Bladder Cancer Treatment: Bladder cancer is a significant health concern affecting numerous individuals worldwide.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of bladder cancer, encompassing its diagnosis, treatment options, and the latest advancements in the field.
What is Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is a medical condition characterized by the growth of malignant cells in the bladder, the organ responsible for storing urine. This type of cancer can develop in the bladder’s lining and may spread to other areas. Recognizing its symptoms, understanding the risk factors, and knowing the types of bladder cancer are crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Statistics: Incidence Rates and Risk Factors
Bladder cancer is among the most common cancers worldwide. The incidence rates vary based on factors like age, gender, and geographical location. It’s more prevalent in older adults, particularly those over 55, and men are at a higher risk compared to women.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of bladder cancer. These include:
- Smoking: The most significant risk factor, as smokers are at a higher risk than non-smokers.
- Occupational Exposure: Certain jobs that involve exposure to chemicals, particularly in the dye, rubber, and leather industries, increase the risk.
- Family History and Genetics: A family history of bladder cancer can elevate an individual’s risk.
- Chronic Bladder Inflammation: Long-term bladder infections or irritations can lead to cell changes in the bladder.
- Previous Cancer Treatments: Certain treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can increase the risk of developing bladder cancer.
Understanding these risk factors helps in taking preventive measures and in early detection, which is crucial for effective treatment.
Types of Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer is classified into several types, primarily based on the cells where the cancer begins. The main types include:
- Urothelial Carcinoma (Transitional Cell Carcinoma): The most common type of bladder cancer, originating in the urothelial cells lining the bladder.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Associated with chronic irritation and inflammation, this type arises from squamous cells.
- Adenocarcinoma: Originating from glandular cells, this type is rarer and more aggressive.
Each type of bladder cancer has distinct characteristics and may require different treatment approaches. Early diagnosis and personalized treatment are key factors in managing bladder cancer effectively.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Bladder Cancer
Identifying these signs early can be crucial for effective treatment. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Blood in Urine: This is often the first and most noticeable sign. The presence of blood, either visible or microscopic, can be a key indicator.
- Frequent Urination: An increase in the frequency of urination, often accompanied by a sense of urgency, even when the bladder is not full.
- Painful Urination: Experiencing pain or burning sensations during urination can be a warning sign.
- Back Pain: Lower back pain, particularly on one side, may be associated with advanced bladder cancer.
- Pelvic Pain: Persistent or intermittent pain in the pelvic area is also a symptom to be aware of.
The Importance of Recognizing Early Signs
Early detection of bladder cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment and recovery. Recognizing the early signs and seeking medical advice promptly is vital for the following reasons:
- Better Treatment Outcomes: Early-stage bladder cancer is generally more treatable and has a higher survival rate.
- Prevention of Spread: Detecting cancer before it spreads to other parts of the body is crucial in managing the disease effectively.
- More Treatment Options: Early detection often means a wider range of treatment options is available, potentially including less invasive methods.
- Reduced Complications: Addressing bladder cancer in its early stages can prevent complications that arise from advanced cancer.
Key Takeaways
Being aware of the common symptoms of bladder cancer and the importance of early detection cannot be overstated. Regular check-ups and consulting a healthcare professional if any of these symptoms are observed is essential. Early detection not only increases the effectiveness of treatment but also contributes to a better quality of life post-treatment.
Diagnosing Bladder Cancer
Let’s delves into the most effective diagnostic procedures and explains the significance of staging in treatment planning.
Diagnostic Procedures for Bladder Cancer
- Cystoscopy: A key diagnostic tool, cystoscopy involves inserting a thin tube with a camera (cystoscope) into the bladder through the urethra. This allows doctors to visually inspect the bladder for tumors or abnormal areas.
- Urine Cytology: This test examines urine samples under a microscope to detect cancer cells. It’s a non-invasive method often used alongside other diagnostic tests.
- Imaging Tests: Various imaging modalities like Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI are employed to visualize the bladder. These tests help in identifying tumors and assessing if cancer has spread beyond the bladder.
- Biopsy (Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor – TURBT): This procedure involves removing a tissue sample from the bladder tumor. The sample is then analyzed to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
- Urine Tests for Tumor Markers: These tests detect specific substances released by bladder cancer cells in urine. They provide additional information to support diagnosis.
