Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment: Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic condition that occurs when your body’s immune system attacks your liver cells, leading to inflammation and potentially serious liver damage.
Understanding the diagnosis and treatment of this condition is crucial for managing its progression and improving patient outcomes.
What is Autoimmune Hepatitis?
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver condition characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking the liver cells, leading to inflammation and damage. This immune response can cause liver fibrosis and, if left untreated, may progress to cirrhosis, liver failure, or even necessitate a liver transplant.
Statistics and Prevalence of AIH
The prevalence of Autoimmune Hepatitis varies globally, with estimates suggesting it affects between 10 to 17 individuals per 100,000 in the general population. It is more common in women, with a female to male ratio of approximately 4:1. AIH can occur at any age, but two peaks are generally observed: one in adolescence and another in women over the age of 40.
Causes and Risk Factors of AIH
The exact cause of Autoimmune Hepatitis remains unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with certain genetic markers are more prone to developing AIH. A family history of autoimmune diseases can also increase risk.
- Environmental Triggers: Exposure to certain drugs, viruses, or toxins might trigger the autoimmune response in genetically susceptible individuals.
- Gender: Women are more likely to develop AIH, suggesting a possible hormonal influence.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Those with other autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or celiac disease, have a higher risk of AIH.
Understanding AIH is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management. If you suspect you may have symptoms related to AIH, consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and treatment plan.
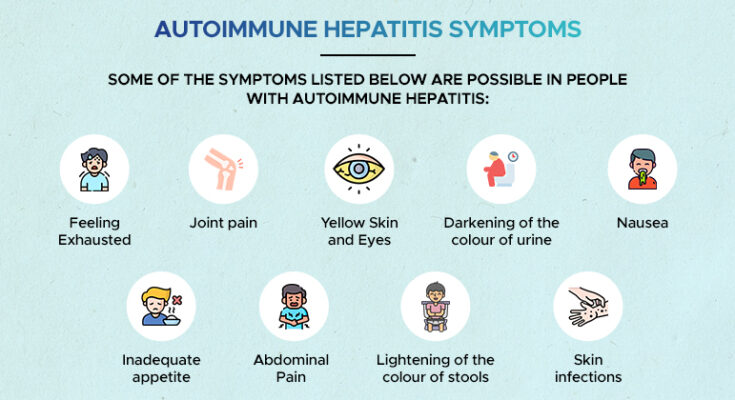
Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Common Symptoms of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Patients with autoimmune hepatitis often experience a range of symptoms, some of which may be common to other liver conditions:
- Fatigue: A pervasive sense of tiredness and lack of energy is a primary symptom, significantly impacting daily activities.
- Jaundice: This condition, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes, occurs due to elevated bilirubin levels in the blood.
- Abdominal Discomfort: Pain or discomfort in the upper right side of the abdomen is common due to liver inflammation.
- Joint Pain: A less known but frequent symptom, joint pain can occur without any underlying arthritis.
- Skin Rashes: Certain types of skin rashes, including those not typically associated with liver disease, can manifest.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles: Women may experience changes or disruptions in their menstrual cycles.
Distinguishing Symptoms from Other Forms of Hepatitis
While some symptoms of autoimmune hepatitis overlap with other hepatitis forms, certain aspects are more characteristic:
- Autoimmune Markers: Unlike viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis shows specific autoantibodies in blood tests.
- Response to Medication: Patients with autoimmune hepatitis often respond positively to immunosuppressive medications, a response not seen in viral forms.
- Progression Pattern: The disease progression in autoimmune hepatitis can be more gradual than in acute viral hepatitis but more aggressive than in chronic viral forms.
- Associated Autoimmune Disorders: Frequently, autoimmune hepatitis is associated with other autoimmune disorders, which is not a characteristic of viral hepatitis.
Understanding these symptoms and their nuances is key to prompt and accurate diagnosis. If you experience any of these symptoms, consulting a healthcare provider is essential for appropriate testing and treatment planning. Remember, early intervention can significantly improve outcomes in autoimmune hepatitis.
Diagnosing Autoimmune Hepatitis
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to diagnosing AIH, distinguishing it from other liver conditions, and highlights the critical role of various diagnostic methods.
Step-by-Step Process of Diagnosing AIH
- Initial Assessment: The process begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination. Symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, and abdominal pain are noted.
