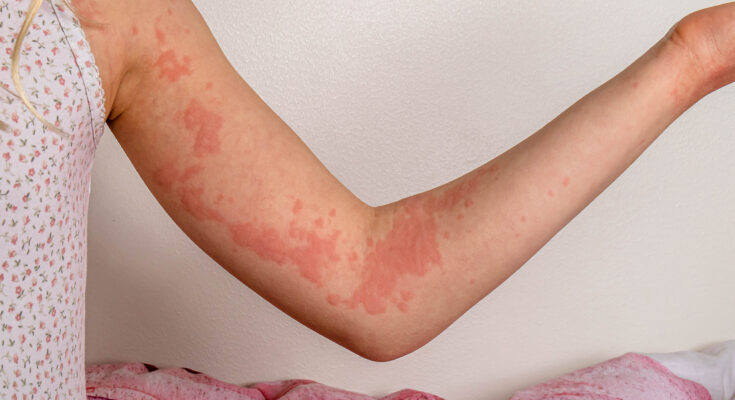
Chronic Hives Symptoms: Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, is a condition that affects many individuals worldwide, leading to uncomfortable, itchy, and often unpredictable outbreaks.
Unlike acute hives, which may last a few days or weeks, chronic hives persist for six weeks or longer, significantly impacting the quality of life of those affected.
Understanding Chronic Hives
Chronic hives stand out from their acute counterparts primarily due to their duration and, often, their idiopathic nature, meaning they have no known cause. While acute hives might result from exposure to certain foods, medications, or other allergens, chronic hives persist without a clear trigger. These welts can appear anywhere on the body and may come and go, with episodes lasting for months or even years. The unpredictability and persistence of chronic hives significantly affect patients’ quality of life, making diagnosis and management a priority for healthcare providers.
Prevalence and Demographics
Chronic hives affect a broad range of individuals across different age groups, genders, and racial backgrounds. However, statistics indicate certain patterns in prevalence and demographics. Research suggests that chronic hives are more common in adults than in children, with a higher incidence among women compared to men. The prevalence rate of chronic hives in the general population is estimated to be around 1% to 2%. This condition does not discriminate by age, as both adults and children can be affected, though the majority of cases are diagnosed in individuals between 20 and 40 years of age.
The demographics affected by chronic hives underscore the importance of understanding this condition from a medical and social perspective. The impact on quality of life, including sleep disruption, social isolation, and emotional distress, highlights the need for effective treatment strategies and support systems for those affected. Awareness and education about chronic hives can aid in early diagnosis and management, offering hope and relief to those living with this challenging condition.
By shedding light on the nature of chronic hives, including their definition, differences from acute hives, and the demographics most affected, individuals and healthcare providers can better navigate the complexities of this condition. The journey toward understanding and managing chronic hives begins with recognizing its significance and the widespread impact it has on the lives of many around the globe.
Symptoms of Chronic Hives
Symptoms of chronic hives can vary significantly from one individual to another but typically include the following:
- Red or Skin-Colored Welts: These can appear anywhere on the body and may change shape, move around, disappear, and reappear over short periods.
- Intense Itching: One of the most common and frustrating symptoms, the itching can be severe and persistent, affecting sleep and daily activities.
- Swelling: Known as angioedema, swelling often accompanies hives, particularly around the eyes, lips, and sometimes the throat, hands, and feet, adding to discomfort and alarm.
Symptoms can be triggered or worsened by heat, stress, and certain medications or foods in some individuals, making management a constant challenge.
Differentiating Between Chronic Hives and Other Skin Conditions
Chronic hives can sometimes be confused with other skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or heat rash, due to overlapping symptoms like redness and itchiness. However, there are key differences:
- Duration and Pattern: Chronic hives last longer than six weeks, with welts that appear and clear within a 24-hour period. Other conditions, like eczema, have more persistent lesions.