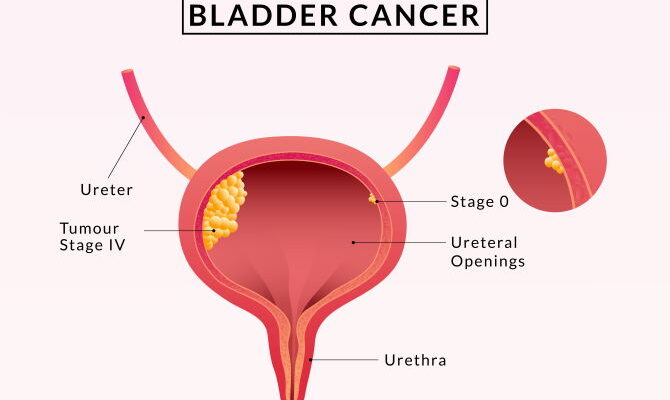
Staging of Bladder Cancer
Staging is crucial in determining the extent of bladder cancer and guides treatment planning. It involves assessing the size of the tumor, its invasion into bladder walls, and spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. Stages range from Stage 0 (non-invasive, confined to bladder lining) to Stage IV (advanced cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body).
- Stage 0: Early stage, where cancer is on the bladder’s inner lining. Treatment often involves surgery and intravesical therapy.
- Stage I: Cancer has invaded the connective tissue of the bladder but not the muscle. Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
- Stage II and III: Cancer has spread to the muscle layer or fat surrounding the bladder. Treatment typically involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
- Stage IV: Advanced stage where cancer has spread to distant organs. Treatment focuses on systemic therapies and palliative care.
Understanding the stage of bladder cancer is vital for selecting the most appropriate treatment approach. Early detection and precise staging significantly improve the prognosis and management of bladder cancer.
Treatment Options for Bladder Cancer
Understanding the available treatment options is crucial for patients and caregivers. This comprehensive guide outlines the various treatments available, ensuring informed decision-making.
Surgical Treatments for Bladder Cancer
Surgery is a cornerstone in bladder cancer management. The type of surgery depends on the cancer’s stage and grade.
- Transurethral Resection of Bladder Tumor (TURBT): This is often the initial treatment for early-stage bladder cancers. It involves removing the tumor using a cystoscope inserted through the urethra.
- Cystectomy: For more invasive cancers, a partial or radical cystectomy may be necessary. Partial cystectomy removes part of the bladder, while radical cystectomy involves removing the entire bladder and nearby lymph nodes. In some cases, surrounding organs might also be removed.
- Reconstructive Surgery: After a radical cystectomy, reconstructive surgery can create a new way for urine to exit the body. Options include a urostomy bag outside the body or a neobladder created from intestinal tissue.
Radiation Therapy in Bladder Cancer Treatment
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. It’s often combined with chemotherapy to enhance effectiveness, especially for invasive bladder cancers.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): EBRT directs radiation at the bladder from an outside source, typically given over several weeks.
- Effectiveness: Radiation therapy can be an alternative to surgery, especially for patients who cannot undergo surgery. It’s also used as adjuvant therapy to eliminate remaining cancer cells post-surgery.
Chemotherapy for Bladder Cancer
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop their growth. It can be administered intravesically (directly into the bladder) or systemically.
- Intravesical Chemotherapy: Used for early-stage bladder cancers, the chemotherapy drug is inserted directly into the bladder through a catheter.
- Systemic Chemotherapy: For advanced stages, drugs are administered orally or intravenously, impacting cancer cells throughout the body.
- Expectations: The effectiveness of chemotherapy varies, depending on the cancer’s stage and individual patient factors. Side effects can include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss.
Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: Innovations in Bladder Cancer Treatment
Recent advancements in bladder cancer treatment include immunotherapy and targeted therapy.
- Immunotherapy: This treatment boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It’s particularly effective for patients with certain types of bladder cancer and can be used when other treatments haven’t worked.
- Targeted Therapy: These drugs target specific genes or proteins that contribute to cancer growth. They offer a more personalized treatment approach and can be used alone or in combination with other treatments.
