Carotid Artery Disease Symptoms: Carotid artery disease, a significant health concern worldwide, poses substantial risks if left undiagnosed or untreated.
This article delves deep into the symptoms and causes of carotid artery disease, offering comprehensive insight into this critical condition.
What is Carotid Artery Disease?
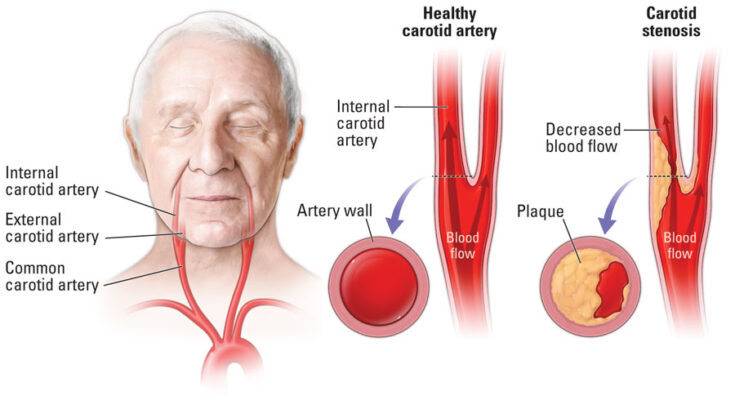
Carotid artery disease, a significant medical condition affecting the blood vessels in the neck, is often underdiscussed yet crucial to understand. It occurs when the carotid arteries, the primary blood vessels that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain, become narrowed or blocked. This blockage is usually due to atherosclerosis, where fatty deposits, or plaques, build up inside the artery walls.
Understanding the mechanics of this disease is essential. The carotid arteries, located on each side of your neck, play a pivotal role in brain health. When these arteries are healthy, they ensure a smooth and efficient blood flow to the brain, which is vital for its proper functioning. However, when these arteries are compromised, it can lead to serious health problems, including strokes, transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), or even potentially fatal consequences.
Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Carotid artery disease is more common than many might assume, affecting a significant portion of the adult population, particularly those over the age of 60. The prevalence increases with age, making it a growing concern in aging societies worldwide. It is also more common in men than in women, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
Several demographic factors contribute to the likelihood of developing this condition. These include a family history of atherosclerosis or heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and lifestyle factors such as smoking and a sedentary lifestyle. Ethnicity also plays a role, with certain groups, such as African Americans, being at higher risk.
It’s crucial to recognize that while some risk factors, like genetics and age, cannot be changed, many can be managed through lifestyle choices and medical interventions. Understanding the prevalence and the demographics affected by carotid artery disease is a step towards better prevention and management of this serious condition.
Understanding the Carotid Arteries: Anatomy and Function
The carotid arteries are vital components of the body’s circulatory system, playing a crucial role in cardiovascular health. These arteries are primarily responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the brain, neck, and face. Understanding their anatomy and function is key to comprehending their significance in overall health.
Anatomy of the Carotid Arteries
The carotid arterial system consists of two main arteries: the right and left carotid arteries. Each of these divides further into two major branches:
- The Internal Carotid Artery: This artery is responsible for providing blood to the brain. Its journey starts from the base of the neck, traveling upward and entering the skull through a specialized opening. It then branches off within the cranial cavity to supply blood to various parts of the brain.
- The External Carotid Artery: This artery supplies blood to the face, neck, and scalp. It branches out into several smaller arteries that reach the surface areas of these regions, ensuring that they receive an adequate blood supply for normal function.
Function of the Carotid Arteries
The primary function of the carotid arteries is to ensure a steady flow of oxygenated blood to some of the most critical areas of the body, including the brain. The brain, being the control center of the body, requires a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to function correctly. The carotid arteries play a pivotal role in this by providing up to 30% of the blood the brain needs.
Role in Circulatory and Cardiovascular Health
The health of the carotid arteries is integral to the overall circulatory and cardiovascular system. These arteries are indicators of vascular health; for instance, a blockage or narrowing in the carotid arteries can significantly increase the risk of stroke. Regular monitoring of the carotid arteries, especially in individuals with risk factors for cardiovascular diseases, is essential for early detection and prevention of serious health issues.
