagnosing cryoglobulinemia is through blood tests that measure the level of cryoglobulins in the blood, known as cryocrit. This test involves cooling a blood sample and then warming it to observe if cryoglobulins precipitate, indicating their presence.
- Biopsy of Affected Organs: In cases where organ involvement is suspected, a biopsy may be performed to assess the extent of damage and the presence of cryoglobulins within tissue. This is particularly common for kidneys and skin, where cryoglobulinemic vasculitis most often manifests.
- Imaging Studies for Organ Involvement: Imaging studies, including ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI, can be used to detect signs of organ involvement and damage. These studies are crucial for evaluating the extent of the condition and guiding treatment decisions.
Challenges in Diagnosing Cryoglobulinemia
Despite advances in medical diagnostics, several challenges remain in diagnosing cryoglobulinemia accurately and promptly. The symptoms of cryoglobulinemia can be nonspecific and mimic those of other conditions, leading to potential misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. Additionally, the cryoglobulins can degrade if the blood sample is not handled properly, resulting in false negatives. Another challenge is the variability in the level of cryoglobulins, which can fluctuate and sometimes be undetectable, necessitating repeated tests over time.
Moreover, the interpretation of test results requires expertise, as the presence of cryoglobulins alone does not confirm cryoglobulinemia unless accompanied by relevant clinical symptoms or organ involvement. Collaboration among healthcare providers across specialties is often necessary to accurately diagnose and manage cryoglobulinemia.
Early detection plays a critical role in preventing severe complications and improving patient outcomes. Despite the challenges in diagnosing cryoglobulinemia, a combination of targeted blood tests, biopsies, and imaging studies can help healthcare providers make an accurate diagnosis and tailor treatment plans to the needs of individual patients.
Treatment Options for Cryoglobulinemia
Managing this condition effectively is crucial to maintaining quality of life and preventing complications. Below, we delve into the general strategies for managing symptoms, medications, lifestyle changes, and the importance of regular monitoring and follow-up care for individuals diagnosed with cryoglobulinemia.
General Strategies for Managing Symptoms
The foundation of managing cryoglobulinemia lies in addressing its underlying cause, if known, and alleviating symptoms. Treatment strategies are tailored to the severity of the condition and the specific symptoms experienced by the patient. For some, this may involve simply avoiding cold temperatures to prevent the proteins from clumping. However, more severe cases might require a comprehensive approach including medications, lifestyle adjustments, and ongoing monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Medications Used to Treat Cryoglobulinemia
The choice of medication for treating cryoglobulinemia depends on the underlying cause and the symptoms presented. Commonly used treatments include:
- Corticosteroids: These are anti-inflammatory medications that can help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
- Rituximab: An immunosuppressive drug used to target specific cells of the immune system, helping to reduce the production of cryoglobulins.
- Plasmapheresis: Although not a medication, this procedure involves filtering the blood to remove cryoglobulins and is often used in severe cases.
- Antiviral Medications: In cases where cryoglobulinemia is linked to viral infections like hepatitis C, antiviral treatments can be effective.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, certain lifestyle adjustments can help manage symptoms:
- Avoiding Cold Exposure: Keeping warm can prevent cryoglobulins from clumping, reducing symptoms.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet supports overall health, potentially mitigating the severity of symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise can improve circulation and overall well-being, though it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
Importance of Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Care
Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential for managing cryoglobulinemia effectively. These appointments allow for the monitoring of the condition’s progression, adjustments to treatment plans as needed, and the management of any complications that may arise. Additionally, regular blood tests can help track the levels of cryoglobulins in the blood, providing valuable information for guiding treatment decisions.
However, managing cryoglobulinemia involves a multifaceted approach that includes medications, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. By working closely with healthcare professionals and adhering to a personalized treatment plan, individuals with cryoglobulinemia can manage their symptoms and maintain a high quality of life.
Preventing Cryoglobulinemia: Strategies and Importance
While it’s challenging to prevent cryoglobulinemia entirely due to its association with other underlying health conditions, adopting strategies to manage these conditions and mitigate risk factors can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing cryoglobulinemia.
Can Cryoglobulinemia Be Prevented?
Direct prevention of cryoglobulinemia might not always be possible, especially when it is secondary to other medical conditions such as hepatitis C, autoimmune diseases, or certain infections. However, early detection and treatment of these underlying conditions can play a crucial role in preventing the development or progression of cryoglobulinemia.
Role of Managing Underlying Conditions and Risk Factors
- Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatitis C: Since hepatitis C is a common cause of cryoglobulinemia, regular screening for hepatitis C in high-risk populations, followed by prompt antiviral treatment, can decrease the risk of developing cryoglobulinemia.
- Autoimmune Disease Management: For individuals with autoimmune diseases, effective management of their condition through medication and lifestyle adjustments can minimize inflammation and reduce the risk of cryoglobulinemia.
- Infection Control: Preventing and promptly treating infections can help avoid the trigger for cryoglobulinemia formation, especially in immunocompromised individuals or those with a history of diseases that could lead to cryoglobulinemia.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption, can support overall immune function and reduce the risk of conditions associated with cryoglobulinemia.
- Regular Monitoring: For those already diagnosed with conditions that could lead to cryoglobulinemia, regular monitoring for the appearance of cryoglobulins in the blood can aid in early detection and management.
- Educating At-Risk Individuals: Education about the signs and symptoms of cryoglobulinemia among individuals with underlying risk factors can encourage early medical consultation and intervention.
However, while it might not be possible to prevent cryoglobulinemia entirely, focusing on the management of underlying conditions and risk factors can significantly lower the chances of its development. Regular medical check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt attention to any symptoms can contribute to early detection and effective management of cryoglobulinemia, improving outcomes and quality of life for those at risk.