This guide provides a snapshot of the current landscape in bladder cancer treatments. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment for your specific case.
Factors Influencing Treatment Choices of Bladder Cancer
The choices made significantly depend on several key factors, each playing a vital role in determining the most effective and suitable treatment plan for patients. Understanding these factors is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers.
1. Impact of Cancer Stage and Grade on Treatment Decisions
The stage and grade of bladder cancer are primary determinants in treatment planning. Early-stage cancers, often confined to the bladder’s lining, may require less aggressive treatment compared to advanced stages, where cancer has spread beyond the bladder. Similarly, the cancer’s grade, indicating how much the cancer cells differ from normal cells, influences the choice of treatment. High-grade cancers, which are more likely to grow and spread quickly, typically necessitate more intensive treatment strategies.
2. Considering Patient Health and Personal Preferences
Patient health and personal preferences play a pivotal role in treatment decisions. Factors such as age, overall health, and existing medical conditions can influence which treatments are viable and safe. Additionally, personal preferences, including lifestyle considerations and risk tolerance, are crucial. Patients are encouraged to communicate openly with their healthcare team about their concerns and preferences, ensuring a treatment plan that aligns with their values and quality of life expectations.
3. The Role of Multidisciplinary Care in Treatment Planning
Multidisciplinary care is a holistic approach that brings together specialists from various fields to create a comprehensive treatment plan. This team may include urologists, oncologists, radiologists, and other healthcare professionals. The collaboration ensures that all aspects of the patient’s health are considered, leading to a more tailored and effective treatment strategy. This approach not only improves treatment outcomes but also provides patients with support and guidance throughout their cancer journey.
However, the treatment of bladder cancer is influenced by a complex interplay of medical factors and personal choices. Understanding the stage and grade of the cancer, considering the patient’s overall health and preferences, and adopting a multidisciplinary approach are crucial in devising an effective treatment plan. Patients are encouraged to actively participate in their treatment planning, fostering a collaborative environment with their healthcare team.
Emerging Treatments and Research in Bladder Cancer
Let’s delves into the latest developments in bladder cancer therapy, underscoring both ongoing clinical trials and emerging research areas.
1. Cutting-Edge Treatments in Bladder Cancer
Recent years have witnessed groundbreaking strides in bladder cancer therapy. Here’s a look at some of the most significant advancements:
- Immunotherapy: Revolutionizing bladder cancer treatment, immunotherapy employs the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. Drugs like pembrolizumab and atezolizumab have shown promise in treating advanced bladder cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: This treatment focuses on specific genes or proteins that contribute to cancer growth. For instance, Erdafitinib, approved for specific genetic alterations in bladder cancer, has offered new hope for patients.
- Intravesical Therapies: These involve delivering treatment directly into the bladder. Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) therapy remains a mainstay for non-invasive bladder cancer, with ongoing research to enhance its efficacy.
2. Ongoing Clinical Trials: Paving the Future of Bladder Cancer Research
Clinical trials are crucial for developing new treatments. Some key focus areas include:
- Combination Therapies: Trials are exploring the synergy of combining different treatment modalities, like immunotherapy with chemotherapy or targeted therapy, to improve outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: With a focus on genetic profiling, trials aim to tailor treatments to individual patient’s genetic makeup, enhancing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
- Early Detection and Prevention: Research is also directed towards identifying biomarkers for early detection and understanding risk factors to develop prevention strategies.
3. Emerging Research Frontiers in Bladder Cancer
The research landscape in bladder cancer is vibrant, with several promising areas:
- Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery: Innovations in nanotechnology are being explored to enhance drug delivery mechanisms, potentially increasing the effectiveness of existing treatments.
- Artificial Intelligence in Diagnosis: AI and machine learning are being employed to improve diagnostic accuracy, aiding in early and precise detection of bladder cancer.
- Understanding Cancer Resistance: Research is increasingly focusing on understanding why some cancers become resistant to treatments, aiming to overcome this challenge for more effective therapy.
The landscape of bladder cancer treatment and research is evolving rapidly, offering new hope and improved outcomes for patients. With ongoing clinical trials and innovative research, the future of bladder cancer therapy looks promising, as it moves towards more personalized, effective, and less invasive treatments.
