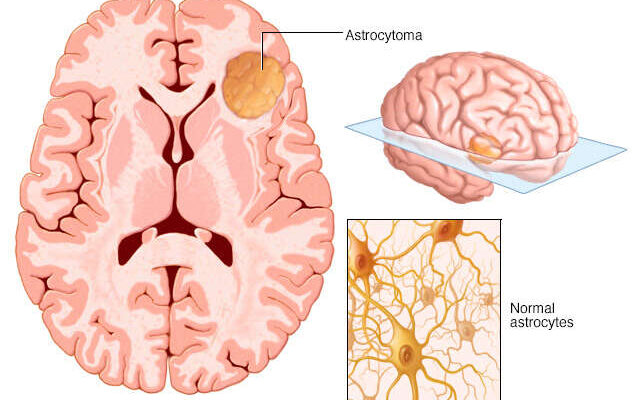
Astrocytoma Treatment: Astrocytoma, a prevalent form of brain tumor, arises from star-shaped brain cells known as astrocytes. These tumors can occur in various parts of the brain and spinal cord, affecting people of all ages.
The significance of early detection and effective treatment of astrocytomas cannot be overstated. Timely diagnosis plays a crucial role in managing these tumors, as early-stage astrocytomas are typically more responsive to treatment.
Furthermore, prompt treatment can significantly improve the quality of life and survival rates for those affected. Understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options available for astrocytoma is essential for patients and healthcare providers alike.
What is Astrocytoma?
Astrocytoma is a type of brain tumor that originates from star-shaped brain cells known as astrocytes. These cells are a part of the glial tissue which supports and nourishes neurons in the brain. Astrocytomas are classified based on their growth rate and potential to spread, with grades ranging from I to IV. The lower-grade astrocytomas (grade I and II) are typically slower-growing and less aggressive, while higher grades (III and IV, with glioblastoma being grade IV) tend to grow more rapidly and are more invasive.
Definition and Types of Astrocytoma
- Pilocytic Astrocytoma (Grade I): This is a slow-growing tumor commonly found in children and young adults. It has a relatively favorable prognosis compared to other types.
- Diffuse Astrocytoma (Grade II): These are also slow-growing but can sometimes transform into higher-grade tumors.
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma (Grade III): These tumors are more aggressive and have a higher likelihood of spreading to nearby tissue.
- Glioblastoma (Grade IV): The most aggressive form, known for rapid growth and a high degree of malignancy.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
The occurrence of astrocytomas can vary based on several factors:
- Age: Different types of astrocytomas are more common in certain age groups. For example, pilocytic astrocytomas are more prevalent in children and young adults.
- Genetic Factors: Certain genetic disorders, like Neurofibromatosis Type 1 and Turcot syndrome, can increase the risk of developing astrocytomas.
- Environmental Exposures: Although the data is not conclusive, some studies suggest a link between exposure to certain chemicals or radiation and the risk of developing brain tumors.
Understanding the epidemiology and risk factors of astrocytomas helps in early detection and effective management of the condition. It’s important for individuals to be aware of the symptoms and seek medical advice if they experience persistent headaches, seizures, or other neurological symptoms.
Symptoms and Early Signs of Astrocytoma
Recognizing these indicators is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Common Symptoms Associated with Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas can manifest through a range of symptoms, which may vary based on the tumor’s location in the brain. Here are some of the most common symptoms:
- Headaches: Frequent and persistent headaches, often worsening in the morning, are a typical symptom.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain can lead to seizures, a common sign of astrocytomas.
- Cognitive Changes: Difficulty with concentration, memory, or performing routine tasks can indicate the presence of an astrocytoma.
- Personality Changes: Alterations in personality or behavior may occur.
- Motor Symptoms: This includes weakness or paralysis in parts of the body, depending on the affected brain area.
- Speech Difficulties: Trouble with speaking or understanding language might be experienced.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision can be symptoms.
Understanding Early Warning Signs
Early detection of astrocytoma significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. Therefore, understanding and recognizing early warning signs is essential. These signs can be subtle and vary from person to person, but generally include:
- Persistent headaches that differ in pattern from usual headaches.
- Gradual onset of seizures, especially in adults with no previous history of seizures.
- Unexplained nausea or vomiting, particularly in the morning.
- Sudden or progressive changes in mental function, including confusion, difficulty concentrating, or memory lapses.
- Unexplained changes in mood, personality, or behavior.
- Gradual development of speech difficulties or understanding conversations.
- Unusual sensory experiences or loss of motor function, such as numbness or weakness in limbs.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms or early signs, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. Early intervention is key in managing astrocytoma effectively.
Diagnosing Astrocytoma: Essential Methods and Tests
Let’s provides an in-depth look at the diagnostic methods and tests essential for identifying astrocytoma, emphasizing the crucial role of medical imaging and the significance of biopsy and histological analysis.
