Constipation in Children Treatment: Constipation in children is a common and often distressing condition, affecting both the physical and emotional well-being of the child and their family.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for this condition is paramount for caregivers looking to alleviate discomfort and restore normal bowel function in their young ones.
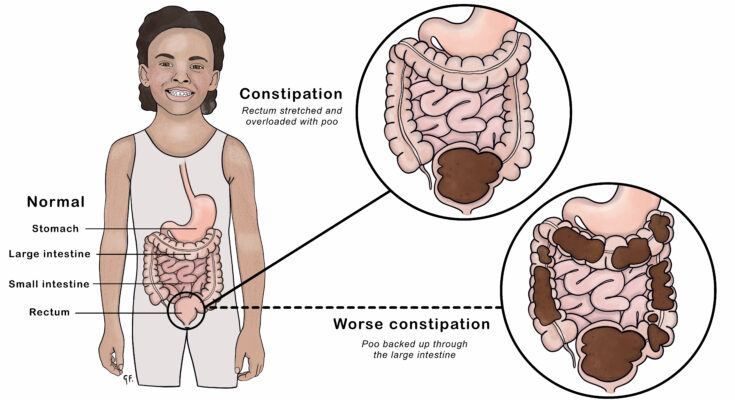
Understanding Constipation in Children
Constipation in children is a common concern that many parents face. It can be uncomfortable for your child and worrying for you, but understanding the causes, signs, and when to seek medical help can make managing this condition easier. By exploring dietary factors, hydration, physical activity, and psychological aspects, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to understanding constipation in children.
What Causes Constipation in Children?
Several factors can contribute to constipation in children, ranging from their diet to their emotional well-being. Here’s a closer look at the primary causes:
- Dietary Factors: The food your child consumes plays a significant role in their bowel movements. A diet low in fiber, which is found in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can lead to constipation. Fiber helps to bulk up stools and makes them easier to pass.
- Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is crucial for preventing constipation. Water and other fluids help soften the stool, making it easier to pass. Children who do not drink enough fluids during the day are more prone to constipation.
- Physical Activity: Regular physical activity helps stimulate intestinal movements, making it easier for the body to process and eliminate waste. A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to constipation in children.
- Psychological Factors: Stress and anxiety can also affect your child’s bowel movements. Children who are anxious about toilet training or who experience changes in their routine may be more susceptible to constipation.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch Out For
Recognizing the signs of constipation in your child is the first step towards helping them. Common symptoms include:
- Less frequent bowel movements than usual, often less than three times a week.
- Difficulty passing stools or pain during bowel movements.
- Hard, dry, or large stools.
- Abdominal pain, bloating, or a feeling of fullness.
- Traces of liquid or clay-like stool in your child’s underwear — a sign that stool is backed up in the rectum.
When to Seek Medical Help
While occasional constipation is common in children, there are times when you should seek medical advice:
- If constipation lasts more than two weeks.
- If there is blood in your child’s stool.
- If constipation is accompanied by fever, vomiting, weight loss, or severe abdominal pain.
- If there are significant changes in your child’s bowel habits or if they are experiencing pain or distress.
Early intervention can prevent complications and help your child feel better. Adjusting their diet, ensuring they drink enough fluids, encouraging regular physical activity, and addressing any psychological factors can effectively manage constipation. However, if you’re concerned about your child’s symptoms or if they persist despite home remedies, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for tailored advice and treatment options.
However, understanding the causes and symptoms of constipation in children, as well as knowing when to seek medical help, can empower you to support your child’s digestive health. With the right approach, you can help alleviate their discomfort and prevent future episodes of constipation.
Diagnosis of Constipation in Children
When it comes to diagnosing constipation in children, a thorough approach is essential for identifying the underlying causes and determining the best course of treatment. This process generally involves a combination of medical history review, physical examinations, and, if necessary, additional tests. By understanding each step, parents and caregivers can better prepare for a visit to the pediatrician and have a clearer picture of what to expect.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing constipation in children involves a comprehensive review of the child’s medical history and a physical examination. During this initial assessment, healthcare providers will ask questions related to the child’s bowel movements, such as frequency, consistency, and any associated symptoms like pain or discomfort. This information helps in understanding the severity and pattern of constipation. Additionally, the physical examination allows the doctor to identify any physical causes of constipation, such as blockages or abnormalities in the abdominal area.