Living with Bladder Cancer
Living with bladder cancer involves a multifaceted approach to managing not only the disease itself but also the side effects of treatment, adapting to necessary lifestyle changes, and addressing the psychological impacts. Here’s a comprehensive guide to navigate these challenges effectively.
Managing Side Effects of Treatment
Bladder cancer treatments, including chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery, can lead to various side effects. It’s essential to be proactive in managing these effects to maintain quality of life.
Key Strategies:
- Stay Informed: Understand potential side effects of your specific treatment plan.
- Regular Check-ups: Keep regular appointments with your healthcare team to monitor and manage side effects.
- Symptom Management: Utilize prescribed medications and therapies to alleviate symptoms like nausea, pain, or fatigue.
- Holistic Approaches: Consider complementary therapies, such as acupuncture or massage, for additional relief.
Lifestyle Changes and Supportive Care
Adopting lifestyle changes can significantly improve your overall health and well-being during and after treatment.
Important Changes:
- Dietary Adjustments: Focus on a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins.
- Physical Activity: Engage in regular, moderate exercise as approved by your doctor.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, seek help to quit, as smoking can worsen bladder cancer.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques like meditation or yoga.
Psychological Impact and Coping Strategies
Coping with the psychological impact of bladder cancer is as crucial as managing physical health.
Effective Strategies:
- Open Communication: Discuss your feelings with loved ones or join a support group.
- Professional Support: Consider therapy or counseling to navigate emotional challenges.
- Mindfulness Practices: Engage in mindfulness or relaxation exercises to maintain mental balance.
- Educate Yourself: Understanding your condition can empower you and reduce anxiety.
Remember, each person’s journey with bladder cancer is unique, and what works for one may not work for another. It’s vital to work closely with your healthcare team to tailor a plan that suits your individual needs and enhances your quality of life.
Prevention and Awareness: Key Strategies for Reducing Bladder Cancer Risk
Understanding and implementing strategies for prevention is crucial for reducing the risk of developing this condition. In this section, we’ll explore effective prevention techniques and highlight the importance of awareness and regular check-ups in combatting bladder cancer.
Strategies for Bladder Cancer Risk Reduction
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for bladder cancer. Quitting smoking or never starting can drastically reduce the risk.
- Limit Exposure to Chemicals: Occupational exposure to certain chemicals used in dyeing and rubber, leather, and textile industries can increase bladder cancer risk. Using appropriate safety measures and minimizing exposure is vital.
- Stay Hydrated: Adequate water intake can dilute potential bladder irritants, reducing the risk.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may lower bladder cancer risk.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can improve overall health and may reduce the risk of bladder cancer.
The Importance of Awareness and Regular Check-Ups
- Early Detection: Regular check-ups and being aware of the symptoms, such as blood in the urine, can lead to early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment.
- Risk Factor Recognition: Being informed about personal and familial risk factors, like age, gender, and family history, can guide individuals in taking appropriate preventive measures.
- Professional Guidance: Regular consultations with healthcare professionals can provide tailored advice and screenings, especially for those at higher risk.
However, prevention and awareness play a pivotal role in reducing the risk of bladder cancer. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, being cognizant of the symptoms, and undergoing regular medical check-ups are fundamental strategies. Remember, early detection and lifestyle modifications can make a significant difference in preventing bladder cancer.
Conclusion
For those who may be experiencing symptoms or are at risk, the importance of consulting a healthcare professional cannot be overstated. Symptoms like blood in urine, frequent urination, or pelvic pain should never be overlooked. Seeking timely medical advice can make a significant difference in the outcome of the disease.
Remember, early detection plays a critical role in the successful treatment of bladder cancer. It not only increases the likelihood of a favorable prognosis but also opens up a wider range of treatment options. By staying informed and proactive about your health, you take an essential step towards protecting your well-being.
In conclusion, the journey of diagnosing and treating bladder cancer is a testament to the advancements in medical science and the importance of early detection. Let this be a reminder to prioritize your health and seek professional advice at the first sign of any concerning symptoms. Your health is your most valuable asset, and taking care of it is the best investment you can make.