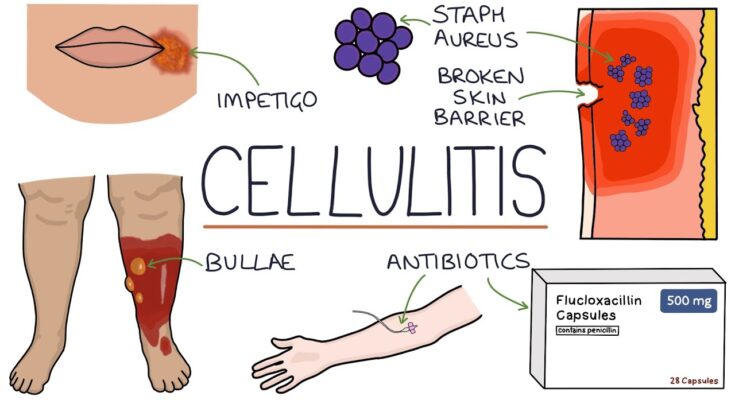
Cellulitis Treatment: Cellulitis is a common, yet potentially serious bacterial skin infection. The condition often presents as a swollen, red area of skin that feels hot and tender, and it can spread rapidly.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment options for cellulitis is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
This comprehensive guide provides essential information to help individuals recognize the symptoms, seek timely medical care, and understand the treatment strategies available.
What is Cellulitis?
Cellulitis is a common, potentially serious bacterial skin infection. It first appears as a swollen, red area that feels hot and tender to the touch and may spread rapidly. Cellulitis typically affects the skin on the lower legs, but it can occur in any area of the body, including the face, arms, and other areas. The condition results from bacteria, usually Staphylococcus or Streptococcus, entering through a crack or break in your skin. Without treatment, cellulitis can become life-threatening. Thus, it’s crucial to identify and treat this condition promptly.
Causes of Cellulitis
Cellulitis can be caused by various factors that introduce bacteria to the skin or underlying tissues:
- Cuts and Abrasions: The most common entry points for bacteria that lead to cellulitis.
- Insect or Animal Bites: Bites can introduce bacteria deep into the skin.
- Surgical Wounds: Post-operative wounds can become gateways for bacteria.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema, psoriasis, or dermatitis create breaks in the skin that can harbor bacteria.
- Ulcers: Existing ulcers, especially in diabetic patients, can be prone to infection.
- Foreign Objects in the Skin: Such as splinters or piercings.
Explanation of How Cellulitis Affects the Skin and Underlying Tissues
Cellulitis begins when bacteria enter through a breach in the skin. Once inside, they rapidly multiply, causing an infection that affects both the skin’s surface and its deeper layers. The immune system responds to the infection by increasing blood flow to the area, causing the redness, swelling, warmth, and pain associated with cellulitis. If not promptly treated with antibiotics, the infection can spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream, becoming a severe health risk.
The Importance of Distinguishing Cellulitis from Other Skin Conditions
Distinguishing cellulitis from other skin conditions, like eczema, dermatitis, or deep vein thrombosis, is crucial for several reasons. First, it ensures the appropriate treatment; cellulitis requires antibiotics, which are not effective against conditions caused by viruses or allergies. Second, misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary delays in treatment, increasing the risk of complications. Finally, understanding the signs and symptoms of cellulitis helps in seeking prompt medical attention, thus preventing the infection from becoming more serious.
However, recognizing the causes, understanding the impact on the skin and tissues, and differentiating cellulitis from other skin conditions are essential steps in managing this potentially severe infection effectively. Prompt treatment not only aids in a quicker recovery but also prevents the infection from becoming life-threatening.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Cellulitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Recognizing the symptoms early can significantly improve the effectiveness of treatments, reducing the risk of complications. In this guide, we’ll explore the hallmark symptoms of cellulitis, touch on less common indicators such as fever and chills, and highlight the importance of early symptom identification.
Key Symptoms of Cellulitis
The symptoms of cellulitis can develop quickly and may vary from mild to severe. The most common signs include:
- Redness: The affected skin area may appear red and may expand over time.
- Swelling: An increase in skin volume, making the area look swollen and feel tight.
- Warmth: The infected area often feels warm or hot to the touch.
- Pain and Tenderness: The area is usually painful, especially when touched or pressed.
