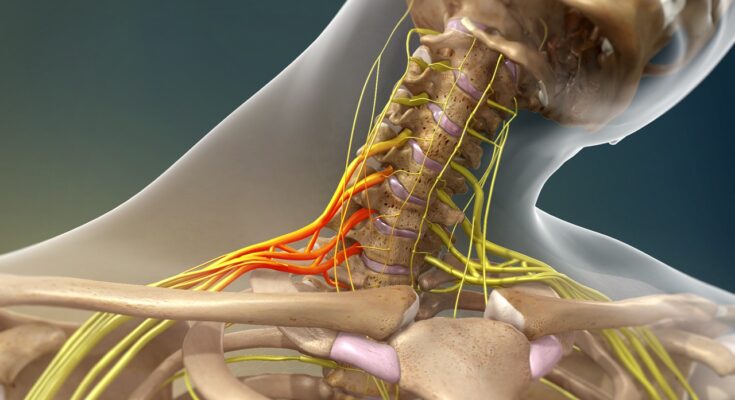
Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms: The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that sends signals from your spine to your shoulder, arm, and hand.
A brachial plexus injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or, in more severe cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord.
Understanding the symptoms and causes of brachial plexus injuries is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
What is a Brachial Plexus Injury?
The brachial plexus is a complex network of nerves that extends from the spinal cord in the neck down into the arm. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm, and hand, controlling muscle movements and sensations in these areas. Understanding the brachial plexus is crucial in comprehending the impact and severity of injuries affecting it.
Brachial Plexus Injuries Explained
Brachial plexus injuries occur when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or in severe cases, ripped apart or torn away from the spinal cord. This can result from various incidents, including traumatic accidents, sports injuries, or even during childbirth. The severity of a brachial plexus injury can range from mild, causing only temporary weakness or numbness, to severe, leading to permanent disability in the affected arm.
These injuries are not just about physical impairment; they can also have profound emotional and psychological effects, especially when they lead to long-term disability. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for the best possible recovery.
Understanding the mechanisms and impact of brachial plexus injuries is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. It helps in devising appropriate treatment plans and setting realistic expectations regarding recovery and rehabilitation.
Symptoms of Brachial Plexus Injury
Understanding the symptoms of a brachial plexus injury is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. This article provides a comprehensive look at the common symptoms, explains the underlying reasons for their occurrence, and discusses how they can vary depending on the severity and type of the injury.
Detailed List of Common Symptoms
The brachial plexus is a network of nerves that sends signals from your spine to your shoulder, arm, and hand. When these nerves are damaged, it can lead to a variety of symptoms, including:
1. Weakness in the Arm or Hand: You may experience a noticeable decrease in muscle strength in these areas.
2. Loss of Sensation: This can include numbness or a tingling sensation in the shoulder, arm, or hand.
3. Pain: This may be a sharp, burning pain or a dull ache, often starting in the shoulder.
4. Limited Movement: Difficulty in moving the affected shoulder, arm, or hand is common.
5. Muscular Atrophy: Over time, muscles may appear smaller or waste away due to lack of use.
6. Partial or Complete Paralysis: In severe cases, there may be an inability to use certain muscles in the arm or hand.
Why These Symptoms Occur
These symptoms occur because the brachial plexus nerves control muscle movements and relay sensation from the arm to the brain. When these nerves are stretched, compressed, or, in severe cases, ripped or torn, they cannot function properly. This disruption leads to the various symptoms experienced.
Variation of Symptoms Based on Severity and Type of Injury
The symptoms of a brachial plexus injury can vary significantly based on the severity and type of injury:
1. Avulsion: The most severe type, where the nerve is torn from the spine, often leads to complete paralysis and loss of sensation.
2. Rupture: This involves a tear in the nerve and can cause severe pain and partial paralysis.
3. Neuroma: This is where scar tissue puts pressure on the injured nerve, leading to pain and sensory disturbances.
4. Neuropraxia: The mildest form, usually resulting from nerve stretching, can cause temporary symptoms like numbness and weakness.
