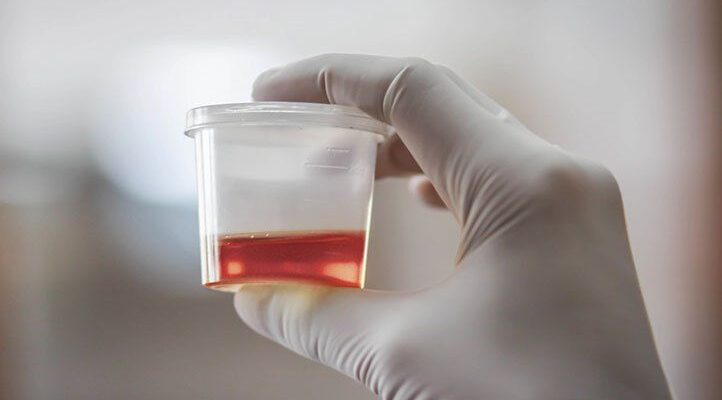
Blood in Urine Symptoms: Blood in the urine, medically known as hematuria, is a condition that can range from a benign, transient occurrence to an indication of a more serious underlying condition.
Hematuria can be visible to the naked eye (gross hematuria) or microscopic (only detected through urine analysis).
What is Hematuria?
Hematuria is a medical term that refers to the presence of blood in the urine, a condition that can be both alarming and indicative of various underlying health issues. It is essential to understand the nature of hematuria, as it plays a critical role in diagnosing and treating potential medical conditions.
Types of Hematuria
Hematuria is categorized into two main types:
- Visible (Gross) Hematuria: This type is noticeable to the naked eye. The urine may appear pink, red, or cola-colored. The discoloration is due to a sufficient amount of red blood cells. Visible hematuria is often more concerning than its counterpart and warrants immediate medical attention.
- Non-Visible (Microscopic) Hematuria: In this case, the blood cells are not visible to the naked eye and are only detectable under a microscope. Microscopic hematuria is often found incidentally during routine medical check-ups or urine tests for other conditions.
However, understanding hematuria, its types, and its potential implications is crucial for maintaining good urological health. Whether it’s visible or microscopic, any sign of blood in the urine should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
It’s important to recognize the various symptoms associated with this condition for prompt medical consultation. The symptoms of hematuria can vary significantly between individuals, but there are common signs to look out for.
Common Symptoms of Hematuria
- Visible Blood in Urine: The most noticeable symptom is the presence of red, pink, or cola-colored urine, indicating the presence of red blood cells.
- Painless Urination: Despite the alarming appearance, urinating blood is usually painless.
- Frequent Urination Urges: An increased need to urinate, often without a significant increase in urine volume.
- Painful Urination: In some cases, you might experience discomfort or pain while urinating.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Pain or discomfort in the lower abdomen area.
Variations in Symptoms
- Gender Differences: Men might experience additional symptoms like swelling in the legs or feet, or fluid buildup in the scrotum. Women may have symptoms related to their menstrual cycle or menopause.
- Age Factors: Older adults might have symptoms related to other underlying conditions like prostate issues in men or postmenopausal changes in women.
- Underlying Conditions: The symptoms can vary if hematuria is associated with other medical conditions such as urinary tract infections, kidney stones, or kidney disease.
Understanding these symptoms and their variations is crucial for early detection and treatment. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Blood in Urine
It’s a condition that warrants attention, as it can be an indicator of different health issues ranging from minor to serious. Understanding the common causes of hematuria and how they impact different age groups and genders is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
1. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
- Prevalence: UTIs are more common in women and can occur at any age.
- Symptoms: Alongside hematuria, symptoms include burning during urination and frequent urges to urinate.
- Importance: Prompt treatment is essential to prevent the infection from spreading to the kidneys.
2. Kidney Stones
- Age Factor: More prevalent in adults, especially between 30 and 60 years.
- Gender Impact: Slightly more common in men than in women.
- Symptoms: Severe pain in the back or side, alongside visible blood in the urine.
3. Enlarged Prostate
- Specific to Men: Occurs in men, generally over the age of 50.
- Symptoms: Difficulty in urinating, a weak urine stream, and presence of blood in urine.
- Management: Regular check-ups are vital for early detection and management.
4. Kidney Diseases
- Across Ages and Genders: Can affect individuals of any age or gender.
- Indicators: Persistent or recurrent hematuria may signal a kidney disease.
5. Physical Trauma
- Age Factor: Common in younger individuals engaged in physical activities.
- Attention Needed: Any trauma to the lower body that results in blood in urine requires immediate medical attention.
6. Medications
- Variable Impact: Certain medications can cause hematuria as a side effect.
- Consultation: Always discuss medication-related risks with your healthcare provider.
7. Cancer
- Age-Related: Higher risk in older adults, especially over 50.
- Types: Includes bladder, kidney, or prostate cancer.
- Symptom Recognition: Persistent hematuria demands a thorough medical examination.
By being aware of these common causes, individuals can seek appropriate medical attention promptly, aiding in early diagnosis and effective management.
