Atrial Flutter Symptoms: Atrial Flutter is a cardiac arrhythmia characterized by rapid, regular heartbeats originating from the atria, the upper chambers of the heart.
This condition can lead to symptoms such as palpitations, fatigue, and shortness of breath. It’s crucial to understand the underlying causes and potential risks associated with Atrial Flutter for effective management and treatment.
What is Atrial Flutter?
Atrial Flutter is a common cardiac condition characterized by a rapid and regular heartbeat. Unlike a normal heartbeat, where the atria (upper chambers of the heart) and ventricles (lower chambers) work in harmony, atrial flutter involves a rapid circuit of electrical impulses in the atria. This causes them to beat faster than the ventricles, leading to an irregular and often fast overall heart rhythm.
Definition and Explanation of Atrial Flutter
Atrial flutter is defined as an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia) originating in the atria. It is distinguished by a rapid, regular rhythm that can reach up to 300 beats per minute in the atria, while the ventricles typically respond at a slower rate. This condition results from a disruption in the heart’s electrical system, causing the atria to contract rapidly and in a synchronized manner, which is different from the normal, sequential contraction of the heart muscles.
In atrial flutter, the electrical impulses circulate in an organized, predictable pattern, which is why the rhythm, although fast, remains regular. This condition can cause symptoms like palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and sometimes, it can be asymptomatic, meaning people might not experience any noticeable symptoms.
Distinction Between Atrial Flutter and Other Cardiac Conditions
Atrial Flutter vs. Atrial Fibrillation:
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): In AFib, the electrical impulses are disorganized, leading to a rapid and irregular heart rhythm. The atria quiver rather than contract effectively, which can lead to blood clots, stroke, and other heart-related complications.
- Atrial Flutter: In contrast, atrial flutter involves a single electrical circuit that moves in an organized, circular pattern within the atria, causing a more regular and less chaotic rhythm than AFib.
It’s important to differentiate between atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation, as their treatments and implications can differ. While both conditions share some common risk factors like high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes, their management strategies may vary. Atrial flutter, due to its regular rhythm, can sometimes be easier to control or convert to a normal rhythm through treatments like medication, electrical cardioversion, or catheter ablation.
However, understanding the nuances between atrial flutter and other cardiac conditions like atrial fibrillation is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment. It’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional if you experience any symptoms or have concerns about your heart health.
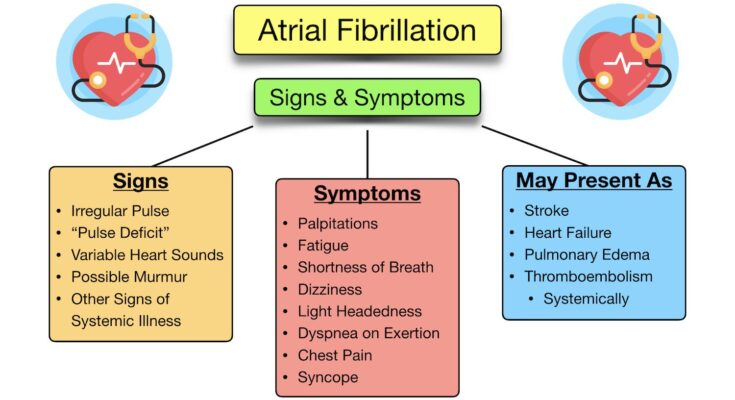
Symptoms of Atrial Flutter
Understanding these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management.
Common Symptoms of Atrial Flutter
1. Rapid Heartbeat (Palpitations): One of the most noticeable symptoms of atrial flutter is a fast and regular heart rate, often described as palpitations. This can feel like a fluttering in the chest or as if the heart is racing.
2. Shortness of Breath: Individuals may experience difficulty breathing, especially during physical activities or even at rest in more severe cases. This occurs because the heart cannot effectively pump blood, reducing oxygen delivery to the body.
3. Fatigue and Weakness: Due to inefficient blood circulation, those suffering from atrial flutter often feel unusually tired or weak, impacting their daily activities and quality of life.
