Common Warts Symptoms: Warts are a common skin condition that affects individuals of all ages, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV).
This article delves into the symptoms and causes of common warts, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of how to identify and understand the origins of these skin growths.
What Are Common Warts?
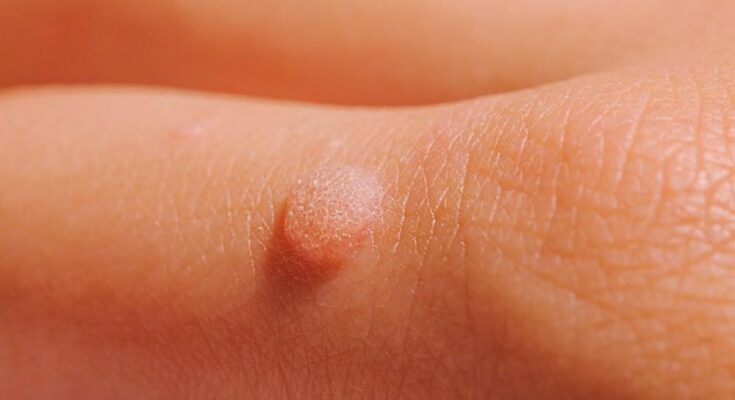
Common warts are small, benign growths on the skin that are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). These growths are usually harmless and can appear on any part of the body but are most commonly found on the hands, feet, elbows, and knees. Warts are characterized by their rough, cauliflower-like appearance and may sometimes be dotted with black pinpoints, which are small, clotted blood vessels.
Types of Warts
There are several types of warts, each with its unique characteristics and preferred locations on the body:
- Common Warts: These warts are typically found on fingers, hands, knees, and elbows. They have a rough surface and are rounded in shape.
- Plantar Warts: Located on the soles of the feet, plantar warts can be painful, especially when walking. They may grow in clusters and are often flat due to the pressure applied by walking.
- Flat Warts: Smaller and smoother than other types, flat warts can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly seen on the face, thighs, or arms.
- Filiform Warts: These warts are long and thin, and typically grow around the mouth, nose, or beard area. They can spread quickly.
- Periungual Warts: Found under and around the toenails and fingernails, these warts can affect nail growth.
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and Its Role in Causing Common Warts
The human papillomavirus (HPV) plays a crucial role in the development of common warts. HPV is a group of more than 100 viruses, with several strains specifically responsible for causing different types of warts. The virus infects the top layer of the skin, usually entering the body through small cuts or breaks. Once inside, it causes cells to grow rapidly, leading to the formation of a wart.
HPV is highly contagious and can be spread through direct contact with a wart or something that touched a wart, such as towels or surfaces. The virus thrives in warm, moist environments, making communal showers and pool areas common sites for transmission. Not everyone who comes into contact with HPV will develop warts, as individual immune system responses play a significant role in whether a person becomes infected.
Understanding the types of warts and the role of HPV in their development is essential for prevention and treatment. While most warts are harmless and may go away on their own, they can be bothersome and may require treatment. Practices such as good hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, and using protective footwear in communal areas can help prevent the spread of HPV and the formation of warts.
Symptoms of Common Warts
Recognizing the symptoms of common warts is the first step toward effective treatment. By understanding their distinct characteristics and how they differ from other skin growths, individuals can take timely action to address them.
Detailed Description of Common Warts Symptoms
- Texture and Appearance: Common warts have a distinctive rough texture. They may appear as a single wart or in clusters, resembling a cauliflower.
- Color: They are usually the same color as your skin, but they can also be slightly lighter or darker.
- Size: The size of common warts can vary. They typically range from a pinhead to 10mm in diameter.
- Location: Commonly found on the hands, especially around the nails, on the fingers, and on the backs of hands. They can also appear on the knees and elbows.
- Pain and Discomfort: While common warts are generally not painful, they can cause discomfort or pain if they are in areas where pressure is applied, such as the fingers or soles of the feet.
- Black Dots: Sometimes, tiny black dots can be observed on the surface of the wart. These are clotted blood vessels.
How to Distinguish Common Warts from Other Skin Growths
- Location and Appearance: Unlike plantar warts, which are found on the soles of the feet, common warts typically appear on the hands and knees. Their rough, cauliflower-like surface distinguishes them from other skin growths, which may have smoother surfaces.
- Pain and Sensation: Common warts usually do not cause pain upon pressure, unlike plantar warts, which can be quite painful when walking.
- Color and Texture: Common warts have a distinct rough texture and color that matches your skin tone, differing from moles, which are smooth and can be various shades of brown or black.
- Growth Pattern: Common warts often grow in clusters, whereas other types of warts or skin growths might appear as solitary lesions.
Images or Diagrams to Help Identify Common Warts
Including images or diagrams can significantly help in identifying common warts. These visuals can illustrate the unique characteristics of common warts, such as their rough texture, typical locations, and the presence of black dots. High-quality images showing the warts in various stages and locations can provide a comprehensive understanding, aiding in self-diagnosis and when to seek medical advice.
