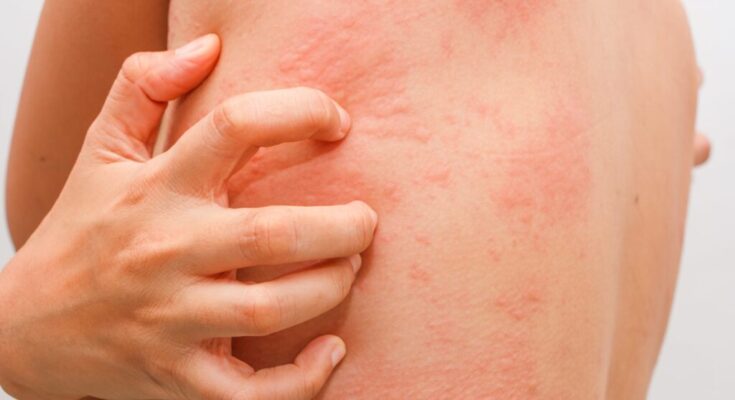
Cold Urticaria Treatment: Cold Urticaria is a rare condition that causes red, itchy welts or hives on the skin after exposure to cold temperatures.
This can include cold weather, water, or objects. Symptoms range from mild irritation to severe swelling and can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected.
Understanding Cold Urticaria
Cold urticaria is a skin condition that triggers an allergic reaction when the skin is exposed to cold temperatures or comes in contact with cold objects. This unique condition can cause a range of symptoms, impacting individuals differently. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and common symptoms of cold urticaria is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Causes and Risk Factors
Cold urticaria is primarily caused by sudden exposure to cold temperatures. This could be from environmental conditions, cold water, or even cold objects. When the skin reacts to the cold, it releases histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream, leading to the symptoms associated with the condition.
While the exact cause of cold urticaria is often unknown, certain factors can increase the risk of developing this condition. These include:
- Genetics: A family history of cold urticaria or other allergic conditions can increase your risk.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Some health issues, such as viral infections or certain immune system disorders, can predispose individuals to cold urticaria.
- Recent Infections: Having had a recent infection or illness can sometimes trigger the onset of cold urticaria.
Common Symptoms and How They Affect Individuals
The symptoms of cold urticaria can vary from mild to severe and can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life. Common symptoms include:
- Redness and Swelling: Exposure to cold can cause affected areas of the skin to turn red, swell, and become itchy.
- Hives: These are raised, itchy welts on the skin that can appear within minutes of cold exposure.
- Severe Reactions: In some cases, severe reactions like anaphylaxis can occur, characterized by difficulty breathing, a rapid drop in blood pressure, and swelling of the throat and tongue. This is a medical emergency.
The impact of these symptoms on individuals can vary. For some, the condition may only cause minor discomfort, while for others, it can lead to severe reactions that limit their ability to engage in activities, especially those involving cold environments. The unpredictability of reactions can also lead to anxiety and stress, further affecting an individual’s well-being.
If you suspect you have cold urticaria, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. With the right care, individuals with cold urticaria can lead full and active lives, despite the challenges posed by this condition.
Diagnosis of Cold Urticaria
Diagnosing Cold Urticaria accurately is crucial for managing this unique allergic condition effectively. Cold Urticaria, or cold hives, is triggered by exposure to cold temperatures, leading to red, itchy welts on the skin. Understanding the steps involved in diagnosing Cold Urticaria can help individuals seek appropriate treatment and manage their symptoms better.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
An accurate diagnosis of Cold Urticaria is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it enables healthcare providers to recommend the most effective treatment plans tailored to the individual’s condition. Secondly, it helps in identifying and avoiding specific triggers, thereby preventing the occurrence of symptoms. Lastly, distinguishing Cold Urticaria from other similar conditions ensures that any underlying health issues are addressed promptly.
