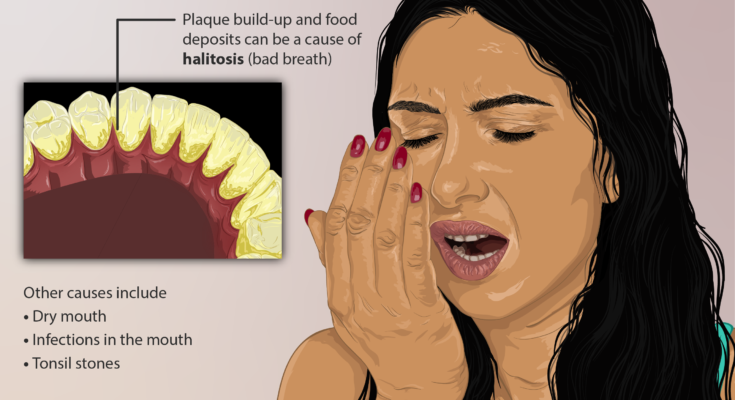
Bad Breath Treatment: Bad breath, also known as halitosis, is a common problem that can cause significant psychological distress.
There are many potential causes, and finding the right treatment depends on accurately identifying the underlying issue.
What is Bad Breath
Bad breath, medically known as halitosis, is a common condition that can affect anyone. It is characterized by an unpleasant odor emanating from the mouth. This condition can be temporary or chronic, depending on its underlying cause.
The primary cause of bad breath is the bacteria that live in the mouth, particularly on the tongue, between the teeth, and along the gumline. These bacteria break down food particles and produce sulfur compounds, leading to the foul smell. Poor dental hygiene is a significant contributor, as it allows food particles to remain in the mouth, further feeding these bacteria.
Other causes include:
- Dental issues: Problems such as cavities, gum disease, or impacted teeth can lead to bad breath.
- Dry mouth: Saliva helps cleanse the mouth; without it, bacteria thrive.
- Diet: Foods like garlic, onions, and certain spices can affect breath.
- Health conditions: Sinus infections, throat infections, gastrointestinal issues, and certain systemic diseases can cause halitosis.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking and alcohol consumption can also contribute to bad breath.
Common Misconceptions About Bad Breath
Several misconceptions surround bad breath, often leading to unnecessary worry or inappropriate treatments. Some common myths include:
- Bad Breath is Only Caused by Poor Hygiene: While poor dental hygiene is a significant factor, other causes like diet, health conditions, and lifestyle choices also play roles.
- Mouthwash Alone Can Cure Bad Breath: Mouthwash can temporarily mask the odor, but it doesn’t address the underlying causes like bacterial growth or dental issues.
- Brushing More Frequently Will Always Solve the Problem: Over-brushing can damage your gums and teeth, and while good oral hygiene is crucial, it may not be the sole solution for chronic bad breath.
- Bad Breath is Always Noticeable by the Person Who Has It: Often, individuals are not aware of their own bad breath, making regular dental check-ups important.
- Chewing Gum or Mints are Effective Long-Term Solutions: These may offer short-term relief but do not tackle the root causes of bad breath.
Understanding these misconceptions is vital in effectively addressing and treating bad breath. If you suspect chronic bad breath, it’s important to consult a dentist or physician to identify and treat any underlying causes.
Symptoms and Signs of Bad Breath
Identifying bad breath involves recognizing specific symptoms and understanding when it’s necessary to seek professional help.
Identifying Bad Breath
- Persistent Unpleasant Odor: The most obvious sign of bad breath is a persistent smell that is unpleasant. This can be noticed by the individual or mentioned by others.
- Taste Changes: A bad or unusual taste in the mouth, often described as sour, metallic, or bitter, can be a symptom of halitosis.
- Dry Mouth: Xerostomia, or dry mouth, often accompanies bad breath. Saliva is crucial in washing away food particles and bacteria; a lack of it can lead to a build-up of odor-causing elements.