The Role of Dietary and Bowel Movement History
A detailed discussion about the child’s diet and bowel movement history plays a critical role in diagnosing constipation. Diet is a major factor influencing bowel habits. A lack of fiber-rich foods, inadequate fluid intake, or an overreliance on processed foods can contribute to constipation. By examining dietary habits, healthcare providers can offer targeted advice on nutritional adjustments that may alleviate constipation. Similarly, understanding the child’s typical bowel movement patterns and any recent changes can provide clues to the underlying causes of constipation.
Additional Tests (If Needed)
In some cases, when the cause of constipation is not clear from the medical history and physical examination, further diagnostic tests may be necessary. These tests help in ruling out specific conditions or identifying underlying health issues that could be contributing to constipation.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can check for signs of a systemic condition that might be causing constipation, such as thyroid disorders.
- X-rays: An abdominal x-ray can provide visual evidence of constipation by showing the amount of stool present in the colon. It can also reveal any blockages or structural abnormalities.
- Anorectal Manometry or Barium Enema: These specialized tests are used to evaluate the functioning of the rectum and lower part of the colon. Anorectal manometry measures the muscle strength of the anus, which can indicate issues with bowel movements. A barium enema helps in visualizing the shape and function of the colon, identifying any abnormalities that could be causing constipation.
By combining the insights gained from the medical history, physical examination, and, if necessary, additional tests, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose constipation in children. This comprehensive approach ensures that any underlying issues are identified and addressed, paving the way for effective treatment and relief for the child.
Treatment Options for Constipation in Children
When it comes to alleviating constipation in children, a multifaceted approach can be highly effective. This guide outlines several strategies, from dietary adjustments to medical interventions, designed to help your child achieve regular bowel movements. Each method prioritizes both safety and efficacy, ensuring that your little one finds relief with minimal discomfort.
Dietary Changes
One of the most natural and first-line strategies involves making specific changes to your child’s diet:
- High-fiber foods: Incorporating fiber-rich foods into your child’s diet can significantly aid digestion and prevent constipation. Foods like fruits (apples, pears, and prunes), vegetables (broccoli, peas, and carrots), legumes, and whole grains are excellent sources of fiber. A gradual increase in fiber is recommended to allow the child’s digestive system to adjust without causing gas or bloating.
- Adequate fluid intake: Ensuring your child drinks enough water throughout the day is crucial. Adequate hydration helps soften the stool, making it easier to pass. Encourage the consumption of water and other fluids, such as natural fruit juices, which can also contribute to a fiber-rich diet.
Behavioral Changes
Adjusting behaviors can also play a significant role in managing constipation:
- Establishing a toilet routine: Encourage your child to use the bathroom at regular times each day, particularly after meals, to take advantage of the body’s natural digestive rhythms. Creating a routine can help establish regular bowel habits.
- Encouragement and positive reinforcement: Support and motivate your child with positive reinforcement. Celebrate successes and maintain a supportive environment to reduce any stress or anxiety associated with bowel movements, which can exacerbate constipation.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
If dietary and behavioral changes are not sufficient, over-the-counter options may be considered with caution:
- Laxatives (with physician guidance): Various over-the-counter laxatives are safe for children, but it’s crucial to use them under the guidance of a physician. They can help stimulate bowel movements or soften the stool but should not be a long-term solution without a doctor’s recommendation.
- Stool softeners: Stool softeners, such as docusate, can be a gentle option for easing constipation in children. They work by moistening the stool, making it easier to pass. As with laxatives, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Prescription Medications
In cases where other treatments have not been effective, a pediatrician may prescribe medication specifically designed to treat constipation. Prescription medications can offer relief for chronic constipation but should be used as part of a broader treatment plan that includes dietary and lifestyle changes.