However, the carotid arteries, with their critical function in supplying blood to the brain, neck, and face, are key players in maintaining cardiovascular and circulatory health. Awareness and understanding of their anatomy and role underscore the importance of vascular health in maintaining overall well-being.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
Here, we will delve into the common symptoms of carotid artery disease, providing a detailed list and explaining how these symptoms manifest and their impact on individuals.
Common Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
- Sudden Weakness or Numbness: Patients may experience sudden weakness, numbness, or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg, typically on one side of the body. This occurs due to reduced blood flow to certain parts of the brain.
- Difficulty in Speaking or Understanding Speech: Carotid artery disease can cause confusion or problems with speaking or understanding speech, signaling a potential transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
- Vision Problems: Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes can occur, often described as a shade being pulled down over the eyes. This is due to a lack of blood flow to the eyes or parts of the brain responsible for vision.
- Dizziness or Loss of Balance: Patients might experience unexpected dizziness, loss of balance, or coordination, which can indicate a transient ischemic attack or stroke.
- Sudden Severe Headache: A sudden, intense headache without a known cause can be a warning sign of a stroke due to carotid artery disease.
- TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack): Often called a mini-stroke, a TIA provides a critical warning. It presents similar symptoms to a stroke but typically lasts only a few minutes and causes no permanent damage.
Understanding the Symptoms and Their Impact
These symptoms often appear suddenly and can significantly impact a person’s daily life. For instance, weakness or numbness can hinder everyday activities, while difficulties with speech or understanding can affect communication and social interactions. Vision problems can lead to challenges in navigating environments, and dizziness or loss of balance increases the risk of falls.
The most concerning aspect of these symptoms is their potential to indicate a stroke, a medical emergency. Immediate attention is crucial when these symptoms appear, as timely treatment can significantly reduce the risk of permanent damage.
Recognizing these symptoms early and seeking prompt medical care is essential for managing carotid artery disease effectively. If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional immediately for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Understanding the symptoms of carotid artery disease can be a key step in maintaining heart and brain health and preventing serious complications like stroke. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your health.
Causes and Risk Factors of Carotid Artery Disease
Understanding the causes and risk factors is crucial in prevention and management. This article offers a comprehensive analysis of the various factors leading to this condition.
A. Comprehensive Analysis of Causes
- Plaque Buildup (Atherosclerosis): The primary cause of carotid artery disease is atherosclerosis, a process where fatty deposits, cholesterol, and calcium accumulate on the artery walls. Over time, this buildup, known as plaque, narrows the arteries, impeding blood flow.
- Blood Clot Formation: Sometimes, these plaques can rupture, leading to blood clots. These clots further restrict or completely block the flow of blood to the brain, which can lead to a stroke.
- Other Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can exacerbate the risk of developing carotid artery disease. These include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and obesity.
B. Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise blood cholesterol levels, contributing to plaque formation.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can worsen other risk factors for carotid artery disease, such as high blood pressure and obesity.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can irritate blood vessels and speed up the hardening of the arteries.
- Excessive Alcohol Intake: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and add extra calories, which may lead to weight gain.
C. Genetic and Environmental Risk Factors
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history of carotid artery disease or other forms of heart disease can increase the risk.
- Age and Gender: The risk increases with age. Men are generally at a higher risk, although the risk for women increases after menopause.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain environmental factors, such as air pollution and secondhand smoke, can also contribute to the development of carotid artery disease.
Recognizing the causes and risk factors of carotid artery disease is a vital step in preventing and managing this condition. Lifestyle changes, such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and quitting smoking, play a crucial role in reducing these risks. Moreover, understanding genetic and environmental factors can help in early detection and effective management. Consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and regular check-ups to monitor your risk factors.
Diagnosis of Carotid Artery Disease
Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for preventing severe complications such as stroke. This article delves into the methods and technologies employed in diagnosing carotid artery disease, emphasizing the significance of early detection and its correlation with symptoms.
Methods and Technologies for Diagnosis
The diagnosis of carotid artery disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation and advanced imaging technologies, designed to assess the extent of artery narrowing and blockage. Here are some key diagnostic tools:
- Physical Examination: The process begins with a physical exam, where healthcare providers listen for a whooshing sound, known as a bruit, in the neck using a stethoscope. This sound may indicate abnormal blood flow, suggesting carotid artery disease.
