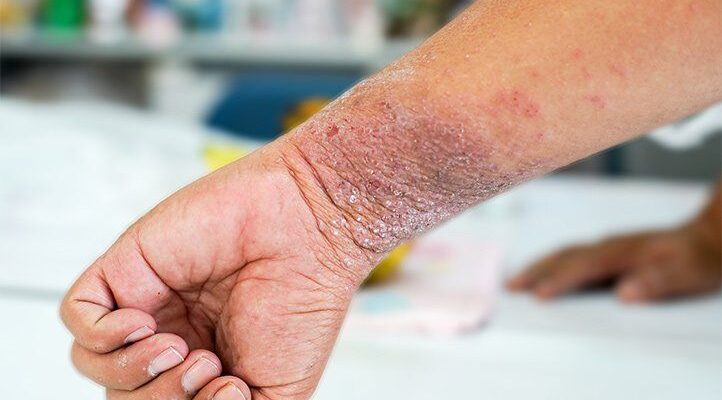
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment: Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. Affecting millions worldwide, this condition can significantly impact quality of life.
Our comprehensive guide provides in-depth insights into the diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis, aiming to offer relief and improve daily living.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy skin. This condition often appears in early childhood and may persist into adulthood. It is part of a group of diseases called atopy, which typically includes asthma and hay fever. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious and varies in severity from person to person. The exact cause remains unclear, but it’s believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. It’s often linked to an overactive immune system that responds aggressively to irritants.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Atopic Dermatitis
The most common symptoms of atopic dermatitis include:
- Dry, itchy skin, which can become red and inflamed when scratched.
- Patches of skin that are darker or lighter in color.
- Small, raised bumps that may leak fluid when scratched.
- Thickened, cracked, or scaly skin.
- Sensitive skin that can be irritated by soaps, detergents, and other substances.
These symptoms can fluctuate in severity and may be triggered or worsened by certain environmental factors, like allergens, stress, or weather changes.
Statistics on Prevalence and Demographics
Atopic dermatitis affects a significant portion of the population globally. It is estimated that:
- Approximately 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide have atopic dermatitis.
- The condition is more common in children, often developing before the age of five.
- There is a higher prevalence in urban areas and developed countries.
- Family history of atopy increases the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
- It affects males and females equally and can occur in people of all races and ethnic backgrounds.
Understanding atopic dermatitis is crucial for managing symptoms and improving quality of life for those affected. Early diagnosis and treatment can help control flare-ups and reduce the impact of the condition.
Causes and Risk Factors of Atopic Dermatitis
While the exact cause is not entirely understood, it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental elements. The skin barrier’s function is crucial in this context, as it typically protects against irritants and allergens. However, in individuals with atopic dermatitis, this barrier is weakened, leading to increased sensitivity and reaction to external factors.
Identifying Common Risk Factors
Several risk factors have been associated with the development of atopic dermatitis. These include:
- Genetic predisposition: A family history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or allergies significantly increases the risk.
- Environmental triggers: Exposure to certain irritants, such as soaps, detergents, dust mites, and pollen, can exacerbate symptoms.
- Climate and temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, along with low humidity levels, can trigger flare-ups.
- Skin infections: Bacterial or viral skin infections can worsen the condition.
- Stress: Emotional stress doesn’t directly cause atopic dermatitis but can trigger or exacerbate symptoms.
The Role of Genetics and Environment
Research has shown a strong genetic component in atopic dermatitis. Specific genes that affect the skin’s barrier function are often altered in people with this condition. However, genetics alone doesn’t explain its occurrence. Environmental factors play a crucial role in triggering the condition in genetically predisposed individuals. This interplay between genes and environment makes each case of atopic dermatitis unique, requiring personalized treatment and management approaches.
Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Guide
Atopic dermatitis, a common and often chronic skin condition, requires accurate diagnosis for effective management. This section delves into the diagnostic procedures for atopic dermatitis, highlighting their importance in identifying this condition.
