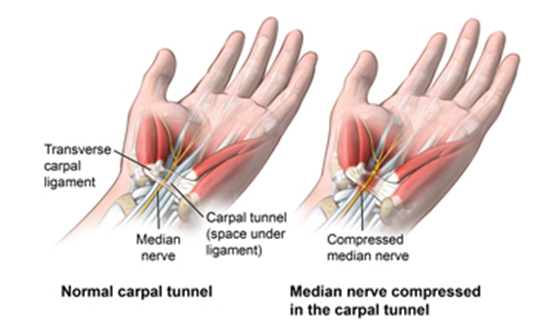
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm.
It occurs when the median nerve, one of the major nerves to the hand, is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist.
In most patients, CTS gets worse over time, so early diagnosis and treatment are essential. Understanding the symptoms and risk factors can help in early recognition and prevention.
What is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that affects the hand and wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling sensations. This syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel—a narrow, rigid passageway of ligament and bones at the base of the hand—houses the median nerve and tendons. Sometimes, thickening from irritated tendons or other swelling narrows the tunnel and causes the median nerve to be compressed.
Statistics and Prevalence of the Condition
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a widespread condition globally. Statistics show that it affects about 3-6% of the adult population, with a higher prevalence in women than men. The condition is most commonly diagnosed in individuals aged 30-60 years. Its prevalence is particularly notable in occupations that involve repetitive hand and wrist motions.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is not always clear, but several risk factors can contribute to its development:
- Repetitive Motion: Activities that involve repetitive hand and wrist movement, such as typing or assembly line work, can increase the risk of developing CTS.
- Health Conditions: Certain conditions, including diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and thyroid gland imbalance, can predispose individuals to CTS.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can cause swelling in the body, including the carpal tunnel, leading to CTS.
- Genetics: Some people may have a smaller carpal tunnel, making them more susceptible to nerve compression.
- Age and Gender: Women and older adults are more commonly affected by CTS.
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome typically develop gradually and can include:
- Numbness, Tingling, and Pain: These sensations usually occur in the thumb, index, and middle fingers.
- Weakness: People may experience weakness in their hand and a tendency to drop objects.
- Discomfort in the Wrist: This can extend to the arm and shoulder.
- Nighttime Symptoms: Many individuals report that their symptoms are worse at night.
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking medical advice is crucial for effective treatment and management of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
This comprehensive overview of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome aims to inform readers about its prevalence, causes, and symptoms, enhancing awareness and encouraging proactive health management.
Diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) is a common condition that can cause pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. Early diagnosis is crucial to manage symptoms effectively and prevent long-term damage. Here, we’ll explore the common methods and tests used in diagnosing CTS, the role of healthcare professionals, and the importance of early detection.
Common Methods and Tests for Diagnosing CTS
- Physical Examination: A healthcare provider will start with a physical examination of your hands, arms, shoulders, and neck to determine if your symptoms are related to daily activities or an underlying disorder.
- Tinel’s Sign Test: This involves tapping over the median nerve at your wrist to see if it causes tingling in the fingers.
- Phalen’s Maneuver: You’ll be asked to press the backs of your hands together in a reverse prayer position. Numbness or tingling in this position can indicate CTS.
- Electromyogram (EMG): This test measures the tiny electrical discharges produced in muscles. It can help to determine if muscle damage has occurred.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: These measure how fast the nerves in your arms and hands send electrical signals. Slowed conduction in the median nerve can indicate CTS.
Role of Healthcare Professionals in Diagnosis
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in diagnosing CTS. They assess symptoms, conduct physical exams, and recommend appropriate tests. They can also distinguish CTS from other conditions with similar symptoms, ensuring accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is vital. It not only alleviates discomfort but also prevents the condition from worsening. Delayed diagnosis can lead to permanent nerve and muscle damage, making early intervention key to recovery.
However, diagnosing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome involves a combination of physical exams and specific tests. Healthcare professionals are instrumental in guiding patients through the diagnosis process. Recognizing symptoms early and seeking medical advice is essential in managing and treating CTS effectively.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Treating Carpal Tunnel Syndrome involves a range of strategies including non-surgical treatments, surgical interventions, alternative therapies, home remedies, and lifestyle changes. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and the individual’s overall health.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are often recommended for mild to moderate symptoms of CTS. These may include:
- Wrist Splinting: Wearing a splint at night can keep your wrist in a straight position, which helps to relieve nighttime symptoms of tingling and numbness.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen can help relieve pain from CTS.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injecting a type of steroid medicine known as corticosteroids into your carpal tunnel can help reduce pain and swelling.