Managing constipation in children often requires a combination of dietary adjustments, behavioral strategies, and, if necessary, medical interventions. By understanding and implementing these treatment options, parents can help their children achieve comfort and regularity. Remember, when introducing any new treatment or remedy, consulting with a pediatric healthcare provider is essential to ensure the safety and well-being of your child.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes for Constipation in Children
With the right home remedies and lifestyle changes, you can effectively relieve constipation and improve your child’s digestive health. Here’s how to manage constipation in children through natural methods, emphasizing the importance of exercise and offering tips for parents and caregivers.
Effective Home Remedies for Relieving Constipation
- Increase Fiber Intake: Incorporate high-fiber foods into your child’s diet, such as fruits (like pears, apples, and plums), vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber helps soften stool and promotes regular bowel movements.
- Encourage Adequate Hydration: Keeping your child well-hydrated is crucial. Encourage them to drink plenty of water throughout the day. For younger children, you can also offer high-water-content fruits and vegetables as snacks.
- Offer Prune Juice: Prune juice is a natural laxative because it contains sorbitol, which helps soften the stool and ease constipation. Start with small amounts and adjust according to your child’s needs and age.
- Warm Baths: A warm bath can help relax your child’s abdominal muscles, reducing discomfort associated with constipation. This method can be particularly soothing before bedtime.
Importance of Exercise and Physical Activity
Exercise plays a vital role in preventing and treating constipation in children. Physical activity helps increase blood flow and stimulates intestinal contractions, aiding in more regular bowel movements. Encourage your child to engage in daily physical activities, such as:
- Outdoor Play: Encourage playing outside, like running, jumping, or cycling, to get their bodies moving.
- Family Walks: Incorporate regular family walks or hikes into your routine.
- Age-appropriate Sports: Enroll your child in sports they enjoy, which can be both fun and beneficial for their bowel health.
Tips for Parents and Caregivers
- Establish a Routine: Encourage your child to use the bathroom at regular times, especially after meals, to help establish a routine.
- Be Patient and Supportive: Understand that managing constipation takes time. Offer support and encouragement rather than pressure.
- Monitor Toilet Posture: Ensure your child is sitting correctly on the toilet. Using a footstool can help younger children achieve a more natural squat position, facilitating easier bowel movements.
- Keep a Food Diary: Tracking what your child eats can help identify potential dietary triggers for constipation.
- Consult a Pediatrician: If constipation persists despite home remedies and lifestyle changes, consult a pediatrician. They can offer additional guidance and rule out any underlying conditions.
Implementing these home remedies and lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate constipation in children. By fostering a supportive environment and encouraging healthy habits, you can help your child overcome constipation and improve their overall digestive health.
The Role of Probiotics in Treating Constipation in Children
Constipation is a common and uncomfortable condition affecting children worldwide. It can lead to infrequent bowel movements, difficulty passing stools, and, in some cases, distress and pain. Traditional treatments have included dietary changes, increased fluid intake, and over-the-counter laxatives. However, recent studies have illuminated the potential of probiotics as a natural and effective way to alleviate constipation in children. This section explores how probiotics can help and highlights recommended probiotic strains and sources.
How Probiotics Can Help
Probiotics are live microorganisms, often referred to as “good” bacteria, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They play a crucial role in maintaining gut health, enhancing the gut microbiota’s balance, and supporting a healthy digestive system. For children experiencing constipation, probiotics can help in several ways:
- Enhancing Stool Consistency: Probiotics can improve stool consistency, making it easier to pass and reducing the strain during bowel movements.
- Increasing Bowel Movement Frequency: Regular consumption of probiotics has been linked to an increase in the frequency of bowel movements, offering relief to children suffering from constipation.
- Promoting Gut Health: By restoring the balance of the gut microbiota, probiotics contribute to the overall health of the digestive system, which is essential for preventing and treating constipation.
Recommended Probiotic Strains and Sources
Not all probiotics are created equal, especially when it comes to treating constipation in children. Certain strains have been identified as particularly beneficial:
- Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG): Widely researched, LGG has been shown to improve bowel regularity and soften stools in children.