4. Dizziness or Light-headedness: A decrease in blood flow to the brain, caused by the irregular heartbeat, can result in feelings of dizziness or faintness.
5. Chest Pain or Discomfort: Some people may experience chest pain or discomfort, which should always be taken seriously as it could indicate a more severe cardiac issue.
6. Anxiety: The physical sensations of atrial flutter, like a pounding heart, can lead to feelings of anxiety or panic, especially if the person is unaware of their heart condition.
Impact on Health
The symptoms of atrial flutter, while not always life-threatening, can significantly affect a person’s daily life. They can lead to a reduced ability to exercise, perform physical tasks, or even carry out routine activities without discomfort. In the long term, untreated atrial flutter can lead to more serious health issues such as heart failure, stroke, or other heart-related complications.
Recognizing these symptoms early and consulting with a healthcare provider can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment. Treatments may include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures like cardioversion or ablation to restore normal heart rhythm. Early intervention can significantly improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of serious complications associated with atrial flutter.
Causes of Atrial Flutter: An In-Depth Analysis
It’s essential to understand the causes and risk factors of atrial flutter to manage and prevent it effectively.
Primary Causes of Atrial Flutter
- Heart-Related Conditions: The primary cause of atrial flutter is often related to other heart conditions. These include high blood pressure, heart attack, and heart failure. These conditions can alter the heart’s structure or function, leading to atrial flutter.
- Surgical Procedures: Heart surgery can sometimes lead to atrial flutter. The procedure itself or post-surgical scarring in the heart can disrupt normal electrical signals.
- Thyroid Disorders: Overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) can increase the risk of atrial flutter by affecting the heart’s rhythm.
- Chronic Lung Diseases: Diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can put extra strain on the heart, potentially leading to atrial flutter.
- Excessive Alcohol Use: Long-term heavy drinking can affect heart health and is a known risk factor for atrial flutter.
Risk Factors Contributing to Atrial Flutter
- Age: The risk of atrial flutter increases with age, particularly in individuals over 60.
- Heart Disease History: Individuals with a history of heart disease or heart-related surgeries are at a higher risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, high alcohol consumption, and obesity can increase the likelihood of developing atrial flutter.
- Diabetes: This condition, especially when poorly controlled, can increase the risk of atrial flutter due to its impact on heart health.
- High Blood Pressure: Uncontrolled high blood pressure can lead to heart damage, which may trigger atrial flutter.
Understanding the causes and risk factors of atrial flutter is crucial for both prevention and management. Lifestyle changes, regular medical check-ups, and managing underlying conditions can significantly reduce the risk of developing this heart rhythm disorder. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment options.
Diagnosis of Atrial Flutter: Understanding the Process
Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for healthcare professionals and patients alike. This article provides an overview of the steps involved in diagnosing atrial flutter, highlighting the importance of early recognition of symptoms for timely intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms: The First Step in Diagnosis
The journey to diagnosing atrial flutter begins with symptom recognition. Common symptoms include palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue, and sometimes dizziness or fainting. These symptoms, while not always specific to atrial flutter, should prompt further investigation.
Diagnostic Tests for Atrial Flutter
Once atrial flutter is suspected based on symptoms, several tests are conducted to confirm the diagnosis:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This is the most crucial test for atrial flutter diagnosis. An ECG records the electrical activity of the heart and can identify the characteristic patterns of atrial flutter.
- Holter Monitor: A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record heart rhythms over a longer period, helping to detect intermittent atrial flutter.
- Echocardiogram: This ultrasound test provides images of the heart’s structure and function, which can indicate underlying conditions contributing to atrial flutter.
- Blood Tests: While not diagnostic for atrial flutter itself, blood tests can help rule out thyroid disorders or other conditions that may be related to the arrhythmia.
- Stress Test: Sometimes used to observe the heart’s activity during exercise, which can bring out heart rhythm abnormalities not present at rest.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of atrial flutter is vital for several reasons:
- Preventing Complications: Untreated atrial flutter can lead to serious complications, including stroke and heart failure.
- Effective Management: Early diagnosis allows for timely management, which can include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures like cardioversion or ablation.