Diagnostic Methods and Tests
Diagnosing astrocytoma typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination, focusing on neurological functions. However, the core of astrocytoma diagnosis lies in advanced testing methods:
- Neurological Exam: Checks for vision, hearing, balance, coordination, strength, and reflexes.
- Imaging Tests: Crucial for visualizing the tumor and planning treatment.
Role of Medical Imaging in Astrocytoma Diagnosis
Medical imaging plays a pivotal role in diagnosing astrocytoma:
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): The most effective imaging test for brain tumors, providing detailed images of the brain.
- CT Scan (Computed Tomography): Sometimes used when MRI is not available.
- PET Scan (Positron Emission Tomography): Helps in assessing the tumor’s activity and response to treatment.
These imaging tests not only help in detecting the tumor but also in determining its size, location, and potential impact on surrounding brain tissue.
Biopsy and Histological Analysis
A biopsy, the removal of a small tissue sample for examination, is often necessary to confirm an astrocytoma diagnosis. The process involves:
- Surgical Biopsy: Performed during surgery to remove the tumor.
- Stereotactic Biopsy: Used when the tumor is in a hard-to-reach area.
The collected tissue undergoes histological analysis, where a pathologist examines the cells under a microscope to determine the type and grade of the tumor. This analysis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Accurate diagnosis of astrocytoma is critical for effective treatment. It involves a combination of neurological examination, advanced imaging techniques, and precise biopsy and histological analysis. Understanding these methods helps in grasping the complexity and importance of diagnosing this challenging condition.
Treatment Options for Astrocytoma
Astrocytoma treatment is tailored to individual cases, depending on factors like the tumor’s size, location, and grade. A multidisciplinary team, including neuro-oncologists, neurosurgeons, and radiation oncologists, collaboratively decide the best treatment plan. The primary goals are to remove or reduce the tumor, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life.
Surgical Options and Techniques
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for astrocytoma. The objective is to remove as much of the tumor as possible without damaging critical brain areas. Advanced techniques, such as awake brain surgery and neuronavigation, have significantly improved surgical outcomes. These methods allow surgeons to precisely target the tumor while preserving healthy brain tissue.
Radiation Therapy: Procedures and Effectiveness
Radiation therapy follows surgery, especially if the tumor couldn’t be entirely removed. This treatment uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells. Techniques like conformal radiation therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) focus the radiation precisely, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Radiation therapy is effective in controlling tumor growth and reducing recurrence chances.
Chemotherapy and Targeted Drug Therapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing. It can be administered orally or intravenously, sometimes in combination with radiation therapy. Recent advancements in targeted drug therapy offer a more personalized approach. These drugs specifically target abnormalities within cancer cells, offering a potentially more effective and less toxic treatment option compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Treating astrocytoma requires a comprehensive, personalized approach. The combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy or targeted drug therapy offers the best chance for tumor control and quality of life improvement. Continuous research and technological advancements are paving the way for more effective and less invasive treatment options.
Innovations in Astrocytoma Treatment
Let’s delves into the latest advancements in astrocytoma treatment, highlighting emerging therapies and ongoing clinical trials that show promise in improving patient outcomes.
Latest Advancements in Astrocytoma Treatment
The field of astrocytoma treatment has witnessed remarkable progress in recent years. With the advent of cutting-edge technologies and a deeper understanding of tumor biology, new treatment strategies have emerged. These advancements include:
- Targeted Therapy: Unlike traditional chemotherapy, targeted therapy focuses on specific genes or proteins that contribute to tumor growth. This approach allows for more precise and effective treatment, reducing damage to healthy cells.
- Immunotherapy: This innovative treatment boosts the body’s immune system to fight the tumor. Immunotherapy has shown promise in treating certain types of astrocytoma, especially when combined with other therapies.
- Radiogenomics: This technique involves studying the genetic makeup of a tumor to predict its response to radiation therapy. Tailoring radiation treatment based on a tumor’s genetic profile can enhance effectiveness and minimize side effects.
Emerging Therapies and Clinical Trials
In addition to established treatments, numerous clinical trials are underway, exploring novel approaches to combat astrocytoma. Some of the most notable include:
- CAR T-Cell Therapy: This groundbreaking approach modifies a patient’s T-cells to target and destroy cancer cells. Clinical trials are assessing its efficacy in treating astrocytoma.
- Vaccine Therapy: Researchers are experimenting with vaccines that stimulate the immune system to attack brain tumor cells. This method holds potential for both treating existing tumors and preventing recurrence.
- Nanotechnology: Utilizing nanoparticles to deliver drugs directly to tumor cells offers a highly targeted treatment approach, potentially increasing efficacy and reducing side effects.
- Gene Therapy: By correcting genetic mutations that cause tumor growth, gene therapy represents a promising frontier in astrocytoma treatment. Ongoing trials are testing various gene therapy techniques.
However, the landscape of astrocytoma treatment is rapidly evolving, with groundbreaking innovations offering new hope to patients. As research continues to advance, these emerging therapies and clinical trials pave the way for more effective and personalized treatment options.