Diagnosing Hematuria: Understanding the Process
Diagnosing hematuria involves a series of steps and tests to identify its root cause. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the diagnostic process for hematuria.
Step 1: Initial Assessment
The diagnostic journey begins with an initial assessment. During this phase, healthcare professionals collect detailed medical history and conduct a physical examination. Key points include:
- Medical History: Inquiring about recent infections, medication usage, family history of kidney diseases, or any history of trauma.
- Physical Examination: Checking for signs of swelling, tenderness, or abnormalities in the abdominal and pelvic regions.
Step 2: Urinalysis
A urinalysis is the cornerstone test for diagnosing hematuria. This simple test can detect:
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs): The presence and number of RBCs in the urine.
- Infections or Crystals: Indications of urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney stones.
Step 3: Imaging Tests
Imaging tests are crucial in visualizing the urinary tract, helping to pinpoint abnormalities or diseases. Common imaging tests include:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive method to visualize kidneys and bladder.
- CT Scan: Offering detailed images of the urinary tract, especially useful in detecting stones, tumors, or other structural abnormalities.
Step 4: Cystoscopy
For certain cases, a cystoscopy might be recommended. This procedure involves:
- Visual Inspection: Using a cystoscope, a thin tube with a camera, to directly view the inside of the bladder and urethra.
Step 5: Additional Tests
Depending on initial findings, additional tests may be required, such as:
- Kidney Function Tests: Assessing how well the kidneys are working.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, to examine the tissue from the bladder or kidney.
The diagnostic process for hematuria is comprehensive, involving a combination of medical history, physical examinations, lab tests, and imaging. Identifying the cause of hematuria is crucial for effective treatment and management. If you notice any signs of blood in your urine, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional promptly.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Hematuria
When left untreated, hematuria poses several potential health risks, making it essential to understand its significance and seek prompt medical attention.
The Link Between Hematuria and Serious Health Conditions
- Kidney Disease and Failure: Persistent hematuria may be a sign of kidney diseases, such as glomerulonephritis or kidney stones. These conditions, if not treated, can lead to kidney damage or even kidney failure.
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Hematuria often occurs in urinary tract infections. Untreated UTIs can escalate to more severe infections, affecting the kidneys and potentially leading to sepsis, a life-threatening response to infection.
- Bladder or Kidney Cancer: One of the more severe risks associated with hematuria is the possibility of bladder or kidney cancer. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment, making ignoring hematuria potentially dangerous.
- Enlarged Prostate: In men, hematuria can indicate an enlarged prostate, a common condition as men age. If left untreated, this can lead to urinary retention and kidney damage.
- Other Serious Conditions: Hematuria can also be indicative of more serious systemic diseases like lupus or sickle cell anemia.
Timely medical intervention is vital for diagnosing and treating the underlying causes of hematuria, safeguarding against the potential risks associated with this condition. Remember, early detection and treatment can be the key to preventing serious health complications.
Treatment Options for Hematuria
When it comes to treating hematuria (the presence of blood in urine), understanding the available treatment options is crucial. Hematuria can stem from various causes, ranging from benign to serious medical conditions. Therefore, the treatment approach varies significantly based on the underlying cause.
- Medication: For certain conditions, such as urinary tract infections or specific kidney diseases, doctors may prescribe antibiotics or other medications. These medications are aimed at treating the root cause, thereby resolving the symptom of blood in the urine.
- Surgical Interventions: In cases where hematuria is caused by physical blockages, such as kidney stones or tumors, surgical procedures might be necessary. These surgeries aim to remove the blockage and alleviate the symptoms.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Sometimes, simple lifestyle changes can help in managing hematuria. This includes increasing water intake, avoiding certain foods or medications known to irritate the bladder, and engaging in healthy physical activities.
The Importance of Personalized Treatment Plans
Each case of hematuria is unique, making personalized treatment plans paramount. Here’s why individualized care is essential:
- Accurate Diagnosis: A thorough examination, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, ensures an accurate diagnosis, which is the cornerstone of effective treatment.
- Tailored Treatment: Personalized treatment plans cater to the specific needs and medical conditions of the patient, increasing the likelihood of successful treatment and recovery.
- Monitoring and Adjustment: Ongoing monitoring allows healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans as necessary, ensuring the most effective and least invasive approach is used.
However, while there are several treatment options for hematuria, the key to effective management lies in a personalized approach, tailored to the individual’s specific condition and needs. Consulting with healthcare professionals and undergoing comprehensive evaluations are crucial steps in developing an effective treatment plan for hematuria.
Preventive Measures and Lifestyle Changes to Avoid Hematuria
While it’s crucial to consult healthcare professionals for diagnosis and treatment, adopting certain preventive measures and lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing hematuria. This section offers practical tips and advice to help you maintain urinary health and potentially prevent the occurrence of hematuria.
1. Stay Hydrated
Importance of Hydration: Adequate water intake is essential for kidney health and to ensure smooth urinary function. Drinking sufficient water helps in diluting the urine and facilitates the flushing out of potential irritants from the urinary tract.
