Bladder Exstrophy Treatment: Bladder exstrophy is a rare and complex urological condition characterized by the malformation of the bladder and surrounding structures.
This congenital anomaly presents significant challenges for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
Understanding the nuances of its diagnosis and treatment is crucial for effective management and improved quality of life for those affected.
What is Bladder Exstrophy?
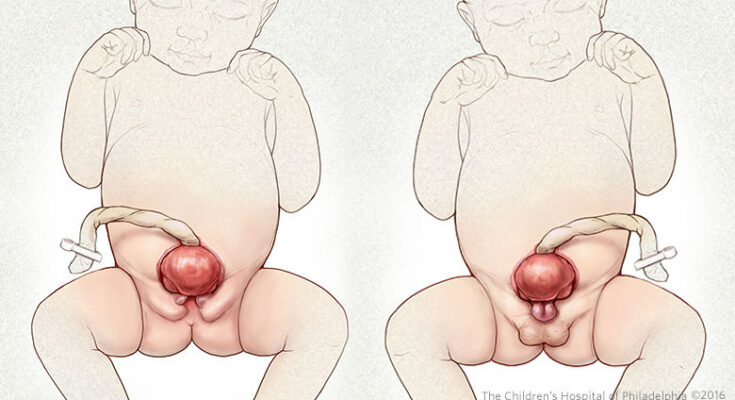
Bladder exstrophy is a rare and complex congenital condition where the bladder and associated structures are developed outside the body. This medical anomaly, present at birth, involves an exposed bladder, an abdominal wall defect, and often abnormalities in the genitalia and urinary system. Understanding bladder exstrophy is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Statistical Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Bladder exstrophy is an uncommon condition, with an estimated occurrence of approximately 1 in 40,000 births. It affects both genders, although it is slightly more prevalent in males. This condition has a worldwide presence, with no specific demographic or geographic population showing a higher incidence rate. Knowing these statistics aids in heightening awareness and improving diagnostic processes across diverse populations.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of bladder exstrophy remains unknown; however, it’s believed to be a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors during fetal development. Key risk factors include:
- Family History: A family history of bladder exstrophy or related disorders can increase the likelihood of this condition.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic mutations or abnormalities may contribute to the development of bladder exstrophy.
- Environmental Influences: While not definitively proven, some researchers suggest that environmental factors during pregnancy, such as medication use or exposure to certain chemicals, might play a role.
Understanding these causes and risk factors is pivotal for expectant parents and healthcare professionals in managing and preventing this complex condition. Regular prenatal screening and genetic counseling are recommended for those at higher risk.
Symptoms and Early Signs of Bladder exstrophy
The most noticeable symptom of bladder exstrophy is the physical appearance of the bladder, which is turned inside out and protrudes from the abdomen. Other symptoms include:
- Visible Bladder Tissue: The bladder is exposed on the lower abdomen, often appearing as a reddish mass.
- Epispadias: In males, the urethra usually opens on the top of the penis rather than at the tip. In females, the urethral opening may be enlarged and positioned between the clitoris and the labia.
- Inguinal Hernias: Hernias in the groin area are common due to the weakness in the abdominal wall.
- Pelvic Bone Abnormalities: There may be a separation of the pubic bones, affecting posture and gait.
- Urinary Incontinence: Due to the bladder’s exposure and lack of control, urine leakage is a common issue.
The Significance of Early Detection
Early detection of bladder exstrophy is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing Complications: Early treatment can prevent complications like infections and kidney damage.
- Improved Outcomes: Surgical procedures have better outcomes when performed at a younger age.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Addressing the condition early can significantly improve the quality of life and social integration for the affected individual.
Challenges in Diagnosing Bladder Exstrophy
Diagnosing bladder exstrophy in its early stages can be challenging due to:
- Rare Occurrence: Being a rare condition, it may not be the first diagnosis considered by healthcare professionals.
- Lack of Awareness: There may be a lack of awareness and knowledge about the condition, even among medical staff.
- Prenatal Diagnosis Difficulties: Although it can be detected through prenatal ultrasounds, the signs may be subtle and easily missed.
However, recognizing the symptoms and early signs of bladder exstrophy is crucial for timely and effective treatment. Early detection plays a significant role in improving the life quality of individuals with this condition. However, challenges in early diagnosis due to its rarity and subtlety of symptoms necessitate increased awareness and knowledge among both healthcare professionals and expectant parents.
Diagnosis of Bladder Exstrophy: Essential Methods and Collaborative Approaches
Comprehensive Diagnostic Methods and Tests
Bladder Exstrophy, a complex medical condition, demands thorough diagnostic methods. The diagnosis typically involves a range of tests. These include:
- Imaging Tests: Advanced imaging techniques like ultrasound, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and CT (Computed Tomography) scans play a pivotal role. They provide detailed images of the bladder and surrounding structures, aiding in accurate diagnosis.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional is crucial. This includes checking for any visible abnormalities in the bladder or genital area.