- Ultrasound: Carotid ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the carotid arteries. It can show the presence, severity, and location of plaques causing narrowing or blockage.
- Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA): CTA is an advanced imaging technique that combines CT scans with an injected contrast material to produce detailed images of the carotid arteries, revealing any plaques or blockages.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA is another non-invasive imaging test that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide detailed images of the blood vessels, including the carotid arteries.
- Carotid Angiography: This invasive procedure involves threading a thin tube through a blood vessel in the arm or leg up to the carotid arteries. A contrast dye is then injected, and X-rays are taken to visualize the arteries’ interior.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of carotid artery disease is paramount for several reasons:
- Symptom Identification: In many cases, carotid artery disease is asymptomatic and goes unnoticed until it becomes severe. However, when symptoms such as transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) or minor strokes occur, they serve as crucial warning signs. Recognizing and addressing these symptoms promptly can be life-saving.
- Prevention of Stroke: Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, such as medication, lifestyle changes, or surgery, to reduce the risk of stroke. Stroke prevention is especially critical as strokes can lead to permanent brain damage or death.
- Progression Monitoring: For patients with mild carotid artery disease, early detection enables healthcare providers to monitor the condition’s progression closely and adjust treatment plans as necessary.
However, the diagnosis of carotid artery disease involves a comprehensive approach using various methods and technologies. Early detection plays a vital role in managing the disease effectively, highlighting the importance of regular check-ups and staying attuned to any symptoms that may suggest carotid artery issues. With timely and accurate diagnosis, individuals can take proactive steps to mitigate the risk of stroke and other severe outcomes associated with carotid artery disease.
Complications Associated with Carotid Artery Disease
Carotid artery disease, a significant health condition affecting the blood vessels that supply blood to your brain, can lead to serious health complications if left unaddressed. Understanding the potential risks and the connection between symptoms and the progression of the disease is crucial for prevention and early intervention.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
If carotid artery disease is not promptly treated, the reduced blood flow to the brain can result in several severe complications:
- Stroke: The most critical complication, a stroke occurs when a part of the brain is deprived of oxygen and nutrients, causing brain cells to die. Strokes can lead to lasting brain damage, long-term disability, or even death.
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Often considered a “mini-stroke,” a TIA is a temporary blockage of blood flow to the brain. While TIAs typically do not cause permanent damage, they serve as warning signs for a potential future stroke and should not be ignored.
- Cognitive Impairment: Over time, reduced blood flow can affect cognitive functions, leading to issues with memory, thinking, and reasoning skills, a condition often referred to as vascular cognitive impairment.
Link Between Symptoms and Progression of the Disease
The progression of carotid artery disease may be silent initially, but as the disease advances, symptoms can become more apparent. Recognizing these symptoms is key to preventing complications:
- Sudden numbness or weakness: Particularly on one side of the body, in the face, arms, or legs.
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech: Experiencing confusion or difficulty in forming words.
- Vision problems: Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
- Dizziness or loss of balance: A sudden loss of coordination or balance, making standing or walking difficult.
- Severe headache: An abrupt, severe headache without any known cause.
The appearance of these symptoms often indicates that the disease has progressed to a point where the risk of stroke and other complications is significantly increased. Early detection and treatment can help manage these symptoms and reduce the risk of severe outcomes.
However, carotid artery disease poses a serious threat to brain health, primarily due to its potential to lead to stroke and other cognitive impairments. Recognizing the symptoms early and seeking prompt medical attention can significantly reduce the risks associated with this condition. If you experience any of the above symptoms or have risk factors for carotid artery disease, consult a healthcare professional for an evaluation and possible treatment options.
Prevention and Management of Carotid Artery Disease
Preventing and managing this disease effectively is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health. In this section, we’ll explore strategies for prevention and the latest approaches to manage its symptoms.
Strategies for Preventing Carotid Artery Disease
- Healthy Diet Choices: Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can reduce the risk of plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week can improve overall cardiovascular health and help maintain a healthy weight.