- Mouth Coating: A thick or sticky coating on the tongue, especially towards the back, can indicate bad breath. This coating can harbor bacteria responsible for odor.
- Other Symptoms: Additional signs might include a white or yellow film on the tongue, chronic throat clearing, or a feeling of something constantly stuck in the throat.
When to Seek Professional Help
- Chronic Bad Breath: If the bad breath persists despite good oral hygiene practices like regular brushing and flossing, it’s time to consult a professional.
- Accompanying Symptoms: If bad breath is accompanied by symptoms like tooth pain, gum inflammation, or frequent sore throats, it may be indicative of underlying dental or medical issues.
- Impact on Social Life: When bad breath starts affecting personal and professional interactions, seeking professional advice can provide both relief and solutions.
- Self-Treatment Failure: If over-the-counter remedies and improved hygiene habits fail to eliminate the problem, professional intervention is recommended.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Sometimes, bad breath is a sign of medical conditions like diabetes, sinus infections, or gastrointestinal issues. A healthcare provider can help in diagnosing and treating these conditions.
However, being aware of the symptoms and understanding when to seek professional help are key steps in addressing and managing bad breath effectively. Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are essential in preventing and treating halitosis.
Diagnosing Bad Breath
Bad breath, medically known as halitosis, can be an embarrassing and sometimes serious issue. Understanding how it is diagnosed is crucial for effective treatment.
Professional Diagnosis Methods for Bad Breath
- Odor Assessment: Dentists often start with a subjective assessment of the breath odor. This method involves the dentist smelling the breath from both the mouth and nose and rating the odor on a scale. This initial assessment provides a basic understanding of the severity of the problem.
- Halimeter Use: A more objective approach involves the use of a halimeter. This specialized instrument measures volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) in the breath, which are often responsible for bad breath. High levels of VSCs typically indicate halitosis.
- Bacterial Culture Tests: In some cases, a sample of saliva or plaque might be taken for bacterial culture. This test identifies specific bacteria that might be contributing to bad breath.
- Gas Chromatography: Advanced diagnosis may involve gas chromatography. This technique can precisely analyze compounds present in the breath, providing detailed information about the causes of bad breath.
The Role of Dental Health in Bad Breath Diagnosis
Dental health is a critical component in diagnosing and treating bad breath.
- Oral Hygiene Check: Poor oral hygiene is a common cause of bad breath. Dentists check for signs of plaque, tartar, and gum disease, which can harbor odor-causing bacteria.
- Dental Issues Identification: Cavities and poorly fitting dental appliances, like crowns or dentures, can trap food particles and bacteria, leading to bad breath. A thorough dental examination can identify these issues.
- Periodontal Examination: Gum disease is a significant cause of bad breath. Dentists perform periodontal examinations to check the health of your gums. This includes measuring the depth of gum pockets which can indicate the presence of periodontal disease.
- Dry Mouth Evaluation: Saliva helps to cleanse the mouth. If you have a dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, it can lead to bad breath. Dentists will evaluate the causes of dry mouth, which can range from certain medications to systemic conditions.
However, diagnosing bad breath involves a combination of professional methods and an in-depth examination of dental health. By identifying the root causes, effective treatment strategies can be implemented to combat this issue. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are key to preventing and managing bad breath.
Common Causes of Bad Breath
Understanding the causes is essential for effective management and prevention. This article explores the common causes of bad breath, focusing on oral hygiene, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors.
Oral Hygiene and Dental Issues
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Not brushing and flossing regularly leads to the accumulation of food particles and the growth of bacteria in the mouth, resulting in bad breath.
- Dental Problems: Cavities and gum diseases, such as gingivitis and periodontitis, create breeding grounds for bacteria, contributing to foul-smelling breath.
- Tongue Accumulations: Bacteria that live on the tongue can produce malodorous compounds, especially on the back part of the tongue where cleaning is often neglected.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): Saliva helps cleanse the mouth. A dry mouth, whether due to medications or salivary gland problems, can lead to bad breath as it allows bacteria to thrive.
