Broken Ankle Symptoms: A broken ankle, medically termed as an ankle fracture, is a common injury that occurs when one or more bones that make up the ankle joint break.
This condition not only causes significant discomfort but also impacts mobility and daily activities.
Understanding the symptoms and causes is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is a Broken Ankle?
A broken ankle refers to a fracture in one or more of the bones that make up the ankle joint. This type of injury is not only painful but can also significantly impact your mobility and daily activities.
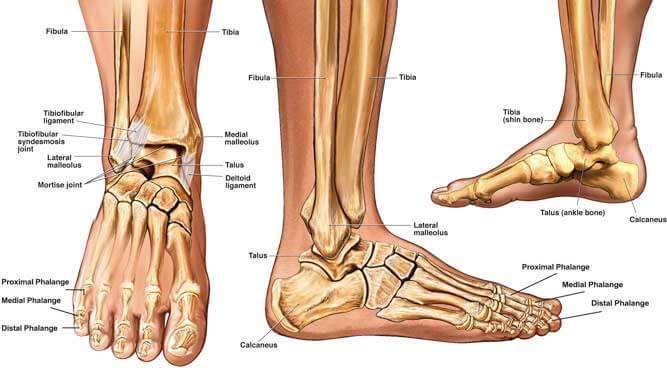
Anatomy of the Ankle
To fully understand what a broken ankle entails, it’s essential to have a basic grasp of the ankle’s anatomy. The ankle joint is a complex structure composed of three bones:
- Tibia: The larger bone of the lower leg, often referred to as the shinbone.
- Fibula: The thinner and smaller bone located alongside the tibia.
- Talus: A small bone that sits above the heel bone (calcaneus) and below the tibia and fibula, playing a crucial role in ankle movement.
These bones are held together by ligaments and surrounded by muscles and tendons that support the joint, allowing for movement and stability.
Common Causes of Ankle Fractures
Ankle fractures can occur due to various reasons, but some of the most common causes include:
- Trips and Falls: An awkward fall or tripping can twist the ankle in an unnatural way, leading to a fracture.
- Sports Injuries: High-impact sports or activities that involve jumping, running, or quick directional changes can cause stress on the ankle bones, resulting in fractures.
- Accidents: Car accidents or heavy impacts can exert extreme force on the ankle, leading to severe fractures.
- Osteoporosis: This condition weakens bones, making them more susceptible to breaks even from minor stresses.
Understanding these causes can help in taking preventive measures and seeking prompt medical attention if an ankle fracture is suspected. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful recovery from a broken ankle.
Identifying Broken Ankle Symptoms
This guide provides an in-depth look at the primary symptoms associated with a broken ankle, an explanation of each symptom, and a comparison with symptoms typical of an ankle sprain.
Primary Symptoms of a Broken Ankle
A broken ankle, also known as an ankle fracture, can manifest through various signs. Here’s a detailed list of the primary symptoms:
- Intense Pain: The most immediate and noticeable symptom is severe pain, especially when attempting to bear weight on the affected ankle.
- Swelling: Swelling often occurs rapidly following the injury.
- Bruising: A visible sign is bruising around the ankle, indicating internal bleeding or tissue damage.
- Tenderness: The ankle becomes tender to the touch, sometimes even without applying pressure.
- Deformity: In severe cases, the ankle may appear deformed or out of place.
- Inability to Bear Weight: Difficulty or inability to stand or walk on the affected foot is common.
- Limited Range of Motion: There may be a noticeable decrease in the ability to move the ankle.
Explanation of Each Symptom
- Intense Pain: Pain occurs due to the nerves around the broken bone being affected.
- Swelling: Swelling is the body’s natural response to injury, aiming to stabilize the area.
- Bruising: Bruising results from blood vessels breaking under the skin.
- Tenderness: Tenderness is caused by inflammation and the body’s response to the injury.
- Deformity: Deformity happens when the bones are displaced.
- Inability to Bear Weight: This is due to the ankle’s inability to support the body’s weight following the fracture.
- Limited Range of Motion: Swelling and pain restrict the movement of the ankle joint.
Comparison: Broken Ankle vs. Ankle Sprain
While some symptoms of a broken ankle and an ankle sprain are similar, key differences help in distinguishing between the two:
Severity of Pain: While both injuries are painful, the pain is generally more severe in a broken ankle.
Swelling and Bruising: These are common in both, but a broken ankle often results in more pronounced swelling and bruising.
Ability to Bear Weight: With a sprain, you might still be able to walk, albeit with discomfort. A broken ankle usually prevents weight-bearing activities.
