Chronic Pelvic Pain Symptoms: Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) represents a complex condition that impacts individuals globally, manifesting as persistent pain in the lower abdomen and pelvic area.
This multifaceted syndrome can significantly impair an individual’s quality of life, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its symptoms and causes for effective management and treatment.
What is Chronic Pelvic Pain?
Chronic pelvic pain (CPP) is a complex condition characterized by persistent pain in the pelvic region, lasting six months or longer. Unlike temporary pain that might arise from a simple injury or short-term illness, CPP can be a symptom of various underlying conditions. It encompasses a wide spectrum of disorders, including, but not limited to, issues related to the reproductive, urinary, digestive, and musculoskeletal systems. Understanding CPP is crucial because it affects individuals’ daily activities, mental health, and overall quality of life.
How Chronic Pelvic Pain Differs from Acute Pain
The primary difference between chronic pelvic pain and acute pain lies in their duration and underlying causes. Acute pain serves as a direct, immediate signal of harm or potential injury to the body, usually resolving once the underlying cause is treated or heals. It typically lasts for a short period, from a few moments up to six months. Chronic pelvic pain, on the other hand, persists beyond the usual course of an acute illness or injury, sometimes without a clear cause. The persistence of pain signifies a complex interplay of factors that may involve the nervous system’s sensitization, emotional and psychological aspects, and chronic inflammation or dysfunction in the pelvic region.
Prevalence and Impact on Quality of Life
Chronic pelvic pain is a significant health issue with a considerable impact on individuals’ lives and the healthcare system. It is estimated to affect around 15% to 20% of women in the United States at some point in their lives, with similar prevalence rates observed worldwide. However, CPP is not exclusive to women; it also affects men, where the causes and conditions might differ.
The impact of CPP on quality of life cannot be understated. It often leads to a reduction in physical activity, absenteeism from work, and decreased participation in social activities. The chronic nature of the pain contributes to emotional distress, including anxiety and depression, further exacerbating the individual’s suffering. The complexity of CPP, coupled with the challenge of diagnosing and treating underlying causes, underscores the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to management, aiming not only to alleviate pain but also to improve function and quality of life.
Understanding chronic pelvic pain, distinguishing it from acute pain, and acknowledging its prevalence and impact are essential steps toward addressing this debilitating condition. By fostering awareness and promoting comprehensive care strategies, we can better support those affected by CPP, enhancing their well-being and daily life.
Symptoms of Chronic Pelvic Pain
Understanding the symptoms associated with CPP is crucial for those affected to seek timely and appropriate medical advice. This section delves into the detailed description of chronic pelvic pain symptoms, how to identify them, and when it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional.
Identifying Chronic Pelvic Pain Symptoms
Recognizing the diverse manifestations of CPP is the first step toward getting the help you need. Here are some common chronic pelvic pain symptoms to be aware of:
- Persistent Lower Abdominal Pain: This can feel like a steady ache or a series of sharp pains in the pelvic region.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Experiencing unusually painful, heavy, or irregular periods is a common symptom.
- Pain During Intercourse: Pain or discomfort during or after sexual activity is a significant indicator of CPP.
- Urinary Symptoms: These can include urgency, frequency, or pain during urination.
- Gastrointestinal Distress: Symptoms such as bloating, constipation, or diarrhea may accompany pelvic pain.
- Lower Back Pain: Chronic lower back pain without apparent cause may be related to CPP.
- Fatigue and Discomfort: General fatigue, discomfort, and a feeling of heaviness in the pelvic area are also associated with this condition.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you recognize any of the above chronic pelvic pain symptoms persisting for an extended period, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing CPP effectively. Here are some guidelines on when to seek medical advice:
- Persistent or Worsening Pain: If the pain does not improve with over-the-counter pain relievers or persists beyond a few days, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Impact on Daily Life: When pain interferes with your daily activities, such as work, exercise, or social engagements, seeking medical advice is essential.
- Associated Symptoms: If pelvic pain is accompanied by symptoms like fever, unusual vaginal discharge, or unexplained weight loss, immediate medical attention is necessary.
Incorporating the keyword naturally, it’s essential to understand that chronic pelvic pain symptoms can be indicative of various underlying health issues, ranging from endometriosis and fibroids to gastrointestinal or urinary disorders. Therefore, identifying and addressing these symptoms promptly is crucial for effective management and improving quality of life.
Understanding the symptoms of chronic pelvic pain is the first step toward seeking help and managing this complex condition. By being attentive to the signs and knowing when to seek medical advice, individuals can take control of their health and work towards alleviating the impact of CPP on their lives. Remember, enduring pain is not a normal part of life, and help is available for those who seek it.