Each type of injury impacts the nerves differently, leading to varying symptoms and requiring specific treatment approaches.
Common Causes of Brachial Plexus Injuries
Understanding the common causes of brachial plexus injuries is essential for both prevention and treatment. Here, we delve into the primary reasons these injuries occur, ranging from birth-related issues to trauma and medical conditions.
Birth Injuries: A Delicate Start
Explanation: Birth injuries are a leading cause of brachial plexus damage, particularly during complicated or difficult deliveries. When a baby’s shoulders become wedged in the birth canal, excessive pressure can be placed on the brachial plexus nerves. This is often associated with a condition known as shoulder dystocia. The use of birth-assisting tools like forceps or vacuum extractors can also increase the risk.
Statistics: Research indicates that brachial plexus birth injuries occur in about 1 to 2 per 1,000 live births. While most infants recover from these injuries, a significant percentage may experience lasting effects or require surgical intervention.
Trauma: Accidents and Injuries
Types of Accidents: Traumatic brachial plexus injuries are commonly associated with high-impact activities or accidents. These include:
Motor Vehicle Accidents: Collisions, especially for motorcyclists or bicyclists, often result in severe brachial plexus injuries.
Sports Injuries: Contact sports like football or wrestling can lead to direct damage to the nerve bundle.
Falls: Falling from a height or in a particular way can stretch or tear the brachial plexus nerves.
Gunshot or Knife Wounds: These can directly damage the nerves.
Understanding the scenarios that lead to trauma-induced brachial plexus injuries can aid in preventive measures and prompt medical attention.
Medical Conditions: Underlying Factors
Certain diseases or disorders might cause or exacerbate brachial plexus injuries. These include:
Tumors: Growths, benign or malignant, near the brachial plexus can compress or invade the nerves.
Inflammation: Conditions like brachitis, an inflammation of the brachial plexus, can cause pain and loss of function.
Radiation Treatment: Cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy near the neck or chest area might experience nerve damage.
Awareness and early detection of these medical conditions are crucial in managing and mitigating the risk of brachial plexus injuries.
Diagnosing Brachial Plexus Injuries
Accurate diagnosis is essential for effective treatment and recovery. In this article, we delve into the common diagnostic procedures, the importance of medical history and physical examination, and the advanced imaging techniques used in diagnosing these injuries.
Common Diagnostic Procedures
The initial step in diagnosing a brachial plexus injury involves a series of standard procedures. These procedures are designed to assess nerve function and pinpoint the location of the injury. They typically include:
Neurological Tests: These tests check for nerve sensation and muscle strength. The doctor may tap or press on nerves in the arm and hand to see if there is a response.
Electromyography (EMG): EMG measures the electrical activity of muscles. A needle electrode is inserted into the muscle to record electrical activity during muscle contractions.
Nerve Conduction Studies: These studies test the speed and strength of nerve signals. Electrodes are placed on the skin over the nerves, and a small shock is passed through the nerve to measure the speed of the signal.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
A thorough medical history and physical examination are critical components in diagnosing brachial plexus injuries. During the medical history, the doctor will ask about the patient’s symptoms, any previous injuries, and overall health history. This information can provide clues about the nature and extent of the injury.
The physical examination allows the doctor to observe the patient’s condition directly. It typically includes:
- Checking for tenderness or deformity.
- Assessing range of motion and muscle strength.
- Evaluating sensation in different parts of the arm and hand.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques offer a more detailed view of the brachial plexus and surrounding structures, aiding in accurate diagnosis:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body. It is particularly useful in visualizing soft tissues and can show the extent of the nerve damage.
Computerized Tomography (CT) Scan: While not as detailed as MRI for nerve injuries, CT scans can be beneficial in visualizing bone structures and any potential impingements on the nerves.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of the inside of the body. It is a non-invasive method and can be used to view the movement and condition of the nerves and muscles.