- Laboratory Tests: Urine tests and blood work can be necessary to evaluate kidney function and overall health, which might be impacted by bladder exstrophy.
Prenatal Imaging and Post-Birth Assessment
The role of Prenatal Imaging cannot be overstated in diagnosing bladder exstrophy:
- Ultrasound: Regular ultrasounds during pregnancy can detect bladder exstrophy. It helps in preparing for immediate care after birth.
- Fetal MRI: In some cases, a fetal MRI might be recommended for a more detailed view.
Post-birth, the assessment includes:
- Immediate Physical Examination: Newborns are thoroughly examined for any signs of bladder exstrophy.
- Follow-up Imaging: Postnatal imaging tests confirm the prenatal findings and help in planning the treatment.
Collaborative Approach in Diagnosis
Diagnosing bladder exstrophy often involves a multidisciplinary team:
- Pediatric Urologists: Specialists in children’s urinary issues lead the diagnostic process.
- Radiologists: Experts in imaging tests provide critical insights through their analyses.
- Neonatologists: These newborn care specialists are essential, especially for post-birth assessments.
- Genetic Counselors: They offer support if there’s a genetic aspect to the condition.
- Pediatric Nephrologists: These kidney specialists monitor and manage any related kidney issues.
However, the diagnosis of bladder exstrophy is a multifaceted process involving various diagnostic methods and a collaborative approach across specialties. Early detection and comprehensive assessment are key to effective management and treatment of this condition.
Treatment Options for Bladder Exstrophy
Bladder exstrophy treatment primarily focuses on restoring the bladder’s functionality and appearance while ensuring the patient’s quality of life. Since this condition affects not just the urinary system but also the reproductive organs and the musculoskeletal system, a comprehensive treatment plan is essential. The approach typically involves a multidisciplinary team, including urologists, surgeons, and supportive care specialists.
Surgical Interventions: Types, Timing, and Outcomes
Surgery is a cornerstone in treating bladder exstrophy. The primary goals are to reconstruct the bladder, provide urinary continence, and achieve cosmetically acceptable genitalia.
- Initial Closure Surgery: Often performed shortly after birth, this surgery aims to close the bladder and abdominal wall.
- Bladder Neck Reconstruction: This is essential for achieving urinary continence and is typically performed around the age of 4-5 years.
- Genital Reconstruction: Depending on the extent of the condition, genital reconstruction may be necessary, either during the initial surgery or as a separate procedure.
- Orthopedic Surgery: In cases where exstrophy affects the bony pelvis, orthopedic interventions might be required.
The timing of these surgeries depends on various factors, including the child’s health and the severity of the condition. Surgical outcomes have improved significantly, with many patients achieving good urinary control and a normal appearance.
Non-Surgical Management and Supportive Therapies
Non-surgical options play a crucial role in managing bladder exstrophy, especially in enhancing the quality of life and aiding in recovery post-surgery.
- Bladder Management: This includes catheterization and medication to manage urinary continence.
- Physical Therapy: Essential for strengthening the pelvic floor muscles and improving mobility, especially after orthopedic surgeries.
- Psychological Support: Dealing with a chronic condition can be challenging, making psychological support vital for both patients and families.
- Nutritional Guidance: Proper nutrition aids in recovery and overall health, especially important for those undergoing multiple surgeries.
However, treating bladder exstrophy requires a personalized, multidisciplinary approach. Surgical interventions are crucial but must be complemented with supportive non-surgical therapies for optimal outcomes. With advancements in medical science, individuals with bladder exstrophy can look forward to a better quality of life and improved health.
Reconstructive Surgery: Bladder Exstrophy Treatment
Let’s delves into the various types of reconstructive surgeries available, the crucial steps for preoperative preparation and postoperative care, and an analysis of success rates and potential complications associated with these procedures.
Types of Reconstructive Surgeries
- Primary Repair of Bladder Exstrophy (CPRE): Often performed in newborns, CPRE aims to restore the normal anatomy and function of the bladder and genitals.
- Osteotomy: Sometimes required in severe cases, osteotomy involves cutting and realigning pelvic bones to support the reconstructed bladder.
- Bladder Neck Reconstruction: Essential for achieving continence, this surgery tightens the bladder neck and urethra.
- Genital Reconstruction: Addresses genital abnormalities often associated with bladder exstrophy.
- Secondary Procedures: These may include bladder augmentation or urinary diversion, typically performed in older children or adults when initial surgeries haven’t fully corrected the condition.
Preoperative Preparation and Postoperative Care
Preoperative Preparation:
- Comprehensive Evaluation: Involves thorough medical and surgical assessments, including imaging studies.
- Counseling: Patients and families receive detailed information about the surgery, expected outcomes, and potential risks.
Postoperative Care:
- Pain Management: Crucial in the immediate postoperative period.
- Wound Care: Regular monitoring and care of the surgical site to prevent infections.
- Bladder Training: Involves exercises and strategies to improve bladder function.
- Long-term Follow-up: Regular check-ups to monitor bladder function and growth, and to address any complications.