- Trigger Response: Chronic hives often flare up in response to specific triggers that can sometimes be identified and avoided, unlike some other conditions that have more complex causes.
- Physical Appearance: The welts of chronic hives are typically round and may have a halo or flare around the edge, distinguishing them from the more uniform rash of eczema or the scaly plaques of psoriasis.
Personal Anecdotes to Illustrate the Impact of Symptoms
One individual’s experience highlights the unpredictable nature of chronic hives: “My life changed drastically. One day I was fine, and the next, I woke up covered in itchy welts. They would disappear and reappear without warning. It wasn’t just the physical discomfort but the mental toll it took, constantly worrying about when the next flare-up would occur.”
Another case study involves a person who initially mistook their symptoms for a food allergy: “I eliminated so many foods from my diet, thinking I was allergic. It was only after seeing a specialist that I was diagnosed with chronic hives. Learning to manage stress and avoiding known triggers has made a significant difference.”
Understanding the symptoms of chronic hives and how they differ from other skin conditions is crucial for effective management and treatment. Personal stories underscore the profound impact chronic hives can have on an individual’s life, emphasizing the importance of seeking medical advice for diagnosis and support.
Triggers and Causes of Chronic Hives
Understanding the triggers and causes of chronic hives is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article provides an in-depth exploration of the known causes and triggers, including autoimmune causes, allergic reactions, environmental factors, stress and lifestyle factors, and a discussion on idiopathic hives, where no cause is found.
Autoimmune Causes
One of the primary triggers of chronic hives is autoimmune dysfunction. In this scenario, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, believing it to be a threat. Specifically, the immune system can target and attack the skin cells, leading to the development of hives. Autoimmune thyroid disease is one commonly associated condition, highlighting the interconnected nature of autoimmune disorders and chronic hives.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions are another significant trigger for chronic hives. These reactions occur when the body’s immune system overreacts to a foreign substance, such as food, medication, or insect stings. The substances, known as allergens, can prompt the release of histamine and other chemicals from skin cells, causing hives and swelling. Identifying and avoiding these allergens is a critical step in managing chronic hives.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a considerable role in triggering chronic hives. Temperature extremes, sunlight, water, and physical pressure on the skin (such as from tight clothing) can all cause hives to flare up. These factors do not cause hives in everyone but can be significant triggers for those with chronic urticaria. Understanding and avoiding these environmental triggers can help reduce the frequency and severity of hives outbreaks.
Stress and Lifestyle Factors
The impact of stress and lifestyle factors on chronic hives is increasingly recognized. Emotional stress, lack of sleep, and poor diet can exacerbate the symptoms of chronic hives. Stress, in particular, can lead to the release of stress hormones that may trigger an outbreak of hives. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including stress management techniques, can be beneficial in managing chronic hives.
Idiopathic Hives
In many cases of chronic hives, a specific cause cannot be found, leading to a diagnosis of idiopathic hives. This diagnosis can be frustrating for patients and clinicians alike. However, it’s important to continue managing the symptoms through lifestyle adjustments, medication, and avoiding known triggers, even when the exact cause remains elusive.
For those with idiopathic hives, ongoing symptom management is key. Consulting with healthcare professionals who specialize in allergies and immunology can provide tailored advice and treatment plans to help manage chronic hives effectively.
Diagnosing Chronic Hives: Understanding the Process
Understanding the steps involved in diagnosing chronic hives, the role of allergy tests and other diagnostic tools, and knowing when it’s time to see a doctor or specialist are crucial in managing this condition effectively.
Steps in Diagnosing Chronic Hives
The diagnosis of chronic hives primarily involves a detailed medical history and a thorough physical examination. Here’s a closer look at the process:
- Medical History: This is the first and most critical step. Your doctor will ask you about the duration of your hives, any potential triggers you’ve noticed, and if you’ve experienced similar episodes in the past. They may also inquire about your exposure to certain allergens, medications, or underlying health conditions.
