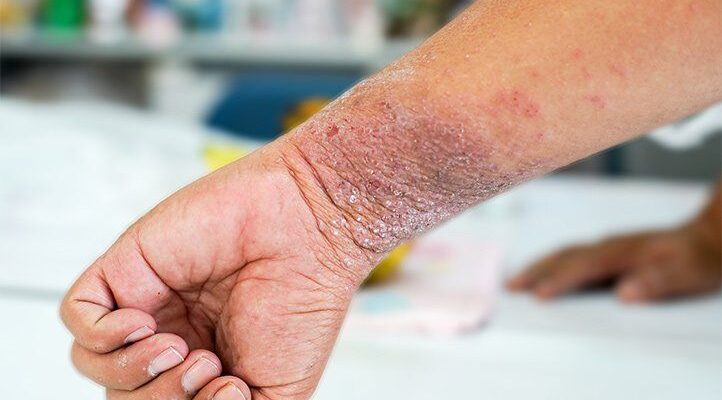
Atopic Dermatitis (eczema) Symptoms: Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition that affects millions worldwide.
Characterized by itchy, inflamed, and often red skin, it is more than just a surface-level concern; it significantly impacts the quality of life of those who suffer from it.
This comprehensive guide delves into the symptoms, causes, and insights into managing this condition effectively.
What is Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)?
Atopic Dermatitis, commonly known as Eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and sometimes red or scaly patches of skin. It’s a type of eczema that typically arises in early childhood but can also develop in adulthood. This condition is often associated with other atopic disorders, such as asthma or hay fever. The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is unknown, but it’s believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The skin’s barrier function is compromised, leading to increased sensitivity and an immune system response that causes the characteristic symptoms.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics Affected
Atopic Dermatitis affects a significant portion of the global population, with varying prevalence rates across different regions and age groups. Studies indicate that about 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide suffer from this condition. The prevalence of atopic dermatitis has been increasing over the past decades, especially in industrialized countries, suggesting environmental factors play a role.
There’s a higher incidence in children, often developing before the age of 5. Many children outgrow the condition by their teenage years, but some continue to have symptoms into adulthood. There’s also a noted genetic component, as individuals with a family history of atopic conditions are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis.
This condition affects all ethnicities, but prevalence rates may vary. It’s equally common in males and females. Environmental factors such as urban living, pollution, climate, and lifestyle can influence the development and severity of atopic dermatitis.
This skin condition significantly impacts the quality of life due to its symptoms and the need for ongoing management. Understanding atopic dermatitis is crucial for effective treatment and improving the lives of those affected by this chronic skin disorder.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis: Understanding the Signs
We aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms associated with atopic dermatitis, focusing on how they can vary across different age groups and highlighting common triggers and environmental factors.
Detailed Description of Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis manifests through a variety of symptoms, the most common being:
- Dry Skin: The skin tends to be dry, scaly, and itchy.
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas often become red and inflamed.
- Itching: This is a hallmark symptom, ranging from mild to severe.
- Rashes: Rashes typically appear on the face, inside the elbows, behind the knees, and on the hands and feet.
- Cracking and Oozing: In severe cases, the skin may crack and ooze.
Symptoms Across Different Age Groups
The presentation of atopic dermatitis symptoms can vary significantly across age groups:
- Infants (under 2 years): Symptoms often include rashes on the scalp and cheeks, which can bubble up and ooze fluid.
- Children (2 years to puberty): Rashes commonly appear in the elbow and knee creases. The skin may become thicker and develop knots.
- Adults: In adults, the rashes are more commonly found on the face, neck, and around the eyes. Skin infections are more frequent in adult cases.
Common Triggers and Environmental Factors
Understanding the triggers and environmental factors that exacerbate atopic dermatitis is crucial. These include:
- Irritants: Soaps, detergents, shampoos, and disinfectants can irritate the skin.
- Allergens: Dust mites, pets, pollens, and mold can trigger symptoms.
- Foods: Certain foods like nuts and dairy can exacerbate the condition.
- Stress: Emotional stress can worsen symptoms.
- Climate: Dry or cold weather can lead to skin dryness and aggravate the condition.
Recognizing the symptoms of atopic dermatitis and understanding how they vary across different age groups, along with being aware of common triggers, is essential for effective management. If you suspect you or a loved one may have atopic dermatitis, consulting a healthcare professional is recommended.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
Understanding its causes is crucial for effective management and treatment. This article delves into the primary causes of atopic dermatitis, providing insights into genetic factors, environmental triggers, and the role of the immune system.
Genetic Factors and Hereditary Aspects
Atopic dermatitis has a strong genetic component, often running in families. Research indicates that individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop atopic dermatitis. Specific genes responsible for skin barrier function, such as the filaggrin gene, play a significant role in the development of this condition. When these genes are mutated or dysfunctional, the skin’s ability to act as a barrier is compromised, leading to increased sensitivity and the likelihood of eczema.