- Blood Tests: Key blood tests include liver function tests (LFTs) to check for elevated liver enzymes, indicating liver damage. Additionally, specific antibodies, like anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) and anti-smooth muscle antibody (ASMA), are tested as they are often present in AIH.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging techniques like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs help assess liver structure and rule out other causes like tumors or biliary obstruction.
- Liver Biopsy: Considered the gold standard in diagnosing AIH. A small liver tissue sample is examined for signs of inflammation and scarring, typical of AIH.
Differentiating AIH from Other Liver Conditions
AIH shares symptoms with other liver diseases, making differentiation crucial. Conditions like viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease must be excluded. The presence of autoantibodies, high immunoglobulin levels, and specific histological findings in liver biopsy are key differentiators for AIH.
Role of Blood Tests, Liver Biopsy, and Imaging in Diagnosis
- Blood Tests: These tests are pivotal for initial screening. They help detect liver damage and the presence of autoantibodies, guiding the diagnosis towards AIH.
- Liver Biopsy: Essential for confirming AIH. It provides detailed information on the extent of liver damage and the presence of autoimmune activity.
- Imaging: While imaging can’t diagnose AIH directly, it’s vital for excluding other liver diseases and assessing overall liver health.
However, diagnosing AIH is a multi-step process requiring a combination of clinical evaluation, blood tests, liver biopsy, and imaging studies. Differentiating AIH from other liver diseases is critical for appropriate management and treatment. This comprehensive approach ensures accurate diagnosis and effective care for those affected by AIH.
Treatment Options for Autoimmune Hepatitis
Effective treatment is crucial to manage symptoms, prevent progression to more severe liver disease, and maintain a good quality of life.
1. Medications Used in AIH Treatment
- Corticosteroids: Prednisone or prednisolone are commonly prescribed as first-line treatments. These medications help reduce liver inflammation quickly.
- Immunosuppressants: To minimize long-term side effects of corticosteroids, drugs like azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine are often added or used as alternatives. These immunosuppressants help in controlling the immune response.
- Other Medications: Depending on individual needs and disease progression, additional medications like budesonide, mycophenolate mofetil, or cyclosporine may be considered.
2. Lifestyle Changes and Supportive Therapies
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean protein, and whole grains supports liver health. Avoid alcohol as it can exacerbate liver damage.
- Regular Exercise: Moderate exercise can help manage symptoms and improve overall health.
- Mental Health Support: Living with a chronic illness can be challenging. Counseling or support groups can provide emotional support.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with a healthcare provider are vital to monitor liver function and adjust treatment as necessary.
3. Advanced Treatment Options
In severe cases or when conventional treatments are ineffective, advanced options such as liver transplantation may be considered. It’s crucial for patients to have ongoing discussions with their healthcare providers about the best treatment approach for their specific condition.
The treatment of autoimmune hepatitis is a multi-faceted approach involving medications, lifestyle adjustments, and regular medical care. Each patient’s treatment plan is tailored to their individual needs, with the goal of reducing inflammation, preventing liver damage, and maintaining a healthy, active lifestyle.
Managing Autoimmune Hepatitis
Understanding the nuances of long-term management, consistent monitoring and treatment adjustments, and the crucial role of patient education and support can significantly improve outcomes for those living with this condition.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Living with autoimmune hepatitis means adapting to a lifestyle that supports liver health. This includes:
- Medication Adherence: Long-term medication is often necessary to control inflammation and prevent liver damage. Patients should understand their medication regimen and adhere strictly to it.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Frequent doctor visits are essential for monitoring liver health and ensuring the effectiveness of treatments.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a liver-friendly diet, avoiding alcohol, and maintaining a healthy weight can drastically reduce liver strain.
- Managing Comorbid Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure can exacerbate autoimmune hepatitis, so managing these effectively is crucial.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatment
Ongoing evaluation of treatment efficacy is vital:
- Blood Tests: Regular blood tests can help track liver function and detect potential side effects of medications.
- Symptom Tracking: Patients should be vigilant about new or worsening symptoms and report these to their healthcare provider.
- Medication Adjustments: Based on test results and symptoms, doctors may adjust medication types and dosages to optimize treatment.
Importance of Patient Education and Support
Education and support play a pivotal role in managing autoimmune hepatitis:
- Understanding the Condition: Patients who understand their condition can make informed decisions about their care and lifestyle.
- Psychological Support: Living with a chronic illness can be challenging. Access to mental health support can help patients cope with the emotional aspects.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups where patients share experiences and strategies can be incredibly beneficial.
