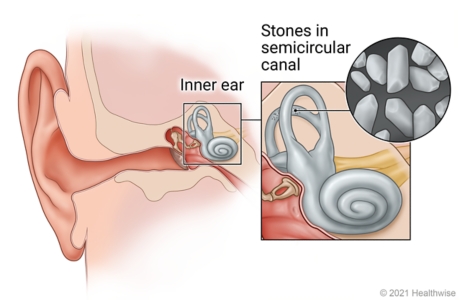
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Symptoms: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is a common vestibular disorder that causes episodes of dizziness and a sensation of spinning, known as vertigo.
This condition is triggered by specific changes in the position of the head. It’s essential to understand the symptoms and causes of BPPV to manage it effectively.
What is Benign Adrenal Tumors
Benign adrenal tumors are noncancerous growths that occur in the adrenal glands, which are located above the kidneys. These tumors are typically harmless and often go unnoticed. They can vary in size and may cause symptoms if they grow large enough or produce hormones. Unlike malignant tumors, benign adrenal tumors do not spread to other parts of the body. Their characteristics include a slow growth rate, a well-defined shape, and a lack of invasion into surrounding tissues.
Statistics and Prevalence
Benign adrenal tumors are relatively common, with many cases being discovered incidentally during imaging tests for unrelated health issues. The prevalence of these tumors increases with age, and they are more commonly diagnosed in people in their middle-age or older. While exact statistics vary, studies suggest that a small percentage of the adult population may have benign adrenal tumors, often without realizing it.
Types of Benign Adrenal Tumors
There are several types of benign adrenal tumors, each with unique features:
- Adenomas: The most common type, adrenal adenomas are usually small and non-functioning, meaning they don’t produce hormones.
- Pheochromocytomas: These are rare and can produce excess hormones like adrenaline, leading to symptoms like high blood pressure, palpitations, and sweating.
- Myelolipomas: Composed of fat and bone marrow-like cells, these tumors are typically asymptomatic.
- Cystic Lesions: These fluid-filled tumors are usually non-functional and found incidentally.
- Ganglioneuromas: These are rare, often asymptomatic, and arise from nerve cells.
Understanding these types, their prevalence, and characteristics is crucial for accurate diagnosis and management. Regular monitoring and medical intervention may be necessary, especially if the tumor affects hormone production or causes other health issues.
Causes and Risk Factors of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Understanding its causes and risk factors is vital for both prevention and effective treatment. This article delves into the various factors contributing to the development of BPPV, highlighting genetic influences, environmental triggers, and the identification of high-risk groups.
Genetic Factors and Environmental Influences in BPPV
- Genetic Predisposition: Research suggests a genetic component in BPPV development, although it’s not the sole cause. Family history of vertigo or balance disorders can slightly increase the risk of developing BPPV.
- Age-Related Changes: BPPV is more common in older adults, likely due to age-related degeneration of the vestibular system in the inner ear.
- Head Trauma: A significant percentage of BPPV cases are linked to a history of head injury, indicating a direct impact on the inner ear structures.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Recent studies have found a correlation between low levels of Vitamin D and increased susceptibility to BPPV.
- Osteoporosis: As a condition that affects bone density, osteoporosis may also have a connection with the onset of BPPV, particularly in postmenopausal women.
Identifying High-Risk Groups for BPPV
Recognizing individuals at higher risk for developing BPPV is crucial for early intervention and management. Key high-risk groups include:
- Older Adults: Individuals over the age of 50 are more prone to BPPV, largely due to natural aging processes affecting the inner ear.
- Women: Studies show that women are slightly more likely to develop BPPV than men, especially post-menopause.
- Individuals with a History of Head Trauma: People who have experienced significant head injuries are at a heightened risk of developing BPPV.
- Those with Osteoporosis or Vitamin D Deficiency: Individuals suffering from osteoporosis or with inadequate Vitamin D levels should be monitored for symptoms of BPPV.
However, BPPV is a multifactorial condition influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Awareness of these risk factors, especially in high-risk groups, is essential for early detection and management of BPPV. Regular check-ups and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate these risks. If you experience symptoms suggestive of BPPV, consulting a healthcare professional is strongly recommended for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Benign Adrenal Tumors
Identifying the symptoms early is crucial for effective management. Common symptoms include:
- High Blood Pressure: These tumors can produce hormones leading to elevated blood pressure.
- Unexplained Weight Gain: Particularly around the abdomen and face.
- Muscle Weakness: Patients may experience a decrease in muscle strength.
- Mood Changes: Fluctuations in mood or increased irritability can be signs.
- Abnormal Hair Growth: In women, this can manifest as increased facial or body hair.