Sound at Injury: Sometimes, a breaking sound is heard with a fracture, which is not the case with a sprain.
Recognizing the symptoms of a broken ankle is vital for seeking appropriate medical care. If you suspect a broken ankle, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional immediately. Understanding these symptoms and their differences from an ankle sprain can significantly aid in early diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of Broken Ankles
Let’s delves into the most prevalent reasons behind ankle fractures, highlighting high-risk activities, the impact of age and bone health, and more.
Common Causes of Ankle Fractures
Ankle fractures occur when one or more bones in the ankle joint break. The complexity and severity of these fractures vary, but they often result from similar causes:
High-Impact Sports: Engaging in sports like basketball, soccer, or football increases the risk of ankle fractures. These activities involve rapid direction changes, jumping, and potential collisions, all of which can lead to severe stress on the ankle bones.
Slips and Falls: Accidental slips, especially on icy or uneven surfaces, are a significant cause of broken ankles. Falls can occur at any age but are particularly problematic for older adults.
Vehicle Accidents: High-force impacts during vehicle accidents can cause multiple types of injuries, including severe ankle fractures.
Age and Bone Health as Risk Factors
Age-Related Risks: As individuals age, their bones often become weaker and more brittle, making them more susceptible to fractures. This is especially true for those with osteoporosis, a condition that significantly weakens bones.
Bone Health: Poor bone health, whether due to age, nutritional deficiencies, or other health conditions, can increase the risk of ankle fractures. Maintaining good bone health through a balanced diet and regular exercise is crucial for prevention.
Understanding the causes of broken ankles is vital for both prevention and effective treatment. High-risk activities, age-related bone deterioration, and overall bone health are key factors to consider. By being aware of these causes and taking appropriate preventative measures, the risk of ankle fractures can be significantly reduced.
Diagnosing a Broken Ankle
When it comes to diagnosing a broken ankle, the process is typically straightforward but necessitates professional medical attention. The initial step in this process involves a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. During this examination, the doctor will assess for signs of bruising, swelling, tenderness, and deformity in the ankle region. They will also evaluate the range of motion and the ability to bear weight on the affected ankle.
The Crucial Role of Medical Evaluation and Imaging Tests
A crucial part of diagnosing a broken ankle involves imaging tests. The most common and first-line imaging test is an X-ray, which provides clear images of bones and can show whether a bone in the ankle has been fractured. In some cases, additional imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI might be recommended. These tests provide more detailed images and can help in identifying complex fractures or additional injuries to the ligaments and soft tissues around the ankle.
Recognizing the Signs for Immediate Medical Attention
It’s important to be aware of the signs that indicate the need for immediate medical attention. These include:
- Intense pain that worsens with movement or pressure
- Significant swelling and bruising around the ankle
- Inability to bear weight on the injured foot
- Visible deformity or bones protruding from the skin
- Numbness or weakness in the ankle or foot
If you experience any of these symptoms following an injury to your ankle, it’s crucial to seek medical care promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to a successful recovery and can prevent further complications.
Treatment Options for a Broken Ankle
Understanding the various treatment options and the importance of a dedicated rehabilitation process is crucial for anyone facing this injury. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the general overview of treatment methods, delve into the rehabilitation and recovery process, and emphasize the significance of adhering to medical advice for a swift and efficient recovery.
General Overview of Treatment Methods
When dealing with a broken ankle, the primary goal is to promote healing while ensuring that the bones are aligned correctly. Treatment methods vary depending on the severity and type of fracture. They can range from conservative approaches like immobilization to surgical interventions in more severe cases.
Non-Surgical Treatment:
Casting and Splinting: For minor fractures, a cast or splint can effectively immobilize the ankle, allowing the bones to heal naturally.
Physical Therapy: Even in non-surgical cases, physical therapy plays a vital role in restoring strength and mobility.
Rest and Elevation: Keeping the ankle elevated and resting adequately aids in reducing swelling and pain.
Surgical Treatment:
Internal Fixation: Severe fractures may require surgery where metal plates, screws, or rods are used to hold the bones in place.
External Fixation: In some cases, external frames are used to stabilize the ankle externally.
Post-Operative Care: Post-surgery, the focus shifts to managing pain, preventing infection, and starting gradual movement under guidance.
Rehabilitation and Recovery Process
The journey to full recovery from a broken ankle involves a structured rehabilitation process, which is as crucial as the initial treatment. Rehabilitation typically includes:
Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises help regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion.
Gradual Weight Bearing: The transition from no weight bearing to full weight bearing is crucial and should be done as advised by the healthcare provider.
Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups ensure the healing process is on track and adjustments are made as needed.
Importance of Following Medical Advice
For a speedy recovery, adhering strictly to the medical advice provided is essential. This includes:
Taking Prescribed Medication: Following the prescribed medication regimen helps manage pain and prevent complications.
Attending Follow-up Appointments: Regular check-ups allow for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments in the treatment plan.
Lifestyle Modifications: Incorporating healthy lifestyle choices like a balanced diet and avoiding smoking can significantly impact the healing process.
However, while a broken ankle can be a challenging experience, understanding and following through with the right treatment and rehabilitation plan can lead to a successful and speedy recovery. Always consult with healthcare professionals and follow their guidance closely for the best outcomes.
Prevention Tips for Ankle Fractures
Ankle fractures are not only painful but can also sideline you from your daily activities and sports. Prevention is always better than cure, especially when it comes to injuries. Here are essential tips to help you avoid ankle fractures.
1. Prioritize Proper Footwear
Choose the Right Shoes for Activities: Different activities require different footwear. Wearing the right shoes for each activity can greatly reduce your risk of an ankle fracture. For instance, hiking boots for trails and sports-specific shoes for activities like basketball or soccer.
Ensure Proper Fit and Support: Shoes that fit well and offer good ankle support can prevent injuries. Avoid high heels or ill-fitting shoes that can cause imbalance and strain.
2. Avoid Hazardous Activities
Be Cautious in Risky Environments: Uneven surfaces, slippery floors, or cluttered areas can increase the risk of tripping or twisting your ankle. Always be mindful of your surroundings.
Modify Activities as Needed: If you have a history of ankle problems, consider modifying high-impact activities. Low-impact exercises like swimming or cycling can be safer alternatives.
3. Maintain Bone Health
Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: A diet rich in calcium and vitamin D is crucial for bone strength. Dairy products, leafy greens, and fortified foods can help maintain bone density.
Regular Exercise: Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones and muscles, making them less prone to fractures. Incorporate activities like walking, jogging, or resistance training into your routine.
Preventing ankle fractures involves a combination of wearing the right footwear, being cautious in your activities, and maintaining good bone health. By following these tips, you can keep your ankles strong and reduce the risk of injury. Remember, taking proactive steps today can save you from pain and inconvenience in the future.
FAQs About Broken Ankles
1. How Do I Know if My Ankle is Broken?
Broken ankles typically present symptoms like severe pain, swelling, bruising, and an inability to bear weight on the affected leg. In some cases, you might even notice an obvious deformity. However, these symptoms can also occur with sprains, so it’s important to consult a medical professional for a proper diagnosis.
2. What Should I Do Immediately After Breaking My Ankle?
First and foremost, avoid putting weight on the injured ankle. Apply ice to reduce swelling and consider using a compression bandage. Elevating your foot above heart level can also help. Most importantly, seek medical attention as soon as possible.
3. How Long Does It Take for a Broken Ankle to Heal?
Healing times can vary depending on the severity of the break. Generally, it takes at least six weeks for the bones to heal. However, full recovery, including regaining strength and mobility, may take several months.
4. Can I Walk on a Broken Ankle?
It’s not advisable to walk on a broken ankle until your doctor gives you the green light. Doing so can worsen the injury or delay healing. You may need to use crutches or a walker to get around without putting weight on the injured ankle.
5. What Are the Treatment Options for a Broken Ankle?
Treatment depends on the break’s severity. Simple fractures may only require a cast or a boot to immobilize the ankle. More complex fractures might need surgical intervention to realign and stabilize the bones.
6. Will I Need Physical Therapy After a Broken Ankle?
Physical therapy is often recommended to help restore strength, flexibility, and balance. Your healthcare provider will advise if and when physical therapy should be started based on your specific situation.
Conclusion
It is essential to underscore the importance of seeking professional medical advice. While recognizing symptoms is the first step, a proper diagnosis and treatment plan can only be provided by a healthcare professional. They have the expertise to differentiate between a simple sprain and a fracture, and to recommend the best course of action. Remember, self-diagnosis and treatment can often do more harm than good.
Finally, we urge our readers to stay informed and cautious. Regularly updating your knowledge about common injuries and their symptoms helps in early recognition and treatment. Being cautious, especially in activities that pose a risk of such injuries, is equally important.
In closing, we encourage you to prioritize your health and well-being. If you suspect a broken ankle, do not hesitate to consult a medical professional. Stay vigilant and informed, and always err on the side of caution when it comes to your health. Let’s embrace a proactive approach to our well-being and ensure a healthier, more informed community.