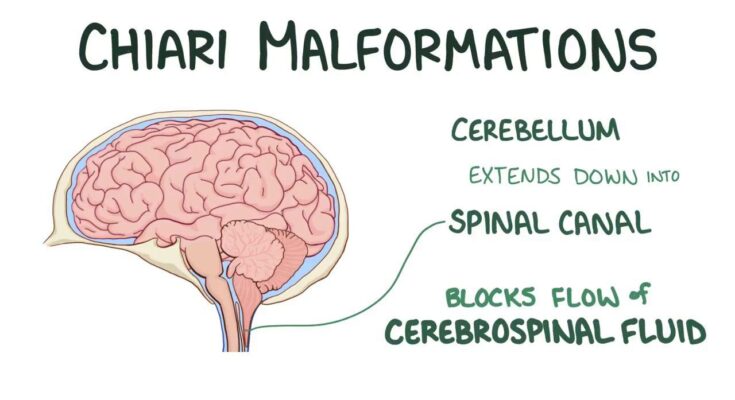
Chiari Malformation Symptoms: Chiari Malformation is a complex condition that affects the structure of the brain, specifically where the brain and spinal cord meet.
This condition leads to the cerebellum (part of the brain that controls balance) protruding into the spinal canal. It can cause a myriad of symptoms and has various causes, each contributing to the severity of the condition.
What is Chiari Malformation?
Chiari malformation is a condition where brain tissue extends into the spinal canal. It occurs when part of the skull is abnormally small or misshapen, pressing on the brain and forcing it downward. This neurological disorder is named after Hans Chiari, the Austrian pathologist who first described it in the late 19th century. Chiari malformation can cause a range of symptoms, from none at all to severe. The most common symptoms include headaches, balance problems, dizziness, muscle weakness, numbness, vision problems, hearing loss, and difficulty swallowing. Diagnosing Chiari malformation often involves magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to provide a detailed image of the area and assess the extent of the brain tissue protrusion.
Types of Chiari Malformation
There are several types of Chiari malformation, classified according to the anatomy of the brain tissue that is displaced into the spinal canal and the presence of associated anomalies. The main types include:
- Type I: The most common form, where the lower part of the cerebellum extends into the foramen magnum without the spinal cord being involved. Symptoms may not appear until adolescence or adulthood.
- Type II: Also known as Arnold-Chiari malformation, it involves both cerebellar and brain stem tissue extending into the spinal canal. It is usually associated with myelomeningocele, a form of spina bifida, and is often diagnosed in infancy or early childhood.
- Type III: The rarest form, characterized by cerebellum and brainstem herniation into the spinal canal through a defect in the back of the skull. This severe form is often associated with significant neurological defects.
- Type IV: Involves an incomplete or underdeveloped cerebellum, a condition known as cerebellar hypoplasia. This type is extremely rare and can be diagnosed via imaging tests.
Prevalence and Demographics
Chiari malformation affects people of all ages, with Type I generally being identified in adolescents or adults and Type II most commonly diagnosed in infants and young children. The prevalence of Chiari malformation varies, but studies suggest that Type I occurs in about 1 in every 1,000 births. However, with the increased use of MRI, more cases are being detected, suggesting that the condition may be more common than previously thought.
Chiari malformations can affect both males and females, although Type I is slightly more common in females. The condition is present at birth (congenital), but symptoms can appear at any age, depending on the type of Chiari malformation and the severity of the tissue displacement.
Understanding Chiari malformation, its types, prevalence, and demographics is crucial for early diagnosis and management. While there is no cure, treatment options such as surgery can alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by this condition.
Symptoms of Chiari Malformation: An In-Depth Look
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early detection and management of this condition. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the symptoms associated with Chiari malformation, offering insights into how they manifest in both children and adults.
Detailed Breakdown of Common Symptoms
The most prevalent symptoms of Chiari malformation include:
- Headaches: Often severe, these headaches are typically felt at the back of the head and may be exacerbated by coughing, sneezing, or bending over.
- Neck pain: A common complaint, sometimes radiating to the shoulders or down the spine.
- Dizziness and balance problems: Individuals may feel unsteady or have a hard time maintaining balance.
- Visual disturbances: This can include blurred vision, double vision, or sensitivity to light.
- Hearing loss or tinnitus: Some people experience a ringing in the ears or a decrease in hearing ability.
- Difficulty swallowing: Known as dysphagia, this can lead to choking or gagging while eating.
- Muscle weakness or numbness: This often occurs in the extremities and can affect coordination.
