Broken Heart Syndrome Symptoms: In today’s fast-paced world, where stress and emotional upheaval are often part of daily life, it’s crucial to understand the impact of these factors on our health. One such condition, often overlooked, is Broken Heart Syndrome.
This article delves deep into the symptoms and causes of Broken Heart Syndrome, providing a comprehensive understanding of this unique cardiac condition.
What is Broken Heart Syndrome
Broken Heart Syndrome, also known as stress cardiomyopathy or Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, is a temporary heart condition often brought on by stressful situations, such as the loss of a loved one. Unlike heart attacks caused by blocked arteries, Broken Heart Syndrome typically involves a sudden, temporary weakening of the heart’s muscles. This condition can mimic symptoms of a heart attack, such as chest pain and shortness of breath, but it’s a different clinical entity.
A Brief History and Discovery
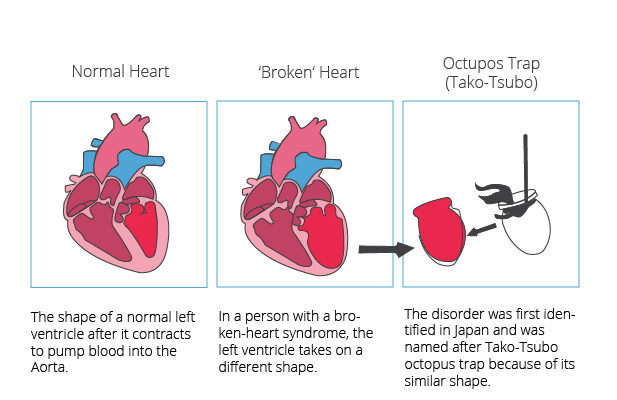
The condition was first described in Japan in 1990 and is named “Takotsubo” because the affected heart takes on a shape resembling a “tako-tsubo”, a Japanese pot used to trap octopuses. This unique visual aspect of the heart during an episode helped distinguish it from other heart-related issues. Researchers initially observed it in postmenopausal women, leading to further studies on how emotional stress could trigger heart complications.
Differences Between Broken Heart Syndrome and a Heart Attack
While Broken Heart Syndrome may feel similar to a heart attack, there are key differences:
Cause: Heart attacks are typically caused by physical blockages in heart arteries. Broken Heart Syndrome, in contrast, is usually triggered by emotional or physical stress.
Heart Appearance: In Broken Heart Syndrome, the heart may change to a distinctive shape, which is not seen in typical heart attacks.
Recovery: Recovery from Broken Heart Syndrome is often quicker and complete, usually within days or weeks, unlike the longer recovery time associated with heart attacks.
Coronary Arteries: In heart attacks, coronary arteries show clear signs of blockages. In Broken Heart Syndrome, these arteries are often found to be normal.
Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate diagnosis and treatment. While Broken Heart Syndrome can be alarming, its prognosis is generally favorable with proper medical attention.
Symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome
Recognizing these signs is crucial for prompt and accurate diagnosis. Here’s a detailed list of primary symptoms:
1. Chest Pain: A sudden, severe chest pain is often the first sign. It can be mistaken for a heart attack.
2. Shortness of Breath: This symptom can occur with or without chest pain.
3. Weakness: A general feeling of fatigue or weakness, often unexpected.
4. Palpitations: Irregular heartbeats or a feeling of your heart pounding.
5. Fainting or Near Fainting: Episodes of lightheadedness or fainting spells.
6. Nausea or Vomiting: Less common but can accompany other symptoms.
Comparing with Other Heart-Related Issues
It’s vital to understand how the symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome differ from other cardiac conditions:
Heart Attack: While both can present with chest pain and shortness of breath, heart attacks are typically caused by blocked coronary arteries. Broken Heart Syndrome, on the other hand, is usually triggered by severe emotional or physical stress and doesn’t involve blocked arteries.
Angina: Angina also involves chest pain but is usually triggered by physical exertion and relieved by rest, unlike Broken Heart Syndrome.
Myocarditis: This involves inflammation of the heart muscle, and symptoms can overlap, but myocarditis often includes symptoms like fever and signs of infection.
Personal Anecdotes and Case Studies
Case studies and personal experiences can provide deeper insight into Broken Heart Syndrome. For instance, a case study published in the ‘Journal of Medical Case Reports’ detailed a patient who developed symptoms after the sudden death of a loved one. Such personal stories highlight the emotional triggers associated with this condition and the diversity of its presentation in different individuals.
Understanding these symptoms is key to not only diagnosing Broken Heart Syndrome but also differentiating it from other heart-related issues. If you experience any of these symptoms, especially after a significant emotional event, it’s important to seek medical attention immediately.