For precise identification and treatment options, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended, especially if the growth changes in appearance, spreads, or causes pain.
Remember, while common warts are mostly harmless, a healthcare provider’s evaluation is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Common Warts: An In-Depth Guide
Understanding the causes of common warts is essential for prevention and effective treatment. This comprehensive guide delves into the root cause of common warts, their transmission, and the risk factors associated with their development.
The Role of HPV in Common Warts
At the heart of common wart development is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV). Specifically, certain strains of HPV are responsible for the growth of these skin abnormalities. HPV is a diverse virus family, with over 100 types, but only a handful are linked to the formation of common warts. These strains of HPV lead to rapid growth of cells on the outer layer of the skin, resulting in the familiar wart texture.
Transmission: How Does HPV Spread?
HPV is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with the wart or something that touched the wart. This transmission can occur through skin-to-skin contact or by touching objects that have come into contact with the virus, such as towels, footwear, and surfaces in communal areas. The virus finds its way through small cuts or breaks in the skin, establishing itself and eventually leading to wart formation.
Risk Factors for Developing Common Warts
Certain factors can increase an individual’s risk of developing common warts. These include:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immunity are more susceptible to HPV infections, making them more likely to develop warts. This can be due to a variety of reasons, including certain medications, diseases that affect immune function, and aging.
- Age: Common warts are most prevalent among children and teenagers due to their frequent contact with others and their still-developing immune systems.
- Use of Communal Showers: Public showers, swimming pools, and locker rooms are breeding grounds for HPV. Walking barefoot or sharing towels in these areas can increase the risk of acquiring the virus.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is crucial for anyone looking to prevent common warts. While common warts can be a nuisance, knowing how they are caused and spread can empower individuals to take proactive steps in avoiding them, such as practicing good personal hygiene, maintaining a healthy immune system, and using protective footwear in communal areas. If you suspect you have a common wart, consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment options.
Diagnosis of Common Warts
Recognizing and diagnosing common warts is crucial, not only for aesthetic and comfort reasons but also to prevent their spread to other parts of the body or to other people. This section delves into the methods healthcare professionals use to diagnose common warts, underscores the importance of professional diagnosis, and highlights when it is essential to seek medical advice.
Methods of Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals typically diagnose common warts through a combination of physical examination and medical history. During the physical exam, a doctor will examine the skin’s appearance. In some cases, they may use a magnifying lens to get a closer look at the wart. A key characteristic of common warts is the presence of tiny black dots within the growth, which are clotted blood vessels.
For uncertain cases, where the diagnosis isn’t straightforward, a biopsy may be performed. This involves removing a small section of the wart and sending it to a laboratory for microscopic examination. This method helps rule out other possible skin conditions, such as skin cancer.
The Importance of Professional Diagnosis
Seeking a professional diagnosis is paramount. While common warts are usually harmless and may eventually disappear on their own, distinguishing them from other skin growths is essential. Some skin conditions, including certain types of skin cancer, can mimic the appearance of warts. A professional diagnosis ensures that any potentially serious issues are identified and addressed promptly.
Moreover, a healthcare provider can recommend the most effective treatment options based on the wart’s type, location, and severity. This tailored approach helps in managing the condition more effectively and prevents unnecessary treatments that might not be effective for wart removal.
When to Seek Medical Advice
It is advisable to seek medical advice for a wart if:
- The wart causes pain, discomfort, or spreads to other parts of the body.
- You notice changes in the wart’s color, size, or appearance.
- The wart interferes with daily activities.
- You have a weakened immune system, either due to a medical condition or medication, making you more susceptible to infections.
- You are unsure whether the growth is a wart or another type of skin lesion.
Early consultation with a healthcare provider not only facilitates proper diagnosis but also allows for timely and appropriate treatment, potentially preventing complications associated with common warts.
Proper diagnosis of common warts is a critical step towards effective management and treatment. By understanding the methods used by healthcare professionals for diagnosis, the importance of professional evaluation, and recognizing when to seek medical advice, individuals can ensure they receive accurate information and appropriate care for their skin condition.
Preventing and Managing Common Warts
There are effective strategies for preventing their spread and managing their presence. By adhering to simple preventive measures and understanding the available treatment options, you can significantly reduce the impact of common warts on your life.
Tips for Preventing the Spread of the Virus That Causes Common Warts
Prevention is key when it comes to common warts. Here are practical steps to minimize the risk of contracting or spreading the virus:
- Avoid Direct Contact: Refrain from touching warts on yourself or others. HPV can spread through skin-to-skin contact.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially if you’ve been in contact with warts.
- Keep Your Skin Healthy: Cuts and abrasions make it easier for the virus to enter your skin. Use protective gear when engaging in activities that might injure your skin.
- Use Foot Protection in Public Areas: Wearing sandals or flip-flops in communal showers, pool areas, and locker rooms can help prevent plantar warts.
Basic Care and Treatment Options for Common Warts
While some warts may disappear on their own, many require treatment to resolve. Here are several approaches:
- Over-the-Counter Solutions: Salicylic acid treatments can effectively remove warts by peeling them away gradually. Always follow the product instructions carefully.