- Breathing problems: In severe cases, sleep apnea or other breathing irregularities may occur.
Symptoms in Children vs. Adults
While many symptoms of Chiari malformation are similar in both children and adults, there are some distinctions worth noting. In children, symptoms can include:
- Changes in feeding or swallowing: Infants may exhibit difficulty feeding, which is related to the muscle weakness associated with Chiari malformation.
- Developmental delays: Delays in reaching typical developmental milestones, such as walking or talking, may be observed.
- Irritability or excessive crying: In babies, this may be one of the few indicators of discomfort or pain.
Adults, on the other hand, are more likely to report:
- Chronic headaches and neck pain: These symptoms are more prevalent and often more severe in adults.
- Cognitive difficulties: Adults may experience problems with memory, concentration, and completing complex tasks.
Recognizing these symptoms early on is key to seeking appropriate medical evaluation and treatment. If you or someone you know is experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, consulting with a healthcare professional is crucial for a proper diagnosis and management plan. Remember, while Chiari malformation presents challenges, many individuals with the condition lead full and active lives with the right treatment and support.
Causes of Chiari Malformation
Understanding these causes can provide insight into the condition’s nature and help in managing or mitigating its effects. Below, we explore the primary causes of Chiari malformation, focusing on genetic factors, developmental issues during fetal growth, and associated conditions and risk factors.
Genetic Factors and Heredity
Research has shown that genetics play a significant role in the development of Chiari malformation. The condition can run in families, suggesting a hereditary component. Although the exact genes involved are not fully identified, familial clusters of the condition indicate that genetic predisposition is a key factor. If a family member is diagnosed with Chiari malformation, it increases the likelihood of the condition appearing in other family members, highlighting the importance of genetic counseling and awareness.
Developmental Issues During Fetal Growth
Chiari malformation can also result from complications during fetal development. The condition is characterized by improper formation or underdevelopment of the skull, which leads to insufficient space for the cerebellum, forcing part of it to extend into the spinal canal. This anomaly may be caused by a variety of factors during pregnancy, including nutritional deficiencies, exposure to harmful substances, or other environmental influences that affect the developing fetus. Ensuring proper health and nutrition during pregnancy can help minimize the risk of developmental issues that could lead to Chiari malformation.
Associated Conditions and Risk Factors
Several conditions and risk factors are associated with an increased likelihood of developing Chiari malformation. These include:
- Spinal Cord Conditions: Disorders that affect the spine can contribute to the development of Chiari malformation by altering the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid or by physically affecting the structure of the spinal canal and skull.
- Connective Tissue Disorders: Conditions that affect the connective tissue, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can lead to structural abnormalities in the skull and spine, increasing the risk of Chiari malformation.
- Other Risk Factors: Certain risk factors, including premature birth and low birth weight, have been associated with an increased risk of Chiari malformation. These factors may reflect underlying developmental issues that contribute to the condition.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with Chiari malformation is crucial for early detection, management, and treatment of the condition. While some factors, like genetics, cannot be changed, awareness and management of associated conditions and environmental influences can help reduce the risk or severity of Chiari malformation. If you or a loved one are experiencing symptoms or have concerns about this condition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and guidance.
Diagnosing Chiari Malformation
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management and treatment. The process typically involves a detailed medical history, a thorough physical examination, and advanced imaging tests.
Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing Chiari malformation involves a comprehensive medical history and physical examination. During this stage, healthcare providers look for telltale symptoms such as headaches, difficulty swallowing, balance problems, and other neurological signs that may suggest Chiari malformation. A detailed account of the patient’s symptoms, their onset, duration, and any factors that alleviate or exacerbate these symptoms is crucial. The physical examination helps to identify any neurological deficits, such as changes in reflexes, muscle weakness, or sensory loss, which might indicate the presence of Chiari malformation or related complications.
Imaging Tests (MRI, CT Scans)
Imaging tests play a pivotal role in the diagnosis of Chiari malformation. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is the most effective tool for visualizing the extent to which brain tissue extends into the spinal canal. MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain and spinal cord, helping in the accurate diagnosis of Chiari malformation types I, II, III, and IV. In some cases, a CT scan may also be used to obtain cross-sectional images of the brain and spinal structures, although it is less commonly used for Chiari malformation due to its limited ability to capture the malformation’s detailed anatomy compared to MRI.
