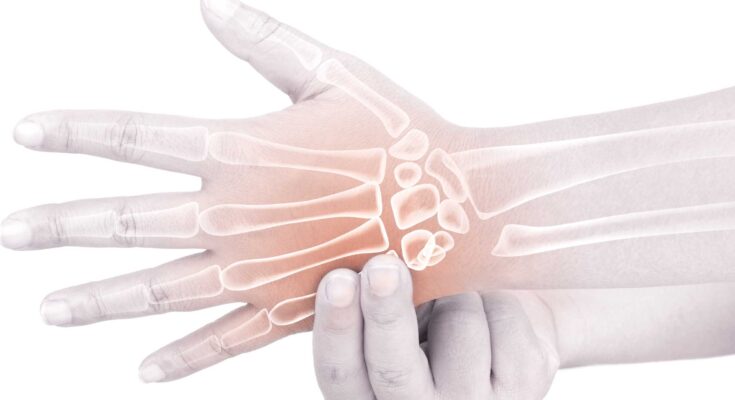
Broken Hand Treatment: In the intricate world of hand injuries, a broken hand stands out as a particularly intricate and challenging ailment.
The hand, a marvel of human anatomy, is not only vital for daily functioning but also for the delicate balance and dexterity that set humans apart.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of a broken hand is crucial for anyone facing this common yet complex injury.
What is a Broken Hand?
A broken hand is a condition that occurs when one of the bones in your hand fractures. This injury can result from various incidents, such as sports injuries, falls, or direct blows. Understanding the prevalence, common causes, and types of hand fractures is essential for recognizing and appropriately responding to this injury.
Statistics: Prevalence and Common Causes
Broken hands are a frequent occurrence, affecting a significant portion of the population. The prevalence of hand fractures varies, but they are among the most common bone injuries treated in hospitals. Factors contributing to these injuries include sports-related activities, accidental falls, motor vehicle accidents, and workplace incidents. The likelihood of experiencing a hand fracture can be influenced by age, occupation, and engagement in high-risk sports or activities.
Types of Hand Fractures
Hand fractures can be categorized into various types, depending on the location and nature of the break. The main types include:
- Metacarpal Fractures: These fractures occur in the long bones within the palm. They are common in boxing and contact sports.
- Phalangeal Fractures: Involving the bones of the fingers, these fractures can happen due to crushing injuries or direct trauma.
- Scaphoid Fractures: The scaphoid bone, located near the wrist, can break from falls onto an outstretched hand. These fractures are notorious for healing complications.
- Intra-articular Fractures: These breaks involve the surfaces of the joints and can lead to chronic pain or arthritis if not treated properly.
Understanding these types helps in the accurate diagnosis and treatment of hand fractures, thereby preventing long-term complications and ensuring a swift recovery.
Symptoms of a Broken Hand
Recognizing the symptoms of a broken hand is crucial for timely treatment. Here are the most common signs to look out for:
Swelling: One of the first and most noticeable signs is swelling. This occurs as the body’s response to the injury, leading to an increase in size and often a feeling of tightness in the skin around the affected area.
Pain: Intense pain is a clear indicator of a possible fracture. The pain is usually immediate and worsens when moving the fingers or wrist, or when applying pressure to the hand.
Bruising or Discoloration: Bruises form as blood from damaged blood vessels pools under the skin. A broken hand may exhibit bruising or changes in skin color, ranging from red to blue or purple.
Deformity: In cases of severe fractures, the hand might appear deformed. This could be in the form of unnatural angles, visible bone protrusions, or fingers that look out of place.
Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in moving fingers or the wrist can signal a fracture. The limited mobility is often due to pain or swelling.
Numbness or Tingling: This sensation, often described as “pins and needles,” can indicate nerve damage associated with a broken hand.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It is essential to seek medical attention if you suspect a broken hand. Here’s when you should see a doctor:
Persistent Pain and Swelling: If the pain and swelling don’t subside with home remedies like ice and rest, it’s time to consult a doctor.
Deformity or Visible Bone: Any visible deformity, especially if the bone is protruding, requires immediate medical attention.
Inability to Move Fingers or Wrist: If you’re unable to move your fingers or wrist without significant pain, it’s crucial to have a medical evaluation.
Numbness or Loss of Finger Function: These symptoms can indicate more severe damage and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
However, understanding and recognizing the symptoms of a broken hand is vital for prompt and effective treatment. Do not hesitate to seek medical advice if you experience any of the above symptoms following a hand injury. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a full and speedy recovery.