Steps in Diagnosing Cold Urticaria
The diagnosis of Cold Urticaria involves a comprehensive approach that includes the following steps:
- Medical History Review: This initial step involves a detailed discussion about the patient’s symptoms, including their onset, duration, and any possible triggers. Healthcare providers may also inquire about the patient’s family history of allergies or autoimmune diseases to understand the potential genetic predisposition.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination helps the healthcare provider to observe any visible symptoms and assess the overall health condition of the patient. This step is critical for ruling out other skin conditions that may mimic Cold Urticaria.
- Cold Stimulation Test: The cold stimulation test is a specific diagnostic procedure for Cold Urticaria. During this test, the healthcare provider applies a cold object (such as an ice cube) to the skin for a brief period, then observes the reaction. A positive test is indicated by the development of a hive in the shape of the object, confirming the diagnosis of Cold Urticaria.
- Other Tests: In some cases, additional tests may be necessary to rule out underlying conditions or to confirm the diagnosis. These may include blood tests to check for other allergic conditions or immune system disorders, and in rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to examine the tissue closely.
Differential Diagnosis: Distinguishing Cold Urticaria from Other Conditions
Differential diagnosis is a critical aspect of diagnosing Cold Urticaria, as it involves distinguishing it from other skin conditions that may present similar symptoms, such as dermatographism, heat urticaria, or aquagenic urticaria. By carefully evaluating the patient’s symptoms, conducting a thorough physical examination, and performing specific tests, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose Cold Urticaria and differentiate it from other conditions.
However, diagnosing Cold Urticaria involves a detailed review of medical history, physical examination, specific diagnostic tests like the cold stimulation test, and sometimes additional tests to ensure an accurate diagnosis. Understanding these steps can help individuals seeking diagnosis and treatment for Cold Urticaria navigate their healthcare journey more effectively. With a precise diagnosis, patients can manage their condition better and improve their quality of life.
Treatment Options for Cold Urticaria
The primary objectives in treating Cold Urticaria include alleviating symptoms, preventing severe reactions, and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. A comprehensive treatment plan is often personalized, taking into account the severity of the condition, the patient’s lifestyle, and their response to various treatments.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Avoiding Cold Exposure
Minimizing exposure to cold environments is a fundamental step in managing Cold Urticaria. Patients are advised to monitor weather conditions closely and avoid activities that could lead to a sudden drop in body temperature, such as swimming in cold water.
Protective Clothing and Strategies
Wearing protective clothing can significantly reduce the risk of cold-induced hives. Layering, using thermal wear, and covering exposed skin areas when in cold environments can provide an effective barrier against the cold. Additionally, adopting strategies to warm up gradually after exposure to cold can help prevent reactions.
Medications
Antihistamines: First-line Treatment for Cold Urticaria
Antihistamines are the cornerstone of medical treatment for Cold Urticaria, effectively reducing itching, redness, and the overall occurrence of hives. Non-sedating antihistamines are preferred for their efficacy and minimal side effects, making them suitable for daily use.
Other Medications
In cases where antihistamines are not sufficiently effective, other medications may be considered, including:
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: These can be added to the treatment regimen to further alleviate symptoms.
- Omalizumab: For chronic and severe cases of Cold Urticaria, omalizumab, an injectable medication designed to target and block IgE antibodies, has shown promise.
- Other Potential Treatments: Research into additional treatments is ongoing, with some patients finding relief with therapies such as cyclosporine, though these are typically reserved for cases resistant to standard treatments.
Emergency Treatment for Severe Reactions
Importance of Carrying Epinephrine Auto-injectors
Individuals with Cold Urticaria, particularly those who have experienced or are at risk of anaphylaxis, should always carry epinephrine auto-injectors. This emergency medication can be life-saving in the event of a severe allergic reaction.
What to Do in Case of Anaphylaxis
Recognizing the signs of anaphylaxis, which can include difficulty breathing, swelling, dizziness, and a rapid drop in blood pressure, is crucial. Immediate administration of epinephrine and calling for emergency medical assistance are vital steps in managing such emergencies.
Managing Cold Urticaria effectively requires a combination of preventive measures, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatments tailored to the individual’s specific needs. By understanding the various treatment options and implementing appropriate strategies, patients can significantly reduce the impact of this condition on their daily lives. Always consult with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan that is right for you.