However, diagnosing brachial plexus injuries involves a combination of clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history and physical examination, as well as advanced imaging techniques. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment and improved outcomes for patients suffering from these complex injuries.
The Impact of Brachial Plexus Injury Symptoms on Daily Life
Brachial plexus injuries can significantly impact an individual’s life, affecting their ability to perform everyday activities and their emotional well-being. This section explores the challenges and psychological impacts of living with brachial plexus injury symptoms through personal anecdotes and case studies.
Personal Anecdotes or Case Studies
Personal stories and case studies provide a window into the real-life experiences of those affected by brachial plexus injuries. For instance, a case study might detail the journey of a young athlete who, after a sports injury, faces the challenge of limited arm mobility. Their story might highlight the struggles with simple tasks such as dressing or cooking, and the adaptations they had to make in their daily routine. These narratives often underscore not just the physical limitations but also the resilience and determination in overcoming these challenges.
Challenges in Performing Everyday Activities
The brachial plexus is crucial for arm and hand movements, making injuries particularly debilitating. Individuals often experience difficulty in performing basic tasks such as brushing teeth, typing, or carrying groceries. This section could delve into the various adaptations and tools that people use to manage these difficulties. It could include insights from occupational therapists on how they assist patients in regaining independence in daily activities, emphasizing the importance of adaptive strategies and rehabilitation.
Psychological and Emotional Impact
Living with a brachial plexus injury is not just a physical challenge; it’s an emotional and psychological journey as well. This part of the content could explore the common emotional responses such as frustration, anxiety, and depression. It’s important to discuss the psychological impact in depth, offering insights from psychologists or counselors specializing in helping patients cope with chronic injuries. This section could also highlight support groups or communities where individuals share experiences and coping strategies, providing a sense of belonging and understanding for those affected.
By presenting a comprehensive view of the impact of brachial plexus injury symptoms on daily life, this content aims to raise awareness, offer support, and provide valuable information to those affected by such injuries.
Treatment Options for Brachial Plexus Injuries
The treatment plan depends on various factors, such as the type and severity of the injury, patient age, and overall health. Understanding the comprehensive treatment options available is essential for optimal recovery.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the recovery from Brachial Plexus injuries. It typically includes:
Range-of-motion exercises: To maintain joint flexibility and muscle strength.
Muscle strengthening exercises: Targeted exercises to improve muscle strength and reduce muscle atrophy.
Nerve gliding exercises: To facilitate nerve movement and prevent stiffness.
Pain management techniques: Including heat and cold therapy, electrical nerve stimulation, and relaxation exercises.
Early intervention with physical therapy can significantly improve functionality and reduce the risk of long-term complications.
Surgical Options and When They are Necessary
Surgery may be considered for more severe Brachial Plexus injuries or when non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief. Surgical options include:
Nerve Repair: To reconnect torn nerves or graft nerves from other parts of the body.
Nerve Transfer: When the original nerve can’t be repaired, a less important nerve is rerouted to restore function.
Muscle Transfer: Transferring muscles from other parts of the body to improve arm function.
Joint Reconstruction: To improve joint stability and function.
Surgery is typically recommended within six months of the injury for optimal results. The decision to opt for surgery depends on various factors, including the type of injury, the patient’s overall health, and the potential for nerve recovery.
However, the treatment of Brachial Plexus injuries involves a multifaceted approach. Working closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan is crucial for achieving the best possible outcome.
Prevention and Risk Reduction of Brachial Plexus Injury
Fortunately, with the right knowledge and practices, the risk of these injuries can be significantly reduced. Here’s a guide to help you understand and prevent brachial plexus injuries.
Understanding the Risk Factors
Repetitive Motion: Engaging in activities that involve repetitive arm and shoulder movements can strain the brachial plexus nerves.