- Physical Examination: During the physical exam, your doctor will look at the hives and check for any accompanying signs, such as swelling or redness. They may also assess your overall skin condition and look for any related symptoms.
- Symptom Diary: You might be asked to keep a diary of your hives, noting when they occur, how long they last, and any potential triggers you’ve encountered. This diary can be a valuable tool in identifying patterns or specific causes.
The Role of Allergy Tests and Other Diagnostic Tools
Allergy tests and other diagnostic tools can play a significant role in pinpointing the cause of chronic hives. Here’s how they fit into the diagnostic process:
- Allergy Tests: These tests, which may include skin prick tests or blood tests for specific IgE antibodies, can help identify allergens that may trigger your hives. However, it’s worth noting that chronic hives are not always caused by allergies.
- Other Diagnostic Tools: Depending on your symptoms and medical history, your doctor may also recommend additional tests. These can include blood tests to check for underlying conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or thyroid disease, which can sometimes cause hives.
- Elimination Diets: If your doctor suspects that your hives may be related to food allergies, they might suggest an elimination diet. This involves removing certain foods from your diet and gradually reintroducing them to observe any reactions.
When to See a Doctor or Specialist
Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial in effectively managing chronic hives. Here are some guidelines:
- Persistent Symptoms: If you’ve been experiencing hives most days for more than six weeks, it’s time to see your doctor.
- Severe Reactions: If your hives are accompanied by severe symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat, or if you feel dizzy or faint, seek immediate medical attention.
- Lack of Response to Treatment: If your hives do not respond to over-the-counter remedies or if they keep returning, a specialist, such as an allergist or dermatologist, can offer more targeted treatments and diagnostic tests.
However, diagnosing chronic hives involves a comprehensive approach that includes evaluating your medical history, conducting a physical examination, and possibly utilizing allergy tests and other diagnostic tools. Understanding when to seek help from a doctor or specialist is essential in managing this condition and improving your quality of life. If you suspect you have chronic hives, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan.
Managing and Treating Chronic Hives: A Comprehensive Guide
With the right treatment approach and symptom management strategies, individuals can find relief and improve their daily lives. This guide provides an overview of the treatment options available for chronic hives, tips for managing symptoms at home, and advice on when to seek emergency care.
List of Treatment Options
The management of chronic hives focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing outbreaks. Treatment options include:
- Antihistamines: These are the cornerstone of treatment for chronic hives. Second-generation antihistamines, which are less likely to cause drowsiness, are often recommended. In some cases, doctors may prescribe a higher dose than what is typically used for allergy relief.
- Corticosteroids: For more severe cases, short-term use of oral corticosteroids may be prescribed to quickly reduce swelling and redness. However, due to potential side effects, their long-term use is generally avoided.
- Leukotriene Receptor Antagonists: Medications like montelukast (Singulair) can be used in conjunction with antihistamines to provide additional symptom relief.
- Immunosuppressants: In cases where chronic hives are resistant to other treatments, drugs that modulate the immune system, such as cyclosporine, might be considered. These treatments require careful monitoring due to their potential for serious side effects.
- Biologics: Omalizumab (Xolair), an injectable medication designed to target and block immunoglobulin E (IgE), a substance in the body that can cause allergic reactions, has been approved for treating chronic hives in individuals 12 years of age and older.
- Lifestyle and Dietary Changes: Identifying and avoiding triggers is also a crucial aspect of managing chronic hives. This may involve keeping a symptom diary to track the relationship between outbreaks and specific activities or foods.
Tips for Managing Symptoms at Home
In addition to medical treatment, there are several strategies you can employ at home to ease the discomfort of chronic hives:
- Cool Compresses: Applying a cold, damp cloth to the affected area can help soothe the itch and reduce inflammation.
- Avoid Known Triggers: If you’ve identified factors that exacerbate your hives, such as certain foods, stress, or physical exertion, try to avoid them as much as possible.
- Dress Comfortably: Wear loose, light clothing to avoid irritating the skin further.