- Skin Rash: A rash that develops rapidly and might spread swiftly across the skin.
These symptoms typically occur on the lower legs but can affect any area of the body, including the face and arms.
Less Common Symptoms
In some cases, individuals with cellulitis may also experience systemic symptoms, indicating that the infection is starting to spread or become more serious. These include:
- Fever: A high temperature that suggests your body is fighting a significant infection.
- Chills and Shivers: Feeling unusually cold or experiencing shivers can be a sign of the body’s response to infection.
- Fatigue: General tiredness and a feeling of being unwell can accompany the infection.
The Significance of Early Symptom Identification
Identifying cellulitis symptoms at an early stage is crucial for several reasons. Early treatment, typically involving antibiotics, can prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the body and the bloodstream, where it can cause severe health problems. Moreover, prompt medical intervention can alleviate symptoms more quickly and reduce the risk of recurrent infections.
Understanding the symptoms of cellulitis, both common and less common, enables individuals to seek timely medical advice. This not only facilitates a faster recovery but also minimizes the potential for complications. If you suspect you or someone you know has symptoms of cellulitis, it’s essential to contact a healthcare provider immediately for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
However, awareness and early recognition of cellulitis symptoms are key to effective treatment and recovery. By being informed and vigilant, individuals can ensure prompt action is taken, leading to better health outcomes.
How is Cellulitis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of cellulitis predominantly hinges on a detailed physical examination and a thorough review of the patient’s medical history. This article delves into the diagnostic process for cellulitis, emphasizing the significance of physical examinations, medical history, and the circumstances necessitating further testing.
Physical Examinations and Medical History
The initial step in diagnosing cellulitis involves a comprehensive physical examination by a healthcare provider. During this examination, the provider will look for common signs of cellulitis, such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. These symptoms can vary in severity and may be accompanied by fever or chills, indicating a systemic infection. The texture of the skin and the presence of any cuts, abrasions, or insect bites that could serve as entry points for bacteria are also assessed.
A patient’s medical history plays a pivotal role in the diagnosis of cellulitis. Healthcare providers will inquire about recent injuries, skin conditions, chronic illnesses, and any history of cellulitis. This information helps in determining the likelihood of cellulitis versus other skin conditions that may present with similar symptoms, such as eczema, deep vein thrombosis, or lymphedema.
The Need for Additional Tests
While the diagnosis of cellulitis is primarily clinical, additional tests may be necessary under certain conditions. Blood tests, for example, can be ordered to check for signs of infection or inflammation in the body, such as a high white blood cell count. These tests are particularly useful in severe cases of cellulitis or when the patient has a weakened immune system, helping to guide the treatment plan.
Imaging tests, like ultrasound or MRI, may be recommended if there is suspicion of an abscess (a collection of pus) beneath the skin or if the cellulitis does not respond to initial treatment. These tests help to visualize the deeper layers of the skin and tissues, providing valuable information on the extent of the infection and guiding further management.
However, the diagnosis of cellulitis is based on a combination of physical examination findings and medical history. Additional tests, though not always required, play a crucial role in certain scenarios to confirm the diagnosis, rule out other conditions, and tailor the treatment approach. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of cellulitis, highlighting the importance of seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms of this condition are observed.
Available Treatments for Cellulitis
Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for managing symptoms and promoting recovery. The primary treatment for cellulitis involves antibiotics, which are selected based on the infection’s severity, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Antibiotics: The Cornerstone of Cellulitis Treatment
Antibiotics play a pivotal role in treating cellulitis, aiming to eradicate the infection-causing bacteria. The choice between oral and intravenous (IV) antibiotics depends on several factors:
- Oral Antibiotics: Typically, for mild to moderate cases of cellulitis, oral antibiotics are the first line of treatment. They are convenient and can be taken at home. The duration of the treatment usually spans from 5 to 14 days, depending on the infection’s response to the medication.
- Intravenous Antibiotics: Severe cases of cellulitis or those not responding to oral antibiotics may require IV antibiotics. This method is also preferred if the patient has underlying conditions that complicate oral administration. IV antibiotics are administered in a hospital or outpatient setting, allowing for closer monitoring of the infection’s response to treatment.