Exploring the Causes of Emotional and Physical Responses
This exploration delves into two primary categories of triggers: emotional and physical, and examines why certain individuals may be more susceptible to these triggers.
Emotional Triggers
Stress: A common emotional trigger, stress can arise from numerous sources such as work pressure, family responsibilities, or financial worries. It activates the body’s “fight or flight” response, leading to various emotional and physical symptoms.
Grief: Loss of a loved one, end of a relationship, or any significant life change can trigger profound grief. This intense emotion can deeply impact mental health, leading to feelings of sadness, anger, or even guilt.
Extreme Emotions: Intense feelings like joy, anger, or fear, if not managed properly, can overwhelm an individual’s emotional balance, leading to stress or anxiety.
Physical Triggers
Medical Procedures: Invasive medical interventions, even those necessary for health, can be significant physical stressors. They can induce fear, anxiety, and sometimes physical discomfort or pain.
Physical Stress: Exhaustion, lack of sleep, or overexertion are physical stressors that can impact one’s emotional state. They may lead to irritability, lack of concentration, and increased vulnerability to emotional triggers.
Susceptibility Variations
Not everyone reacts to these triggers in the same way. This difference in susceptibility can be attributed to various factors:
Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals are genetically more prone to certain emotional and physical responses.
Past Experiences: Personal history plays a crucial role. Those with traumatic past experiences may be more sensitive to similar triggers.
Personality Traits: Certain personality types are more susceptible to stress and emotional upheaval.
Environmental Factors: The environment in which one lives and works can significantly influence their response to triggers.
However, understanding these triggers and recognizing personal susceptibility levels can aid in better managing emotional and physical responses. This knowledge is vital for maintaining mental and physical wellbeing.
Diagnosis and Detection of Broken Heart Syndrome
It’s crucial for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose this syndrome to ensure proper treatment and care. Here’s a look at the common procedures used in diagnosing Broken Heart Syndrome:
Echocardiogram: This is the first step in the diagnosis. An echocardiogram uses sound waves to create images of the heart, allowing doctors to observe its functioning and to detect any abnormal movements or shapes typical of Broken Heart Syndrome.
Blood Tests: These tests check for heart damage markers. In cases of Broken Heart Syndrome, certain enzymes typically released during a heart attack might be present, but not always at the same levels as in a typical heart attack.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): This test records the heart’s electrical activity. While it can resemble the readings of a heart attack, certain patterns can help differentiate Broken Heart Syndrome from other cardiac events.
Coronary Angiogram: This involves using dye and X-rays to view the heart’s blood vessels. It helps in ruling out a heart attack, as the coronary arteries are usually normal in Broken Heart Syndrome cases.
The Role of Healthcare Professionals in Identifying Broken Heart Syndrome
Healthcare professionals play a pivotal role in diagnosing Broken Heart Syndrome. Their expertise is crucial in:
Recognizing Symptoms: Identifying the signs that are distinct from those of a heart attack.
Patient History: Understanding any recent emotional or physical stresses that could trigger the syndrome.
Comprehensive Analysis: Considering all tests and patient history to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
Challenges in Diagnosing Due to Similarity with Other Heart Conditions
One of the main challenges in diagnosing Broken Heart Syndrome is its striking resemblance to other heart conditions, particularly heart attacks. The symptoms – chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting – are almost identical. Additionally, initial tests like ECGs and blood tests can show similar results to those of heart attacks. This overlap necessitates a thorough and careful examination by healthcare professionals to distinguish between these conditions and provide the appropriate care.
Treatment and Management of Broken Heart Syndrome
The treatment for this syndrome focuses on relieving the heart’s workload and minimizing stress on the heart. Here’s a brief overview:
Medications: Doctors may prescribe heart medications that are similar to those used for heart attack patients. These can include beta-blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, or diuretics. These medications help improve heart function and prevent further complications.
Monitoring: Close monitoring in a hospital setting is crucial, especially in the initial stages. This includes regular electrocardiograms (ECGs) and echocardiograms to monitor heart function.
Stress Management: Since emotional stress is a significant trigger for broken heart syndrome, stress management techniques such as therapy, meditation, or yoga can be beneficial.
2. Lifestyle Changes and Management Strategies
Lifestyle changes play a vital role in managing and preventing broken heart syndrome. These include:
Healthy Diet: Eating a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can boost heart health.
Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity helps improve cardiovascular health and reduce stress.
Avoiding Stressors: Identifying and avoiding stressors or learning coping mechanisms to deal with stress can be crucial in preventing recurrences.
Limiting Alcohol and Quitting Smoking: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can adversely affect heart health.
Regular Medical Check-ups: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are important to monitor heart health and any potential relapses.