Diagnosing a Broken Hand
Initial Assessment by a Healthcare Professional
When suspecting a broken hand, the first step is a thorough initial assessment by a healthcare professional. This part of the diagnosis process is critical. The healthcare provider will begin with a detailed medical history to understand past injuries and current symptoms. They will ask about the incident that may have caused the injury, the pain level, and any difficulties in hand movement.
During the physical examination, the professional will gently palpate (touch) different areas of the hand to identify swelling, tenderness, or deformity. Range of motion tests are conducted to see if movement increases pain or if there are limitations in mobility. This careful examination helps in forming a preliminary diagnosis and determining if further imaging tests are necessary.
Imaging Tests Used for Diagnosis
Following the initial assessment, imaging tests play a vital role in diagnosing a broken hand. The most common imaging tests include:
- X-rays: The primary tool for diagnosing bone fractures. X-rays can show the location and severity of the break.
- CT scans: More detailed than X-rays, CT scans can help in assessing more complex fractures.
- MRI scans: Useful in identifying injuries to soft tissues, ligaments, and tendons, which can accompany a hand fracture.
These tests provide different perspectives and details, enabling a comprehensive view of the injury. The choice of imaging depends on the initial assessment findings and the specific nature of the suspected injury.
Understanding the Results and Diagnosis
Interpreting the results of these tests is crucial for a definitive diagnosis. A radiologist will examine the images for signs of fractures, such as breaks in the continuity of the bone, abnormal positioning, or bone fragments. The healthcare provider will then discuss these findings with the patient.
The diagnosis will inform the treatment plan, which may vary from immobilization with a cast or splint to surgical intervention in more severe cases. Understanding the diagnosis helps patients in grasping the extent of their injury and the necessary steps for effective healing. It also sets expectations regarding recovery time and rehabilitation.
However, diagnosing a broken hand involves a methodical approach, starting with a careful physical examination, followed by appropriate imaging tests, and culminating in a detailed analysis of the results. This process ensures accurate diagnosis and optimal treatment planning.
Treatment Options for a Broken Hand
Whether you’ve sustained a minor fracture or a more severe break, knowing what treatments are on offer can help you make informed decisions about your healthcare. This guide outlines the various treatment options for a broken hand, covering both non-surgical and surgical methods, as well as the critical role of physical therapy in your recovery.
Non-Surgical Treatments
1. Casting and Splinting
- Casting: A cast is often the go-to solution for immobilizing a broken hand. It’s essential for ensuring that the bones heal in the correct alignment. Casts are typically made of plaster or fiberglass and are custom-fitted to your hand and wrist to provide the necessary support.
- Splinting: Splints are similar to casts but are more flexible. They are often used in situations where swelling may be a concern, or if the injury requires a less rigid form of support. Splints can be adjusted to accommodate changes in swelling during the healing process.
2. Pain Management
Pain management is a crucial aspect of treating a broken hand. Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be effective. In some cases, your doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication. It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice and dosage recommendations to manage pain effectively and safely.
Surgical Treatments
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to properly align and secure the bones in your hand. Here are the common types of surgical treatments:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF): This procedure involves the use of screws, plates, or rods to stabilize the bone fragments.
- External Fixation: Involves placing a stabilizing frame outside the hand to hold the bones in the correct position while they heal.
- Bone Grafting: This is sometimes required if there’s significant bone loss. Bone grafting involves transplanting bone tissue to help reconstruct the damaged areas.
Role of Physical Therapy in Recovery
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the recovery process following a broken hand. A physical therapist will work with you to:
- Restore hand strength and flexibility.
- Reduce pain and swelling.
- Improve hand function and dexterity.
- Design a personalized rehabilitation program.
Regular physical therapy sessions can significantly enhance your recovery and ensure a return to normal function as quickly and safely as possible.
Home Care and Management: Tips for Managing a Broken Hand
Following the right steps can significantly contribute to a smoother recovery process. In this guide, we’ll provide you with valuable tips and insights on home care and management for a broken hand, emphasizing the importance of adhering to medical advice and making lifestyle modifications to expedite your healing journey.
1. Immediate First Aid
The first step in managing a broken hand is to administer immediate first aid. Here are some key actions to take:
- Immobilization: Stabilize the broken hand by splinting it. You can use a rolled-up newspaper, a board, or any rigid material to prevent further movement.
- Elevation: Keep your hand elevated above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Ice Pack: Applying an ice pack to the injured area can help alleviate pain and reduce swelling. Remember to wrap the ice pack in a cloth to avoid direct contact with the skin.