Tips for Staying Hydrated:
- Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Include hydrating foods like fruits and vegetables in your diet.
- Carry a water bottle and sip throughout the day.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Balanced Diet Benefits: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help in maintaining a healthy urinary system. Avoiding excessive salt and processed foods can also contribute to better kidney health.
Dietary Tips:
- Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables.
- Limit intake of salt and processed foods.
- Choose whole grains and lean protein sources.
3. Regular Exercise
Exercise and Urinary Health: Regular physical activity can reduce the risk of conditions like obesity and high blood pressure, which are linked to urinary health issues.
Exercise Recommendations:
- Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days.
- Include a mix of cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
- Consult a healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regime.
4. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Impact of Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking can harm the bladder and increase the risk of bladder cancer, while excessive alcohol consumption can disrupt the normal function of the kidneys and urinary tract.
Tips for Reducing Smoking and Alcohol:
- Seek professional help to quit smoking.
- Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels.
5. Regular Health Check-ups
Importance of Regular Check-ups: Regular health screenings can help detect any underlying conditions that may cause hematuria. Early detection often leads to more effective management.
Health Check-up Tips:
- Schedule annual physical examinations.
- Discuss any urinary changes or concerns with a healthcare provider.
Adopting these preventive measures and lifestyle changes can contribute significantly to reducing the risk of hematuria. However, it’s important to remember that these tips should complement, not replace, professional medical advice. If you notice blood in your urine, or have other concerns, consult a healthcare provider promptly.
When to See a Doctor for Blood in Urine
Recognizing when to seek medical help is crucial for prompt diagnosis and effective treatment.
- Immediate Symptoms: If you notice a visible change in the color of your urine, turning pink, red, or cola-colored, it’s a clear indication to consult a healthcare provider. This change can occur once or over multiple instances.
- Associated Symptoms: Pay attention to other symptoms accompanying the blood in your urine, such as pain while urinating, an increased urge to urinate, pain in the abdomen, or back pain. These could be signs of infections, stones, or other serious conditions.
- Risk Factors and History: Individuals with a history of kidney stones, urinary tract infections, or a family history of kidney disease should be more vigilant. Smokers and older adults are also at higher risk.
- No Symptoms: Sometimes, blood in urine can occur without any pain or additional symptoms. This ‘painless hematuria’ still warrants a doctor’s visit as it might indicate serious conditions like cancer.
The Importance of Early Medical Intervention
Early medical intervention plays a pivotal role in managing hematuria effectively:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Early consultation helps in diagnosing the underlying cause, which can range from benign conditions like urinary tract infections to serious concerns like cancer.
- Preventing Complications: Addressing the issue early can prevent complications, especially if it’s related to conditions like kidney stones or infections.
- Peace of Mind: Getting a professional evaluation relieves anxiety and provides clarity about the necessary steps for treatment and management.
Blood in urine should not be ignored. Consult a healthcare provider immediately if you experience this symptom, especially if it’s accompanied by other signs or you fall into a higher risk category. Early intervention can make a significant difference in outcomes and overall health.
FAQs on Hematuria
What is Hematuria?
Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in urine, a condition that can indicate various underlying health issues. It is important to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any signs of blood in your urine.
What Causes Hematuria?
There are numerous potential causes of hematuria, ranging from benign conditions like strenuous exercise to more serious issues such as infections, kidney stones, or cancers. A detailed medical evaluation is necessary to determine the exact cause.
What are the Symptoms of Hematuria?
The primary symptom of hematuria is blood in the urine, which can appear red, pink, or brown. However, some cases of hematuria might be microscopic and not visible to the naked eye. Other symptoms may include pain during urination or lower back pain.
How is Hematuria Diagnosed?
Diagnosing hematuria involves a physical examination, medical history review, urine tests, and sometimes additional imaging tests like CT scans or ultrasounds. These tests help in identifying the underlying cause of blood in the urine.
What are the Treatment Options for Hematuria?
Treatment for hematuria depends on its underlying cause. It may range from simple lifestyle changes and antibiotics for infections to more complex treatments for kidney stones or cancers.
Can Hematuria be Prevented?
Prevention of hematuria involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and regular medical check-ups. Early detection and treatment of urinary tract infections or other conditions can also help prevent hematuria.
When Should I See a Doctor for Hematuria?
It is crucial to seek medical attention if you notice blood in your urine or experience other related symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are key in managing the underlying causes effectively.
Conclusion
Awareness and proactive health management play a pivotal role in addressing this condition. Early detection of blood in urine symptoms can lead to a more successful diagnosis and treatment of the underlying causes, which may include urinary tract infections, kidney stones, or more severe conditions like cancer. It is vital to consult a healthcare professional if you notice any signs of blood in your urine.
Remember, your health is in your hands. Regular check-ups, a keen observation of your body’s signals, and immediate action when something seems amiss, are key to maintaining good health. By being aware and proactive, you can ensure a quicker response to potential health issues and a better overall outcome.