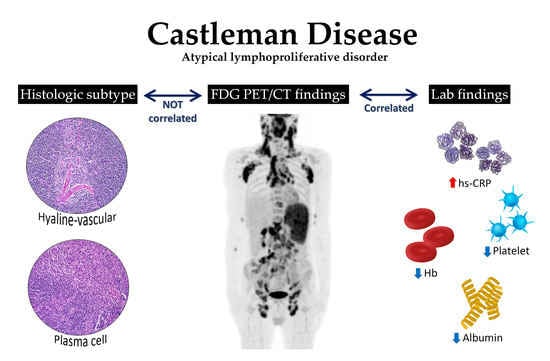
Castleman Disease Symptoms: Castleman disease, a rare and complex disorder, presents a myriad of challenges to those affected.
This article aims to demystify the symptoms and causes of Castleman disease, providing a comprehensive overview for better understanding and awareness.
What is Castleman Disease?
Castleman disease is a rare and complex condition that affects the lymph nodes and related tissues. It is a type of lymphoproliferative disorder, which means it involves an abnormal overgrowth of cells of the lymph system. This disease can occur in a single lymph node (localized) or multiple lymph nodes (systemic) throughout the body. Despite its classification as a lymphoproliferative disorder, it’s important to note that Castleman disease is not a form of cancer. Instead, it is a unique condition that can manifest in various ways, mimicking symptoms similar to those of cancer.
Types of Castleman Disease
Castleman disease is categorized into two primary types, each with distinct characteristics:
- Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD): This type affects a single lymph node or a single group of lymph nodes in one area of the body. UCD is typically the less severe form and often does not present with systemic symptoms. Treatment usually involves surgical removal of the affected node, leading to recovery in most cases.
- Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD): MCD involves multiple lymph nodes and can affect several regions of the body. This form is more severe and can present with systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss, and fatigue. MCD can be associated with HIV and human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) infections. Treatment for MCD is more complex and may include medications to regulate the immune system.
Epidemiology and Demographics Affected
Castleman disease is relatively rare, affecting individuals across various age groups. However, certain forms of the disease have specific demographic patterns:
- Unicentric Castleman Disease: UCD can occur at any age but is more commonly diagnosed in young adults. There is no significant gender predilection, and it affects both males and females equally.
- Multicentric Castleman Disease: MCD is more commonly seen in adults, particularly those in their 50s and 60s. Patients with HIV are at a higher risk for developing MCD, particularly the HHV-8-associated type.
Understanding the types and demographics affected by Castleman disease is crucial for early detection and effective management. Although rare, awareness of this condition can lead to better outcomes through timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment strategies.
Symptoms of Castleman Disease: A Comprehensive Guide
Castleman Disease, a rare and complex lymphoproliferative disorder, presents with a spectrum of symptoms that vary significantly between its two main forms: Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD) and Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD). Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the common symptoms of each type, explore how they differ, and provide insights through case studies or anecdotes when available.
Symptoms of Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD)
Unicentric Castleman Disease is characterized by the enlargement of a single lymph node. The symptoms are often localized and less severe than its multicentric counterpart. Common signs include:
- Swollen Lymph Node: The most apparent symptom is a noticeable swelling in one lymph node, often in the chest or abdomen. This can be detected through physical examination or imaging tests.
- Pressure Effects: Depending on the location of the swollen node, individuals may experience cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain due to pressure on nearby structures.
- Asymptomatic Cases: In many cases, UCD doesn’t cause any noticeable symptoms and is often discovered incidentally during investigations for other conditions.
Symptoms of Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD)
Multicentric Castleman Disease involves multiple lymph nodes and presents more systemic symptoms, which can be severe:
- Fever and Night Sweats: Persistent fever and night sweats are common, often resembling flu-like symptoms.
- Generalized Lymphadenopathy: Swelling of multiple lymph nodes throughout the body, not limited to a single region.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Chronic fatigue is a frequent complaint, impacting daily activities.
- Unintended Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without trying is a concerning symptom.
- Enlarged Liver or Spleen: Hepatosplenomegaly may occur, often detected through physical examination or imaging studies.
Variations in Symptoms Between UCD and MCD
The distinction in symptoms between UCD and MCD is primarily due to their scope of impact:
- Localized vs Systemic: UCD typically presents localized symptoms due to a single affected lymph node, whereas MCD exhibits systemic symptoms, affecting multiple parts of the body.
- Severity: Symptoms in MCD are generally more severe and debilitating compared to UCD.