Living with Astrocytoma
Managing Symptoms and Side Effects
Effective management of these symptoms is crucial for improving the quality of life.
- Symptom Management: Tailoring treatment plans to individual needs is key. This involves regular consultations with healthcare providers to monitor and manage symptoms like headaches, seizures, or cognitive changes.
- Medication Adherence: Adherence to prescribed medication regimes helps in controlling symptoms effectively.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Simple lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise, can significantly alleviate some symptoms.
Rehabilitation and Post-Treatment Care
Post-treatment care for Astrocytoma patients is vital in aiding recovery and enhancing overall well-being.
- Physical Therapy: Engaging in physical therapy helps in regaining strength and mobility, often affected by the tumor or treatment.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Therapy sessions focusing on memory, attention, and other cognitive skills can be beneficial.
- Regular Follow-ups: Regular medical check-ups are essential to monitor health status and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
Support Systems and Resources for Patients and Families
The journey with Astrocytoma is not just medical but also emotional and social. Support systems play a crucial role in this journey.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups where experiences and tips are shared can be immensely beneficial.
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling can help in dealing with the emotional and psychological impact of the diagnosis and treatment.
- Educational Resources: Accessing accurate and comprehensive information about Astrocytoma aids in making informed decisions about care and treatment.
Living with Astrocytoma is a challenging journey, but with the right management, rehabilitation, and support, patients and their families can navigate this path more effectively. Building a strong support network and staying informed are key to facing the challenges that come with this condition.
Prognosis and Survival Rates of Astrocytoma
Understanding these factors and the associated statistics can help patients and their families better comprehend the disease’s trajectory.
Factors Influencing Prognosis
- Grade of the Tumor: Astrocytomas are graded from I to IV, with higher grades indicating more aggressive tumors. Grade I tumors typically have a better prognosis than Grade IV (glioblastoma).
- Patient Age: Younger patients generally have a more favorable prognosis.
- Tumor Location and Size: Tumors in accessible locations that can be more completely removed often have better outcomes.
- Patient’s Overall Health: A patient’s general health status can impact the ability to withstand treatments and recovery.
- Genetic Mutations: Certain genetic markers can influence the behavior of the tumor and response to therapy.
Survival Rates and Outcomes
- 5-Year Survival Rates: These vary significantly based on tumor grade. Grade I astrocytomas have high survival rates, often above 90%, while Grade IV tumors have much lower rates, sometimes below 20%.
- Long-Term Survival: Grade I and II astrocytomas often allow for long-term survival, with many living for decades post-diagnosis. Grade III and IV tumors, however, are more challenging, with survival often measured in months to a few years.
- Quality of Life: Advances in treatment have not only improved survival rates but also the quality of life during and after treatment.
- Ongoing Research: Continuous research and clinical trials are progressively improving the outlook for astrocytoma patients, with new therapies and personalized medicine approaches.
However, while the prognosis of astrocytoma can vary greatly, understanding the factors influencing it and being aware of the survival statistics can equip patients and caregivers with valuable knowledge to navigate the course of the disease.
Prevention and Awareness
Strategies for Prevention and Early Detection
Understanding the strategies for prevention and early detection can empower individuals and communities. Here are key approaches:
- Healthy Lifestyle Choices: Emphasize a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoidance of known carcinogens. Though there’s no direct link between lifestyle and astrocytoma, overall health can impact recovery and risk.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Early detection often hinges on noticing subtle symptoms. Regular check-ups can help in identifying unusual changes in health that might suggest a problem.
- Understanding Risk Factors: Some factors, like exposure to certain chemicals or a family history of brain tumors, can increase risk. Awareness of these factors can guide individuals in their health choices and monitoring.
- Educational Programs: Informative sessions about the signs and symptoms of astrocytoma can lead to earlier diagnosis. Knowledge is a powerful tool in the fight against any disease.
Raising Awareness about Astrocytoma
Awareness is a vital part of the battle against astrocytoma. Here’s how it can be effectively raised:
- Community Engagement: Engage local communities through workshops, seminars, and health fairs. Real stories and experiences can make a profound impact.
- Utilizing Social Media and Online Platforms: These are powerful tools for spreading information quickly and widely. Sharing accurate, easy-to-understand information about astrocytoma can reach a diverse audience.
- Collaborating with Healthcare Providers: Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare professionals can provide valuable insights and disseminate information effectively during routine healthcare visits.
- Support Groups and Advocacy: Support groups not only provide comfort to those affected but also serve as platforms for advocacy and awareness.
By focusing on prevention, early detection, and raising awareness, the journey to manage and combat astrocytoma becomes more effective and inclusive. Remember, knowledge and proactive health management are key in this fight.
Conclusion
Astrocytoma diagnosis and treatment require a multi-faceted approach, combining medical expertise, advanced technology, and comprehensive patient support.
Continued research and personalized care strategies are essential in improving prognosis and quality of life for patients with astrocytoma.