Blocked Tear Duct Symptoms: Tear ducts play a crucial role in maintaining the health and comfort of our eyes. However, when these ducts become blocked, a condition known as a blocked tear duct, or dacryostenosis, can occur.
This article delves into the symptoms and causes of blocked tear ducts, providing comprehensive insight into this common yet often misunderstood eye condition.
What is a Blocked Tear Duct?
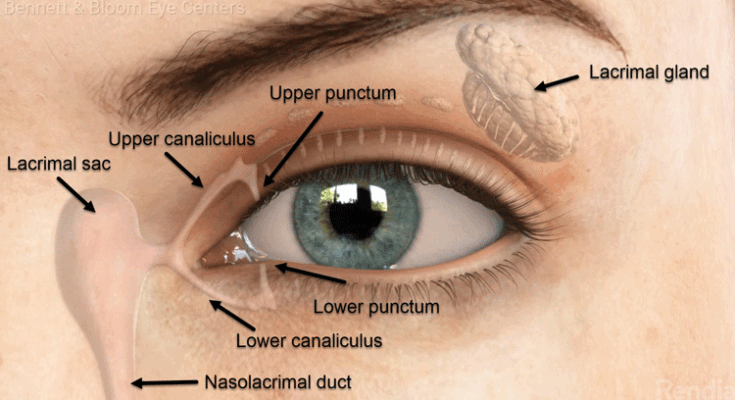
Tear ducts are essential components of our eye health system, playing a pivotal role in maintaining the well-being of our eyes. These small tubes, medically known as nasolacrimal ducts, are responsible for draining tears from the eyes into the nasal cavity. This process is crucial for keeping the eyes lubricated, clear of debris, and free from infection.
In normal conditions, tear ducts work seamlessly in the background. Tears, produced by the lacrimal glands, wash across the surface of the eye with each blink. These tears collect dust, debris, and microorganisms, which are then funneled into the tear ducts located at the corners of the eyelids. From there, the tears flow through a network of small canals, ultimately draining into the nasal cavity. This continuous cycle not only keeps our eyes comfortable but also plays a vital role in protecting them from environmental irritants and pathogens.
A blocked tear duct, however, interrupts this natural process. When a blockage occurs, it prevents tears from draining effectively, leading to a range of symptoms including watery eyes, irritation, and even increased risk of eye infections. Understanding the importance of tear ducts in eye health highlights the significance of addressing any issues like blockages promptly and effectively.
By ensuring the proper functioning of our tear ducts, we not only maintain clear and comfortable vision but also support the overall health of our eyes.
Blocked Tear Duct Symptoms: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to identifying blocked tear ducts, recognizing the symptoms is crucial. Blocked tear ducts, medically known as dacryostenosis, can occur in people of all ages and, if left untreated, may lead to discomfort and more serious eye conditions. Below is a detailed list of common symptoms associated with blocked tear ducts:
- Persistent Tearing: One of the most noticeable signs of a blocked tear duct is excessive tearing. This occurs because the tears cannot drain normally, causing a buildup that overflows.
- Recurrent Eye Infections: Blocked tear ducts can lead to frequent eye infections, such as conjunctivitis, as the stagnant fluid becomes a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Blurred Vision: Accumulated tears can cause temporary blurring of vision, impacting daily activities.
- Eye Redness and Swelling: The affected eye may appear red, swollen, or irritated, often a response to the trapped fluid and potential infection.
- Discharge from the Eye: A clear, white, or yellowish discharge from the eye is common, especially upon waking up.
- Crusting Around the Eyes: The continual overflow of tears can lead to crusting around the eyelids and eyelashes, particularly noticeable after sleep.
- Difficulty with Tear Flow in Cold or Windy Conditions: People with blocked tear ducts often report a marked increase in tear flow in windy or cold environments.
- Pain and Tenderness around the Eye: There can be discomfort or tenderness in the area around the eye and nasal bridge.
- Mucus or Pus in the Tear Film: The presence of mucus or pus in the tears is a sign of infection and is often associated with blocked tear ducts.
- Swelling at the Corner of the Eye: In some cases, a noticeable swelling may appear near the nose, where the tear ducts are located.
Recognizing these symptoms early and consulting an eye care professional is vital for effective treatment and prevention of complications. Regular eye exams, maintaining eye hygiene, and addressing any eye discomfort promptly can help in managing and preventing blocked tear ducts.
Common Causes of Blocked Tear Ducts: An Insightful Guide
When it comes to understanding blocked tear ducts, it’s essential to recognize that this condition can stem from various causes, differing notably between adults and children. This comprehensive guide delves into these causes, offering a clear, reader-friendly breakdown.
Causes in Adults
- Aging: As we age, the tear ducts can narrow, leading to blockages.
- Infections or Inflammation: Conditions like conjunctivitis or sinusitis can cause blockages.
- Injury or Trauma: Facial injuries can damage tear ducts.
- Tumors: Both benign and malignant growths in the nasal or eye area can obstruct tear ducts.