- Stress Management: Since stress can trigger or worsen hives, consider incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises into your routine.
When to Seek Emergency Care
While chronic hives are typically not life-threatening, there are situations where immediate medical attention is necessary:
- Difficulty Breathing: If hives develop around the throat or tongue, swelling can interfere with breathing, constituting a medical emergency.
- Severe Allergic Reaction: Signs of a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), such as difficulty breathing, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, rapid heartbeat, and dizziness, require immediate emergency care.
- Lack of Response to Treatment: If your symptoms do not improve with treatment, or if you experience severe side effects from medication, consult your healthcare provider.
By understanding the treatment options available and implementing strategies to manage symptoms at home, individuals living with chronic hives can lead more comfortable and fulfilling lives. Remember, it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific needs and to determine when emergency care is needed.
Living with Chronic Hives
Living with chronic hives can be a challenging and often frustrating experience. Chronic hives, also known as chronic urticaria, manifest as red, itchy welts on the skin that can last for six weeks or longer. This condition not only affects your physical well-being but can also have a significant impact on your mental health. However, with the right management strategies and support systems in place, individuals living with chronic hives can lead fulfilling lives. Here are some tips on daily management and coping strategies, emphasizing the importance of mental health and support networks.
1. Understand Your Triggers
The first step in managing chronic hives is to understand what triggers your symptoms. Common triggers include stress, certain foods, medications, temperature changes, and infections. Keep a diary to track your activities, what you eat, and when your symptoms flare up. This can help you identify patterns and avoid potential triggers.
2. Develop a Daily Care Routine
Developing a daily skincare routine can help manage the physical symptoms of chronic hives. Use gentle, unscented skin products to avoid irritation. Taking cool baths or applying cool, wet cloths to the affected areas can also provide relief. Over-the-counter antihistamines may help reduce itching and swelling, but it’s important to consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
3. Prioritize Mental Health
Living with a chronic condition can take a toll on your mental health. Feelings of frustration, anxiety, and depression are common. It’s essential to prioritize your mental health by practicing stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises. If your mental health is significantly affected, consider seeking support from a mental health professional who can provide coping strategies and therapy.
4. Build a Support Network
Having a strong support network is crucial for individuals living with chronic hives. Connect with friends and family who understand your condition and can provide emotional support. Joining support groups, whether in-person or online, can connect you with others who are going through similar experiences. Sharing stories and tips can be incredibly empowering and reduce feelings of isolation.
5. Collaborate with Healthcare Providers
Work closely with your healthcare providers to manage your chronic hives effectively. This may include regular check-ups, medication management, and exploring treatment options. Your healthcare team can also provide referrals to specialists, such as allergists or dermatologists, who have experience treating chronic hives.
6. Educate Yourself and Others
Educating yourself about chronic hives will empower you to make informed decisions about your care. Additionally, educating those around you can foster a supportive environment and increase understanding of your condition. Resources are available through healthcare providers and reputable websites dedicated to chronic hives and allergy research.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage individuals experiencing symptoms consistent with chronic hives to consult healthcare professionals. A tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment is essential, as it can significantly alleviate symptoms, improve quality of life, and, in some instances, lead to complete remission. Dermatologists and allergists can offer a range of solutions, from lifestyle adjustments to medication, aimed at controlling the condition effectively.
Furthermore, the landscape of chronic hives treatment is evolving, with ongoing research shedding new light on potential causes and innovative therapies. Advances in medical science promise more targeted and effective treatments, enhancing the outlook for those living with this condition. The future holds promise for improved management strategies and, hopefully, permanent solutions to chronic hives.
In closing, while chronic hives can be a distressing and persistent condition, the combination of professional healthcare guidance, personal vigilance, and the promising horizon of medical research offers a path forward. By staying informed and proactive in seeking treatment, individuals affected by chronic hives can look forward to better health outcomes and an improved quality of life.