Medical Conditions Leading to Bad Breath
- Respiratory Tract Infections: Conditions like bronchitis, sinusitis, and pneumonia can cause bad breath due to the presence of nasal or respiratory secretions.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: Acid reflux or GERD can bring up stomach acids into the esophagus and mouth, leading to bad breath.
- Systemic Diseases: Conditions such as diabetes, liver or kidney disease can cause distinctive breath odors due to the specific chemicals they produce.
- Tonsil Stones: Small stones that form in the tonsils and contain high amounts of bacteria can produce a foul odor.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Breath Quality
- Diet: Foods like garlic, onions, and spices are absorbed into the bloodstream and lungs, affecting breath until they are fully metabolized.
- Smoking and Tobacco Use: These habits not only cause their own odor but also dry out the mouth and increase the risk of gum disease, further worsening breath quality.
- Alcohol Consumption: Similar to smoking, alcohol can dry out the mouth and lead to a lingering bad breath.
- Poor Dieting Habits: Extreme diets, especially those that cause ‘ketosis,’ can produce a fruity or acetone-like breath odor.
However, bad breath can stem from a variety of sources ranging from oral hygiene practices to systemic medical conditions and lifestyle choices. Addressing these factors is key to managing and preventing halitosis. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene, a balanced diet, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol are effective strategies for maintaining fresh breath.
Treatment Options for Bad Breath
These solutions range from simple home remedies and lifestyle adjustments to professional treatments, ensuring that individuals can find a method that works best for their specific needs.
1. Home Remedies and Lifestyle Changes
For many, combating bad breath starts at home. Simple yet effective strategies include:
- Maintaining Oral Hygiene: Regular brushing and flossing are crucial. It’s recommended to brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss daily to remove food particles and plaque.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated helps maintain saliva flow, which naturally cleanses the mouth.
- Dietary Adjustments: Reducing intake of odorous foods like garlic and onions, and acidic or sugary items can help.
- Natural Mouthwashes: Rinsing with a solution of water and baking soda or a mixture of water and hydrogen peroxide (in a safe dilution) can neutralize bad breath.
- Chewing Sugar-Free Gum: This stimulates saliva production, helping cleanse the mouth.
2. Over-the-Counter Solutions
If home remedies aren’t enough, over-the-counter products can offer additional help:
- Antibacterial Mouthwashes: These products target the bacteria that cause bad breath.
- Tongue Scrapers: These tools can remove bacteria, food debris, and dead cells from the tongue’s surface.
- Breath Fresheners: Breath sprays and mints can provide temporary relief.
3. Professional Treatments Available
For chronic or severe cases of bad breath, professional intervention might be necessary:
- Dental Cleaning: Regular cleanings by a dentist can remove hard-to-reach plaque and tartar.
- Treatment of Dental Issues: Cavities, gum disease, and other oral health problems can contribute to bad breath and need professional treatment.
- Specialized Mouthwashes and Medications: In some cases, prescription-strength mouthwashes or medications may be required to address underlying causes.
It’s important to remember that while these treatments can be highly effective, they work best when combined with a consistent oral hygiene routine. If bad breath persists despite these efforts, consulting a dentist or physician is advised to rule out any underlying health issues.
Preventative Measures for Bad Breath
Daily Oral Hygiene Best Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial in preventing bad breath. This includes several key practices:
- Brushing and Flossing: Brush your teeth at least twice a day using fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth, where your toothbrush can’t reach.
- Tongue Cleaning: Bacteria often reside on your tongue, contributing to bad breath. Use a tongue scraper or your toothbrush to clean your tongue regularly.
- Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce bacteria that cause bad breath. Use it as a part of your daily oral hygiene routine.