2. Seek Medical Advice
While initial first aid is crucial, it’s equally important to consult a medical professional promptly. Here’s why:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Only a doctor can provide a proper diagnosis through X-rays and physical examination. They can determine the extent of the injury and whether surgery is necessary.
- Treatment Plan: Medical professionals will create a tailored treatment plan, which may include casting, surgery, or other interventions.
- Pain Management: Doctors can prescribe pain medication to alleviate discomfort and ensure a more comfortable recovery.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
To facilitate a quicker recovery and prevent further complications, consider making these lifestyle modifications:
- Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone healing. Consult a nutritionist for guidance.
- Physical Therapy: Follow any prescribed physical therapy exercises to improve hand strength and flexibility.
- Avoid Harmful Activities: Refrain from activities that can worsen the injury, such as heavy lifting or strenuous exercises.
- Use Assistive Devices: Depending on your condition, you may need assistive devices like a sling or crutches to reduce strain on your hand.
- Frequent Follow-ups: Attend all follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider to monitor your progress and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
However, managing a broken hand at home requires a combination of immediate first aid, seeking professional medical advice, and making lifestyle adjustments. By following these guidelines and prioritizing your health, you can contribute to a successful recovery and regain full functionality of your hand. Remember, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance and treatment options.
Always prioritize your health and well-being when dealing with a broken hand, and don’t hesitate to reach out to a medical professional for expert care and advice.
How to Prevent Hand Injuries
Hand injuries can be painful and debilitating, but they are often preventable with some simple precautions. Here are some essential tips on how to prevent hand injuries:
Wear Appropriate Protective Gear: Depending on your activities, make sure to wear the right protective gear. This may include gloves, wrist guards, or hand shields. Proper gear can significantly reduce the risk of hand injuries in various settings such as sports, construction, and gardening.
Maintain Proper Hand Hygiene: Keeping your hands clean is crucial in preventing infections and injuries. Wash your hands regularly with soap and water, especially before handling food or after contact with potentially harmful substances.
Use Tools and Equipment Safely: Whether you’re working with hand tools, power tools, or kitchen utensils, always use them according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Misuse or improper handling can lead to accidents and hand injuries.
Practice Safe Sports and Recreation: If you’re involved in sports or recreational activities, follow the rules and safety guidelines. Wear appropriate sports gloves and protective equipment to minimize the risk of hand injuries during games and exercises.
Be Cautious Around Machinery: When operating machinery or heavy equipment, be extra cautious with your hands. Keep them away from moving parts, and use safety mechanisms like emergency stop buttons when needed.
Avoid Distractions: In everyday activities like walking or driving, avoid distractions like texting or talking on the phone. These distractions can lead to accidents, including hand injuries.
Secure Loose Clothing and Jewelry: Loose clothing and dangling jewelry can get caught in machinery or doors, leading to hand injuries. Keep them secured or remove them before engaging in activities where they could pose a risk.
Childproof Your Home: If you have young children at home, make sure to childproof your surroundings. Lock cabinets with harmful substances, install safety gates, and keep sharp objects out of reach to prevent accidents that can harm children’s hands.
Protective Gear and Safety Measures
Protective gear and safety measures play a vital role in preventing hand injuries. Here’s what you need to know:
Gloves: When working with chemicals, tools, or in harsh environmental conditions, wear appropriate gloves. These gloves provide a protective barrier against cuts, abrasions, and chemical exposure.
Wrist Guards: In sports like skateboarding or rollerblading, wrist guards can prevent wrist and hand injuries by providing support and cushioning during falls.
Hand Shields and Barriers: In industrial settings, use hand shields and barriers to protect against flying debris, sparks, and other hazards. These safety measures can prevent serious hand injuries.
Safety Training: Ensure that employees and individuals are trained in proper safety procedures when handling equipment or working in potentially hazardous environments. Proper training can go a long way in preventing hand injuries.
Regular Maintenance: Regularly inspect and maintain equipment and machinery to ensure they are in good working condition. Faulty equipment can pose a significant risk of hand injuries.
By following these prevention tips and using protective gear and safety measures, you can significantly reduce the risk of hand injuries in various aspects of your life. Remember that safety should always be a priority to keep your hands healthy and injury-free.
Complications of Untreated Broken Hands
Timely and appropriate treatment is crucial to prevent these complications and ensure a full recovery. In this article, we’ll explore the potential consequences of neglecting a broken hand and emphasize the importance of seeking medical care promptly.
Short-Term Complications
Pain and Discomfort: One of the immediate consequences of an untreated broken hand is persistent pain and discomfort. The broken bones may continue to rub against each other, causing significant pain that can interfere with daily activities.