Managing Cold Urticaria
With the right long-term management strategies, coping mechanisms, and regular follow-ups with healthcare providers, individuals living with cold urticaria can lead comfortable and fulfilling lives. This article outlines effective ways to manage and cope with cold urticaria, emphasizing the importance of ongoing medical care.
Long-term Management Strategies
- Avoidance of Cold Exposure: One of the most effective long-term strategies is to minimize exposure to cold environments. Wearing protective clothing in cold weather, avoiding cold foods and beverages, and using warm water for bathing can help prevent the onset of symptoms.
- Medication Management: Antihistamines are commonly prescribed to reduce symptoms of cold urticaria. In some cases, doctors may recommend other medications, such as leukotriene receptor antagonists or omalizumab (an injectable medicine), for more severe cases. Consistent medication management, under the guidance of a healthcare provider, is crucial.
- Desensitization Therapy: This involves gradual exposure to cold under medical supervision, helping some individuals reduce their sensitivity over time. Desensitization should only be attempted with a healthcare provider’s guidance.
Coping Mechanisms and Lifestyle Adjustments
- Educate Yourself and Others: Understanding your condition and educating those around you can foster a supportive environment. Knowledge about cold urticaria can also help in emergency situations.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate symptoms, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or regular exercise into your routine can be beneficial.
- Plan Ahead: Checking weather forecasts and preparing for cold exposure can help manage unexpected flare-ups. Keep warm clothing and emergency medication handy, especially when traveling.
Importance of Regular Follow-ups with Healthcare Providers
Regular appointments with your healthcare provider are essential for managing cold urticaria effectively. These follow-ups allow for:
- Monitoring Condition Progression: Your healthcare provider can assess how your condition is evolving and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Medication Adjustments: Over time, your medication needs may change. Regular check-ups ensure that you are receiving the most effective and appropriate treatment.
- Addressing New Symptoms: New symptoms or side effects can arise. Prompt discussion with your healthcare provider ensures that these are addressed timely.
- Support and Guidance: Regular interaction with healthcare professionals provides emotional support and guidance, helping you to cope better with your condition.
However, managing cold urticaria involves a comprehensive approach that includes long-term management strategies, lifestyle adjustments, coping mechanisms, and regular medical follow-ups. By taking proactive steps and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with cold urticaria can lead healthy and active lives despite their condition. Remember, you are not alone, and with the right strategies, you can manage your symptoms and enjoy a high quality of life.
Recent Advances in Cold Urticaria Treatment
Recent advances in cold urticaria treatment have marked a significant step forward in managing this challenging condition. Cold urticaria, characterized by red, itchy welts or hives on the skin after exposure to cold temperatures, can range from mild to severe cases, impacting daily life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the latest research findings and sheds light on emerging treatments and therapies that promise improved outcomes for patients.
Summary of Current Research Findings
Recent studies have focused on understanding the underlying mechanisms of cold urticaria to develop more effective treatments. Research has identified that in some patients, cold urticaria is linked to an abnormal response by the immune system. Specifically, exposure to cold triggers the release of histamine and other inflammatory substances from mast cells, leading to the symptoms associated with the condition.
A pivotal area of research has been the exploration of genetic factors that may predispose individuals to cold urticaria. Studies have found mutations in certain genes that influence the immune system’s response to cold, offering potential targets for therapy.
Moreover, the role of autoimmunity in cold urticaria has gained attention, with evidence suggesting that autoantibodies against certain receptors in the skin may be involved in some cases. This discovery opens the door to treatments aimed at modulating the immune system’s activity.
Emerging Treatments and Therapies
The understanding gleaned from current research has led to the development of several promising treatments and therapies for cold urticaria:
- Biologic Therapies: Biologics, which are drugs made from living organisms or their products, are at the forefront of emerging treatments. These therapies target specific pathways in the immune system involved in the development of cold urticaria symptoms. Omalizumab, an anti-IgE antibody, has shown promise in treating cold urticaria by reducing the immune system’s sensitivity to cold.