- Associated Conditions: MCD patients are at a higher risk of developing other conditions, such as severe infections, organ dysfunction, and malignancies.
Case Studies and Anecdotes
While rare, insightful case studies and personal anecdotes provide a deeper understanding of Castleman Disease:
- Case Study 1: A 35-year-old individual diagnosed with UCD, initially mistaking the swollen lymph node for a muscular injury.
- Case Study 2: A 50-year-old patient with MCD, experiencing rapid weight loss and severe fatigue, leading to a challenging journey towards diagnosis.
These real-life examples highlight the diverse and often challenging nature of diagnosing and managing Castleman Disease.
Causes and Risk Factors of Castleman Disease
Understanding its causes and risk factors is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. This article delves into the known causes, genetic and environmental risk factors, and the current understanding of the etiology of Castleman Disease, presenting the information in an SEO and readability-friendly manner.
Known Causes of Castleman Disease
Unlike many other diseases, the exact causes of Castleman Disease are not fully understood. However, researchers have identified certain factors that may contribute to its development:
- Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8): Strongly linked with the multicentric form of Castleman Disease, HHV-8 infection is considered a significant cause, especially in individuals with weakened immune systems.
- Immunological Abnormalities: Aberrations in the immune system, including excessive production of interleukin-6 (IL-6), a protein that promotes inflammation, have been observed in patients.
Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
While the genetic and environmental risk factors for Castleman Disease are not definitively established, several aspects are being studied:
- Genetic Predisposition: Although not classified as a genetic disease, certain genetic markers may increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Exposures: Some studies suggest a link between environmental factors and the development of Castleman Disease, but conclusive evidence is yet to be found.
Current Understanding of its Etiology
The etiology of Castleman Disease involves a combination of factors. Researchers believe that an interplay of viral infections (like HHV-8), immune system dysfunction, and possibly genetic predispositions contribute to its onset. The multicentric form of Castleman Disease is particularly complex, often associated with other conditions like HIV/AIDS, which further complicates the understanding of its etiology.
However, Castleman Disease is a multifaceted disorder with a yet-to-be-fully-elucidated etiology. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the potential causes and risk factors, paving the way for improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Understanding these aspects is vital for healthcare professionals and patients alike in managing this rare condition.
Diagnosing Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease, a rare and complex lymphoproliferative disorder, often poses diagnostic challenges. Understanding the medical tests, the role of symptoms, and differential diagnosis is crucial in accurately identifying and managing this condition.
Medical Tests and Procedures Used for Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Castleman Disease begins with a combination of laboratory and imaging tests:
- Blood Tests: These are essential first steps. Doctors look for abnormal levels of certain blood cells and proteins, which can indicate the presence of Castleman Disease.
- Imaging Techniques: CT scans, MRI, or PET scans help visualize lymph node enlargement and other abnormalities.
- Lymph Node Biopsy: This is the definitive test for Castleman Disease. A sample of lymph node tissue is examined under a microscope for characteristic changes.
- Immunohistochemistry: This specialized test further examines the biopsy tissue to detect specific proteins that are often present in Castleman Disease.
The Role of Symptoms in Diagnosis
Symptoms play a significant role in leading to a suspicion of Castleman Disease. They include:
- Swollen lymph nodes, typically in the neck, collarbone area, or underarm.
- Unexplained fever and night sweats.
- Unintentional weight loss.
- Fatigue and weakness.
While these symptoms are not unique to Castleman Disease, their persistence without any apparent cause often triggers further investigation.
Differential Diagnosis (Distinguishing from Similar Conditions)
Distinguishing Castleman Disease from other conditions is a critical aspect of its diagnosis. It shares symptoms with several other diseases, making differential diagnosis essential. Key conditions to differentiate from include:
- Lymphoma: Both Castleman Disease and lymphomas involve lymph nodes, but they are different in their pathology.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Some symptoms of Castleman Disease overlap with autoimmune conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- Infections: Certain infections can mimic the lymph node enlargement seen in Castleman Disease.
However, diagnosing Castleman Disease requires a thorough evaluation involving a combination of tests, careful symptom assessment, and differentiation from similar conditions. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital for effective management and treatment of this rare disease.
Impact of Symptoms on Patients of Castleman Disease
Castleman disease, a rare condition affecting the lymph nodes and related tissues, has a profound impact on those diagnosed with it. Understanding the physical, psychological, and social implications of this disease, as well as hearing from patients and experts, is crucial for awareness and empathy.