3. Long-Term Outlook and Recovery Statistics
The long-term outlook for patients with broken heart syndrome is generally favorable. Most patients fully recover within weeks to months with appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications. Recovery statistics show that the recurrence rate of this condition is low, but it’s still important to manage stress and follow a heart-healthy lifestyle to prevent future episodes.
However, while broken heart syndrome is a serious condition, effective treatment and lifestyle changes can lead to a full recovery. It’s essential for individuals to work closely with their healthcare providers to tailor a treatment and management plan that suits their specific needs.
Preventive Measures of Broken Heart Syndrome
Maintaining emotional health and managing stress are vital in preventing Broken Heart Syndrome, a condition often triggered by extreme emotional distress. Here are some strategies:
Practice Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can significantly reduce stress levels.
Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is not only good for physical health but also for emotional well-being. It releases endorphins, which are natural stress-busters.
Healthy Eating Habits: A balanced diet can improve mood and energy levels, reducing the impact of stress.
Adequate Sleep: Ensure you get enough rest. Sleep helps in emotional regulation and stress management.
Seek Professional Help if Needed: Don’t hesitate to consult a mental health professional if stress becomes overwhelming.
Importance of Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups play a crucial role in the prevention of Broken Heart Syndrome:
Early Detection: Regular health screenings can detect underlying health issues that might contribute to the condition.
Risk Factor Management: Doctors can help manage risk factors like hypertension or diabetes, which are linked to heart health.
Personalized Health Advice: Healthcare professionals can provide tailored advice based on your health history and lifestyle.
Role of Support Systems and Mental Health Care
Building a Strong Support Network: Surrounding yourself with family and friends who provide emotional support is crucial.
Professional Counseling: Therapists and counselors can offer strategies to manage stress and cope with emotional upheaval.
Community Resources: Engaging in community activities or support groups can provide a sense of belonging and additional support.
Remember, proactive steps in managing stress, regular health check-ups, and a strong support system are key in preventing Broken Heart Syndrome. Always consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
FAQs: Understanding Broken Heart Syndrome
1. What is Broken Heart Syndrome?
Broken Heart Syndrome, also known as stress cardiomyopathy or Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, is a temporary heart condition often triggered by extreme emotional or physical stress. It mimics the symptoms of a heart attack but is distinct in its causes and treatment.
2. What causes Broken Heart Syndrome?
The exact cause of Broken Heart Syndrome is not fully understood, but it is often precipitated by intense emotional or physical stress, such as the loss of a loved one, a severe illness, or a major life change. This stress leads to a surge of stress hormones that temporarily weaken the heart’s ability to pump effectively.
3. What are the symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome?
Symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome resemble those of a heart attack and can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and an irregular heartbeat. Unlike a heart attack, these symptoms are not caused by heart artery blockages.
4. How is Broken Heart Syndrome diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, an electrocardiogram (ECG), blood tests, and often an echocardiogram. These tests help distinguish it from a heart attack and other heart conditions.
5. Can Broken Heart Syndrome be treated?
Yes, Broken Heart Syndrome is treatable. Treatment usually focuses on relieving the symptoms and may include medications like beta-blockers or ACE inhibitors. Most people recover fully within weeks.
6. Is Broken Heart Syndrome dangerous?
While it can be alarming, most people recover fully from Broken Heart Syndrome. However, in rare cases, it can lead to severe complications like heart failure, which underscores the importance of prompt medical care.
7. Can Broken Heart Syndrome be prevented?
Preventing Broken Heart Syndrome involves managing stress and emotional well-being. Techniques like mindfulness, regular exercise, and seeking emotional support can be helpful.
8. Who is at risk for Broken Heart Syndrome?
It predominantly affects middle-aged or older women, though it can occur in anyone. People with a history of mental health issues or neurologic conditions may be at higher risk.
9. Does Broken Heart Syndrome have any long-term effects?
Typically, there are no long-term effects once recovered. However, a small percentage of people might experience a recurrence.
10. Where can I find more information and support?
For more information and support, consult your healthcare provider and consider reaching out to heart health organizations and support groups.
Conclusion:
If you or someone you know exhibits symptoms of Broken Heart Syndrome, immediate medical attention is vital. Delaying care can lead to critical complications, much like those associated with heart attacks. Health professionals can provide necessary treatment and guidance, ensuring the best possible outcome.
The profound connection between emotional and physical health cannot be overstated. Emotional turmoil doesn’t just affect mental well-being; it can manifest physically, as seen in Broken Heart Syndrome. This highlights the importance of managing stress and seeking support in times of emotional distress. Remember, taking care of your emotional health is as essential as looking after your physical health.
In summary, understanding and acting upon the signs of Broken Heart Syndrome is crucial. It serves as a reminder of how closely linked our emotional and physical health are, and the need for timely medical intervention. Your heart’s health, both emotionally and physically, is indispensable.