Surgical Treatments
In cases where non-surgical treatments fail to relieve symptoms, or in severe cases of CTS, surgery might be necessary. The two main types of surgery for CTS are:
- Open Carpal Tunnel Release: This involves making an incision in the wrist and then cutting the carpal ligament to enlarge the tunnel and relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Release: This is a less invasive procedure where a tiny camera is used to guide the surgery, involving smaller incisions and potentially quicker recovery times.
Alternative Therapies and Home Remedies
Several alternative therapies and home remedies can be used alongside medical treatments to provide relief:
- Yoga: Specific postures may help to improve the strength and flexibility of the wrist and hand.
- Hand Therapy: Various hand exercises can help to reduce symptoms and improve hand function.
- Acupuncture and chiropractic care: These have been reported to help some people with CTS.
Role of Lifestyle Changes and Ergonomics
Lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments are crucial in both preventing and treating CTS. This includes:
- Taking Frequent Breaks: To rest the hands and wrists during repetitive activities.
- Correcting Posture: Poor posture can cause your shoulders to roll forward, shortening your neck and shoulder muscles, and compressing nerves in your neck, affecting your wrists, hands, and fingers.
- Ergonomic Equipment: Use of ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and tools that keep the wrist in a more neutral position can be very beneficial.
However, a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle changes, and ergonomic adjustments can effectively manage the symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. It’s essential for individuals experiencing symptoms to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Prevention Strategies for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
This guide focuses on practical tips, workplace ergonomics, and lifestyle modifications that are crucial in managing and preventing CTS. Understanding these strategies is essential for anyone who spends significant time performing repetitive hand or wrist activities.
Tips to Prevent CTS or Prevent Its Worsening
- Maintain a Neutral Wrist Position: Keeping your wrist in a straight, natural position can reduce the pressure on the median nerve. Avoid bending your wrists excessively, especially when typing or using hand tools.
- Use Ergonomic Tools: Opt for keyboards, mice, and tools that are designed to keep your wrist in a more relaxed position.
- Reduce Force and Relax Your Grip: Minimize the force you use to perform tasks like typing or writing. If possible, use a softer touch and hold tools with a relaxed grip.
- Keep Hands Warm: Cold environments can lead to stiffness and pain. Keeping your hands warm can help prevent discomfort.
Workplace Ergonomics
- Adjust Your Workstation: Ensure that your desk, chair, and computer setup support a comfortable, neutral posture. Your keyboard should be at elbow height, allowing your wrists to remain straight.
- Ergonomic Accessories: Invest in accessories like wrist rests, ergonomic chairs, and adjustable desks to enhance your workplace ergonomics.
- Proper Keyboard and Mouse Use: Position your keyboard and mouse close to your body to avoid reaching. Keep them at a height where your wrists aren’t bending upwards.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Regular Exercise: Engage in activities that strengthen your wrist and arm muscles. Yoga and stretching can also improve flexibility and reduce pressure on your hands and wrists.
- Healthy Weight Maintenance: Being overweight can increase the risk of developing CTS, so maintaining a healthy weight is beneficial.
- Limit Repetitive Hand Movements: If possible, alternate tasks to avoid prolonged repetition of the same hand movements.
Importance of Regular Breaks and Exercises
- Take Frequent Short Breaks: Regular breaks, even if brief, can significantly reduce the strain on your wrists and hands. Every hour, take a few minutes to stretch or rest your hands.
- Wrist Exercises: Perform simple wrist exercises and stretches throughout the day to improve circulation and relieve tension.
- Stay Hydrated and Eat Healthily: Hydration and a balanced diet contribute to overall joint and muscle health, indirectly aiding in CTS prevention.
By implementing these prevention strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome or alleviate existing symptoms. Remember, early intervention and consistent application of these tips are key to effective prevention and management of CTS.
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) can be a challenging condition, but with the right strategies and support, it’s possible to manage daily life effectively. CTS, characterized by numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand due to pressure on the median nerve, can impact routine activities. However, with some adjustments, living with this condition can be more comfortable.