- Medical Procedures: Certain surgeries or radiation treatments can contribute to blockage.
Causes in Children
- Congenital Blockage: Many infants are born with underdeveloped tear ducts, leading to blockages.
- Infections: Newborns are susceptible to infections that can cause duct blockages.
- Nasal Bone Abnormalities: Any irregularity in the nasal bone structure can affect the tear ducts.
- Trauma at Birth: Physical stress during birth can result in blocked tear ducts.
Understanding these causes is vital for effective diagnosis and treatment. For adults, lifestyle factors and health history play a significant role, whereas in children, developmental aspects are more prevalent. Stay informed and consult a healthcare professional if you suspect a blocked tear duct.
Risk Factors and Complications of Blocked Tear Ducts
Understanding the Risk Factors
Blocked tear ducts, a common condition affecting individuals of all ages, can lead to discomfort and, in some cases, more serious eye issues. Several factors increase the likelihood of developing this condition:
- Age-Related Changes: As people age, the tear ducts may narrow, leading to blockages.
- Infants’ Nasolacrimal Duct Development: Newborns often have underdeveloped nasolacrimal ducts, making them more susceptible to blockages.
- Infections and Inflammation: Chronic eye infections or inflammation can lead to scarring and blockage of the tear ducts.
- Trauma or Injury: Any injury or trauma near the eyes can cause tear duct damage.
- Nasal Problems: Issues like chronic sinusitis or nasal polyps can exert pressure on the tear ducts.
- Systemic Health Conditions: Certain systemic diseases, such as Sjogren’s syndrome or rheumatoid arthritis, can affect tear ducts.
- Use of Certain Medications: Some medications, particularly those used in chemotherapy, can contribute to blocked tear ducts.
Potential Complications if Left Untreated
Neglecting blocked tear ducts can lead to a range of complications, making early intervention crucial:
- Chronic Infections: The stagnation of tears can create a breeding ground for bacteria, leading to recurring eye infections.
- Conjunctivitis: Persistent blockage often results in inflammation of the eye surface, known as conjunctivitis.
- Dacryocystitis: This painful infection of the tear sac can occur if blockages are not addressed.
- Damage to the Cornea: Chronic tear overflow and exposure can lead to corneal damage, affecting vision.
- Quality of Life Impact: Constant tearing and discomfort can significantly impair daily activities and overall quality of life.
Early detection and addressing risk factors can greatly reduce the likelihood of developing blocked tear ducts and the associated complications. Regular eye examinations and consulting with a healthcare provider when symptoms arise are essential steps in maintaining eye health.
Diagnosing Blocked Tear Ducts
The process of diagnosing a blocked tear duct is comprehensive, designed to accurately identify the cause and severity of the blockage.
Initially, healthcare professionals start with a thorough review of the patient’s medical history. This step is crucial to understand any underlying health conditions or previous surgeries that might contribute to tear duct blockages. Following this, a physical examination of the eyes and surrounding areas is conducted. This examination is pivotal to observe any apparent signs of blockage or infection.
Types of Tests and Examinations Used by Healthcare Professionals
The diagnosis of blocked tear ducts involves a variety of tests and examinations, each serving a specific purpose:
- Tear Drainage Test: This simple test evaluates the drainage efficiency of the tear ducts. A special dye is placed in the eyes, and the specialist observes how quickly it disappears from the surface of the eye, which helps to determine if there’s a blockage.
- Eye Imaging Tests: Techniques like CT scans or MRI might be employed to get a detailed view of the tear duct system. These imaging tests are beneficial in identifying the exact location and extent of the blockage.
- Dacryocystography: In this specialized test, a contrast dye is injected into the tear ducts, and X-rays are taken. These images provide a clear view of the tear ducts, highlighting any blockages or abnormalities.
- Nasal Endoscopy: Since the tear ducts are connected to the nasal cavity, an endoscopy can be performed to examine this area. It involves using a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera to look inside the nose and tear duct openings.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a biopsy may be required if there’s a suspicion of a more serious underlying condition causing the blockage.
Healthcare providers may choose one or more of these tests based on the individual’s symptoms and medical history. Early and accurate diagnosis is key to effective treatment, preventing complications, and improving overall eye health.
Treatment Options for Blocked Tear Ducts
Understanding the various treatment options available is crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Home Remedies
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses gently to the affected eye can help relieve blockage. This method helps to loosen any debris and facilitate tear drainage.
- Massage: Gently massaging the lacrimal sac (the area where tears collect) can also aid in unclogging tear ducts. This should be done with clean hands and gentle pressure.
- Eye Hygiene: Maintaining good eye hygiene is essential. Regularly cleaning your eyelids with mild soap or prescribed solutions can prevent further blockages.
Medical Procedures
- Dilation and Irrigation: This procedure involves dilating the tear duct opening and flushing it with a saline solution to clear the blockage.