- Improving Quality of Life: Proper treatment following early diagnosis can significantly improve symptoms and overall quality of life.
Atrial flutter diagnosis is a multi-step process that starts with recognizing symptoms and leads to a range of diagnostic tests. Early detection and diagnosis are key to effective management, reducing the risk of complications and enhancing the patient’s quality of life. If you experience symptoms suggestive of atrial flutter, consult your healthcare provider promptly for an evaluation.
Impact of Atrial Flutter on Overall Health
Atrial flutter, a type of heart rhythm disorder, poses significant risks to cardiovascular health. This condition, characterized by a rapid heart rate, can lead to various complications if not properly managed.
Understanding Atrial Flutter and Cardiovascular Health
Atrial flutter occurs when the upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat too quickly, causing an irregular heart rhythm. This can impede efficient blood flow and may result in palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue. In the cardiovascular system, this irregular rhythm can strain the heart muscle, leading to decreased cardiac efficiency.
The Long-Term Health Implications
The long-term effects of unmanaged atrial flutter are considerable. It can increase the risk of stroke, as the irregular heartbeat can lead to blood clots, which may travel to the brain. Moreover, the condition can exacerbate or lead to heart failure, where the heart is unable to pump blood effectively. This increased workload on the heart can result in chronic fatigue and reduced physical capability.
Importance of Early Intervention
Early diagnosis and treatment of atrial flutter are crucial. Effective management strategies can include medications, lifestyle changes, or procedures like cardioversion or ablation. These interventions aim to restore normal heart rhythm, improve blood flow, and reduce the risks associated with atrial flutter.
Atrial flutter is not just a transient cardiac issue; it can have profound impacts on overall health, particularly the cardiovascular system. Understanding its potential complications underscores the importance of prompt and effective treatment. For individuals with atrial flutter, regular medical check-ups and adherence to treatment plans are essential for maintaining heart health and overall well-being.
Treatment Options for Atrial Flutter
The condition, characterized by rapid heartbeats in the atria, can lead to significant health complications if not treated appropriately. In this article, we explore the various treatment options available for atrial flutter, emphasizing the importance of personalized medical consultation.
Overview of Atrial Flutter Treatments
- Medications: Patients with atrial flutter are often prescribed medications to control the heart rate and rhythm. These may include beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and antiarrhythmic drugs. Medications can help manage symptoms and prevent complications but should be used under a doctor’s supervision due to potential side effects.
- Electrical Cardioversion: In some cases, a procedure called electrical cardioversion is used to restore normal heart rhythm. This treatment involves delivering a controlled electric shock to the heart under anesthesia, which resets the heart’s rhythm.
- Catheter Ablation: A more long-term solution, catheter ablation, involves destroying the tissue causing abnormal electrical signals. This minimally invasive procedure has a high success rate and is often recommended for recurrent atrial flutter.
- Lifestyle Changes: Alongside medical treatments, lifestyle changes can significantly impact the management of atrial flutter. These include regular exercise, a healthy diet, avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine, and managing stress levels.
The Importance of Medical Consultation
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Every individual’s case of atrial flutter is unique, making personalized treatment plans crucial. A healthcare professional can assess the specific needs and health status of the patient to recommend the most effective treatment strategy.
- Regular Monitoring and Adjustments: Treatment for atrial flutter may require regular monitoring and adjustments. This ensures the most effective management of the condition and minimizes potential risks or side effects.
- Addressing Underlying Causes: It’s essential to address any underlying health issues contributing to atrial flutter. A medical professional can identify these factors and incorporate them into the treatment plan.
Atrial flutter, while a serious medical condition, can be effectively managed with the right combination of treatments. It’s vital for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a tailored treatment plan that addresses their specific needs. Regular medical consultations ensure that the treatment remains effective and responsive to changes in the patient’s condition.
Prevention and Management of Atrial Flutter: Essential Tips and Lifestyle Changes
By understanding and implementing certain lifestyle changes and habits, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of developing atrial flutter or manage its symptoms more effectively. This section provides essential tips and guidance for those seeking to improve their heart health and prevent atrial flutter.