- Smoking Cessation: Smoking is a major risk factor for carotid artery disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce this risk.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity increases the risk of carotid artery disease. Weight loss and maintaining a healthy body mass index (BMI) can lower this risk.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Conditions like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes increase the risk of carotid artery disease. Proper management of these conditions is essential.
- Regular Health Screenings: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect carotid artery disease early. This may include physical exams, blood tests, or specific imaging tests.
Lifestyle Changes and Treatments to Manage Symptoms
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe medications to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, or prevent blood clots. It’s crucial to take these medications as prescribed.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Continuing the lifestyle changes mentioned above not only helps in prevention but also in managing the disease.
- Surgical Procedures: In severe cases, procedures like carotid endarterectomy or angioplasty and stenting may be necessary to remove blockages or widen the artery.
- Regular Monitoring: Individuals with carotid artery disease need regular monitoring to assess the progression of the disease and the effectiveness of treatments.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact cardiovascular health. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or therapy can be beneficial.
- Patient Education: Understanding the disease, its risks, and management strategies is crucial. Educated patients are more likely to adhere to treatment plans and make informed decisions about their health.
By incorporating these preventive strategies and management techniques, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of carotid artery disease and manage its symptoms effectively. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and treatment plans.
Living with Carotid Artery Disease: Navigating Daily Life and Adjustments
Living with Carotid Artery Disease (CAD) can be a challenging journey, but with the right knowledge and adjustments, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. This condition, where the carotid arteries become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, significantly increases the risk of stroke. Understanding the implications and management of this disease is crucial for those diagnosed with it.
Daily Life with CAD: Adjustments and Management
Individuals with CAD often need to make lifestyle adjustments to manage their condition effectively. This involves:
- Dietary Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol can help reduce plaque buildup in the arteries.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular, doctor-approved exercise improves cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
- Medication Adherence: Taking prescribed medications regularly is essential to manage CAD symptoms and prevent complications.
- Monitoring Health: Regular check-ups with healthcare providers are critical for monitoring the condition and making necessary adjustments.
Emotional and Psychological Impact
Living with CAD can also have emotional and psychological impacts. Many individuals may experience anxiety about their health, particularly the risk of stroke. Support from family, friends, and support groups, along with professional counseling, can be beneficial.
Patient Stories: Real-life Insights
Hearing from individuals who live with CAD can provide valuable insights and encouragement:
- John’s Story: John, a 60-year-old retiree, adjusted his diet and exercise routine after being diagnosed with CAD. He found that walking daily and eating a Mediterranean-style diet helped him manage his symptoms and improve his overall health.
- Sarah’s Experience: Sarah, a 45-year-old teacher, experienced anxiety after her diagnosis. Through support groups and counseling, she learned coping strategies that helped her deal with her condition more positively.
The Importance of Early Detection and Management
Early detection and proper management of Carotid Artery Disease are vital. Individuals should be aware of the symptoms, such as sudden numbness in limbs, difficulty speaking, or severe headaches, and seek medical advice immediately if they experience them.
Living with Carotid Artery Disease requires adjustments, but it is possible to lead a healthy and active life. Embracing lifestyle changes, staying informed, and seeking support can make a significant difference in managing this condition.
Recent Advances and Research in Carotid Artery Disease
Let’s delves into the latest scientific progress and explores the future prospects in understanding and treating this critical condition.
Recent Scientific Advancements
Innovative Diagnostic Techniques: Recent years have seen the development of more sophisticated diagnostic tools for carotid artery disease. High-resolution MRI and advanced ultrasound technologies offer more detailed imaging, enabling early detection and better evaluation of the disease’s severity.
Advances in Genetic Research: A deeper understanding of the genetic factors contributing to carotid artery disease has emerged. Researchers have identified specific genetic markers that increase the risk, paving the way for personalized medicine approaches.
Drug Development and Therapies: There’s been significant progress in pharmaceutical treatments. New medications designed to reduce plaque buildup and improve blood flow in the carotid arteries have shown promise in clinical trials. Additionally, advancements in anti-inflammatory drugs are playing a crucial role in managing the disease.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques: The evolution of endovascular procedures, such as carotid artery stenting and angioplasty, has improved patient outcomes. These minimally invasive techniques reduce recovery time and the risk of complications compared to traditional surgeries.