Common Causes of Chronic Pelvic Pain
Understanding the common causes of CPP is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers as it aids in the accurate diagnosis and development of targeted treatment plans. This article delves into the various potential causes of CPP, emphasizing the importance of identifying the underlying issue for effective management.
Gynecological Causes
One of the primary categories of CPP origins is gynecological conditions. These include, but are not limited to, endometriosis and fibroids. Endometriosis is a painful disorder where tissue similar to the lining inside the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing severe pain and menstrual irregularities. Fibroids are benign tumors that develop in or on the uterus, which can lead to heavy bleeding and pain in the pelvic region. Recognizing these conditions as possible causes of CPP is a significant step toward relief for many sufferers.
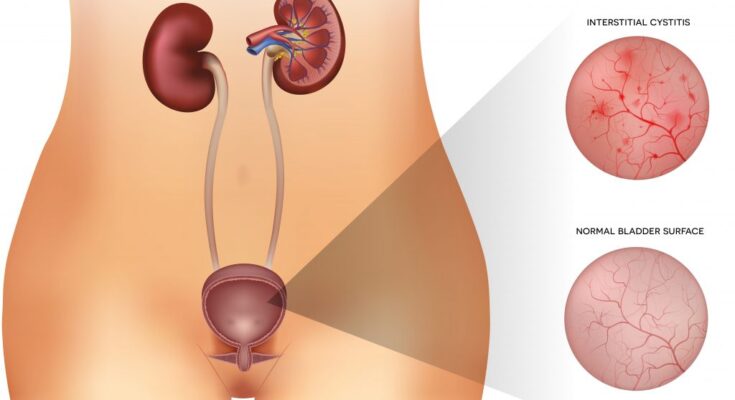
Urological Causes
CPP can also stem from urological issues, such as interstitial cystitis (IC), a condition characterized by chronic bladder pressure and pain, and frequent, painful urination. Although the exact cause of IC remains unclear, it plays a substantial role in CPP and highlights the need for a thorough urological evaluation in patients presenting with pelvic pain.
Gastrointestinal Causes
Gastrointestinal disorders are another crucial aspect of CPP causes. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common condition associated with CPP, characterized by a combination of symptoms such as abdominal pain, bloating, constipation, and diarrhea. Identifying IBS as a potential cause of CPP is essential for managing the condition effectively, as targeted dietary and lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Musculoskeletal Causes
Musculoskeletal issues, though often overlooked, can contribute significantly to CPP. Conditions such as pelvic floor dysfunction, where muscles in the pelvic area spasm or are too weak, can cause chronic pain and discomfort. Addressing these musculoskeletal causes through physical therapy or specific exercises can offer notable relief.
The Importance of Identifying the Underlying Cause
Determining the specific cause of CPP is paramount for effective treatment. Each cause requires a tailored approach; for example, hormonal therapies may be beneficial for endometriosis, while dietary modifications could be key for managing IBS. Without identifying the underlying issue, treatments may be less effective or even exacerbate the condition. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation, often involving multiple specialties, is essential for diagnosing and effectively managing CPP.
However, CPP is a multifaceted condition with various potential causes, including gynecological, urological, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal issues. Understanding these causes is critical for developing targeted treatment strategies that address the specific needs of each patient. By focusing on the underlying cause, healthcare providers can offer more effective relief, improving the quality of life for individuals affected by chronic pelvic pain.
Diagnosing Chronic Pelvic Pain: A Comprehensive Guide
The diagnostic process for CPP is multifaceted, involving a thorough medical history, physical examination, and a range of diagnostic tests. Understanding this process is crucial for individuals experiencing CPP, as it can lead to a more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing chronic pelvic pain involves a detailed medical history and physical examination. Healthcare providers will ask about the nature, duration, and intensity of the pain, as well as any factors that may exacerbate or alleviate it. This conversation might also cover aspects of your menstrual cycle, sexual health, urinary and bowel habits, and previous medical or surgical history that could be relevant to your current condition.
The physical examination is equally critical. It allows the healthcare provider to identify any physical abnormalities that might be contributing to the pain. This examination typically includes assessing the abdomen and pelvis, which can help in identifying tenderness, masses, or other signs that could point towards the underlying cause of CPP.