Criteria for Choosing Antibiotic Type
The decision between oral and IV antibiotics hinges on:
- The severity of the infection
- The presence of or risk for complications
- The patient’s immune system status
- Previous responses to antibiotic treatments
Pain Relief and Home Care Recommendations
Aside from antibiotics, managing cellulitis symptoms includes pain relief measures. Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help reduce discomfort and fever. Additionally, home care practices play a vital role in recovery:
- Resting the affected area to reduce swelling
- Elevating the infected part of the body to decrease swelling and discomfort
- Applying cool, damp cloths to the area to soothe pain
It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations closely and complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished. Early and appropriate treatment of cellulitis can prevent the infection from becoming more severe, ensuring a smoother and quicker recovery process.
However, effective management of cellulitis involves a combination of the right antibiotics—whether oral or IV—pain relief measures, and supportive home care. By understanding the available treatments and following medical advice, patients can achieve the best possible outcomes in their recovery from cellulitis.
Preventing Cellulitis Recurrence: Essential Tips and Strategies
Understanding how to effectively protect your skin and promptly treat injuries can significantly reduce the risk of another infection. Here are vital tips to keep in mind for cellulitis prevention, focusing on skin care, injury prevention, and the importance of timely treatment for cuts and bites.
1. Maintain Rigorous Skin Hygiene
Regular and thorough skin care is paramount in preventing cellulitis. Use a mild soap and lukewarm water to clean your skin daily, especially after sweating heavily or exposure to potentially contaminated environments. Moisturizing regularly helps maintain the skin’s natural barrier, reducing the likelihood of cracks and dryness that can invite bacteria.
2. Protect Your Skin From Injury
Injuries to the skin, such as cuts, scrapes, or burns, provide an entry point for bacteria. Always wear appropriate protective clothing when engaging in activities that might injure your skin. This includes gloves for gardening or long sleeves and pants when hiking in brushy areas.
3. Treat Cuts and Bites Promptly
Immediate care for any skin break is crucial. Cleanse wounds with soap and water, apply an antibiotic ointment, and cover with a sterile bandage to reduce the risk of infection. For animal or insect bites, seek medical advice, as these can carry a higher risk of causing cellulitis.
4. Keep Nails Trimmed and Clean
Fingernails and toenails can harbor bacteria and fungi, posing a risk if they cause scratches or punctures. Keeping your nails trimmed and clean minimizes this risk. Avoid biting your nails or picking at hangnails, as these habits can damage the skin around your nails.
5. Stay Hydrated and Maintain a Healthy Diet
A well-hydrated body and a diet rich in vitamins and minerals support skin health, boosting its defense against infections. Ensure your diet includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to support overall health and skin integrity.
6. Seek Timely Medical Attention for Skin Infections
At the first sign of a skin infection—redness, swelling, warmth, and pain—consult a healthcare provider. Early treatment of cellulitis, often with antibiotics, can prevent its spread and recurrence.
However, preventing the recurrence of cellulitis involves a comprehensive approach that includes diligent skin care, protective measures against skin injuries, and prompt treatment of wounds. By adopting these strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of cellulitis and maintain healthy, resilient skin.
When to Seek Medical Help for Cellulitis
Recognizing these signs early can be crucial in preventing complications. This guide emphasizes the critical importance of seeking professional medical advice for cellulitis treatment, highlighting the conditions under which medical help should be promptly sought.
Recognizing Urgent Symptoms
Promptly seek medical attention if you experience any of the following symptoms associated with cellulitis:
- Rapid Spread of Redness: If the red, inflamed area on your skin quickly expands, it’s a clear signal that the infection is worsening.
- Fever: Developing a fever or chills indicates that the infection might be spreading to other parts of your body.
- Increasing Pain: An escalation in pain or tenderness in the affected area signifies that the infection is not under control.
- Swelling and Warmth: An increase in swelling or a significant warmth in the infected area can indicate a worsening condition.
- Blisters or Red Streaks: The appearance of blisters or red streaks emanating from the infected area are signs of a serious infection that requires immediate medical intervention.
- Feeling Unwell: Symptoms such as fatigue, dizziness, or a general feeling of illness should not be ignored.
The Importance of Professional Medical Advice
Self-diagnosing and treating cellulitis can lead to delayed treatment and potentially severe complications, including sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection. It is crucial to seek professional medical advice for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Healthcare professionals can provide:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Through physical examination and, if necessary, additional tests to confirm cellulitis and rule out other conditions.