Swelling and Bruising: Without proper treatment, swelling and bruising around the injured area may worsen. Swelling can lead to decreased mobility and further discomfort.
Infection Risk: An open fracture, where the broken bone pierces the skin, can expose the area to infection. Untreated infections can become serious and even life-threatening if left unchecked.
Deformity: The bones in the hand are intricately connected, and if a fracture is left untreated, it may heal incorrectly, leading to a permanent deformity. This can affect the hand’s function and appearance.
Long-Term Complications
Chronic Pain: Neglected broken hands can result in chronic pain, making it challenging to perform everyday tasks and reducing the overall quality of life.
Limited Mobility: Improper healing or untreated fractures can restrict the range of motion in the hand. This limitation may become permanent if not addressed promptly.
Arthritis: The risk of developing arthritis in the affected hand increases if the broken bones do not heal correctly. Arthritis can cause pain, stiffness, and joint deformities.
Weakness: Untreated fractures can lead to muscle weakness in the hand, making it difficult to grip objects and perform fine motor tasks.
Importance of Timely and Appropriate Treatment
Seeking prompt medical attention for a broken hand is crucial to avoid these complications. Here’s why timely treatment matters:
Faster Healing: Proper medical care can ensure that the broken bones are aligned correctly, promoting quicker and more effective healing.
Pain Management: Medical professionals can provide pain relief and manage discomfort during the recovery process.
Prevention of Complications: Timely treatment reduces the risk of infections, deformities, and long-term mobility issues.
Restored Function: With appropriate care, individuals can regain full hand function and mobility, minimizing the impact on their daily lives.
However, untreated broken hands can lead to a host of complications, both in the short term and the long term. To prevent these issues and ensure a successful recovery, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly and follow the prescribed treatment plan. Don’t delay in getting the help you need for a broken hand to ensure a healthy and functional future.
FAQs
1. What Is a Broken Hand?
A broken hand, also known as a metacarpal fracture, occurs when one or more of the bones in the hand are fractured. This can result from various causes, such as falls, sports injuries, or accidents. Understanding what constitutes a broken hand is the first step in seeking proper treatment.
2. How Can I Tell If My Hand Is Broken?
Common symptoms of a broken hand include severe pain, swelling, bruising, deformity of the hand, and difficulty moving or using the affected hand. If you experience any of these symptoms after an injury, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly for an accurate diagnosis.
3. What Should I Do If I Suspect a Broken Hand?
If you suspect that you have a broken hand, it’s crucial to immobilize the hand as much as possible to prevent further damage. You can use a splint or a makeshift brace, and apply ice to reduce swelling. However, seeking immediate medical care is essential for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.
4. How Are Broken Hands Treated?
The treatment for a broken hand depends on the severity and location of the fracture. In some cases, a cast or splint may be applied to immobilize the hand and promote healing. For more complex fractures, surgery may be required. Your orthopedic specialist will determine the best course of action based on your specific injury.
5. What Is the Recovery Time for a Broken Hand?
The recovery time for a broken hand can vary depending on the type of fracture and the treatment provided. On average, it may take several weeks to a few months for the hand to heal fully. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises may be necessary to regain strength and mobility in the hand.
6. Can I Prevent Hand Fractures?
While accidents can happen, you can take precautions to reduce the risk of hand fractures. Wear protective gear during sports activities, be cautious when using hand tools, and practice hand safety in your daily activities. Proper preventive measures can help minimize the chances of a broken hand.
7. When Can I Resume Normal Activities After a Broken Hand?
The timeline for resuming normal activities after a broken hand depends on the individual and the extent of the injury. Your healthcare provider will guide you on when it’s safe to gradually return to your regular activities. It’s essential to follow their recommendations to avoid re-injury.
8. What Complications Can Arise from a Broken Hand?
In some cases, untreated or improperly treated hand fractures can lead to complications such as stiffness, deformity, or chronic pain. It’s crucial to follow your doctor’s advice and attend follow-up appointments to monitor your hand’s progress and address any potential issues.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage our readers to seek immediate medical attention if they suspect a hand injury or experience any of the symptoms discussed. Early intervention by a medical specialist can make a significant difference in the outcome and ensure the best possible recovery.
Remember, your health and well-being are of paramount importance, so don’t hesitate to consult with a healthcare professional for any concerns related to hand injuries.
Thank you for taking the time to read this article, and we hope it has been informative and helpful in raising awareness about the importance of hand injury prevention and prompt medical care.