Blood in Urine Treatment: Blood in the urine, medically termed as Hematuria, is a condition that warrants immediate attention due to its association with various underlying medical issues. Hematuria is not a disease in itself but a symptom of numerous potential disorders.
Understanding Hematuria, its causes, diagnostic procedures, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and health maintenance.
What is Hematuria?
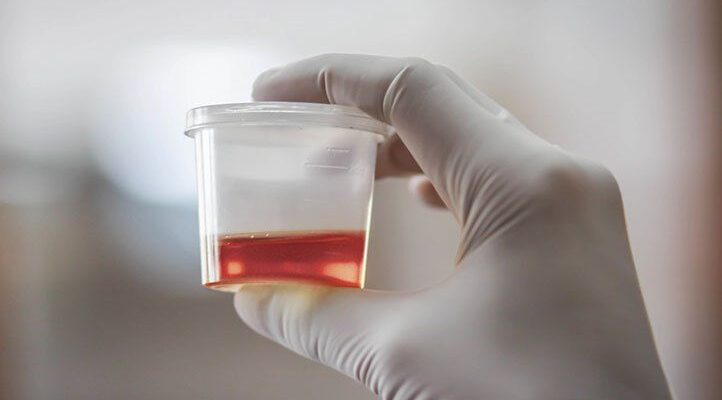
Hematuria, commonly referred to as blood in the urine, is a condition that can serve as an indicator of various health issues. This occurrence may range from microscopic levels, where blood cells are only detectable under a microscope, to gross hematuria, where the blood is visible to the naked eye, often turning the urine pink, red, or cola-colored. Understanding hematuria is crucial as it can be a symptom of benign conditions or more serious diseases.
Types of Hematuria
Hematuria is classified into two main types:
- Microscopic Hematuria: This type is usually detected during routine medical testing and is characterized by the presence of blood cells in the urine that are only visible under a microscope.
- Gross Hematuria: In this more noticeable form, urine appears discolored due to the presence of blood, varying from light pink to deep red or brown, easily seen without magnification.
Common Causes of Hematuria
Various factors can contribute to the occurrence of hematuria. Some of the common causes include:
- Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Infections in the urinary system often lead to blood in the urine.
- Kidney Stones: These hard mineral and salt deposits can cause bleeding as they pass through the urinary tract.
- Enlarged Prostate: Common in older men, an enlarged prostate can lead to urinary bleeding.
- Kidney Disease: A disorder originating in the kidneys, like glomerulonephritis, can cause hematuria.
- Cancer: Advanced kidney, bladder, or prostate cancer might manifest as visible urinary bleeding.
- Inherited Disorders: Conditions like sickle cell anemia and Alport syndrome can cause blood in the urine.
- Kidney Injury: A direct blow or trauma to the kidneys from an accident or contact sports can lead to visible blood in the urine.
- Medications: Certain drugs, including blood thinners, aspirin, and anti-cancer drugs, can cause urinary bleeding.
- Strenuous Exercise: Rarely, intense physical activity can lead to hematuria.
Identifying the underlying cause of hematuria is vital for appropriate treatment. If you notice any form of blood in your urine, it is important to consult a healthcare provider for diagnosis and management. Remember, hematuria might be the first sign of something more serious, and early detection is key to effective treatment.
Symptoms Associated with Hematuria
It’s crucial to understand the associated symptoms for prompt and accurate diagnosis.
Key Symptoms to Watch For
- Visible Blood in Urine: The most apparent sign of hematuria is the presence of red, pink, or cola-colored urine. This change in color is due to the presence of red blood cells.
- Painful Urination: Pain or burning sensations during urination can often accompany hematuria, indicating potential infections or stones in the urinary tract.
- Frequent Urination: An increased urge to urinate, often with small amounts, may be associated with hematuria, especially if an infection is present.
- Lower Abdominal Pain: Discomfort or pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area can occur, possibly indicating a more serious condition like a bladder or kidney infection.
- Fever and Chills: These are general signs of infection and, when combined with hematuria, should be promptly addressed.
- Fatigue and General Weakness: Unexplained tiredness or weakness might accompany hematuria, especially in cases of kidney-related issues.
Importance of Recognizing Symptoms
Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial. Hematuria can be a sign of various conditions ranging from urinary tract infections and kidney stones to more serious issues like kidney disease or bladder cancer. Timely diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment and a better prognosis.