Environmental Triggers and Allergens
Environmental factors significantly influence the onset and exacerbation of atopic dermatitis. Common triggers include:
- Irritants: Everyday substances like soaps, detergents, and shampoos can irritate sensitive skin and worsen eczema.
- Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, dust mites, and certain foods can trigger allergic reactions, contributing to atopic dermatitis flare-ups.
- Climate: Extreme temperatures, dry air, and humidity changes can affect the skin’s moisture levels, exacerbating eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress doesn’t directly cause atopic dermatitis but can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Understanding and avoiding these triggers can help manage atopic dermatitis more effectively.
The Role of Immune System Dysfunction
Atopic dermatitis is partly an immune-mediated condition. The immune system in individuals with atopic dermatitis often overreacts to harmless substances, leading to inflammation and eczema symptoms. This hyperactive response may result from a combination of genetic predispositions and environmental factors. Recent studies also suggest that the immune system’s dysfunction in atopic dermatitis may involve an imbalance of certain cells and proteins, such as T-cells and cytokines, responsible for immune responses and inflammation.
Atopic dermatitis is a multifactorial condition with genetic, environmental, and immunological influences. Recognizing and understanding these factors are pivotal in effectively managing and treating atopic dermatitis, improving the quality of life for those affected. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals, personalized treatment plans, and lifestyle adjustments are key to controlling this chronic skin condition.
Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis is crucial for effective management and treatment. This comprehensive guide outlines the key steps involved in diagnosing this condition, emphasizing the importance of medical history, physical examination, and differentiating it from other skin conditions. We also highlight when it is essential to see a healthcare professional.
1. Medical History and Physical Examination
The first step in diagnosing atopic dermatitis involves a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical examination. Here’s what to expect:
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, family history of allergies or skin conditions, and any factors that may aggravate your skin. This information helps in understanding the pattern and triggers of your condition.
- Physical Examination: The doctor will examine the affected skin areas, noting the appearance, location, and nature of the rash. Atopic dermatitis typically affects the face, inside of the elbows, and behind the knees, but can occur anywhere on the body.
2. Differentiating from Other Skin Conditions
Atopic dermatitis can be confused with other skin conditions like psoriasis, contact dermatitis, or seborrheic dermatitis. Here are key differentiators:
- Texture and Location: Unlike psoriasis, atopic dermatitis rashes are generally more itchy than scaly and appear in different locations.
- Reaction Pattern: Contact dermatitis is usually localized to the area of contact with an irritant, whereas atopic dermatitis is more widespread.
- Age of Onset: Atopic dermatitis often starts in childhood, while conditions like seborrheic dermatitis are more common in adults.
3. When to See a Healthcare Professional
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional if:
- Persistent Symptoms: If the rash doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments or if symptoms worsen.
- Infection Signs: If there are signs of infection like fever, red streaks, or pus.
- Impact on Daily Life: If the condition is affecting sleep or daily activities.
Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve the quality of life for those with atopic dermatitis. Remember, while online resources provide valuable information, they cannot replace professional medical advice.
Complications Associated with Atopic Dermatitis
Understanding these complications is crucial for managing the condition effectively. Here we delve into the primary concerns associated with atopic dermatitis.
Risk of Infections
Atopic dermatitis often compromises the skin’s barrier function, making it more susceptible to infections. Bacterial infections, such as those caused by Staphylococcus aureus, are common in areas affected by eczema. Viral infections like herpes simplex can also pose a significant risk, leading to more severe conditions such as eczema herpeticum. It’s vital for individuals with atopic dermatitis to maintain good skin hygiene and seek prompt treatment for any signs of infection.
Impact on Quality of Life and Mental Health
Living with atopic dermatitis can be challenging, affecting not just the skin but also the emotional and psychological well-being of an individual. The constant itchiness and discomfort can disrupt sleep, lead to decreased concentration, and impact daily activities. This ongoing struggle often leads to stress, anxiety, and in some cases, depression. It’s important for healthcare providers to address these mental health aspects alongside the physical symptoms of the condition.
Potential for Long-term Skin Damage
Chronic atopic dermatitis can lead to long-term skin damage, including scarring and changes in skin color. Repeated scratching and inflammation can cause the skin to thicken, a condition known as lichenification. This can make the skin leathery and more prone to further irritation. Early and effective management of atopic dermatitis is crucial to minimize these long-term effects and maintain healthy skin.
However, while atopic dermatitis primarily affects the skin, its impact can be far-reaching, affecting various aspects of an individual’s life. Awareness and proper management of these complications are key to improving the lives of those suffering from this condition.
Management and Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Effective management of this condition involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and staying abreast of emerging research. Here, we explore these options in detail.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
- Moisturizing Regularly: Keeping the skin hydrated is crucial. Using fragrance-free moisturizers immediately after bathing helps lock in moisture.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and avoiding irritants that trigger flare-ups, such as certain fabrics, soaps, or foods, can significantly reduce symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate eczema. Techniques like meditation, yoga, or even counseling can be beneficial.