Poor Posture: Slouching or maintaining a poor posture, especially during activities like typing or driving, can compress these nerves.
Contact Sports: Sports like football or wrestling increase the risk of sudden, traumatic brachial plexus injuries.
Birth Trauma: Newborns can suffer brachial plexus injuries during a difficult delivery.
Heavy Lifting: Lifting objects that are too heavy can stretch or tear the nerves.
Tips for Prevention
Practice Good Ergonomics: If you work at a desk, ensure your workstation is ergonomically set up to reduce strain on your shoulders and arms.
Regular Breaks and Stretching: Take frequent breaks during repetitive tasks to stretch and relieve pressure on your nerves.
Proper Sporting Techniques: Athletes should learn and apply proper techniques to avoid overstraining the brachial plexus.
Strength Training: Strengthening the muscles around your shoulders, neck, and arms can provide better support to the brachial plexus.
Use Assistive Devices: When lifting heavy objects, use tools or ask for assistance to distribute the weight more evenly.
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
If you’re at risk or have experienced symptoms like numbness, weakness, or pain in your arm or hand, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide personalized advice and, if necessary, treatment plans to manage or prevent brachial plexus injuries.
By understanding the risk factors and adopting preventive measures, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of a brachial plexus injury, ensuring better health and mobility in your daily life.
Frequently Asked Questions About Brachial Plexus Injury: Symptoms and Causes
1. What is a Brachial Plexus Injury?
A brachial plexus injury involves damage to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that send signals from your spinal cord to your shoulder, arm, and hand. Such injuries can result in varying degrees of arm and hand function loss.
2. What Causes Brachial Plexus Injuries?
These injuries are often caused by physical trauma, such as motorcycle or car accidents, sports injuries, or during childbirth. In some cases, inflammation or tumors may also affect the brachial plexus.
3. What are the Common Symptoms of a Brachial Plexus Injury?
Symptoms typically include weakness or total inability to use certain muscles in the shoulder, arm, or hand. Other signs can be numbness, tingling sensations, and severe pain in these areas.
4. Can a Brachial Plexus Injury be Mistaken for Other Conditions?
Yes, due to the similarity in symptoms, these injuries can be misdiagnosed as other nerve-related conditions. Consulting a specialist is important for an accurate diagnosis.
5. Are There Different Types of Brachial Plexus Injuries?
Brachial plexus injuries vary in severity, ranging from mild nerve stretching to complete nerve rupture or avulsion. The type of injury impacts both treatment and recovery prospects.
6. How is a Brachial Plexus Injury Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, medical history analysis, and imaging tests like MRI or CT scans, along with nerve conduction studies.
7. Is Recovery from a Brachial Plexus Injury Possible?
Recovery depends on the injury’s severity. While some injuries heal on their own, others may require physical therapy, medication, or even surgery.
8. What Long-Term Effects Can a Brachial Plexus Injury Have?
Long-term effects can range from mild weakness to permanent disability in the affected limb. Early treatment can significantly improve the prognosis.
9. Are Certain Groups More at Risk for Brachial Plexus Injuries?
Athletes, motorcyclists, and newborns (during childbirth) are at a higher risk. However, these injuries can happen to anyone.
10. How Can Brachial Plexus Injuries be Prevented?
While not all brachial plexus injuries can be prevented, wearing protective gear during high-risk activities and practicing safe driving can reduce the risk.
Conclusion
By prioritizing your health and consulting with healthcare professionals, you can access the necessary care and support for managing this condition. Medical intervention, ranging from physical therapy to surgery, can play a pivotal role in restoring function and improving your overall well-being.
In conclusion, awareness and proactive healthcare are key in addressing Brachial Plexus Injuries. If you suspect that you or someone you know might be suffering from this condition, do not hesitate to seek medical advice. Your health is your most valuable asset; taking timely action can make a significant difference in your recovery journey.