Physical Impact of the Symptoms
The physical symptoms of Castleman disease, which may include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, fatigue, and night sweats, can significantly affect a patient’s quality of life. These symptoms can range from mild to severe, often leading to a compromised immune system and increased vulnerability to infections. In some cases, the disease can affect organ function, leading to more serious health complications. Addressing these physical challenges is a cornerstone of managing Castleman disease effectively.
Psychological and Social Implications
Beyond the physical symptoms, Castleman disease can have deep psychological and social impacts. Patients often experience anxiety and depression, stemming from the uncertainty and severity of the condition. The chronic nature of the disease can lead to social isolation, as patients may find it challenging to participate in regular social activities or maintain employment. This social withdrawal can exacerbate feelings of loneliness and anxiety, creating a cycle that is difficult to break.
Patient Testimonials and Expert Opinions
Hearing directly from patients and medical experts provides invaluable insights into the realities of living with Castleman disease. Patients often describe the emotional toll of dealing with a rare disease, including the frustration of misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis. Experts emphasize the importance of early detection and individualized treatment plans to manage symptoms effectively. Personal stories and expert perspectives highlight the need for increased research and awareness, offering hope and guidance to those affected by Castleman disease.
Treatment and Management of Symptoms in Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease, a rare disorder characterized by an overgrowth of cells in the body’s lymph nodes, requires a nuanced treatment approach. The cornerstone of managing Castleman Disease lies in its diagnosis, which determines the specific treatment regimen. Treatments often involve therapies to control the abnormal lymph node overgrowth and manage the systemic symptoms.
- Medication: The first line of treatment typically includes medications like corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs. These medications aim to reduce inflammation and control the immune system’s overactivity.
- Targeted Therapies: For patients with multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD), targeted therapies such as monoclonal antibodies (e.g., rituximab) are commonly used. These therapies specifically target and inhibit the overactive immune cells.
- Chemotherapy: In some cases, particularly where there is a significant lymph node enlargement or severe symptoms, chemotherapy may be prescribed. This approach helps in controlling the rapid division of abnormal cells.
- Surgery: For unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD), where the disease affects only one lymph node region, surgery to remove the affected node can be curative.
- Radiation Therapy: In situations where surgery is not feasible, radiation therapy may be used to shrink the lymph nodes.
How Treatment Varies Based on Symptoms
The treatment for Castleman Disease is highly individualized, depending on the form of the disease (unicentric or multicentric) and the patient’s symptoms.
- In UCD, surgery is often the primary treatment. Post-surgery, patients are monitored for recurrence, but additional therapy is usually not required if the entire affected node is removed.
- In MCD, where multiple regions are involved, and systemic symptoms are present, a combination of medications, targeted therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy is necessary.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies to Manage Symptoms
Alongside medical treatment, lifestyle modifications and home remedies play a crucial role in managing the symptoms of Castleman Disease:
- Nutritious Diet: Emphasizing a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost overall health and immune function.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps in maintaining muscle strength, reducing fatigue, and improving mood.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which is crucial for individuals with Castleman Disease.
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring sufficient sleep is vital for the body’s recovery and maintaining a robust immune system.
- Avoiding Infections: Regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can help prevent infections.
- Community Support: Joining support groups for rare diseases can provide emotional support and valuable information.
However, the treatment and management of Castleman Disease involve a combination of medical interventions tailored to the individual’s symptoms and supportive lifestyle practices. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the disease’s progression and adjust treatments as necessary. Remember, while these approaches can effectively manage symptoms, it is crucial to work closely with a healthcare team experienced in treating Castleman Disease.
Prevention and Early Detection of Castleman Disease
Preventing Castleman Disease, a complex and rare lymphoproliferative disorder, poses a significant challenge due to its unclear etiology. However, understanding potential risk factors and adopting a proactive approach towards overall health can play a crucial role in reducing the risk of developing this condition. While it’s not currently possible to entirely prevent Castleman Disease, certain lifestyle choices and health awareness can potentially mitigate some risks.
Key Prevention Strategies:
- Maintain a Healthy Immune System: Given the disease’s association with the immune system, maintaining a robust immune system is advisable. This includes following a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, and ensuring adequate sleep.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular health check-ups can help in identifying any early signs of lymph node enlargement or other related symptoms. Early detection of abnormalities can lead to prompt and more effective treatment.
- Awareness of Risk Factors: Understanding personal health history, especially any autoimmune conditions or viral infections like HIV or HHV-8, is crucial. Awareness and monitoring can lead to early consultation with healthcare providers if symptoms arise.