Key Diagnostic Procedures
- Clinical Evaluation: A thorough examination by a healthcare professional, typically focusing on the history of symptoms and physical signs.
- Skin Patch Testing: Used to rule out allergic reactions that might mimic atopic dermatitis.
- Blood Tests: May be conducted to check for markers of inflammation or allergies.
- Skin Biopsy: Rarely required, but can be helpful in uncertain cases to differentiate from other skin disorders.
The Role of Dermatologists in Diagnosing Atopic Dermatitis
Dermatologists play a pivotal role in diagnosing atopic dermatitis. Their expertise in skin conditions enables them to:
- Conduct Detailed Assessments: Including patient history and physical examination.
- Interpret Test Results: Accurately distinguishing atopic dermatitis from other skin conditions.
- Develop a Management Plan: Tailored to the patient’s specific needs.
Differentiating Atopic Dermatitis from Other Skin Conditions
It’s crucial to distinguish atopic dermatitis from other skin conditions such as psoriasis, contact dermatitis, or seborrheic dermatitis. This differentiation is based on:
- Appearance of Skin Lesions: Location, shape, and characteristics.
- Symptom Profile: Including itchiness, duration, and triggers.
- Response to Treatments: How the skin reacts to various therapies.
However, a comprehensive diagnostic approach, primarily led by dermatologists, is essential in accurately identifying and managing atopic dermatitis. This ensures that patients receive the most effective and appropriate treatment for their specific condition.
Conventional Treatment Options for Atopic Dermatitis
While there is no cure, effective management is possible through various conventional treatment options. Understanding these treatments can help individuals make informed choices about their skin health.
Medications for Atopic Dermatitis
1. Topical Medications: The first line of treatment often includes topical medications. These are applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and itchiness.
- Corticosteroids: These creams or ointments vary in strength and help in reducing inflammation and itchiness.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Options like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are used for sensitive areas and work by suppressing the immune system’s response.
- Moisturizers: Essential for maintaining the skin barrier, they help in reducing dryness and itching.
2. Systemic Medications: In more severe cases, oral or injected medications that work throughout the body may be prescribed.
- Corticosteroids: Pills or injections for short-term control in severe cases.
- Immunosuppressants: Medications like cyclosporine, methotrexate, or mycophenolate mofetil are used to suppress the immune system.
- Biologic Drugs: Newer options like dupilumab target specific parts of the immune system and are used for long-term control.
Phototherapy and Clinical Treatments
1. Phototherapy: This involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural sunlight or artificial UV light. It helps in reducing itch and inflammation and is often used for moderate to severe cases.
2. Other Clinical Treatments: Include:
- Wet Wrap Therapy: Involves wrapping the affected area with wet bandages after applying medication to boost effectiveness and hydration.
- Bleach Baths: Diluted bleach baths may reduce the risk of skin infections, a common complication of atopic dermatitis.
Understanding these treatment options is crucial for anyone managing atopic dermatitis. Always consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your individual needs.
Emerging Treatments in Atopic Dermatitis: An Insight into the Future
Now, lets provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging treatments in atopic dermatitis, delving into the latest research findings and the potential future treatments that are currently under development.
1. Insight into New and Upcoming Treatment Methods:
- Biologic Therapies: Biologics are a new class of drugs that target specific parts of the immune system. Dupilumab, the first biologic approved for atopic dermatitis, has shown great promise in reducing symptoms. Research is ongoing to develop more biologics with different targets.
- Topical Treatments: Advances in topical treatments, such as crisaborole and tapinarof, offer improved efficacy with fewer side effects. These new agents work by modulating the skin’s immune response and restoring the skin barrier.
- JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors are oral medications showing effectiveness in reducing inflammation and itching in atopic dermatitis patients. Ongoing trials are exploring their long-term efficacy and safety.