Diagnostic Tests
Following the initial assessment, several diagnostic tests may be employed to further investigate the causes of chronic pelvic pain. These tests can vary widely based on the initial findings and the healthcare provider’s suspicion of the potential underlying condition. Common diagnostic tools include:
- Ultrasounds: A non-invasive imaging technique that uses sound waves to create images of the pelvic organs. Ultrasounds can help identify abnormalities such as ovarian cysts, fibroids, and other potential sources of pelvic pain.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure that allows a physician to view the pelvic organs. During a laparoscopy, a small camera is inserted through a tiny incision, offering a direct look at the internal organs. This procedure can diagnose conditions like endometriosis, adhesions, and pelvic inflammatory disease.
These tests are not exhaustive, and depending on the individual’s symptoms and medical history, additional assessments such as MRI scans, CT scans, or specialized tests for urinary and gastrointestinal disorders may be recommended.
The Role of Symptom Documentation
An essential yet often overlooked aspect of diagnosing chronic pelvic pain is the role of symptom documentation. Keeping a detailed pain diary, where you note the intensity, duration, and triggers of your pelvic pain, can provide invaluable insights for your healthcare provider. This documentation assists in identifying patterns or specific conditions that may be contributing to your pain. Moreover, it can enhance the dialogue between you and your healthcare provider, leading to a more tailored and effective diagnostic process.
Through a detailed medical history, physical examination, diagnostic tests, and diligent symptom documentation, it’s possible to identify the underlying causes of CPP and embark on an appropriate treatment path. If you’re experiencing persistent pelvic pain, it’s crucial to seek medical advice to begin this diagnostic journey.
Treatment Options for Chronic Pelvic Pain (CPP)
Treatment strategies often depend on the underlying causes of CPP, highlighting the importance of a personalized and multidisciplinary approach to care. Here, we explore the diverse treatment options for CPP, emphasizing the significance of integrating various healthcare disciplines to achieve the best outcomes.
List of Treatment Strategies Based on Underlying Causes
- Medication Management: Medications are often the first line of treatment for CPP. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can reduce inflammation and pain. For more severe cases, antidepressants or anticonvulsants may be prescribed to manage nerve pain. Hormonal therapies can also be effective, especially if the pain is related to conditions like endometriosis or menstrual cycles.
- Physical Therapy: A specialized physical therapy program can address musculoskeletal issues contributing to CPP. Techniques may include pelvic floor muscle rehabilitation, manual therapy to relieve muscle tension, and exercises to strengthen the pelvic muscles.
- Surgical Interventions: Surgery may be considered for certain conditions underlying CPP, such as endometriosis, fibroids, or adhesions. Minimally invasive techniques, like laparoscopy, are preferred to reduce recovery time and complications.
- Psychological Support: Chronic pain can have a significant psychological impact. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and other counseling services can help manage the emotional aspects of living with CPP.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture, biofeedback, and nerve stimulation techniques may offer relief for some individuals. These methods can be used alongside conventional treatments to manage pain.
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: Modifications to diet and lifestyle can play a supportive role in managing CPP. For instance, reducing inflammatory foods, practicing stress reduction techniques, and engaging in regular physical activity may help alleviate symptoms.
Importance of a Multidisciplinary Approach to Managing CPP Symptoms
A multidisciplinary approach is paramount in treating CPP effectively. This strategy involves the collaboration of various healthcare professionals, including gynecologists, urologists, pain management specialists, physical therapists, and mental health professionals. By integrating different areas of expertise, healthcare providers can address the multifaceted nature of CPP, tailoring treatment plans to meet the unique needs of each individual.
The multidisciplinary model allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the patient, considering not only the physical but also the psychological, social, and environmental factors contributing to their pain. This holistic perspective ensures that all potential causes of CPP are explored and that treatment strategies are more effective and patient-centered.
However, managing Chronic Pelvic Pain requires a thoughtful and coordinated approach, emphasizing the need for personalized treatment plans based on the underlying causes. Incorporating a multidisciplinary team into the care process ensures that patients receive the most comprehensive and effective treatment, offering the best chance for symptom relief and improved quality of life. With ongoing research and advancements in medical treatments, the outlook for individuals suffering from CPP continues to improve, promising more effective and targeted therapies in the future.
Managing Chronic Pelvic Pain Symptoms at Home
Several strategies can be employed at home to manage symptoms effectively. Through lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, stress management techniques, and exercise recommendations, individuals can find relief and improve their overall well-being. Let’s explore these strategies in detail.
Lifestyle Modifications and Home Remedies to Alleviate Symptoms
Adopting certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can play a crucial role in managing chronic pelvic pain. Here are some tips to consider:
- Heat Therapy: Applying a warm compress or a heating pad to the pelvic area can help reduce muscle tension and pain.