Challenges in Diagnosing
Diagnosing Chiari malformation presents several challenges. The condition’s symptoms can be nonspecific and overlap with those of many other neurological disorders, which can lead to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. Some individuals with Chiari malformation may not show any symptoms (asymptomatic), making the condition harder to identify without imaging tests. Moreover, interpreting MRI and CT scan results requires expertise, as minor anomalies must be distinguished from normal anatomical variations. Thus, a multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, radiologists, and neurosurgeons is often necessary to confirm a diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
However, diagnosing Chiari malformation involves a systematic approach that includes taking a detailed medical history, conducting a thorough physical examination, and utilizing advanced imaging techniques. Despite the challenges in diagnosing this condition, accurate identification is essential for managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Treatment Options for Chiari Malformation
Here, we explore the various treatment options ranging from non-surgical methods to surgical interventions, as well as the importance of long-term management and follow-up care.
Non-surgical Treatments
For individuals with Chiari malformation who experience mild symptoms or are asymptomatic, non-surgical treatments can be an effective way to manage the condition. These include:
- Medications: Pain relievers can be prescribed to manage symptoms such as headaches and neck pain. Additionally, medication may also be used to address other symptoms like dizziness or muscle weakness.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Modifying certain activities that exacerbate symptoms can help manage the condition. Patients are often advised to avoid activities that involve straining. Physical therapy may also be recommended to strengthen muscle and improve flexibility, potentially alleviating some symptoms.
These non-invasive approaches are aimed at symptom management and improving the quality of life for patients without the need for surgery.
Surgical Treatments
Surgery may be recommended for patients experiencing severe symptoms or if there is evidence of nerve damage or significant obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid flow. The most common surgical procedure for Chiari malformation is:
Posterior Fossa Decompression: This surgery involves removing a small section of bone from the back of the skull and, sometimes, part of the spinal column to relieve pressure on the brain and allow for normal cerebrospinal fluid flow. The surgeon may also open and widen the dura mater, the brain’s protective covering, to create more space for the cerebrospinal fluid to circulate.
Other surgical options depend on the patient’s specific condition and may include addressing related conditions such as syringomyelia (cysts in the spinal cord).
Long-term Management and Follow-up Care
Long-term management is crucial for individuals diagnosed with Chiari malformation. Regular follow-up care allows healthcare providers to monitor the condition and address any changes in symptoms. It may include:
- Routine Imaging Tests: MRI scans are often used to monitor the progression of the condition and assess the effectiveness of the treatment plan.
- Symptom Monitoring: Patients should report any new or worsening symptoms to their healthcare provider promptly. This includes tracking headaches, balance issues, and any changes in muscle strength or sensation.
- Lifestyle Considerations: Continuing with lifestyle adjustments and physical therapy as recommended by healthcare professionals can help manage symptoms and maintain quality of life.
The goal of long-term management is to ensure that individuals with Chiari malformation can lead as normal and active lives as possible while minimizing the impact of the condition on their daily activities.
However, the treatment of Chiari malformation varies widely and is highly individualized. A multidisciplinary approach involving neurologists, neurosurgeons, and other specialists is often necessary to develop an effective treatment plan. Whether through non-surgical methods, surgical intervention, or a combination of both, the focus is always on improving patient outcomes and enhancing quality of life.
Living with Chiari Malformation
Living with Chiari Malformation can be challenging, but with the right lifestyle modifications and coping strategies, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Understanding the condition and knowing where to find support are crucial steps in managing symptoms and improving quality of life. Here, we will explore practical tips for daily living, alongside highlighting the importance of connecting with patient groups and online forums for support.
Lifestyle Modifications and Coping Strategies
- Adopt a Gentle Exercise Regime: Regular, low-impact exercise such as walking, swimming, or yoga can help improve overall health without exacerbating symptoms. Consult with a healthcare professional to tailor a workout plan that’s safe for you.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet can support general well-being. Some individuals with Chiari Malformation may find relief from symptoms by managing their diet to avoid foods that trigger headaches or other symptoms.
- Prioritize Rest: Adequate sleep and rest are essential. Use ergonomic pillows or mattresses designed to reduce neck strain, and establish a regular sleep schedule to help manage fatigue.
- Stress Management Techniques: Stress can worsen symptoms, so it’s important to incorporate stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep-breathing exercises, or mindfulness into your daily routine.
- Avoid Certain Activities: Activities that strain the neck or involve sudden jolts (like roller coasters or high-impact sports) should be avoided to prevent symptom flare-ups.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used under a doctor’s guidance. Some may also find relief through alternative treatments like acupuncture or chiropractic care, though it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying these options.