- Home Remedies: Some people find success with duct tape occlusion therapy, where duct tape is applied to the wart continuously for weeks. However, the effectiveness of this method varies.
- When to See a Doctor: If warts are painful, spreading, or persistent, it’s wise to consult a healthcare provider. They can offer treatments such as cryotherapy (freezing the wart) or other procedures.
Lifestyle and Hygiene Practices to Reduce the Risk of Developing Common Warts
Adopting healthy lifestyle and hygiene practices can lessen your risk of developing common warts:
- Maintain a Strong Immune System: A healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep can boost your immune system, making it harder for HPV to cause warts.
- Keep Your Feet Dry and Clean: Moist environments promote the growth of fungi and viruses, including HPV. Dry your feet thoroughly after washing them.
- Use Your Own Personal Items: Avoid sharing towels, razors, or other personal items that may come into contact with warts.
By integrating these preventive and management strategies into your daily routine, you can protect yourself and others from the spread of common warts. Remember, if warts are causing you discomfort or concern, seeking professional medical advice is always the best course of action.
When to See a Doctor for Common Warts
Dealing with common warts can often be managed with over-the-counter treatments and home remedies. However, there are specific signs that suggest it might be time to seek professional medical advice. Understanding when to consult a healthcare provider can ensure timely and effective treatment, preventing complications. This article outlines the key indicators that warrant a doctor’s visit for common warts and discusses the treatment options available through healthcare providers.
Signs Indicating the Need for Professional Medical Evaluation
- Rapid Growth or Multiplication: If you notice that the wart or warts are growing quickly or spreading, it’s important to see a doctor. Rapid growth could indicate an underlying issue that requires professional attention.
- Pain and Discomfort: While common warts are generally not painful, if you experience pain or discomfort, especially if the wart is in a location that interferes with daily activities like walking or writing, professional evaluation is advised.
- Change in Appearance or Color: Any changes in the color, shape, or texture of the wart should prompt a visit to the doctor. These changes could suggest malignancy or other skin conditions.
- Interference with Daily Activities: Warts located on the fingers, feet, or any area that affects your daily tasks or quality of life should be examined by a healthcare provider to explore treatment options that can alleviate symptoms and remove the warts.
- Immune System Concerns: Individuals with weakened immune systems, either due to medical conditions (like HIV/AIDS or diabetes) or medications (such as immunosuppressants), should consult a doctor for any warts due to a potentially higher risk of complications.
- Uncertainty About the Diagnosis: If you’re unsure whether the growth is a wart or another skin condition, a professional diagnosis is crucial. Accurate identification is essential for effective treatment.
Treatment Options Available Through Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers can offer several treatment options that might not be available over the counter. These include:
- Cryotherapy: This procedure involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing it to blister and eventually fall off.
- Cantharidin: A doctor may apply a substance called cantharidin to the wart, which causes a blister to form underneath it, lifting it off the skin.
- Excision: The wart can be cut out surgically, which is a direct method to remove the growth.
- Laser Treatment: This involves using a laser to burn and destroy wart tissue. It is often used for warts that haven’t responded to other treatments.
- Immunotherapy: This method boosts the immune system’s ability to fight the wart virus.
- Chemical Peels: Applying acids to the wart to help exfoliate the top layers, encouraging the wart to peel away.
These treatments may require multiple visits and can vary in effectiveness, depending on the individual’s condition and the type of wart. Your healthcare provider will discuss the best option for you based on the wart’s location, your health status, and previous treatments.
While common warts are mostly harmless, certain signs necessitate a visit to the doctor. Paying attention to your body and responding to changes can prevent potential complications. With a range of treatments available, healthcare providers can offer personalized care that over-the-counter remedies cannot. If you’re experiencing any of the signs mentioned above, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical advice.
Conclusion
In summary, recognizing the symptoms and understanding the causes of common warts is paramount. These benign yet often bothersome skin growths, caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV), can appear on any part of the body, especially on the hands and feet. Identifying warts early on can prevent their spread, both to other parts of your body and to other people.
We’ve explored the various factors that contribute to the development of warts, including direct contact with HPV and weakened immune systems. With this knowledge, you can take proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones. Simple preventive measures, such as maintaining good personal hygiene, avoiding direct contact with warts, and using protective barriers in communal showers and pools, can significantly reduce your risk.
However, if you find yourself or a family member affected by warts, it’s crucial not to resort to home remedies without proper guidance. Instead, we encourage you to seek medical advice. Healthcare professionals can offer safe and effective treatments tailored to your specific needs. Remember, while common warts are mostly harmless, getting professional advice ensures you manage them correctly and avoid unnecessary complications.
In conclusion, awareness and understanding are your best defenses against common warts. By following preventive measures and consulting with medical professionals when necessary, you can keep your skin healthy and wart-free. Let’s prioritize our health and well-being by taking informed steps towards prevention and treatment.