2. Discussion of Recent Research Findings:
- Microbiome and Atopic Dermatitis: Emerging research suggests that the skin microbiome plays a crucial role in atopic dermatitis. Modifying the skin microbiome could be a potential therapeutic avenue.
- Genetic Factors: Studies are increasingly focusing on the genetic aspects of atopic dermatitis, which might lead to personalized treatment strategies based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
3. Potential Future Treatments:
- Vaccine Development: There is ongoing research into developing vaccines that could potentially prevent or treat atopic dermatitis.
- Cell-based Therapies: Innovations in cell-based therapies, including stem cell treatments, are being explored for their potential to provide long-term relief from atopic dermatitis symptoms.
This field is rapidly evolving, with new discoveries and treatment modalities offering hope to those suffering from atopic dermatitis. Staying informed about these advancements is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike, as they hold the key to more effective and personalized treatments in the near future.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies for Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Effective management of this condition heavily relies on self-care practices. These practices not only alleviate symptoms but also prevent exacerbation of the condition. Understanding and incorporating self-care routines in daily life is crucial for those living with eczema.
Adopting Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies for Atopic Dermatitis Relief
- Moisturize Regularly: Applying moisturizer several times a day helps in maintaining the skin’s barrier. Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products designed for sensitive skin.
- Choose Gentle Skin Care Products: Use mild, unscented soaps and detergents. Harsh chemicals can irritate eczema-prone skin, so it’s essential to select products wisely.
- Avoid Triggers: Common irritants like dust, pollen, and certain fabrics can trigger eczema flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is a significant step towards managing the condition.
- Maintain a Cool and Humid Environment: Extreme temperatures and dry air can worsen eczema. Using a humidifier and keeping the environment cool can help soothe the skin.
- Wear Soft, Breathable Clothing: Choose clothing made of soft, natural fibers like cotton. Avoid tight-fitting or rough-textured fabrics.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate eczema symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
- Dietary Considerations: While diet may not directly impact eczema, eating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can support overall skin health.
Practical Tips for Skin Care and Reducing Irritation
- Short, Lukewarm Showers: Long, hot showers can strip the skin of its natural oils. Opt for shorter showers with lukewarm water.
- Pat Dry, Don’t Rub: After bathing, gently pat the skin dry with a soft towel instead of rubbing, which can aggravate the skin.
- Apply Moisturizer on Damp Skin: This helps to lock in moisture and keep the skin hydrated.
- Wear Gloves During Chores: Protect your hands from irritants and allergens when cleaning or doing other household tasks.
- Regular Check-ups: Regular visits to a healthcare provider can help monitor the condition and adjust treatment as needed.
Incorporating these lifestyle changes and home remedies can significantly impact the management of atopic dermatitis, leading to improved quality of life and skin health. Remember, every individual is unique, and what works for one might not work for another. It’s important to experiment and find out what best suits your skin.
Complications and Management of Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)
Atopic dermatitis, commonly known as eczema, can lead to several complications if not properly managed. These complications include:
- Skin Infections: The most common complication. Frequent scratching can break the skin, making it vulnerable to infections by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
- Sleep Problems: Itching and discomfort can disrupt sleep, leading to fatigue and reduced quality of life.
- Asthma and Hay Fever: People with atopic dermatitis often develop other allergic conditions like asthma or hay fever.
- Psychological Impact: Chronic skin conditions can lead to anxiety, depression, and a negative self-image.
Strategies for Managing and Preventing Complications
Managing atopic dermatitis effectively reduces the risk of complications. Key strategies include:
- Moisturizing Regularly: Keeping the skin moisturized helps maintain its barrier function and reduces itching.
- Avoiding Triggers: Identify and avoid irritants that worsen symptoms, like certain fabrics, soaps, or allergens.
- Medication Adherence: Use prescribed medications, such as topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors, as directed.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate eczema, so practices like meditation or yoga can be beneficial.