Living with Cryoglobulinemia
Managing symptoms and navigating daily activities requires patience, knowledge, and support. This guide aims to provide practical advice and resources to help patients with cryoglobulinemia live fuller, more comfortable lives.
Managing Daily Life and Symptoms
1. Stay Warm: One of the most crucial steps in managing cryoglobulinemia is to maintain a warm body temperature. Cold temperatures can cause the proteins in your blood (cryoglobulins) to clump together, leading to various symptoms. Dress in layers, use thermal clothing, and keep your home at a comfortable temperature. Portable hand warmers can be a handy accessory for outings.
2. Healthy Lifestyle Choices: A balanced diet and regular exercise can improve general health and help manage symptoms. Focus on foods rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support your immune system. Gentle exercises, like walking or yoga, can improve circulation and reduce symptoms, but always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
3. Medication Management: If you’re on medication to manage your condition, adherence is key. Understand your medications, their purposes, and potential side effects. Set reminders to take your medications at the same time every day and keep regular appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your condition.
4. Avoid Triggers: Besides cold, other factors like stress, fatigue, and certain medications can trigger or worsen symptoms. Identify your triggers and develop strategies to avoid or mitigate them. This might include stress management techniques, ensuring adequate rest, and discussing medication adjustments with your doctor.
Support and Resources
1. Specialist Care: Regular consultations with healthcare professionals who specialize in cryoglobulinemia or related fields (like rheumatology or hematology) are vital. These specialists can provide tailored advice, monitor your condition, and adjust treatments as necessary.
2. Support Groups: Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can be incredibly beneficial. Look for cryoglobulinemia support groups, both in-person and online. These communities offer emotional support, share practical tips, and provide information about managing the condition.
3. Educational Resources: Educate yourself about cryoglobulinemia through reliable sources such as the Mayo Clinic, the National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD), and the Vasculitis Foundation. Understanding your condition can empower you to make informed decisions about your care.
4. Mental Health Support: Living with a chronic condition can be challenging, not just physically but also emotionally and mentally. Consider seeking support from a mental health professional experienced in dealing with chronic illnesses. They can provide strategies to cope with the emotional aspects of living with cryoglobulinemia.
Living with cryoglobulinemia requires adapting to a new normal, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Remember, you are not alone—resources and communities are available to help you navigate this journey.
FAQs about Cryoglobulinemia
What is Cryoglobulinemia?
Cryoglobulinemia is a medical condition characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood, known as cryoglobulins, which can clump together in colder temperatures. This clumping can lead to blockages in blood vessels, causing a range of symptoms and potentially affecting various organs.
What Causes Cryoglobulinemia?
The exact cause of cryoglobulinemia can vary. It is often associated with other diseases, such as hepatitis C, autoimmune diseases, and certain types of cancer. In some cases, the cause remains unknown, which is referred to as idiopathic cryoglobulinemia.
What Are the Symptoms of Cryoglobulinemia?
Symptoms of cryoglobulinemia can vary widely depending on the individual and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes (particularly on the legs), weakness, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. More severe cases can lead to complications such as kidney damage or circulatory problems.
How is Cryoglobulinemia Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of cryoglobulinemia typically involves a combination of blood tests, which can detect the presence of cryoglobulins, along with tests to assess any associated conditions or organ damage. A thorough medical history and physical examination are also crucial to the diagnostic process.
Can Cryoglobulinemia Be Treated?
Yes, cryoglobulinemia can be treated, although the specific approach depends on the underlying cause, if known, and the severity of the symptoms. Treatment options may include medications to manage symptoms, treatments to address the underlying condition (if applicable), and in some cases, plasmapheresis, a procedure to remove the cryoglobulins from the blood.
Is Cryoglobulinemia Contagious?
No, cryoglobulinemia is not contagious. It is a condition related to the immune system and the blood, not caused by an infectious agent that can be passed from person to person.
Can Lifestyle Changes Help with Cryoglobulinemia?
While lifestyle changes cannot cure cryoglobulinemia, they can help manage symptoms and improve overall health. Staying warm, avoiding cold temperatures, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise can be beneficial. It’s also important for individuals with cryoglobulinemia to avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as these can exacerbate symptoms.
Is Cryoglobulinemia a Common Condition?
No, cryoglobulinemia is considered a rare condition. However, its exact prevalence is difficult to determine due to the wide range of symptoms and the association with other diseases.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of cryoglobulinemia is paramount for anyone concerned about their health or experiencing unexplained symptoms. This condition, characterized by the presence of abnormal proteins in the blood that clump together at lower temperatures, can lead to a range of complications if left untreated. Symptoms such as joint pain, skin rashes, weakness, and more severe manifestations like kidney damage underline the significance of early detection and diagnosis.
It’s crucial to remember that while this information serves as a guide to understanding cryoglobulinemia, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms that align with those associated with cryoglobulinemia, it’s essential to seek advice from a healthcare professional. Early consultation can lead to a timely diagnosis, enabling an effective treatment plan to be put in place. Healthcare providers can offer comprehensive care and guidance tailored to each individual’s condition, enhancing the chances of managing the symptoms effectively and maintaining a good quality of life.
We encourage readers to be proactive about their health. If you suspect that you may have symptoms of cryoglobulinemia, do not hesitate to consult with a medical professional. Early intervention is key to managing this condition effectively and preventing potential complications. Remember, your health is worth the time and effort to ensure you receive the appropriate care and support.
By staying informed and attentive to your body’s signals, you can take a significant step towards safeguarding your health against conditions like cryoglobulinemia. Let this knowledge empower you to make informed decisions about your health care and encourage you to seek medical advice when necessary.