Lifestyle Changes for Heart Health
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is crucial. Avoid excessive intake of caffeine, alcohol, and foods high in sugar and saturated fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, swimming, or cycling, can strengthen the heart and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as obesity is a significant risk factor for atrial flutter.
- Stress Management: High stress levels can adversely affect heart health. Techniques like yoga, meditation, and mindfulness can be beneficial in managing stress.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for many heart conditions, including atrial flutter. Quitting smoking can drastically improve heart health.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can trigger atrial flutter episodes. It’s advisable to limit alcohol or avoid it altogether.
- Regular Health Check-Ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider for heart health assessments can help in early detection and management of potential issues.
Managing Atrial Flutter Symptoms
If you are already experiencing atrial flutter, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage the condition. This might include:
- Medication: Depending on your situation, your doctor might prescribe medication to control heart rate, rhythm, or reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Alongside medical treatment, the lifestyle changes mentioned above are equally important.
- Monitoring Heart Rhythm: Regular monitoring of your heart rhythm, sometimes with the help of devices like a Holter monitor, can be crucial in managing atrial flutter.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes and habits, individuals can play a significant role in preventing atrial flutter or managing its symptoms. Remember, a healthy heart requires a lifelong commitment to good habits and regular healthcare consultation. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized advice and treatment plans.
FAQs About Atrial Flutter: Understanding Symptoms and Causes
1. What is Atrial Flutter?
Atrial Flutter is a heart condition characterized by a rapid heartbeat, often caused by irregular electrical signals in the heart’s upper chambers. This condition can lead to various symptoms and requires medical attention.
2. What are the Common Symptoms of Atrial Flutter?
Symptoms of atrial flutter can vary, but often include palpitations, shortness of breath, anxiety, fatigue, and sometimes dizziness or fainting. It’s important to consult a healthcare provider if these symptoms are experienced.
3. How is Atrial Flutter Different from Atrial Fibrillation?
While both conditions involve irregular heart rhythms, atrial flutter is typically more organized and less chaotic than atrial fibrillation. The diagnosis and treatment for each condition can differ significantly.
4. What Causes Atrial Flutter?
Atrial Flutter can be caused by various factors, including heart disease, high blood pressure, diabetes, thyroid disorders, and excessive alcohol or caffeine consumption. Stress and certain medications can also trigger this condition.
5. Can Lifestyle Changes Help Manage Atrial Flutter?
Yes, lifestyle changes like regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding excessive alcohol and caffeine, and managing stress can help in controlling atrial flutter. However, these should complement medical treatments prescribed by a doctor.
6. Is Atrial Flutter a Serious Condition?
Atrial Flutter can be serious, especially if left untreated, as it may lead to more severe heart conditions or stroke. Prompt medical diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing this condition effectively.
7. How is Atrial Flutter Diagnosed?
Atrial Flutter is typically diagnosed using an electrocardiogram (ECG), which records the electrical activity of the heart. Additional tests, like echocardiograms or stress tests, might also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
8. What are the Treatment Options for Atrial Flutter?
Treatment options for atrial flutter include medications to control heart rate and rhythm, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, procedures like catheter ablation. The treatment plan depends on the individual’s overall health and the severity of the condition.
9. Can Atrial Flutter be Prevented?
While not all cases of atrial flutter can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and managing underlying conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes can reduce the risk.
10. Should I See a Doctor if I Suspect Atrial Flutter?
Yes, if you experience symptoms like heart palpitations or shortness of breath, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to managing atrial flutter effectively.
Conclusion
We strongly encourage anyone experiencing these symptoms to seek medical advice promptly. Consulting a healthcare professional not only brings peace of mind but also ensures that you receive the correct diagnosis and treatment plan. Early detection and management of atrial flutter are key to preventing potential complications and maintaining a healthy heart.
Remember, your health is your most valuable asset. By staying informed and proactive about conditions like atrial flutter, you take a crucial step towards safeguarding it. If you’re experiencing any symptoms or have concerns about your heart health, don’t hesitate to reach out to a medical professional. Taking action today can make a significant difference in your health journey tomorrow.