When to Seek Further Medical Attention
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider when:
- Symptoms Worsen: If eczema symptoms intensify or do not respond to treatment.
- Signs of Infection: Symptoms like increased redness, warmth, swelling, or oozing from the skin.
- Impact on Daily Life: When eczema significantly interferes with sleep, daily activities, or mental well-being.
Remember, effective management of atopic dermatitis is a continuous process that involves both medical treatment and lifestyle adjustments. Regular consultations with healthcare professionals are key to keeping eczema under control and preventing complications.
FAQs about Atopic Dermatitis
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis, often referred to as eczema, is a chronic skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin. It’s commonly seen in children but can affect individuals at any age.
What Causes Atopic Dermatitis?
The exact cause is unknown, but it’s believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Allergens, irritants, stress, and weather changes can trigger or worsen symptoms.
Is Atopic Dermatitis Contagious?
No, atopic dermatitis is not contagious. You cannot catch it from or transmit it to other people.
What are the Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis?
Symptoms include dry, itchy skin, red or brownish-gray patches, small, raised bumps that may leak fluid, and thickened, cracked, or scaly skin.
How is Atopic Dermatitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves examining the skin and reviewing medical history. In some cases, skin tests or blood tests are conducted to rule out other conditions.
Can Atopic Dermatitis be Cured?
There is no cure for atopic dermatitis, but treatments and self-care measures can relieve itching and prevent new outbreaks.
What Treatments are Available?
Treatment options include moisturizers, prescription topical medications, phototherapy, and in severe cases, systemic medications.
How Can I Manage My Symptoms?
Managing symptoms involves regular skin care, avoiding triggers, using prescribed medications, and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
Can Diet Affect Atopic Dermatitis?
While diet doesn’t cause atopic dermatitis, certain foods may trigger symptoms in some people. It’s important to identify and avoid these triggers.
When Should I See a Doctor?
If you notice symptoms of atopic dermatitis, or if your symptoms worsen or don’t respond to home treatments, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
In summarizing our exploration of atopic dermatitis treatments, it’s vital to highlight several key points. Firstly, effective management of this condition often requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing topical treatments, lifestyle changes, and sometimes systemic medications. Moisturizers and topical steroids frequently serve as the cornerstone of treatment, aiming to reduce skin inflammation and dryness. Furthermore, identifying and avoiding specific triggers that exacerbate symptoms is crucial in long-term management.
It’s also important to recognize that atopic dermatitis varies greatly among individuals, meaning treatments that work for one person might not be as effective for another. This variability underscores the importance of personalized treatment plans.
While this guide provides a comprehensive overview of atopic dermatitis treatments, it’s essential to remember that it cannot replace professional medical advice. Each case of atopic dermatitis is unique, and what works for one person may not be suitable for another. Therefore, we strongly encourage you to consult with healthcare professionals to devise a treatment plan that’s tailored to your specific needs and circumstances. Their expertise and guidance are invaluable in managing this often complex and persistent skin condition effectively.
References
For those seeking further information on Atopic Dermatitis and its treatments, referencing reputable sources is essential. Below are some key resources that provide additional insight and validation for the treatments discussed:
- National Eczema Association: Explore a comprehensive overview of Atopic Dermatitis, including detailed sections on treatment options, self-care tips, and the latest research. Visit their official website here.
- American Academy of Dermatology: This resource offers extensive guidance on the management and treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Find practical advice and professional recommendations here.
- PubMed Central: For peer-reviewed scientific studies and articles on the latest developments in Atopic Dermatitis treatments, PubMed is a valuable resource. Access the database here.
- Mayo Clinic: Providing patient-friendly information on symptoms, causes, and treatment options, the Mayo Clinic is a trusted source for health information. Read more about Atopic Dermatitis here.
Each of these sources is recognized for their authority and reliability in dermatology and medical information, making them excellent starting points for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of Atopic Dermatitis.