Future Prospects
Regenerative Medicine: The field of regenerative medicine holds immense potential. Research is underway to explore how stem cell therapy and tissue engineering can aid in repairing damaged carotid arteries and restoring their normal function.
AI and Machine Learning: The integration of AI and machine learning in diagnostic processes is a promising area. These technologies can help in the early detection and precise analysis of carotid artery disease, leading to more effective treatment plans.
Preventive Strategies and Public Health Initiatives: Future research aims to develop more comprehensive preventive strategies. This includes public health initiatives focusing on lifestyle modifications, early screening programs, and education about risk factors.
Personalized Treatment Approaches: Tailoring treatments based on individual genetic makeup is a promising direction. This personalized approach will ensure more effective and targeted therapies, reducing the risk of side effects and improving outcomes.
The research and advancements in carotid artery disease are rapidly evolving, offering hope for better diagnostic, treatment, and preventive strategies. With continued scientific exploration and technological innovation, the future looks promising for those affected by this condition.
FAQs About Carotid Artery Disease: Symptoms and Causes
1. What are the Main Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease?
Carotid artery disease often does not present noticeable symptoms until a significant blockage or a stroke occurs. However, possible warning signs include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arms, or legs, especially on one side of the body; confusion or difficulty in understanding speech; vision problems in one or both eyes; difficulty walking, dizziness, or loss of balance; and sudden, severe headaches with no known cause.
2. Can Carotid Artery Disease be Asymptomatic?
Yes, carotid artery disease can be asymptomatic, meaning it shows no symptoms. Many people are unaware they have this condition until it is detected through a routine health examination or after a stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) occurs.
3. What Causes Carotid Artery Disease?
The primary cause of carotid artery disease is the buildup of plaques (made of fat, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances) in the arteries. This buildup narrows the arteries and reduces blood flow to the brain, leading to the disease. Risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and a family history of atherosclerosis or heart disease.
4. Are There Any Risk Factors for Carotid Artery Disease that Can Be Controlled?
Yes, several risk factors can be managed through lifestyle changes or medication. These include controlling high blood pressure, reducing cholesterol levels, quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and managing diabetes effectively. Regular exercise and a healthy diet also play a crucial role in prevention.
5. How is Carotid Artery Disease Diagnosed?
Carotid artery disease is usually diagnosed through a physical examination and medical history evaluation. Healthcare providers may use several tests, such as carotid ultrasound, computerized tomography (CT) angiography, or magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), to evaluate the health of the carotid arteries.
6. Is Carotid Artery Disease Reversible?
While carotid artery disease itself isn’t entirely reversible, its progression can be slowed or stopped. This is achieved through lifestyle modifications and medications to control contributing factors such as high cholesterol and high blood pressure. In some cases, surgical procedures may be necessary to remove or bypass plaque build-up.
7. Can Exercise Help with Carotid Artery Disease?
Regular exercise can be beneficial in managing carotid artery disease. It helps improve overall cardiovascular health, lowers blood pressure, reduces cholesterol levels, and aids in weight management. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise regimen, especially if you have existing health conditions.
8. What Dietary Changes Can Help with Carotid Artery Disease?
Dietary changes that can help manage carotid artery disease include eating more fruits and vegetables, choosing whole grains, limiting saturated and trans fats, reducing salt intake, and controlling portion sizes. A heart-healthy diet can help lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure, key factors in carotid artery disease management.
Conclusion
As we conclude, it’s vital to emphasize the importance of seeking medical advice if you experience any of the mentioned symptoms or if you have risk factors for the disease. Early diagnosis and treatment can be lifesaving and can significantly reduce the risk of stroke and other serious complications. Remember, your health is paramount, and staying informed about conditions like carotid artery disease is a proactive step towards maintaining it.
In summary, carotid artery disease is a condition that requires attention and awareness. By understanding its symptoms and causes, you’re better equipped to seek timely medical intervention, which is crucial for managing the disease effectively. Your health journey matters, and taking the necessary steps to safeguard it is always a wise decision.