If you experience these symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen, seeking medical advice is essential. Remember, hematuria isn’t always visible to the naked eye; sometimes, it’s detected only through a urine test. Therefore, regular health check-ups can play a vital role in early detection and management of any underlying health issues.
Diagnosing Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
This comprehensive guide outlines the various tests and evaluations doctors use to diagnose hematuria, ensuring readers are well-informed about their healthcare options.
Diagnostic Procedures for Hematuria
Urinalysis: The initial step in diagnosing hematuria is a urinalysis. This simple test checks for blood, protein, and other substances in a urine sample. It helps in identifying infections, kidney disease, and other urinary tract issues.
Blood Tests: Blood tests can assess kidney function and detect conditions that might cause hematuria. These tests typically measure creatinine levels and blood urea nitrogen (BUN).
Imaging Tests: To get a clearer view of the urinary tract, doctors often recommend imaging tests. These may include:
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of the kidneys and bladder.
- CT Scan: Provides detailed cross-sectional images of the urinary tract, helpful in identifying stones, tumors, or other abnormalities.
- MRI: Utilized in specific cases where detailed images are necessary.
Cystoscopy: For a direct look inside the bladder and urethra, a cystoscopy may be performed. This involves inserting a thin scope equipped with a camera into the bladder through the urethra.
Kidney Biopsy: In some cases, particularly if kidney disease is suspected, a biopsy may be needed. This procedure involves taking a small tissue sample from the kidney for microscopic examination.
24-Hour Urine Collection: This test measures various components in the urine collected over a 24-hour period, providing valuable information about kidney function and health.
Prompt and accurate diagnosis of blood in urine is crucial for effective treatment. If you notice any signs of hematuria, consult your healthcare provider to determine the appropriate diagnostic approach. Remember, early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes in most urinary tract conditions.
Treatment Options for Blood in Urine
Understanding the treatment options available is crucial for addressing this symptom effectively. The treatment largely depends on the underlying cause, and it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
1. Antibiotics for Infections
If an infection, such as a urinary tract infection (UTI), is causing blood in your urine, antibiotics are the typical treatment. They effectively eliminate the bacteria causing the infection, resolving the symptoms, including hematuria.
2. Medication Adjustments
Sometimes, certain medications can lead to hematuria. If your doctor suspects this, they might adjust your medication regimen or suggest alternative treatments that don’t have this side effect.
3. Surgical Interventions
In cases where blood in urine is due to kidney stones or tumors, surgical procedures may be necessary. Minimally invasive techniques are often used to remove kidney stones, while tumors might require more complex surgeries.
4. Lifestyle and Dietary Changes
For some individuals, making lifestyle and dietary changes can help. Increasing water intake, reducing salt, and avoiding certain foods may be recommended to alleviate symptoms.
5. Monitoring and Follow-Up
In situations where the cause is not immediately apparent, or if it’s a minor issue, your doctor might suggest a wait-and-see approach. Regular monitoring and follow-up tests can ensure that the condition doesn’t worsen.
6. Specialized Treatments for Underlying Conditions
For hematuria caused by chronic conditions like cancer or kidney disease, specialized treatments targeting these illnesses are necessary. These might include chemotherapy, radiation, or specific medications for kidney disease.
Blood in urine should not be ignored. Seeking medical advice is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment. Remember, the effectiveness of the treatment depends on the underlying cause, making professional guidance crucial.
Lifestyle and Prevention Tips for Hematuria
While it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment, there are lifestyle changes and prevention tips that can help reduce the risk or severity of this condition.
Healthy Hydration Habits
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of fluids, especially water, helps dilute your urine and ensures regular bladder emptying. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily.
- Cranberry Juice: Some studies suggest cranberry juice can help prevent urinary tract infections (UTIs), a common cause of hematuria.
Diet and Nutrition
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can support overall kidney and urinary health.
- Limit Salt and Protein: Excessive salt and protein intake can stress your kidneys, potentially leading to problems like hematuria.
Physical Activity
- Regular Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise can reduce the risk of kidney stones, another cause of hematuria.
- Avoid High Impact Sports: If prone to urinary bleeding, opt for low-impact exercises to reduce the risk of injury.
Healthy Habits
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a risk factor for bladder cancer, which can cause hematuria. Quitting smoking reduces this risk significantly.
