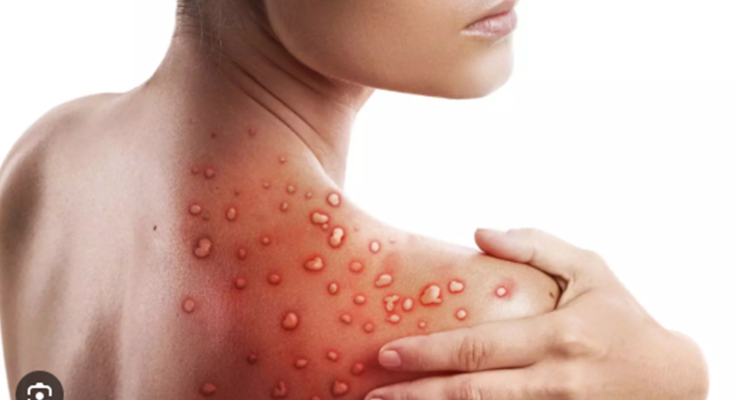
Bullous Pemphigoid Symptoms: Bullous pemphigoid is a rare, chronic skin disorder characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters (bullae) that predominantly appear on areas of skin that are often flexible and move, such as the lower abdomen, armpits, and thighs.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of this condition is critical for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous Pemphigoid is a rare, chronic autoimmune skin disorder primarily characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters known as bullae. These blisters mainly appear on areas of the skin that often flex, such as the lower abdomen, armpits, and thighs. The condition is part of a group of skin diseases called pemphigoid diseases, which affect the skin and mucous membranes.
Prevalence and Demographics
While Bullous Pemphigoid is not widely common, it significantly impacts certain demographics. The disorder predominantly affects older adults, usually those over the age of 60, with a higher incidence noted in individuals aged 80 and above. Its prevalence seems to be slightly higher in males than in females. Additionally, certain geographical regions might report varying rates of occurrence, though it is not restricted to any specific ethnicity or race.
Relevance in Dermatology
In the field of dermatology, Bullous Pemphigoid holds a significant place due to its complexity and the need for accurate diagnosis and management. Dermatologists play a crucial role in identifying this condition early, as misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment and complications. Its study also contributes to the broader understanding of autoimmune disorders and their impact on the skin, a major area of concern in dermatological practice.
Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid
Understanding the symptoms is crucial. Here’s a comprehensive list and a description of how these symptoms typically present and evolve, emphasizing the importance of early recognition.
Comprehensive List of Symptoms
- Red Rash: Often the first sign, a red rash can appear in areas such as the lower abdomen, arms, or legs.
- Itchy Skin: Before blisters appear, intense itching is common.
- Blisters: The hallmark symptom, these fluid-filled blisters are large and don’t easily rupture.
- Eczema-like Skin Changes: In some cases, skin may look eczematous before blistering begins.
- Mucous Membrane Lesions: Though less common, blisters can form on mucous membranes like the mouth or eyes.
How These Symptoms Typically Present and Evolve
Initially, Bullous Pemphigoid may mimic less severe skin conditions, starting as a red, itchy rash. Gradually, this evolves into the characteristic large, tense blisters. These blisters are typically filled with clear fluid and can appear on different parts of the body, including the arms, legs, and abdomen. In some cases, the skin may appear eczematous, or blisters may develop on mucous membranes.
The Importance of Recognizing Symptoms Early
Early recognition and diagnosis of Bullous Pemphigoid are vital. If left untreated, the condition can lead to severe complications, especially in older adults. Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of complications. It is important for individuals to seek medical advice if they notice unusual blisters or rashes, particularly if they are over the age of 60, as this condition more commonly affects the elderly.
By being aware of the early signs and how they progress, individuals can seek timely medical attention, leading to better management and outcomes for those affected by Bullous Pemphigoid.
Causes of Bullous Pemphigoid
Understanding its causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. This section explores the known and hypothesized causes of BP, focusing on genetic, environmental, and other risk factors, and how these causes contribute to the symptoms of the disorder.
Genetic Factors in BP
Genetic predispositions play a significant role in the development of BP. Research suggests a link between certain genes and the increased likelihood of developing this condition. These genetic markers can influence the body’s immune response, leading to an autoimmune reaction where the body mistakenly attacks its own skin cells, resulting in blister formation.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors are also significant in triggering BP. These can include:
- Medications: Certain drugs, like diuretics, antibiotics, and NSAIDs, have been associated with triggering BP.
- UV Radiation: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet light can exacerbate the condition.
- Trauma: Physical trauma or injury to the skin can sometimes precipitate BP.