- Skin Changes: Such as thinning or bruising.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection plays a pivotal role in the effective treatment of benign adrenal tumors. When diagnosed early, treatment can be more straightforward and less invasive. This early intervention can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with the tumor, such as hormonal imbalances and the associated symptoms.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience any of the above symptoms, especially if they persist or worsen over time. It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also be related to other health conditions, so professional evaluation is essential for an accurate diagnosis. Seeking medical advice promptly ensures that, if a benign adrenal tumor is present, it can be managed effectively and with the best possible outcomes.
Diagnosing Benign Adrenal Tumors: A Comprehensive Guide
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management. This guide provides a clear, reader-friendly overview of the diagnostic procedures, the significance of medical history and physical examination, and discusses the challenges and advancements in the field.
Imaging Tests: A cornerstone in diagnosing benign adrenal tumors, imaging tests like CT scans and MRIs provide detailed pictures of the adrenal glands. These non-invasive techniques help doctors identify the size, shape, and location of tumors, distinguishing benign from potentially malignant ones.
Blood and Urine Tests: Essential for understanding the hormonal activity of the adrenal glands, these tests can detect abnormal levels of hormones like cortisol, aldosterone, or adrenaline, which are often produced in excess by adrenal tumors.
The Role of Medical History and Physical Examination
Medical History: A thorough medical history helps identify symptoms like high blood pressure, weight gain, or changes in glucose levels, which may indicate a hormone imbalance caused by an adrenal tumor.
Physical Examination: While benign adrenal tumors are often asymptomatic, a physical exam can sometimes reveal signs of hormone excess, such as high blood pressure or physical changes.
Navigating Challenges and Advancements
Challenges in Diagnosis: Differentiating benign adrenal tumors from malignant ones remains a challenge. Also, identifying the exact type of hormone excess can be complex, as symptoms often overlap with other conditions.
Advancements: Recent developments in imaging technologies and biochemical testing have improved accuracy in diagnosing these tumors. Innovations in genetic testing also offer new insights into tumor behavior, aiding in better management and treatment strategies.
This guide aims to demystify the process of diagnosing benign adrenal tumors, empowering patients and practitioners with knowledge for better health outcomes. Remember, an early and accurate diagnosis is key to managing these tumors effectively.
Treatment Options for Benign Adrenal Tumors
Treatment strategies are tailored to each individual’s needs, factoring in the tumor’s characteristics and the patient’s overall health.
Surgical Approaches and When Surgery is Necessary
Surgery is a primary treatment for many benign adrenal tumors, especially when they are large or producing excess hormones. The most common surgical procedure is an adrenalectomy, where the affected adrenal gland is removed. This method is highly effective and often recommended when the tumor poses a risk of turning cancerous or causes significant symptoms.
Non-Surgical Treatments and Lifestyle Adjustments
Not all benign adrenal tumors require surgery. Smaller, non-functioning tumors may be managed with regular monitoring and lifestyle changes. These include stress management, dietary adjustments, and regular exercise, which can be crucial for maintaining overall adrenal health. In some cases, medication may be used to control symptoms or hormone production.
Role of Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular follow-up is critical in managing benign adrenal tumors. This often involves imaging tests, such as CT scans or MRIs, and blood tests to monitor hormone levels. These check-ups help in tracking the tumor’s growth and assessing if treatment strategies need to be adjusted. Ongoing monitoring ensures any changes are detected early, allowing for timely intervention.
Living with Benign Adrenal Tumors: A Comprehensive Guide
Living with benign adrenal tumors requires not just medical management but also a focused approach to lifestyle and diet. Optimal health can be supported by:
- Balanced Nutrition: Emphasizing a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Minimize processed foods, excessive sugar, and saturated fats.
- Hydration: Adequate water intake is crucial for overall health and can help in managing symptoms.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight helps in reducing the burden on your body and can alleviate some symptoms associated with adrenal tumors.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate, consistent physical activity improves cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Dealing with symptoms is a significant aspect of living with benign adrenal tumors. Effective strategies include:
- Regular Medical Checkups: Ongoing monitoring of the tumor’s status and your overall health is essential.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which is particularly important for adrenal health.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring you get enough sleep helps in hormone regulation and improves general health.
- Supportive Therapies: Alternative therapies like acupuncture or massage can be complementary to traditional medical treatments for symptom relief.
Psychological Impact and Support Resources
The psychological impact of living with a benign adrenal tumor can be profound. Addressing mental health is as crucial as managing physical symptoms:
- Counseling and Therapy: Professional mental health support can help in coping with anxiety, stress, or depression that might arise.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who are facing similar challenges can provide comfort and practical advice.
- Education and Awareness: Understanding your condition empowers you to make informed decisions about your health and treatment.
- Family and Social Support: Maintaining a strong support network is vital for emotional well-being.