Support Resources
- Patient Groups: Joining a Chiari Malformation patient group can provide a sense of community and belonging. These groups offer a platform to share experiences, advice, and encouragement with others who understand what you’re going through.
- Online Forums: Websites such as Reddit, HealthUnlocked, or specific Chiari Malformation forums host vibrant communities where individuals can seek advice, share stories, and find emotional support from the comfort of their home.
- Educational Resources: Utilizing educational resources provided by organizations like the Chiari & Syringomyelia Foundation (CSF) or the American Syringomyelia & Chiari Alliance Project (ASAP) can be incredibly helpful. These organizations offer a wealth of information on treatment options, research updates, and tips for managing symptoms.
- Social Media Groups: Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter have numerous Chiari Malformation groups and hashtags that connect individuals across the globe. These platforms can be used to find support, learn from others’ experiences, and stay informed about the latest research and treatment options.
By embracing these lifestyle modifications and tapping into the wealth of support resources available, individuals living with Chiari Malformation can navigate their diagnosis with confidence. Remember, you’re not alone, and with the right strategies and support network, you can manage your symptoms and lead a healthy, active life.
Prevention and Research on Chiari Malformation
Current Research on Chiari Malformation
Research into Chiari Malformation has made significant strides in recent years, focusing on understanding the genetic, developmental, and environmental factors that contribute to the condition. Scientists are exploring the genetic markers and anomalies associated with Chiari Malformation to better predict its occurrence and severity. Advanced imaging techniques and technologies are also being developed to improve the diagnosis and understanding of the anatomical changes in the brain and spinal cord associated with this condition. Through these efforts, the medical community aims to enhance the precision of diagnosis, tailor treatments to individual needs, and improve overall patient outcomes.
Potential Prevention Strategies
Preventing Chiari Malformation is challenging, as it often involves congenital (present at birth) factors. However, ongoing research into the genetic aspects of the condition may eventually lead to strategies for identifying those at higher risk and potentially mitigating those risks. Currently, the focus remains on early detection and intervention to prevent the progression of symptoms and complications. For individuals diagnosed with conditions associated with Chiari Malformation, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome or other connective tissue disorders, proactive management of these conditions may help in reducing the risk of developing Chiari Malformation or its severity.
Future Directions in Treatment and Diagnosis
The future of treating and diagnosing Chiari Malformation looks promising, with several key areas of focus. One area is the development of minimally invasive surgical techniques aimed at reducing recovery times and improving outcomes for patients. Researchers are also investigating the effectiveness of various surgical and non-surgical treatments to establish more standardized treatment protocols.
Additionally, there is a growing interest in the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to analyze imaging data, which could lead to more accurate and earlier diagnosis of Chiari Malformation. These technologies have the potential to identify subtle anomalies that might be missed by traditional methods, thereby allowing for earlier intervention.
In the realm of non-invasive treatments, there is ongoing research into physical therapy and other rehabilitation strategies to manage symptoms and improve quality of life for those affected by Chiari Malformation. These approaches focus on alleviating symptoms, improving neurological function, and preventing further complications.
The continued collaboration between neurologists, geneticists, and researchers across various disciplines is crucial for the advancement of knowledge and treatment of Chiari Malformation. With ongoing research and the development of new technologies and treatments, the future holds the promise of more effective management and better outcomes for individuals with this condition.
However, while prevention of Chiari Malformation remains a complex issue, advancements in research are paving the way for more effective treatments and diagnostic tools. Through a combination of genetic research, innovative treatment approaches, and the development of new technologies, there is hope for significant improvements in the care and quality of life for individuals with Chiari Malformation.
Conclusion
It is essential to remember that while self-awareness is important, it is equally vital to seek professional medical advice when symptoms arise. Self-diagnosis can lead to misinterpretation and delays in receiving the appropriate care. Healthcare professionals are equipped with the knowledge and tools to accurately diagnose and treat various conditions, ensuring that you receive the most effective treatment plan tailored to your specific needs.
We encourage everyone not to overlook or dismiss any unusual changes in their health. Taking action by consulting with a medical professional can make a profound difference in your overall well-being. Remember, prioritizing your health is one of the most important investments you can make for yourself. Let’s embrace the importance of health awareness and make informed decisions towards a healthier future.
In conclusion, the journey to better health begins with recognizing the signs your body gives and understanding the reasons behind them. Don’t hesitate to seek medical advice for any symptoms you experience. Your health is your most valuable asset; treat it with the care and attention it deserves.