- New Antihistamines: While antihistamines have been a mainstay in treating cold urticaria, newer formulations offer longer-lasting relief with fewer side effects. These advanced antihistamines work by more effectively blocking the action of histamine, which is responsible for the symptoms of itching and swelling.
- Cryotherapy: A novel approach to treatment involves controlled exposure to cold under medical supervision, known as cryotherapy. This method aims to desensitize the skin to cold, reducing the severity of reactions over time.
- Immunomodulatory Treatments: Therapies that modulate the immune system’s response are also being explored. These treatments aim to correct the abnormal immune reaction to cold, providing a more targeted approach to managing cold urticaria.
- Lifestyle Modifications and Patient Education: Beyond pharmacological treatments, educating patients about managing their condition and avoiding triggers is crucial. Strategies include wearing protective clothing in cold environments and gradually acclimating the body to colder temperatures.
However, the landscape of cold urticaria treatment is evolving rapidly, with research paving the way for innovative therapies that offer hope to those affected by this condition. As understanding of the underlying mechanisms expands, the potential for more effective and personalized treatments grows, promising a future where cold urticaria can be managed more effectively and with fewer limitations on patients’ lives.
FAQs about Cold Urticaria
What is Cold Urticaria?
Cold Urticaria is a skin condition that reacts to cold temperatures. When exposed to the cold, individuals with this condition may experience redness, itching, swelling, or hives on the skin. These reactions can occur within minutes of exposure to cold air, water, or objects.
What causes Cold Urticaria?
The exact cause of Cold Urticaria is often unknown, but it is thought to be related to the release of histamine and other chemicals into the bloodstream in response to cold exposure. In some cases, it may be linked to underlying health issues or genetic factors.
How is Cold Urticaria diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and medical history review. Doctors may conduct an ice cube test, where an ice cube is placed on the skin for a short period to see if a reaction occurs. Additional tests might be necessary to rule out other conditions or identify underlying causes.
Who is at risk for developing Cold Urticaria?
Anyone can develop Cold Urticaria, but it is more common in young adults and tends to affect women more than men. Those with a family history of the condition or other allergic disorders may also be at a higher risk.
Can Cold Urticaria be treated?
Yes, Cold Urticaria can be managed with treatment. Options include avoiding cold exposure, taking antihistamines to reduce symptoms, and, in severe cases, other medications may be prescribed to prevent reactions. Lifestyle adjustments and protective clothing can also help minimize exposure to cold.
Is Cold Urticaria contagious?
No, Cold Urticaria is not contagious. It is an allergic reaction of the skin to cold temperatures and cannot be passed from person to person.
Can Cold Urticaria go away on its own?
In many cases, Cold Urticaria improves over time and can even disappear on its own, usually within a few years. However, the duration and severity of the condition vary among individuals.
What should I do if I think I have Cold Urticaria?
If you suspect you have Cold Urticaria, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. They can help diagnose the condition, offer advice on managing symptoms, and provide treatment options tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
It is crucial for individuals experiencing symptoms of Cold Urticaria to seek professional medical advice. A healthcare provider can offer a comprehensive diagnosis, tailor treatment plans to individual needs, and provide guidance on managing symptoms effectively. Early consultation with a healthcare professional is key to preventing severe reactions and improving quality of life.
Looking towards the future of Cold Urticaria management, ongoing research and advancements in medical science hold promise for new and improved treatment methods. With continued efforts in understanding the underlying mechanisms of Cold Urticaria, we anticipate the development of innovative therapies that offer better control of symptoms and potentially longer-term solutions.
We encourage patients and their families to stay informed about the latest developments in Cold Urticaria treatment and to maintain open communication with their healthcare providers. By doing so, individuals affected by Cold Urticaria can navigate the challenges of this condition more effectively and lead fulfilling lives despite the limitations it may impose.
In summary, while Cold Urticaria can be a daunting condition, understanding its nature, seeking timely medical advice, and keeping abreast of emerging treatments can empower patients to manage their symptoms better. The future of Cold Urticaria management looks promising, with the potential for more effective treatments on the horizon, offering hope to those affected by this cold-induced ailment.