By integrating these considerations into your daily life, you can effectively manage your condition and enhance your quality of life while living with benign adrenal tumors. Remember, every individual’s journey is unique, and it’s important to work closely with healthcare professionals to tailor these recommendations to your specific needs.
Recent Advances and Future Directions in Treatment
Embracing Innovative Research and Emerging Treatments
Recent years have seen groundbreaking research, introducing new approaches that promise more effective and less invasive options for patients. These advances stem from a deeper understanding of tumor biology and the application of cutting-edge technologies in medical practice.
- Targeted Therapy and Precision Medicine: Leveraging genetic insights, researchers are developing targeted therapies tailored to individual tumor characteristics. This precision medicine approach offers hope for more personalized and effective treatments, minimizing side effects and improving outcomes.
- Minimally Invasive Surgical Techniques: Surgeons are increasingly adopting minimally invasive procedures for adrenal tumor removal. Techniques like laparoscopic and robotic surgery offer patients shorter recovery times, reduced pain, and lower risks of complications.
- Advancements in Imaging Technologies: Enhanced imaging techniques provide more accurate diagnoses and detailed tumor profiling. This progress aids in better treatment planning and monitoring, ensuring a more targeted approach to tumor management.
Peering into the Future: Emerging Trends in Adrenal Tumor Management
The horizon of adrenal tumor treatment is bright with potential, marked by several emerging trends that are set to redefine patient care.
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI and machine learning algorithms are being explored for their potential in diagnosing and predicting the behavior of benign adrenal tumors. This technology could lead to more accurate early detection and customized treatment plans.
- Focus on Quality of Life: Future treatments are likely to emphasize not just the eradication of tumors but also the overall quality of life for patients. This holistic approach would consider the physical, emotional, and psychological impacts of both the disease and its treatment.
- Gene Therapy and Molecular Treatments: The exploration of gene therapy and molecular-based treatments is gaining momentum. These innovative strategies could offer non-invasive alternatives to traditional surgery, especially for patients with specific genetic markers.
- Collaborative and Multidisciplinary Care: A trend towards more collaborative, multidisciplinary care models is emerging. This approach brings together specialists from different fields, ensuring comprehensive care that addresses all aspects of the patient’s health and well-being.
However, the landscape of benign adrenal tumor management is evolving rapidly, with recent advances paving the way for more personalized and effective treatments. The future promises even more exciting developments, with a focus on minimally invasive techniques, quality of life, and the integration of innovative technologies like AI and gene therapy. As these trends continue to unfold, patients can look forward to more effective and holistic care options.
FAQs Section:
1. What are Benign Adrenal Tumors?
Benign adrenal tumors are non-cancerous growths that form in the adrenal glands, which are located above your kidneys. These tumors typically do not spread to other parts of the body and are often discovered incidentally during imaging tests for other conditions.
2. What Causes Benign Adrenal Tumors?
The exact cause of benign adrenal tumors is not fully understood. However, factors like genetics, certain medical conditions, and hormonal imbalances may contribute to their development.
3. What are the Symptoms of Benign Adrenal Tumors?
Many benign adrenal tumors do not cause symptoms and are often found accidentally. When symptoms do occur, they can include high blood pressure, weight gain, muscle weakness, and hormonal imbalances.
4. How are Benign Adrenal Tumors Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging tests such as CT scans or MRI, as well as blood and urine tests to assess hormone levels and rule out cancerous growths.
5. What are the Treatment Options for Benign Adrenal Tumors?
Treatment depends on the size of the tumor and whether it’s causing symptoms. Options include monitoring, medication to manage symptoms, or surgery to remove the tumor if it’s large or causing significant issues.
6. Can Benign Adrenal Tumors Become Cancerous?
Most benign adrenal tumors do not become cancerous. Regular monitoring is important to track any changes in the tumor.
7. What Lifestyle Changes Can Help Manage Benign Adrenal Tumors?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management can be beneficial, especially if the tumor affects hormone levels.
8. Are There Any Risks Associated with Treatment?
As with any medical procedure, there are potential risks. Surgery, for instance, carries risks like infection or bleeding. Discuss with your healthcare provider to understand the risks and benefits of your treatment plan.
9. How Often Should I Follow Up with My Doctor?
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial. Your doctor will recommend a schedule based on the specifics of your condition.
10. Can Benign Adrenal Tumors Recur After Treatment?
There’s a low risk of recurrence after treatment. However, ongoing monitoring is advised to detect any changes early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while benign adrenal tumors present a complex medical challenge, understanding their diagnosis and treatment is crucial. Remember, early detection and a tailored approach to treatment are key, and consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice cannot be overstated. Stay informed, stay proactive, and prioritize your health by seeking the guidance of medical experts.