- Hydration: Keeping your mouth moist helps wash away food particles and bacteria. Drink plenty of water and avoid excessive coffee or alcohol, as they can lead to a dry mouth.
Dietary Considerations
What you eat significantly impacts your breath. To prevent bad breath:
- Limit Foods with Strong Odors: Avoid foods like garlic, onions, and spicy dishes, which can contribute to bad breath.
- Healthy Choices: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, grains, and lean proteins. These foods are not only good for your overall health but also help maintain a healthier oral environment.
- Sugar Intake: Reduce your sugar consumption, as sugar is a primary food source for bacteria that cause bad breath.
Regular Dental Check-ups
Routine dental visits are essential:
- Professional Cleaning: Regular cleanings by a dentist or dental hygienist remove plaque and tartar build-up, which can cause bad breath.
- Check for Oral Problems: Regular check-ups can detect problems such as gum disease, which is a common cause of bad breath.
- Personalized Advice: Your dentist can provide tailored advice and treatments to help keep your breath fresh.
However, preventing bad breath involves a combination of good oral hygiene, mindful eating habits, and regular dental visits. Implementing these practices will not only improve your breath but also your overall oral health.
When to See a Dentist or Doctor for Bad Breath
Knowing when to consult a dentist or doctor is crucial for effective management and treatment. This guide will explore the scenarios that necessitate professional consultation and what you can expect during a professional evaluation.
Scenarios Warranting Professional Consultation
- Persistent Bad Breath: If you experience bad breath that persists despite good oral hygiene practices, it’s time to see a professional. Persistent bad breath could indicate dental issues like cavities or gum disease.
- Associated Symptoms: Bad breath accompanied by symptoms like tooth pain, bleeding gums, or difficulty swallowing should prompt a visit to a dentist or doctor. These symptoms could point to more serious conditions like oral infections or throat issues.
- Dry Mouth: Chronic dry mouth, known as xerostomia, can lead to bad breath. If you’re experiencing dry mouth regularly, a healthcare professional can help determine the cause and recommend treatment.
- Systemic Health Concerns: If you have systemic health issues like diabetes, gastrointestinal problems, or respiratory infections, and notice bad breath, it’s important to consult a doctor as it could be related to your underlying health condition.
- Change in Breath Odor: A noticeable change in the smell of your breath can be a cause for concern. Different odors can be indicative of specific health issues, which a professional can diagnose.
What to Expect During a Professional Evaluation
- Medical and Dental History Review: Expect to discuss your medical and dental history, including any existing conditions, medications, and lifestyle habits that might contribute to bad breath.
- Oral Examination: A dentist will thoroughly examine your mouth, checking for signs of dental problems like cavities, gum disease, or plaque build-up.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the suspected cause, you may undergo tests. These can include saliva tests, breath tests, or blood tests to check for conditions contributing to bad breath.
- Discussion of Findings and Treatment Plan: After the evaluation, the dentist or doctor will discuss their findings with you and propose a treatment plan. This may include dental treatments, lifestyle changes, or referrals to specialists for further evaluation.
- Follow-up Recommendations: Finally, you’ll receive recommendations for follow-up care and how to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent future occurrences of bad breath.
Addressing bad breath promptly with professional guidance ensures not only the alleviation of this uncomfortable condition but also the detection and treatment of any underlying health issues. Remember, your oral health is a window to your overall health, and timely intervention is key to maintaining both.
Addressing the Psychological Impact of Bad Breath
Bad breath, or halitosis, is not just a physical ailment; it has profound psychological implications that can affect an individual’s social and emotional well-being. Understanding and addressing these aspects is crucial for overall health and quality of life.
Social and Emotional Effects
- Self-Esteem and Confidence: Persistent bad breath can severely impact a person’s self-esteem and confidence. It may lead to heightened self-consciousness, making individuals hesitant to engage in conversations or avoid social interactions altogether.
- Social Isolation: The fear of judgment or embarrassment about bad breath can drive individuals into social isolation. This withdrawal can further exacerbate feelings of loneliness and depression, creating a vicious cycle.