- Regular Sleep Patterns: Ensuring you get enough rest and maintain a consistent sleep schedule can help reduce stress and improve pain management.
- Avoidance of Trigger Activities: Identify activities that exacerbate your pain and try to modify or avoid them.
Dietary Changes
What you eat can affect your pelvic pain. Implementing dietary changes can help reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms:
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon, chia seeds, and walnuts, to help reduce inflammation.
- High-fiber Foods: A diet high in fiber can help prevent constipation, which can exacerbate pelvic pain. Include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains in your meals.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps prevent urinary tract infections and constipation, both of which can cause pelvic discomfort.
Stress Management Techniques
Stress can worsen chronic pelvic pain, making it essential to incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: These practices can help you stay present and reduce anxiety and stress levels.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Engaging in deep breathing can help relax your pelvic floor muscles and alleviate pain.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Gentle forms of exercise like yoga and tai chi can promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Exercise and Physical Activity Recommendations
Physical activity is beneficial for managing chronic pelvic pain, but it’s important to choose the right type of exercise:
- Pelvic Floor Physiotherapy: Working with a physiotherapist can help strengthen and relax your pelvic floor muscles, reducing pain.
- Low-impact Exercise: Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling can increase blood flow and reduce pain without putting too much strain on your body.
- Stretching: Regular stretching can help relieve tension in the pelvic area and improve flexibility.
Managing chronic pelvic pain requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle adjustments, dietary modifications, stress management, and appropriate exercise. By incorporating these strategies into your daily routine, you can take control of your symptoms and improve your quality of life. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment plan to ensure it’s safe and suitable for your specific needs.
When to See a Doctor
Deciphering when to seek medical advice for chronic pelvic pain can be challenging. Understanding the signs that necessitate a professional evaluation is crucial for your health and well-being. Early intervention plays a pivotal role in effectively managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving the quality of life. This guide provides insights into recognizing the critical indicators that it’s time to see a doctor.
Identifying Symptoms That Require Attention
Chronic pelvic pain is a persistent discomfort that may indicate underlying health issues. Here are some signs that you should not ignore:
- Persistent or Intermittent Pain: If you experience continuous or occasional pain in the pelvic region that lasts for six months or more, it’s essential to seek medical advice.
- Severe Pain: Sudden, intense pelvic pain, especially if it’s a new symptom, warrants immediate medical evaluation.
- Pain Associated with Other Symptoms: Pelvic pain accompanied by symptoms such as fever, nausea, vomiting, abnormal bleeding, or changes in urinary or bowel habits should prompt a visit to the doctor.
- Impact on Daily Activities: When pelvic pain affects your ability to perform daily tasks, work, or enjoy leisure activities, it’s time to consult a healthcare professional.
- Changes in Pain Patterns: A noticeable increase in pain intensity, frequency, or a change in the pain’s nature (sharp, dull, throbbing) should be evaluated.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is key in managing chronic pelvic pain. It can help in:
- Diagnosing Underlying Conditions: Early diagnosis of conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, or pelvic inflammatory disease can lead to more effective management strategies.
- Preventing Complications: Timely medical intervention can prevent potential complications associated with untreated conditions.
- Improving Quality of Life: Early treatment can alleviate pain and improve your overall quality of life, allowing you to return to your daily activities without discomfort.
- Customized Treatment Plans: Seeking help early enables healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and symptoms.
Recognizing when to seek medical advice for chronic pelvic pain is critical. Paying attention to the signs and understanding the importance of early intervention can make a significant difference in your health outcomes. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, do not hesitate to consult a healthcare provider. Prioritizing your health is a step towards a pain-free life.
By incorporating these insights into your health awareness routine, you can ensure that you’re taking the right steps towards managing chronic pelvic pain effectively. Remember, your health is invaluable, and seeking professional advice at the right time can lead to better management of your symptoms and an improved quality of life.
Conclusion:
If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms of chronic pelvic pain, it’s important to remember that you’re not alone. Many people face similar challenges, and there’s a wealth of resources and support available to help you navigate this condition. Seeking professional help is a critical step towards understanding your pain and finding relief. Healthcare professionals can offer comprehensive assessments, diagnostic tests, and a range of treatment options tailored to your specific needs.
Don’t let chronic pelvic pain control your life. With the right knowledge and support, you can manage your symptoms and improve your quality of life. We encourage you to take that first step towards healing by consulting with a medical professional who can guide you through this journey. Remember, seeking help is a sign of strength and the first step towards reclaiming your health and wellbeing.