- Limit Alcohol and Caffeine: Excessive alcohol and caffeine can irritate the bladder and potentially lead to hematuria.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
- Routine Screenings: Regular health screenings can help detect issues like UTIs or kidney stones early, preventing the progression to hematuria.
- Medication Review: Some medications can cause or worsen hematuria. Regularly review your medications with your healthcare provider.
While not all cases of hematuria can be prevented, adopting these lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
When to See a Doctor for Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Experiencing blood in your urine, medically known as hematuria, can be alarming. Understanding when to seek medical attention is crucial for your health. This article provides guidance on recognizing serious symptoms associated with hematuria and encourages timely medical consultation.
Recognizing Serious Symptoms
Immediate medical attention is required if you experience any of the following symptoms along with blood in your urine:
- Severe pain in the back, side, or lower abdomen
- Difficulty urinating or a burning sensation during urination
- Urine that is red, pink, or cola-colored
- Fever, nausea, or vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss or fatigue
- Swelling in the legs or fluid retention
These symptoms can indicate underlying health problems like kidney stones, infections, or more serious conditions such as cancer.
The Importance of Timely Medical Consultation
Delaying a doctor’s visit can lead to the progression of potentially serious conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing health issues effectively. It’s better to err on the side of caution and get a professional evaluation if you notice blood in your urine.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Visit
When you decide to see a doctor, prepare to provide details about your symptoms, medical history, and any medications you’re taking. This information helps the doctor make an accurate diagnosis and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Blood in urine should not be ignored. If you experience hematuria with any concerning symptoms, seek medical attention promptly. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in your health outcome.
FAQs Section: Blood in Urine and Its Treatment
1. What Causes Blood in Urine?
Answer: Blood in urine, medically known as hematuria, can be caused by various conditions ranging from benign (such as urinary tract infections or kidney stones) to more serious issues (like kidney disease or bladder cancer). It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
2. Is Blood in Urine Always a Sign of a Serious Condition?
Answer: Not always. While it can be alarming, blood in urine isn’t always indicative of a serious medical condition. However, it’s important to get it checked by a doctor to rule out any serious health issues.
3. How is Blood in Urine Diagnosed?
Answer: Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, urine tests, and sometimes imaging tests like CT scans or ultrasounds. In some cases, a cystoscopy may be required to examine the bladder and urethra.
4. What Are the Treatment Options for Blood in Urine?
Answer: Treatment depends on the underlying cause. It may range from antibiotics for infections to more complex treatments for kidney stones or cancer. Always follow your healthcare provider’s advice.
5. Can Diet or Lifestyle Changes Help with Blood in Urine?
Answer: While lifestyle changes cannot cure underlying medical conditions, maintaining a healthy diet, staying hydrated, and avoiding irritants like tobacco and certain medications might help manage symptoms.
6. When Should I See a Doctor for Blood in Urine?
Answer: You should consult a doctor if you notice blood in your urine, experience pain while urinating, or have persistent urinary symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best outcomes.
7. Can Blood in Urine be Prevented?
Answer: While not all causes of blood in urine can be prevented, you can reduce risk factors by staying hydrated, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and managing underlying health conditions like hypertension or diabetes.
8. Are There Any Risk Factors for Blood in Urine?
Answer: Yes, risk factors include age, a history of kidney stones, certain medications, and chronic conditions like diabetes or hypertension. Smoking is also a significant risk factor.
9. Is There a Difference Between Visible and Invisible Blood in Urine?
Answer: Yes. Visible blood in urine is known as gross hematuria, while blood that can only be detected under a microscope is called microscopic hematuria. Both types require medical evaluation.
10. Can Exercise Cause Blood in Urine?
Answer: Strenuous exercise can sometimes lead to blood in urine, likely due to bladder trauma or dehydration. However, it’s important to rule out other causes with your doctor.
Conclusion
We encourage individuals to adopt a proactive approach to their health management. This involves regularly consulting healthcare professionals for check-ups and not delaying medical advice when symptoms such as blood in urine are observed. Proactive health management can significantly improve the chances of early detection and successful treatment of potential underlying health issues.
Being informed about the potential causes and implications of blood in urine is the first step in taking control of one’s health. Remember, your health is in your hands, and timely medical intervention can make a substantial difference. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and never hesitate to seek professional medical advice for a healthier future.