Understanding these triggers is vital for both prevention and managing flare-ups in individuals diagnosed with BP.
Other Risk Factors
Apart from genetic and environmental factors, other risk elements include:
- Age: BP predominantly affects the elderly, usually people over 60 years of age.
- Chronic Diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune disorders or chronic diseases are at a higher risk.
The Path to Symptoms
The interaction between these genetic and environmental factors leads to the development of BP’s characteristic symptoms. The immune system’s erroneous attack on the skin cells causes inflammation and the formation of large blisters. These blisters are typically filled with fluid and can be itchy and painful, significantly impacting the quality of life.
However, the causes of Bullous Pemphigoid are multifaceted, involving genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, and various risk factors. Recognizing these causes is essential for effective treatment and improving the lives of those affected by BP. Regular medical consultations and tailored treatment plans are key to managing this complex condition.
Differentiating Bullous Pemphigoid from Other Skin Conditions
Understanding the differences between these conditions is crucial for anyone seeking not only accurate diagnosis but also effective treatment. This section delves into the distinctive features of Bullous Pemphigoid, and how it stands apart from other common skin ailments.
Comparison with Other Dermatological Conditions
Bullous Pemphigoid often presents symptoms that can superficially resemble those of eczema or psoriasis, but there are key differences:
- Appearance of Blisters: Bullous Pemphigoid is characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters that are usually not seen in eczema or psoriasis.
- Location and Spread: The blisters in Bullous Pemphigoid typically appear on areas like the lower abdomen, arms, legs, and in some cases, the mucous membranes. This pattern of spread can help differentiate it from eczema, which often appears on the bends of elbows and knees, and psoriasis, known for its scaly patches on the scalp, knees, and elbows.
- Itchiness and Discomfort: While all three conditions can cause itching, the intensity and nature of the itch in Bullous Pemphigoid can be different. The itching in eczema is often more severe, whereas psoriasis itching is typically associated with the flaky, scaly skin.
- Age of Onset: Bullous Pemphigoid usually affects older adults, typically over the age of 60, which is different from eczema and psoriasis that can start at any age.
Importance of Correct Diagnosis for Effective Treatment
Getting the right diagnosis is not just a matter of naming the condition; it’s about ensuring the right treatment strategy. Bullous Pemphigoid requires a specific approach to management:
- Targeted Medication: Treatment often involves corticosteroids and immunosuppressant drugs, which are different from the treatments for eczema or psoriasis.
- Monitoring and Management: Due to its potential severity, Bullous Pemphigoid needs regular monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans, which is different from the often more consistent management of eczema and psoriasis.
- Impact on Quality of Life: Misdiagnosis can lead to ineffective treatment, prolonging discomfort and possibly leading to complications. Accurate diagnosis ensures a better quality of life and quicker symptom resolution.
However, while Bullous Pemphigoid shares some superficial similarities with conditions like eczema and psoriasis, its unique characteristics necessitate a distinct approach to diagnosis and treatment. Awareness and understanding of these differences are key to managing the condition effectively.
Diagnosis of Bullous Pemphigoid
Accurate diagnosis is critical for effective treatment and management. Here’s a detailed guide to the diagnostic procedures for BP.
- Clinical Evaluation: The first step involves a thorough examination by a healthcare professional. They will review your medical history and conduct a physical examination, focusing on the skin lesions.
- Skin Biopsy: A key diagnostic tool for BP is a skin biopsy. A small piece of the affected skin is removed and examined under a microscope. This helps in identifying the characteristic features of BP, such as the separation of the epidermis from the dermis and the presence of immune deposits.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests may be conducted to check for antibodies commonly associated with BP. The presence of specific autoantibodies, such as BP180 and BP230, supports the diagnosis.
- Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF): This test involves taking a skin sample from the area surrounding the blisters. The sample is treated with fluorescent dyes to detect the presence of immune proteins at the separation site within the skin layers.
- Indirect Immunofluorescence: In contrast to DIF, indirect immunofluorescence tests for antibodies in the blood that may bind to specific skin components. This can help in confirming the diagnosis.
- Eosinophil Count: Elevated levels of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell, can be indicative of BP. This is assessed through a complete blood count (CBC).
The Importance of Healthcare Professional Evaluation for Symptoms
Self-diagnosis of BP is not advisable due to the complexity of the condition and similarity to other skin disorders. Consulting a healthcare professional is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: BP can be mistaken for other blistering diseases. Professionals can distinguish BP from similar conditions through specific tests.
- Treatment Guidance: Once diagnosed, a healthcare professional can provide a tailored treatment plan, which may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or other therapies.
- Monitoring and Management: BP requires ongoing monitoring to assess treatment effectiveness and manage potential side effects.