- Relationship Strain: Personal relationships, whether platonic or romantic, can be strained by the presence of bad breath. It can cause misunderstandings and create a barrier to intimacy.
- Professional Impact: In professional settings, bad breath can influence perceptions, potentially impacting job opportunities, career advancement, and workplace interactions.
Coping Strategies and Support
- Medical Consultation: Firstly, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to identify any underlying causes of bad breath, which can range from dental issues to systemic health problems.
- Regular Oral Hygiene: Practicing good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash, can help manage bad breath effectively.
- Dietary Adjustments: Be mindful of foods that contribute to bad breath. Reducing the intake of such items and increasing water consumption can help.
- Social Support: Openly discussing the issue with close friends or family can provide emotional support and understanding.
- Professional Help: If bad breath significantly impacts mental health, seeking help from a psychologist or counselor can be beneficial. They can provide strategies to improve self-esteem and cope with social anxiety.
- Mindfulness and Self-Acceptance: Practicing mindfulness and self-compassion can help individuals accept and cope with their condition without harsh self-judgment.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups with people facing similar challenges can provide a sense of community and shared solutions.
However, the psychological impact of bad breath is substantial but often overlooked. Addressing both the physical and emotional aspects is crucial for a holistic approach to health and well-being. By employing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support, individuals can significantly improve their quality of life and mental health.
FAQ Section: Bad Breath Treatment
1. What Causes Bad Breath?
Bad breath, or halitosis, is often caused by poor dental hygiene. However, other factors such as certain foods, smoking, dry mouth, medical conditions, and gastrointestinal issues can also contribute to it.
2. How Can I Prevent Bad Breath?
Preventing bad breath starts with maintaining good oral hygiene. This includes regular brushing and flossing, using mouthwash, and cleaning your tongue. Staying hydrated and avoiding foods with strong odors can also help.
3. Are There Any Home Remedies for Bad Breath?
Yes, home remedies like chewing sugar-free gum, using baking soda as a toothpaste, consuming fresh fruits and vegetables, and drinking green tea can help combat bad breath.
4. When Should I See a Dentist for Bad Breath?
If your bad breath persists despite good oral hygiene, or if you suspect it’s related to a medical condition, consult a dentist or physician for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
5. Can Certain Foods Cause Bad Breath?
Yes, foods like garlic, onions, and some spices can cause temporary bad breath. Additionally, high-sugar diets can increase the risk of bad breath.
6. Is Bad Breath a Sign of a Serious Health Issue?
While bad breath is often not serious, persistent bad breath can be a sign of dental problems like gum disease or medical conditions such as sinus infections, diabetes, or liver and kidney problems.
7. How Effective Are Over-the-Counter Products for Bad Breath?
Over-the-counter products like mouthwashes and breath mints can provide temporary relief. However, for long-term solutions, addressing the underlying cause is essential.
8. Can Lifestyle Changes Improve Bad Breath?
Yes, lifestyle changes like quitting smoking, reducing alcohol consumption, and improving your diet can significantly improve bad breath.
9. Is Bad Breath Contagious?
No, bad breath is not contagious. However, certain conditions that cause bad breath, like infections, can be transmitted.
10. How Long Does It Take to Treat Bad Breath?
The time it takes to treat bad breath depends on its cause. Simple hygiene-related issues can be resolved quickly, while medical conditions may require more time and treatment.
Conclusion
It’s crucial to remember that bad breath is not just a cosmetic issue but can be a sign of underlying health problems. Seeking treatment is not only about improving your breath but also about ensuring overall health and well-being. If you’re experiencing persistent bad breath, it’s highly recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can provide tailored advice and treatment options suited to your specific needs.
Remember, bad breath is a common issue, and there’s no shame in seeking help. Taking that step towards treatment can greatly enhance your quality of life and social interactions. So, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional advice if you need it.