- Bifidobacterium lactis: Studies suggest that this strain can significantly increase bowel movement frequency and improve stool consistency.
- Lactobacillus reuteri: Known for its gut health benefits, L. reuteri can help alleviate constipation and enhance overall digestive health.
When selecting a probiotic supplement, it’s essential to choose products specifically designed for children, as these will contain appropriate strains and dosages. Probiotic sources include:
- Supplements: Available in various forms, including powders, capsules, and chewables, tailored for children’s needs.
- Fermented Foods: Natural sources of probiotics, such as yogurt, kefir, and certain types of cheese, can be a delicious way to incorporate beneficial bacteria into a child’s diet.
- Fortified Foods: Some products are fortified with probiotics, offering an easy way to boost a child’s intake of beneficial bacteria.
Incorporating probiotics into a child’s diet can be a safe and effective way to address constipation. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplement, especially in children with underlying health conditions or those taking other medications. With the right approach, probiotics can play a significant role in improving digestive health and relieving constipation in children, contributing to their overall well-being and quality of life.
When to See a Doctor for Constipation in Children
Knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial for parents and guardians. This guide outlines symptoms that warrant a doctor’s visit, what to expect during the consultation, and how to prepare for your child’s appointment.
Symptoms that Require Medical Attention
While occasional constipation might not be alarming, certain symptoms should prompt you to seek medical advice:
- Persistent Constipation: If your child has been experiencing constipation for more than two weeks, despite home remedies or dietary changes.
- Painful Bowel Movements: Severe discomfort or pain during bowel movements.
- Blood in Stool: The presence of blood in your child’s stool or on toilet paper may indicate an underlying condition.
- Abdominal Pain: Ongoing or severe abdominal pain can be a sign of constipation complications.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss along with constipation should be evaluated.
- Vomiting: Vomiting along with constipation is a symptom that needs immediate attention.
What to Expect During the Consultation
When you visit the doctor for your child’s constipation, here’s what typically happens:
- Medical History Review: The doctor will ask about your child’s medical history, diet, and symptoms.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical exam, including an abdominal examination, to check for any abnormalities.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the situation, the doctor may recommend tests like blood tests, X-rays, or a rectal examination to diagnose the cause of constipation.
Preparing for Your Child’s Doctor Visit
To make the most out of the consultation, preparation is key:
- Symptom Diary: Keep a record of your child’s bowel movements, diet, and any symptoms they experience.
- Medical History: Be ready to discuss your child’s medical history, including any previous episodes of constipation, current medications, and dietary habits.
- Questions: Prepare a list of questions you have for the doctor to ensure all your concerns are addressed.
- Comfort Items: Bring along a favorite toy or book to help your child feel more comfortable during the visit.
Recognizing the signs that indicate a need for medical evaluation and being prepared for the doctor’s visit can lead to more effective management of constipation in children. Always prioritize your child’s health and wellbeing by seeking timely medical advice.
Preventing Constipation in Children
With the right preventive measures, it’s possible to maintain healthy bowel movements in your child. Here’s how you can help prevent constipation in children, monitor their bowel habits effectively, and create a supportive environment for their bowel health.
List of Preventive Measures
- Increase Fiber Intake: Incorporate a variety of high-fiber foods into your child’s diet, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes. Fiber helps to soften the stool and promotes regular bowel movements.
- Encourage Hydration: Ensure your child drinks plenty of fluids throughout the day. Water is the best choice, but other fluids like natural fruit juices can also contribute to hydration and help prevent constipation.
- Promote Regular Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps stimulate digestion and can prevent constipation. Encourage your child to engage in physical activities they enjoy, such as biking, swimming, or playing outdoor games.
- Establish a Routine: Setting a regular schedule for bathroom breaks can help your child develop consistent bowel habits. Encourage them to take their time and not to rush the process.