- Gentle Skincare: Using mild soaps and lukewarm water for bathing, followed by patting the skin dry and applying moisturizer, can soothe the skin.
- Wearing Comfortable Clothing: Soft, breathable fabrics like cotton can prevent skin irritation.
Medical Treatments and Therapies
- Topical Medications: Corticosteroid creams and ointments are commonly prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching.
- Systemic Medications: For severe cases, oral medications or injectables, like cyclosporine or biologics, may be recommended.
- Phototherapy: Exposure to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light can improve symptoms in some cases.
- Wet Wrap Therapy: This involves applying topical corticosteroids and then covering the area with wet bandages to enhance the medication’s effectiveness and hydration.
Emerging Research and Future Prospects
- New Biologic Drugs: Research is focused on developing biologic drugs that target specific parts of the immune system involved in atopic dermatitis.
- Microbiome Treatments: Understanding the skin’s microbiome may lead to new treatments that restore healthy bacteria balance.
- Gene Therapy: Advances in understanding the genetic factors of eczema could pave the way for gene-editing treatments.
- Holistic and Integrative Approaches: Research is also exploring the role of diet, supplements, and alternative therapies in managing eczema.
By combining these strategies, individuals with atopic dermatitis can manage their symptoms more effectively. Remember, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to tailor the treatment plan to your specific needs.
Prevention Strategies for Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Managing and preventing atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, requires a holistic approach that encompasses lifestyle adjustments, skincare routines, and environmental controls. By implementing the following strategies, individuals can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of eczema flare-ups.
Tips for Reducing Flare-Ups
- Moisturize Regularly: Keeping skin hydrated is crucial. Use a fragrance-free, hypoallergenic moisturizer right after bathing and throughout the day.
- Gentle Skin Care: Choose mild, unscented soaps and avoid scrubbing your skin harshly. Pat your skin dry instead of rubbing.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and steer clear of irritants like certain fabrics, soaps, and stress, which can worsen eczema.
- Wear Comfortable Clothing: Opt for soft, breathable fabrics like cotton. Avoid wool and synthetic materials that can irritate the skin.
- Control Scratching: Keep nails short and consider wearing gloves at night to prevent scratching in your sleep.
Skincare Routines and Products
- Selecting the Right Products: Look for skincare products labeled as “for sensitive skin” or “non-comedogenic.” Avoid those containing alcohol, fragrances, or dyes.
- Bathing Practices: Limit showers or baths to 10-15 minutes and use lukewarm water. Apply moisturizer while your skin is still damp.
- Patch Testing: Before using a new product, do a patch test on a small area of skin to ensure it doesn’t cause a reaction.
Importance of Environmental Control
- Humidity Control: Maintain a comfortable level of humidity in your home to prevent your skin from becoming too dry.
- Dust Reduction: Regularly clean your home to reduce dust mites and pet dander, which can trigger eczema.
- Filter Air: Consider using an air purifier to remove potential irritants from your indoor environment.
By adhering to these guidelines, individuals with atopic dermatitis can better manage their condition, leading to a significant improvement in their quality of life. Remember, while these tips can help, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment.
FAQ Section: Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic Dermatitis, often known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed skin. It’s common in children but can occur at any age. It’s part of a group of diseases that includes hay fever and asthma and often runs in families.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis?
The exact cause of Atopic Dermatitis is unknown, but it’s believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Triggers can include certain soaps, fabrics, allergens, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Is Atopic Dermatitis Contagious?
No, Atopic Dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from someone nor pass it to others.
How Is Atopic Dermatitis Treated?
Treatment aims to relieve itching and reduce inflammation. This includes moisturizing skin care, avoiding triggers, and using prescribed medications like topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors. In severe cases, systemic treatments or phototherapy may be recommended.
Can Diet Affect Atopic Dermatitis?
While diet doesn’t directly cause Atopic Dermatitis, certain foods may trigger symptoms in some people. It’s essential to notice any food-related flare-ups and discuss them with a healthcare provider.
Can Atopic Dermatitis Be Cured?
Currently, there is no cure for Atopic Dermatitis, but many people see their symptoms improve with age. Effective management can significantly reduce symptoms and improve quality of life.
How Can I Prevent Atopic Dermatitis Flare-Ups?
Preventing flare-ups involves moisturizing regularly, avoiding known triggers, and following your healthcare provider’s advice. Identifying and managing stress and allergens also plays a crucial role.
When Should I See a Doctor for Atopic Dermatitis?
You should consult a healthcare provider if you or your child has symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis, especially if it interferes with daily life or doesn’t improve with over-the-counter treatments.
Conclusion
Dealing with Atopic Dermatitis can be challenging, but it’s important to remember that you’re not alone. We strongly encourage our readers to seek professional medical advice.
Dermatologists and healthcare providers can offer tailored treatment plans and guidance to manage symptoms effectively. Remember, early intervention can make a significant difference in your journey towards healthier skin.
Stay informed, stay hopeful, and take the step towards better skin health today.