- Balloon Catheter Dilation: In this method, a tiny balloon is inserted into the tear duct and then inflated to widen the duct and facilitate tear flow.
- Stenting or Intubation: Here, a thin tube or stent is placed in the duct to keep it open and ensure proper drainage of tears.
- Surgery: In severe cases, dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) surgery may be required. This procedure creates a new route for tears to drain from the eye to the nose.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional if:
- Symptoms persist despite home remedies
- There is noticeable swelling or redness around the eye
- Recurrent eye infections occur
- The condition affects vision
Early intervention can prevent complications and ensure optimal eye health.
Blocked tear ducts, while often treatable with home remedies, may require medical intervention in persistent or severe cases. Consulting with an eye specialist is recommended to determine the best course of treatment tailored to individual needs.
Prevention Tips for Blocked Tear Ducts
Dealing with blocked tear ducts can be uncomfortable and inconvenient. While not all causes of blocked tear ducts can be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk. Here are some essential prevention tips to keep in mind:
1. Maintain Good Eye Hygiene
Regular Cleaning: Gently clean the eyelids with a clean, warm cloth, especially before sleep.
Avoid Eye Irritants: Minimize exposure to irritants like smoke, dust, and strong chemicals.
2. Use Eye Protection
Safety Eyewear: Wear protective glasses or goggles when exposed to potential irritants or during activities that might risk eye injury.
Sunglasses: Use UV-protective sunglasses to shield your eyes from sun damage.
3. Be Mindful of Makeup Use
Quality Products: Use hypoallergenic makeup to reduce the risk of allergic reactions.
Regular Removal: Ensure you remove eye makeup thoroughly every day.
4. Stay Hydrated
Adequate Water Intake: Keeping your body well-hydrated helps maintain healthy tear production.
5. Manage Allergies
Allergy Control: Use allergy medications as prescribed and try to avoid known allergens.
6. Follow Contact Lens Hygiene
Proper Cleaning: Clean and replace your contact lenses as recommended by your eye care professional.
7. Seek Regular Eye Check-Ups
Professional Advice: Regular visits to an eye care professional can help identify and manage potential problems early.
8. Practice Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall eye health.
Avoid Smoking: Smoking can contribute to eye issues, including blocked tear ducts.
9. Address Nasal Issues
Nasal Care: Treat nasal congestion or sinus problems promptly, as these can impact tear ducts.
10. Be Aware of Medications
Consult Your Doctor: Some medications can affect tear production, so consult with your healthcare provider about potential side effects.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can help prevent the occurrence or recurrence of blocked tear ducts. Remember, consistent care and attention to eye health play a crucial role in preventing this uncomfortable condition.
Frequently Asked Questions About Blocked Tear Ducts
What are the common symptoms of a blocked tear duct?
Answer: Common symptoms include watery eyes, discharge, redness, and swelling near the eye. You might also notice crusting around the eyelids and lashes, especially after sleep.
Can a blocked tear duct cause vision problems?
Answer: While a blocked tear duct typically does not directly affect vision, the excessive tearing and discharge can cause temporary blurriness. It’s important to consult an eye care professional if you experience any changes in vision.
What are the primary causes of blocked tear ducts?
Answer: Blocked tear ducts can be caused by infections, injuries, or structural problems with the tear duct system. In adults, chronic infections and inflammation are common causes, while in newborns, tear ducts that are not fully open at birth can lead to blockages.
Are infants more prone to blocked tear ducts?
Answer: Yes, infants are more prone as their tear ducts may not be fully developed at birth. Most cases in infants improve on their own within the first year of life.
Is there a connection between allergies and blocked tear ducts?
Answer: Allergies can contribute to tear duct blockages by causing inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and surrounding tissues, which can affect the tear drainage system.
How can I differentiate between a blocked tear duct and an eye infection?
Answer: A blocked tear duct usually causes consistent tearing and discharge without pain or severe redness. In contrast, eye infections often involve pain, intense redness, and might affect vision. Consult an eye doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
Can blocked tear ducts resolve on their own?
Answer: Yes, especially in infants, blocked tear ducts often resolve without treatment. In adults, the condition might require medical intervention depending on the underlying cause.
When should I see a doctor for a blocked tear duct?
Answer: If symptoms persist, worsen, or if you experience pain, redness, and changes in vision, it’s important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
In wrapping up our discussion on blocked tear ducts, it’s essential to reiterate the key points. A blocked tear duct is a condition that can affect individuals of any age, characterized by a blockage in the system that drains tears from the surface of the eye into the nose. This blockage leads to symptoms such as watery eyes, recurrent eye infections, and even blurred vision.
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider. While information online, including this article, can be informative and helpful, it doesn’t replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Healthcare professionals can offer personalized advice and treatment options based on your specific condition and medical history.
Remember, addressing symptoms early can prevent complications and ensure better outcomes. So, if you suspect you might have a blocked tear duct or any other eye-related issues, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider. Taking this step is pivotal in safeguarding your eye health and overall well-being.