- Limit High-Fat and Sugary Foods: Foods that are high in fat and sugar can contribute to constipation. While it’s okay to enjoy these foods in moderation, focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
The Importance of Monitoring Bowel Habits
Keeping an eye on your child’s bowel habits is crucial in preventing and managing constipation. Regular bowel movements vary from child to child; however, less than three bowel movements a week might indicate constipation. Look out for signs such as difficulty passing stool, discomfort, or stool that is hard and dry. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and discomfort.
Creating a Supportive Environment for Bowel Health
Creating a supportive environment involves both physical and emotional support:
- Physical Support: Make sure your child has easy access to bathrooms and feels comfortable using them. A small stool under their feet can help children achieve a more natural and comfortable position to facilitate bowel movements.
- Emotional Support: Be patient and understanding. Some children may feel embarrassed or anxious about discussing bowel movements. Encourage open and positive conversations about body functions to reduce any stigma or embarrassment.
- Educational Support: Teach your child about the importance of a healthy diet, hydration, and regular exercise for maintaining bowel health. Educating them on how their body works can empower them to take proactive steps in their health.
By implementing these preventive measures, monitoring your child’s bowel habits, and creating a supportive and understanding environment, you can significantly reduce the risk of constipation in children. Remember, if constipation becomes a recurring problem or you’re concerned about your child’s bowel health, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
FAQs on Treating Constipation in Children
What are the signs of constipation in children?
Constipation in children can present in several ways, including less frequent bowel movements than usual (less than three times a week), hard or dry stools, difficulty or pain when passing stools, and a feeling of not being able to empty the bowel completely. Children may also show signs of discomfort, abdominal pain, or changes in appetite.
How can I help my child at home if they are constipated?
There are several home remedies you can try to alleviate your child’s constipation:
- Increase fiber intake: Incorporate more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your child’s diet.
- Encourage hydration: Ensure your child drinks plenty of fluids, especially water, to help soften stools.
- Promote physical activity: Regular physical activity can help stimulate bowel movements.
- Establish a routine: Encouraging your child to use the bathroom at regular times, especially after meals, can help establish a consistent bowel routine.
When should I take my child to see a doctor for constipation?
You should consider taking your child to see a healthcare provider if:
- Home remedies do not improve symptoms.
- Your child experiences persistent abdominal pain.
- There is blood in the stool.
- Constipation is accompanied by fever or vomiting.
- Your child shows signs of weight loss or delayed growth.
Can medication be used to treat constipation in children?
Yes, in some cases, a healthcare provider may recommend over-the-counter or prescription medications to help relieve constipation. These may include laxatives or stool softeners. However, it’s important to use these under the guidance of a healthcare provider, as the type and dosage must be suitable for the child’s age and health status.
Is constipation in children a sign of a more serious condition?
While constipation in children is usually not serious and can be treated with lifestyle changes and home remedies, it can sometimes be a symptom of an underlying condition. If constipation is persistent and does not respond to conventional treatments, or if it’s accompanied by other concerning symptoms, a healthcare provider may conduct further investigations to rule out other conditions.
How can I prevent constipation in my child?
Preventing constipation in children involves a combination of a healthy diet rich in fiber, adequate hydration, regular physical activity, and establishing a routine bathroom schedule. Encouraging these healthy habits from a young age can help maintain regular bowel movements and prevent constipation.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing constipation in children is crucial for their overall health and well-being. This condition, though common, can have significant impacts if left untreated. It’s important for parents and caregivers to recognize the signs of constipation early and to seek medical advice to ensure an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
We encourage parents to not only seek professional help but also to be diligent in following through with the recommended treatments and dietary or lifestyle changes. Adherence to these plans can greatly alleviate discomfort and prevent future occurrences of constipation.
Preventing constipation in children primarily involves ensuring they have a diet rich in fiber, adequate hydration, and regular physical activity. Encouraging healthy bathroom habits and making sure children feel comfortable discussing these issues can also play a significant role in both prevention and management of constipation.
In conclusion, with the right knowledge and actions, managing and preventing constipation in children is entirely achievable. By taking proactive steps, parents can help their children lead more comfortable and healthy lives.