However, a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare professional, backed by a series of diagnostic procedures, is essential for the accurate diagnosis and effective management of Bullous Pemphigoid. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Treatment and Management of Bullous Pemphigoid
Proper management and treatment are crucial for alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. Here we discuss current treatment methods, lifestyle modifications, and the importance of medical guidance in treating BP.
Current Treatment Methods
- Corticosteroids: Topical or oral corticosteroids are often the first line of treatment. They help reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system’s response.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like azathioprine or mycophenolate mofetil may be used alongside corticosteroids to reduce the body’s immune response.
- Biologics: Rituximab, a biologic therapy, has shown promise in treating BP, especially in severe cases or for those who don’t respond to traditional therapies.
- Tetracyclines and Nicotinamide: These antibiotics, combined with nicotinamide, can be alternatives for those who cannot tolerate steroids.
- Anti-inflammatory Drugs: Dapsone or sulfapyridine can be effective, particularly in milder cases.
- IVIG (Intravenous Immunoglobulin): This treatment is reserved for severe or refractory cases of BP.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Care Tips
- Skin Care: Gentle skincare routines with mild soaps and moisturizers can help soothe irritated skin. Avoiding harsh chemicals or fragrances is also recommended.
- Diet: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can support overall skin health. Some patients find benefit in a diet low in salt and spices.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate BP symptoms. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or counseling can be helpful.
- Sun Protection: Protecting skin from the sun can prevent further irritation. Use sunscreens and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly check your skin for new blisters or changes in existing ones.
Importance of Medical Guidance
- Personalized Treatment: BP varies greatly among individuals; a healthcare professional can tailor treatment plans to your specific needs.
- Monitoring Side Effects: Medications used in BP treatment can have side effects. Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor and manage these effects.
- Adjusting Treatments: The course of BP can change over time, necessitating adjustments in treatment strategies.
- Support and Education: Medical professionals provide valuable education about the condition and support through its emotional and physical challenges.
However, the management of Bullous Pemphigoid involves a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and continuous care under the guidance of healthcare professionals. It’s essential to stay informed and actively engage in the treatment process for the best outcomes.
FAQs: Understanding Bullous Pemphigoid
What is Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous Pemphigoid is a rare skin condition characterized by large, fluid-filled blisters. It’s primarily seen in older adults and is caused by an autoimmune reaction where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the skin.
What are the Symptoms of Bullous Pemphigoid?
The hallmark symptom of Bullous Pemphigoid is the appearance of large, tense blisters that don’t easily rupture. These blisters usually develop on areas of the skin that often flex, like the lower abdomen, upper thighs, or armpits. In some cases, a red rash or itching may precede the blisters.
What Causes Bullous Pemphigoid?
The exact cause of Bullous Pemphigoid remains unknown. However, it’s believed to be an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thin layer of tissue below the outer layer of skin.
Who is at Risk for Bullous Pemphigoid?
Bullous Pemphigoid typically affects older adults, usually over the age of 60. Risk factors may include certain genetic predispositions, other autoimmune disorders, and possibly some medications or therapies, but the precise triggers are still being studied.
How is Bullous Pemphigoid Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, patient history, and specific tests. These tests may include a skin biopsy or blood tests to detect antibodies typically present in the disease.
What are the Treatment Options for Bullous Pemphigoid?
Treatment for Bullous Pemphigoid usually involves medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system. These may include corticosteroids, immunosuppressant drugs, and sometimes, antibiotics if secondary infections occur. Your healthcare provider will tailor the treatment plan to your specific condition.
Is Bullous Pemphigoid Contagious?
No, Bullous Pemphigoid is not contagious. It cannot be transmitted from person to person. It is an autoimmune disorder and is caused by the body’s immune response.
Can Bullous Pemphigoid be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for Bullous Pemphigoid, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications. Most people with proper treatment can live a normal life, although ongoing medical care may be necessary.
Conclusion
It cannot be stressed enough how important it is to consult healthcare professionals if you have any concerns regarding Bullous Pemphigoid. Self-diagnosis or delay in seeking expert advice can lead to complications. Dermatologists and other medical experts are equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to provide accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Remember, your health and well-being should always be a priority. If you or someone you know is showing signs of Bullous Pemphigoid or if you have any health concerns, do not hesitate to reach out to a medical professional. Early intervention can make a significant difference in managing this condition effectively.
In conclusion, staying informed about the symptoms and causes of Bullous Pemphigoid, and seeking timely medical advice, are essential steps in ensuring your health and well-being. Let’s prioritize our health by being vigilant and proactive in our approach to this and other medical conditions.