However, effectively managing autoimmune hepatitis involves a comprehensive approach that includes medication adherence, regular monitoring, lifestyle changes, and strong patient education and support. By focusing on these areas, patients can lead healthier, more fulfilling lives despite their diagnosis.
Complications and Challenges in Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
Managing autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) involves navigating a range of potential complications and treatment challenges. This article provides insights into these complexities, aiming to guide patients and healthcare professionals in better understanding and handling this condition.
Understanding the Complications of Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune hepatitis can lead to various complications, primarily impacting liver function. The most significant include:
- Cirrhosis: Progressive liver damage can result in cirrhosis, where normal liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, severely affecting liver function.
- Liver Failure: Advanced stages of autoimmune hepatitis may progress to liver failure, necessitating urgent medical intervention.
- Increased Risk of Liver Cancer: Chronic inflammation in the liver can elevate the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma, a type of liver cancer.
Tackling Treatment Resistance and Side Effects
Treatment for autoimmune hepatitis typically involves immunosuppressants, which can sometimes lead to resistance or significant side effects:
- Managing Medication Resistance: Over time, some patients may find that their bodies become less responsive to standard treatments, requiring alternative therapeutic strategies.
- Handling Side Effects: Common side effects of AIH medications include weight gain, hypertension, and increased susceptibility to infections. Careful monitoring and adjustments in treatment can mitigate these effects.
The Role of Liver Transplantation
In advanced cases of autoimmune hepatitis, where the liver is severely damaged, liver transplantation may become a necessary option:
- Assessing Eligibility: Not all patients are suitable for a liver transplant. A thorough evaluation is required to determine if transplantation is the best course of action.
- Post-Transplant Considerations: After a successful liver transplant, lifelong immunosuppression is usually necessary to prevent organ rejection, along with regular follow-ups to monitor liver function and overall health.
Advancements in Autoimmune Hepatitis Treatment
Embracing New Horizons in AIH Treatment
Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic liver condition marked by the immune system mistakenly attacking liver cells, leading to inflammation and, potentially, liver failure. Recent advancements in AIH treatment spotlight significant progress, promising a brighter future for those affected by this condition.
The Latest Research and Developments
In the realm of AIH treatment, recent research has made significant strides. Scientists and medical professionals are constantly unearthing new insights into how AIH develops, which has led to more effective and targeted treatments. These developments not only aim to manage symptoms more effectively but also strive to reduce the long-term impact of the disease on patients’ lives.
Emerging Therapies: A Glimpse into the Future
Emerging therapies in AIH treatment are particularly exciting. These include:
- Biological Therapies: These therapies use substances made from living organisms to treat disease. They are designed to target specific parts of the immune system that are involved in the autoimmune process, offering a more focused approach than traditional treatments.
- Gene Therapy: Researchers are exploring gene therapy as a potential treatment for AIH. This involves altering the genes inside a patient’s cells to stop or reduce the immune system’s attack on the liver.
- Personalized Medicine: This approach tailors treatment to the individual, based on their genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. It promises more effective and less invasive treatment options.
- Advanced Immunosuppressants: Newer immunosuppressant drugs are being developed to better control the immune system’s response, minimizing liver damage while reducing side effects.
Future Prospects: Hope on the Horizon
The future of AIH treatment looks promising. With ongoing research and the potential of new therapies, there is hope for more effective and less burdensome treatments. This could mean a significant improvement in the quality of life for AIH patients, as well as a reduction in the long-term complications associated with the disease.
However, the landscape of Autoimmune Hepatitis treatment is evolving rapidly, offering new hope and possibilities for those affected by this challenging condition. As research continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative and effective treatments to emerge in the near future.
Conclusion
Living with Autoimmune Hepatitis can be challenging, but with the right treatment and support, patients can lead fulfilling lives. We encourage individuals with AIH to stay informed, remain proactive in their healthcare, and foster a supportive network with healthcare providers, family, and friends. Remember, while AIH is a lifelong condition, it can be managed successfully with the right approach and determination.
In conclusion, managing Autoimmune Hepatitis involves a combination of medical treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and patient commitment. We hope this article provides valuable insights and encourages patients to actively participate in their treatment journey. Remember, effective management of AIH is a collaborative effort between the patient and the healthcare team, paving the way for a healthier and more manageable life with AIH.