Making Everyday Activities Easier
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Invest in ergonomic keyboards, mouse pads, and wrist supports to reduce strain on your hands and wrists while working.
- Regular Breaks: Taking short, frequent breaks during repetitive tasks can alleviate discomfort.
- Hand and Wrist Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can improve flexibility and strength.
- Splints or Braces: Wearing these at night or during activities that trigger symptoms can offer support and relieve pressure on the nerve.
- Mindful Movement: Be conscious of your wrist positions during activities; avoid bending them excessively.
Coping Strategies and Enhancing Quality of Life
- Pain Management Techniques: Over-the-counter pain relievers, ice packs, or heat therapy can help manage pain and swelling.
- Stress Reduction: Stress can exacerbate CTS symptoms. Techniques like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can be beneficial.
- Adapt to Limitations: Modify tasks or use assistive devices to make them more manageable.
- Stay Active: Engaging in regular physical activity can improve overall health and reduce the impact of CTS.
Seeking Support and Utilizing Resources
- Medical Advice: Regular check-ins with healthcare providers for monitoring and management of CTS.
- Physical or Occupational Therapy: Professional guidance to learn exercises and strategies to reduce symptoms.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have CTS can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Educational Resources: Utilize reliable sources for information about managing CTS, like health websites, webinars, and books.
Living with Carpal Tunnel Syndrome involves adapting to certain limitations and finding effective ways to manage symptoms. With the right approach, it’s possible to maintain a good quality of life. Remember, individual experiences may vary, so it’s important to consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
The Future of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Treatment
Emerging Treatments and Research
The landscape of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) treatment is rapidly evolving, with emerging treatments and groundbreaking research paving the way for more effective and less invasive solutions. One of the most promising areas of development is in the field of regenerative medicine. Researchers are exploring the potential of stem cell therapy and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatments to repair and regenerate the damaged nerve tissues in the wrist. These innovative approaches aim to not only alleviate the symptoms of CTS but also address the underlying causes of the condition.
Additionally, advancements in pharmacology are leading to the development of new medications that specifically target the inflammation and nerve compression associated with CTS. These medications are designed to provide more targeted relief without the side effects commonly associated with general anti-inflammatory drugs.
Technological Advancements in Diagnosis and Treatment
The future of CTS treatment is also being shaped by technological advancements in diagnosis and treatment methods. Cutting-edge diagnostic tools, such as high-resolution ultrasound and MRI, are allowing doctors to diagnose CTS with greater accuracy and at earlier stages. This early detection is crucial for effective treatment and can prevent the progression of the syndrome to more severe stages.
Moreover, technology is revolutionizing the treatment of CTS. For example, the use of minimally invasive surgical techniques, guided by advanced imaging technologies, has significantly reduced recovery times and improved outcomes for patients undergoing surgery for CTS. Robotic-assisted surgery is another area that is showing great promise, offering greater precision and control during the procedure.
Wearable technology and smart devices are also emerging as powerful tools in both the treatment and prevention of CTS. These devices can monitor the wrist’s movement and provide feedback to encourage ergonomically correct positions, reducing the risk of developing CTS. Additionally, they can be used in rehabilitation, helping patients perform exercises accurately and consistently.
However, the future of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome treatment is bright, with ongoing research and technological advancements leading to more effective, less invasive, and more patient-friendly treatment options. As we continue to explore and innovate in this field, patients suffering from CTS can look forward to more promising and efficient methods of relief and recovery.
Conclusion
Treatment options vary, ranging from lifestyle changes and ergonomic adjustments to more intensive interventions like physical therapy, medications, or in severe cases, surgery. Non-surgical treatments like wrist splinting, especially during nighttime, and anti-inflammatory medications can significantly alleviate symptoms for many individuals.
However, it’s important to emphasize the value of professional medical advice. If you’re experiencing symptoms of CTS, or if you’re at risk due to repetitive hand movements or other factors, seeking guidance from a healthcare provider is essential. They can offer personalized advice and tailor a treatment plan that suits your specific needs.
In conclusion, while Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be a challenging condition, understanding its symptoms, getting an accurate diagnosis, and following a comprehensive treatment plan can lead to effective management and relief. Remember, with the right approach and professional guidance, overcoming CTS is entirely possible. Your journey towards recovery and regaining hand function starts with taking that first step towards seeking professional help. Stay informed, proactive, and optimistic about your path to managing and overcoming Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.