Success Rates and Potential Complications
Success Rates:
- High Success in Continence: Many patients achieve urinary continence post-surgery.
- Improved Quality of Life: Successful surgeries significantly improve the patient’s social and psychological well-being.
Potential Complications:
- Infections: Can occur at the surgical site or in the urinary tract.
- Bladder Stones: Patients are at risk of developing stones in the bladder.
- Continence Issues: Some may require additional surgeries for complete continence.
- Orthopedic Problems: Due to the involvement of pelvic bones in the surgery.
Understanding the complexities of reconstructive surgery for bladder exstrophy is vital. It not only involves intricate surgical techniques but also requires comprehensive care before and after the surgery. The success of these surgeries can profoundly impact the patient’s quality of life, making awareness and expertise in this field crucial.
Long-Term Management and Follow-Up for Bladder Exstrophy
Emphasizing the Need for Ongoing Care and Monitoring
Bladder exstrophy is a complex medical condition requiring consistent, long-term management. It’s crucial to emphasize the importance of ongoing care and monitoring in patients with bladder exstrophy. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals are vital for monitoring the condition’s progress and identifying any changes that might require adjustments in treatment. Patients should be encouraged to maintain a close relationship with their medical team, ensuring that any health concerns are addressed promptly and efficiently.
Navigating Complications and Secondary Conditions
Patients with bladder exstrophy often face various complications and secondary conditions. It’s essential to provide comprehensive information on managing these challenges effectively. This includes understanding the common complications associated with bladder exstrophy, such as urinary incontinence, kidney problems, and challenges with sexual function. Providing guidance on how to manage these complications, either through medical intervention or lifestyle adjustments, can significantly enhance the quality of life for these patients.
Addressing Psychosocial Aspects and Support Systems
The impact of bladder exstrophy isn’t limited to physical health; it also encompasses psychosocial aspects. Patients and their families may face emotional and social challenges. Articles on this topic should offer insights into the importance of mental health support, including counseling, support groups, and community resources. Highlighting the role of family, friends, and support networks in providing emotional and practical support is also essential. By addressing these psychosocial aspects, patients and their families can navigate the complexities of bladder exstrophy with greater resilience and confidence.
Recent Advances and Future Directions in Treatment for Bladder Exstrophy
Summary of Recent Research and Advancements
Recent years have witnessed significant progress in the treatment of bladder exstrophy, a complex congenital anomaly affecting the bladder and surrounding regions. Cutting-edge research has introduced innovative surgical techniques, enhancing the efficacy and safety of treatments. Pioneering studies have focused on refining reconstructive surgeries, minimizing complications, and improving the quality of life for patients.
One notable advancement is the integration of robotic-assisted surgery. This approach offers greater precision and has been instrumental in reducing recovery times and post-operative complications. Additionally, advancements in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine are opening new frontiers. Researchers are exploring the potential of bioengineered tissues and organs, which could revolutionize the way bladder exstrophy is treated.
Emerging Treatments and Technologies
Emerging treatments and technologies are shaping the future of bladder exstrophy management. One exciting area is the use of stem cell therapy. This innovative approach involves using stem cells to regenerate or repair the bladder tissue, offering a less invasive alternative to traditional surgeries. Clinical trials are currently underway to evaluate the efficacy and safety of these treatments.
Another promising development is the application of personalized medicine. By leveraging genetic and molecular profiling, treatments can be tailored to the individual needs of each patient, enhancing the effectiveness of the therapy. This personalized approach not only improves outcomes but also reduces the risk of complications.
Future Prospects in the Management of Bladder Exstrophy
Looking to the future, the management of bladder exstrophy is poised for transformative changes. Advances in genomic medicine and biotechnology are expected to lead to more targeted and less invasive treatment options. Researchers are also focusing on early detection and intervention strategies, which are crucial in improving long-term outcomes.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in diagnostic and treatment processes is another area of potential. AI-driven models could enhance the accuracy of diagnoses, optimize treatment planning, and predict patient outcomes more effectively. As these technologies evolve, they promise to bring a new level of precision and personalization to the treatment of bladder exstrophy.
However, the field of bladder exstrophy treatment is advancing rapidly, with research and technology paving the way for more effective, personalized, and less invasive treatments. These developments hold great promise for improving the lives of those affected by this challenging condition.
Conclusion
As we look towards the future, the impetus for ongoing research and improved care cannot be overstated. Every new discovery, every advancement in treatment, brings us closer to a world where bladder exstrophy is not a daunting prognosis but a manageable condition. This journey of medical exploration and innovation is fuelled by hope – hope for better treatments, hope for less invasive procedures, and ultimately, hope for a life unencumbered by the limitations of this condition.
In conclusion, our discourse on bladder exstrophy is more than an academic discussion; it’s a clarion call for heightened awareness, early intervention, and relentless pursuit of medical excellence. Let us collectively stride forward, armed with knowledge and compassion, towards a future where bladder exstrophy is but a small detour in the journey of life.