- Avoiding Exposure to Infections: Since infections can potentially trigger or worsen the condition, avoiding known infectious agents and practicing good hygiene can be a preventive measure.
Importance of Early Detection and Awareness of Symptoms
Early detection of Castleman Disease is paramount for effective treatment and better prognosis. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking medical advice promptly can significantly alter the disease’s course.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Enlarged Lymph Nodes: One of the most common signs is enlarged lymph nodes, especially around the neck, armpits, and groin.
- Unexplained Fever and Night Sweats: Persistent fever and night sweats without any obvious cause should be evaluated.
- Unintentional Weight Loss: Sudden weight loss that is not linked to diet or exercise changes needs medical attention.
- Fatigue and Weakness: Persistent fatigue and weakness that doesn’t improve with rest can be an early warning sign.
Raising Awareness:
- Education: Educating the public about Castleman Disease and its symptoms is crucial. Awareness campaigns can lead to more people recognizing symptoms and seeking timely medical advice.
- Encouraging Routine Health Checks: Regular health check-ups can aid in the early detection of abnormalities, even in asymptomatic individuals.
- Advocating for Research: Supporting research in understanding the causes and mechanisms of Castleman Disease can eventually lead to better prevention strategies.
However, while prevention of Castleman Disease is challenging due to its unclear causes, adopting a healthy lifestyle and being vigilant about changes in one’s health can be beneficial. Early detection, primarily through awareness of symptoms and regular medical check-ups, is essential for timely and effective management of the disease.
Recent Research and Developments in Castleman Disease
Castleman Disease, a rare and complex lymphoproliferative disorder, has been the subject of intense research in recent years. The latest findings in this field have significantly expanded our understanding of both the symptoms and causes of the disease.
- Understanding the Symptoms: Recent studies have shed light on the diverse symptoms of Castleman Disease, which can range from mild lymph node enlargement to severe systemic symptoms. Researchers have identified that these symptoms vary greatly depending on the subtype of the disease – Unicentric Castleman Disease (UCD) or Multicentric Castleman Disease (MCD). This differentiation is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Investigating the Causes: The etiology of Castleman Disease is complex and not fully understood. However, the latest research has made strides in identifying potential causes. One significant discovery is the association of the Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8) with MCD, especially in patients who are also HIV-positive. Additionally, studies are exploring genetic factors and the role of the immune system in the development of the disease.
- Biomarker Development: A promising area of research involves identifying specific biomarkers that can aid in the diagnosis and monitoring of Castleman Disease. These biomarkers have the potential to revolutionize the way the disease is managed, allowing for more personalized treatment approaches.
Future Directions in Castleman Disease Research
The journey towards fully understanding and effectively treating Castleman Disease continues. Future research directions include:
- Targeted Therapies: There is a growing focus on developing targeted therapies that specifically address the underlying mechanisms of the disease. This includes treatments that modulate the immune system and therapies targeting specific pathways involved in lymph node proliferation.
- Genomic Studies: Advancements in genomic technologies are enabling researchers to delve deeper into the genetic aspects of Castleman Disease. These studies aim to uncover genetic mutations and alterations that may contribute to the disease’s development.
- Clinical Trials: Increasing the number and scope of clinical trials is vital for testing new treatments and understanding the disease’s progression. These trials are essential for translating laboratory findings into effective therapies for patients.
- Collaborative Research Efforts: Recognizing the rarity and complexity of Castleman Disease, there is a push towards collaborative research efforts. Bringing together experts from various fields and international collaborations can accelerate the pace of discovery and lead to more comprehensive approaches to treatment.
However, the field of Castleman Disease research is dynamic and evolving. With continued research and collaboration, there is hope for more effective treatments and a deeper understanding of this challenging disease. Stay tuned for more updates as researchers unveil new insights into Castleman Disease.
Conclusion
As we conclude, I extend a call to action to you, our readers. Whether you’re a medical professional, a patient, a caregiver, or simply an interested individual, your role in this journey is vital. Engage with and support organizations dedicated to Castleman disease research. Share the knowledge you’ve gained; talk about Castleman disease with your peers, and on your social platforms. Every conversation sparked and every penny donated makes a difference.
In closing, let us remember that behind the statistics and medical terms are real people battling Castleman disease every day. By staying informed, fostering research, and spreading awareness, we stand in solidarity with them, contributing to a future where Castleman disease is not a formidable foe, but a conquerable challenge.