- Appropriate Treatment: Typically involving prescription antibiotics to fight the infection. The treatment plan may be adjusted based on your symptoms’ severity and response to initial therapy.
- Follow-up Care: Ensuring the infection is responding to treatment and advising on any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
At the first sign of any symptoms suggesting cellulitis, especially if they worsen or do not improve with initial care, seeking medical help is imperative. Timely intervention not only facilitates a quicker recovery but also prevents the development of serious complications. Always prioritize professional medical advice to manage cellulitis effectively. Your health and well-being depend on prompt and appropriate care.
FAQ Section: Cellulitis Treatment and Prevention
Q1: What is cellulitis?
A1: Cellulitis is a common and potentially serious bacterial skin infection. It appears as a swollen, red area of skin that feels hot and tender, and it may spread rapidly. Skin on lower legs is most commonly affected, though cellulitis can occur anywhere on the body or face.
Q2: How can cellulitis be prevented?
A2: To help prevent cellulitis, protect your skin from cuts, scrapes, and animal bites. Keep skin moisturized to prevent cracking, promptly treat wounds with proper cleaning and dressings, and maintain good personal hygiene.
Q3: What are the signs and symptoms of cellulitis?
A3: Symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. Fever and chills can also occur if the infection spreads. Seek medical attention if you notice signs of cellulitis, especially if symptoms are accompanied by a fever.
Q4: How is cellulitis treated?
A4: Cellulitis treatment typically involves antibiotics to fight the infection. For mild cases, oral antibiotics are prescribed. For more severe infections, or if symptoms don’t improve with oral antibiotics, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics may be required.
Q5: Are there any home remedies for cellulitis?
A5: While home remedies cannot replace medical treatment for cellulitis, certain practices can aid recovery. Resting the affected area, elevating the infected part of the body to reduce swelling, and applying cool, damp cloths to the area may provide comfort. However, medical treatment should not be delayed in favor of home remedies.
Q6: Can cellulitis lead to complications?
A6: If not treated promptly, cellulitis can lead to serious complications such as abscess formation, lymphangitis, and septicemia. It can also spread to the lymph nodes and bloodstream. Immediate medical treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
Q7: Who is at risk for cellulitis?
A7: Individuals with a weakened immune system, chronic skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, history of cellulitis, and those with edema in their limbs are at higher risk. Breaks in the skin from wounds or surgery also increase the risk of infection.
Q8: Can cellulitis be contagious?
A8: Cellulitis is not usually spread from person to person. It is caused by bacteria entering through breaks in the skin. However, the bacteria causing cellulitis can spread from person to person if they enter through a cut or scrape.
Q9: Is there a vaccine for cellulitis?
A9: There is no vaccine for cellulitis. The best prevention involves protecting the skin from injuries and maintaining good skin hygiene.
Q10: When should I see a doctor for cellulitis?
A10: See a doctor if you experience symptoms of cellulitis, especially if the area of redness expands, if you develop a fever, or if the condition does not improve after a few days of treatment. Early medical intervention is key to preventing complications.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, cellulitis is a common but potentially serious bacterial skin infection that demands prompt attention. The key points to remember about diagnosing and treating cellulitis include recognizing the early signs, such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pain in the affected area. It’s crucial to seek medical advice as soon as these symptoms are observed to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to combat the infection, and in some cases, hospitalization may be necessary if the infection is severe or does not respond to oral antibiotics.
The significance of awareness and early intervention cannot be overstated when it comes to managing cellulitis effectively. Understanding the risk factors, such as skin injuries, chronic conditions like diabetes, or a weakened immune system, can help in taking preventive measures. Additionally, being informed about the necessity of completing the full course of prescribed antibiotics even if symptoms improve early on is vital to prevent recurrence or complications.
Early intervention not only facilitates a quicker recovery but also reduces the risk of the infection spreading and leading to more serious health issues. Therefore, awareness and education about cellulitis are crucial for both individuals and healthcare providers to ensure timely and effective treatment.
By prioritizing knowledge and proactive measures towards cellulitis, we can significantly minimize its impact. Remember, when it comes to health concerns like cellulitis, being informed and acting promptly can make all the difference in outcomes.